文章目錄
- 前言
- 一、poll
- 二、poll使用步驟
- 總結
前言
上一章我們學習了select,但是select作為早期的多路轉接接口,缺點十分明顯,于是又出現poll和epoll等接口,今天我們就來學習一下poll的使用
提示:以下是本篇文章正文內容,下面案例可供參考
一、poll
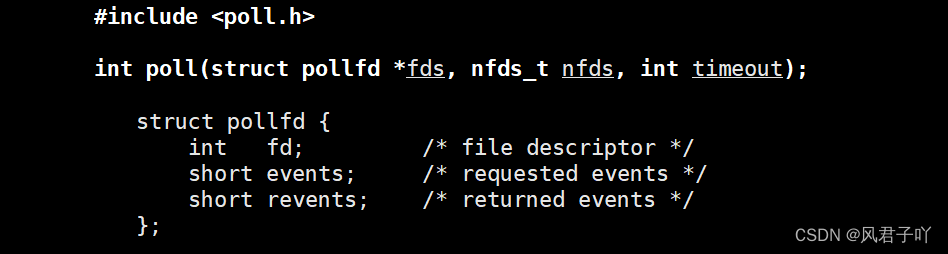
參數struct pollfd *fds,它其實傳的是一個struct pollfd數組,其結構體成員介紹如下。
- fd設置為要關心的fd;
- events是一個輸入型參數,用來告知poll要關心的事件,比如說POLLIN就是讓它關心讀事件;
- revents是一個輸出型參數,當poll檢測到關心的fd有events的資源就緒時,就會返回并將該fd對應的revents設置為就緒events。
之前我們使用select,還需要用到一個輔助數組來保存我們需要關心的fds,因為它的大部分參數都是輸入輸出型參數。而poll采用了struct pollfd結構體的方式讓輸入輸出型參數分離互不影響,也是彌補了select的這一缺點。
參數nfds_t nfds,它用于告知poll需要關心的fd數量,其實就是fds數組的元素個數。
參數int timeout,功能上與select的timeout一樣,不過poll舍棄了傳struct timeval結構體的方式,直接傳一個int整形就可以了,其單位為ms。
二、poll使用步驟
poll的使用步驟與select類似。
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include <poll.h>#define MAX_POLLFDS 1024
#define INVALID_FD -1const std::string default_ip = "0.0.0.0";
const uint16_t default_port = 8080;class PollServer
{
public:PollServer(uint16_t port = default_port): _port(port) {}inline void InitFds(){_pollfds[0].fd = _listensock._sockfd;_pollfds[0].events = POLLIN;for (int i = 1; i < MAX_POLLFDS; ++i){_pollfds[i].fd = INVALID_FD;}}void Init(){_listensock.Init();_listensock.Bind(AF_INET, default_ip, _port);_listensock.Listen();InitFds();}void Print(){std::cout << "現有fds: ";for (int i = 0; i < MAX_POLLFDS; ++i){if (_pollfds[i].fd == INVALID_FD){continue;}std::cout << _pollfds[i].fd << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;}void Accepter(){struct sockaddr_in tmp;socklen_t len = sizeof tmp;int newfd = accept(_listensock._sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&tmp, &len);for (int i = 0; i < MAX_POLLFDS; ++i){if (_pollfds[i].fd == INVALID_FD){_pollfds[i].fd = newfd;_pollfds[i].events = POLLIN;_pollfds[i].revents = 0;lg(Info, "Get A New Sockfd:%d", newfd);break;}if (i == MAX_POLLFDS){lg(Warning, "Fds Is Full, Newfd:%d Closed...", newfd);close(newfd);return;}}}void Handler(int fd, int i){char buffer[1024];memset(buffer, 0, sizeof buffer);int n = read(fd, buffer, sizeof buffer - 1);if (n > 0){buffer[n] = 0;std::string mes = buffer;std::cout << mes;_pollfds[i].revents = 0;}else if (n < 0){lg(Warning, "Read Error...");close(fd);_pollfds[i].fd = INVALID_FD;}else{lg(Info, "Foreign Host Closed...");close(fd);_pollfds[i].fd = INVALID_FD;}}void Dispatcher(){for (int i = 0; i < MAX_POLLFDS; ++i){if (_pollfds[i].fd == INVALID_FD){continue;}else if (_pollfds[i].revents & POLLIN){if (_pollfds[i].fd == _listensock._sockfd){// acceptAccepter();continue;}Handler(_pollfds[i].fd, i);}}}void Start(){while (1){Print();int n = poll(_pollfds, MAX_POLLFDS, 5000);if (n == 0){lg(Info, "Poll Time Out...");continue;}else if (n < 0){lg(Warning, "Poll Error...");std::cout << "errno:" << errno << " strerror:" << strerror(errno) << std::endl;}else{Dispatcher();}}}~PollServer(){_listensock.Close();}private:struct pollfd _pollfds[MAX_POLLFDS];Socket _listensock;uint16_t _port;
};
總結
poll相比較于select,彌補了兩個缺點。
- 不再需要繁瑣地更新需要關心的fd和其對應事件。
- 可關心的fd數量不再受其接口內置的數據結構大小限制,可以根據用戶需求自由調整。
但是仍然還有缺點,那就是每次進行一次poll都是一次從用戶態拷貝數據到內核態的過程。 還有還是需要一些for循環遍歷那些已經就緒了的fd。








編輯 12 編輯模版)

))
)




eslint-plugin-vue版本問題 安裝axios時npm ERR! code ERESOLVE)
)

