上一篇我們通過如下一段基礎代碼作為切入點,最終找到核心的處理是refresh方法,從今天開始正式進入refresh方法的解讀。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");JmUser jmUser = (JmUser)context.getBean("jmUser");System.out.println(jmUser.getName());System.out.println(jmUser.getAge());}
}初始化容器上下文
首先還是整體看下refresh方法
@Overridepublic void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing. 1、初始化上下文信息,替換占位符、必要參數的校驗prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 2、解析類Xml、初始化BeanFactoryConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // 這一步主要是對初級容器的基礎設計// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 3、準備BeanFactory內容:prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 對beanFactory容器的功能的擴展:try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 4、擴展點加一:空實現,主要用于處理特殊Bean的后置處理器postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 5、spring bean容器的后置處理器invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 6、注冊bean的后置處理器registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context. 7、初始化消息源initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context. 8、初始化事件廣播器initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 9、擴展點加一:空實現;主要是在實例化之前做些bean初始化擴展onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them. 10、初始化監聽器registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 11、實例化:非蘭加載BeanfinishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event. 12、發布相應的事件通知finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();}}}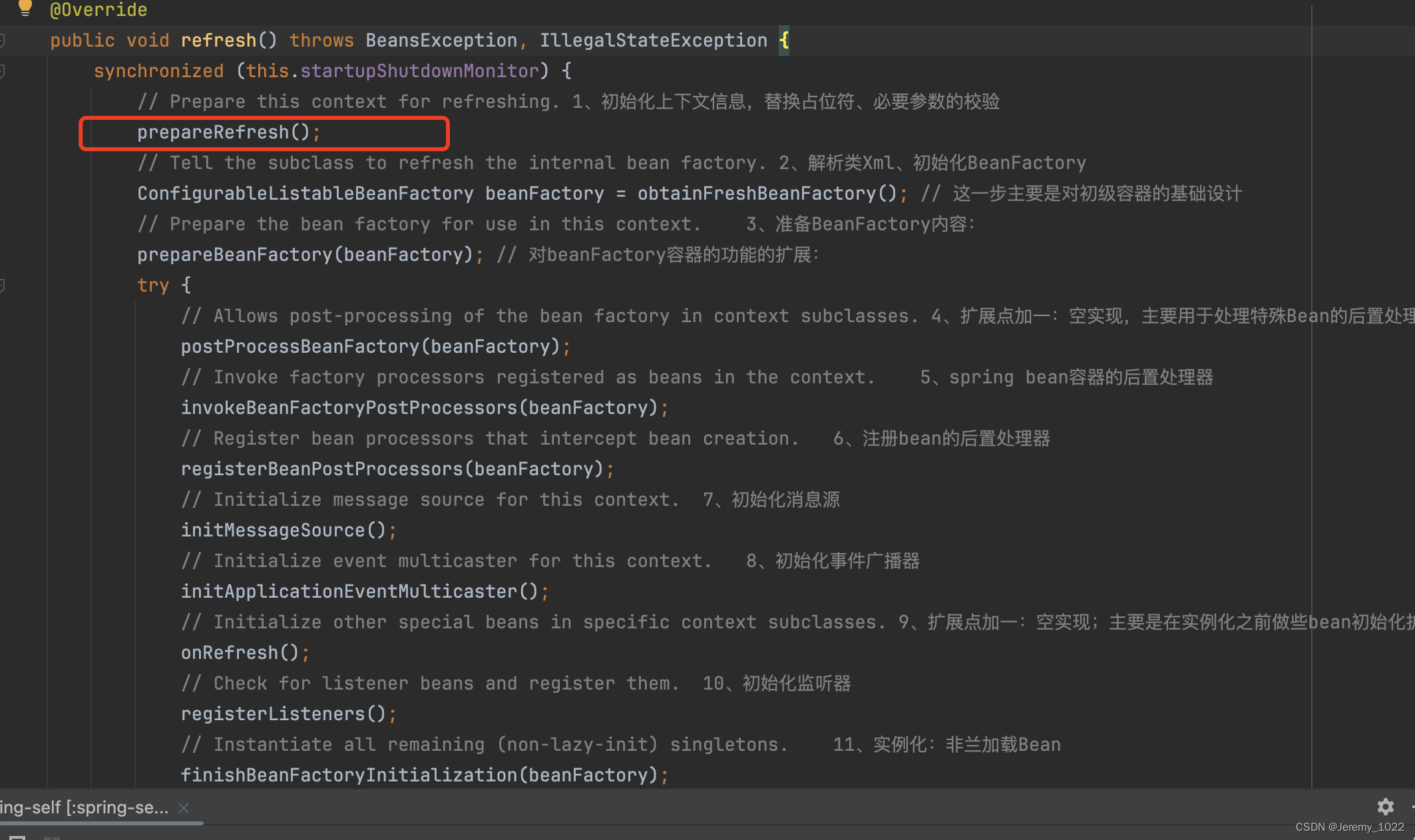
首先將目標聚焦在第一個方法prepareRefresh方法上,根據方法名稱和注釋,我們大概可以猜測到該方法是在容器初始化前做些準備工作。
有了這個想法我來具體看下這個方法到底干了什么?
/*** Prepare this context for refreshing, setting its startup date and* active flag as well as performing any initialization of property sources.* 一些初始化設置如:設置容器開始事件、容器狀態active設置激活】初始化配置源等。* 1.1、其中關注初始化配置源:這個也是留給子類自己實現,擴展點加一* 1.2、容器初始化的時候,校驗必須的配置是否為空,當我們自己對原框架修改的時候,可以通過這個屬性加上必要的配置判斷**/protected void prepareRefresh() {// Switch to active.this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();this.closed.set(false);this.active.set(true);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);}else {logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());}}// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.// 初始化替換占位符為實際值initPropertySources();// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties// 容器初始化的時候,校驗必須的配置是否為空getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);}else {// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.this.applicationListeners.clear();this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);}// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,// to be published once the multicaster is available...this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();}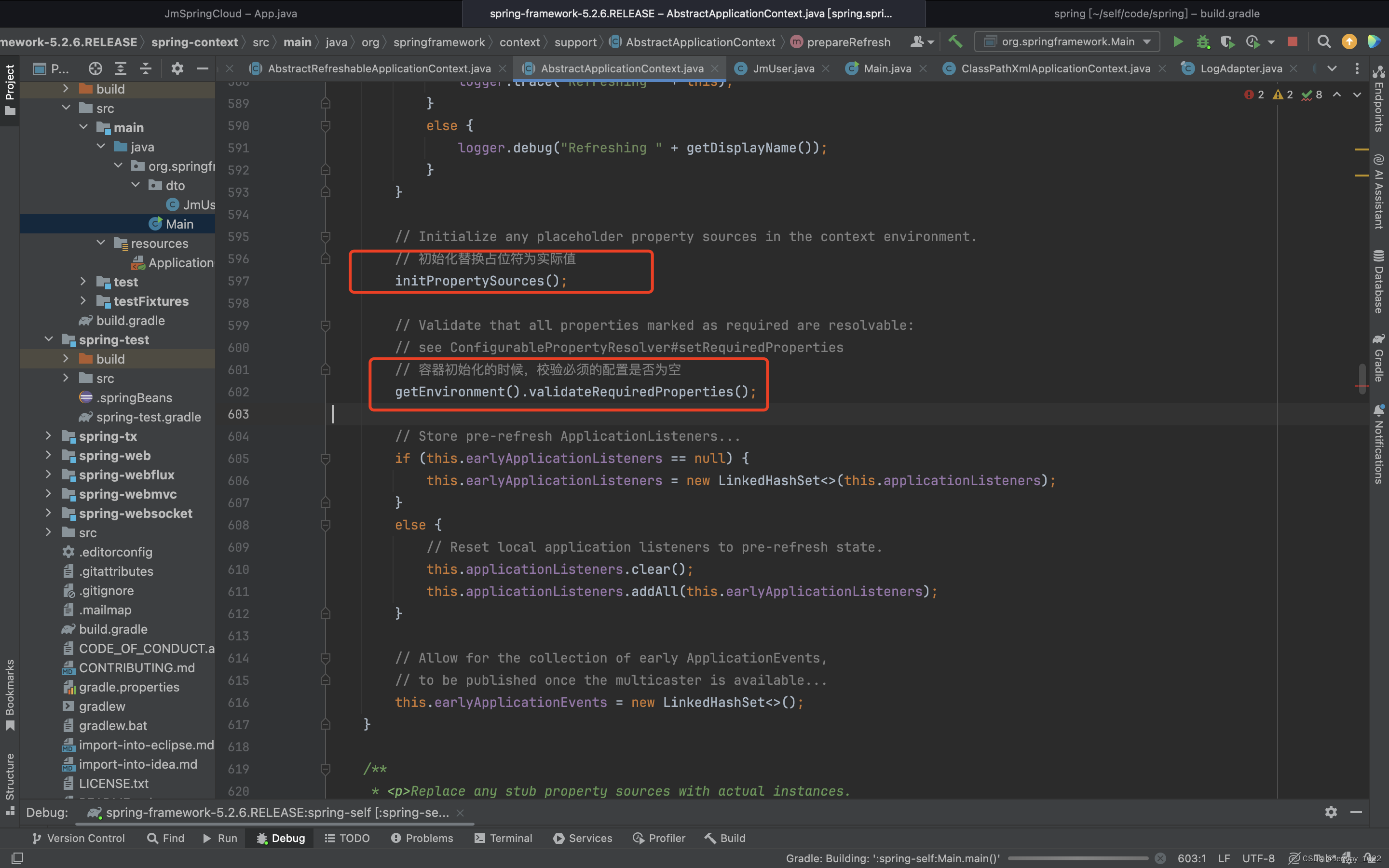
可以看到,該方法大部分時間只是做了初始化的設置如開始時間、容器狀態初始化等,聚焦下
initPropertySources方法
/*** <p>Replace any stub property sources with actual instances.* @see org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource.StubPropertySource* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#initServletPropertySources*/protected void initPropertySources() {// For subclasses: do nothing by default.}Spring最經典的設計之一,空實現方法方法的權限級別為protected。給子類自己實現,擴展點加一。這里單獨提出來和大家看看,因為后面我們能看到很多類似的代碼。這也是Spring是一個易擴展框架的原因之一。
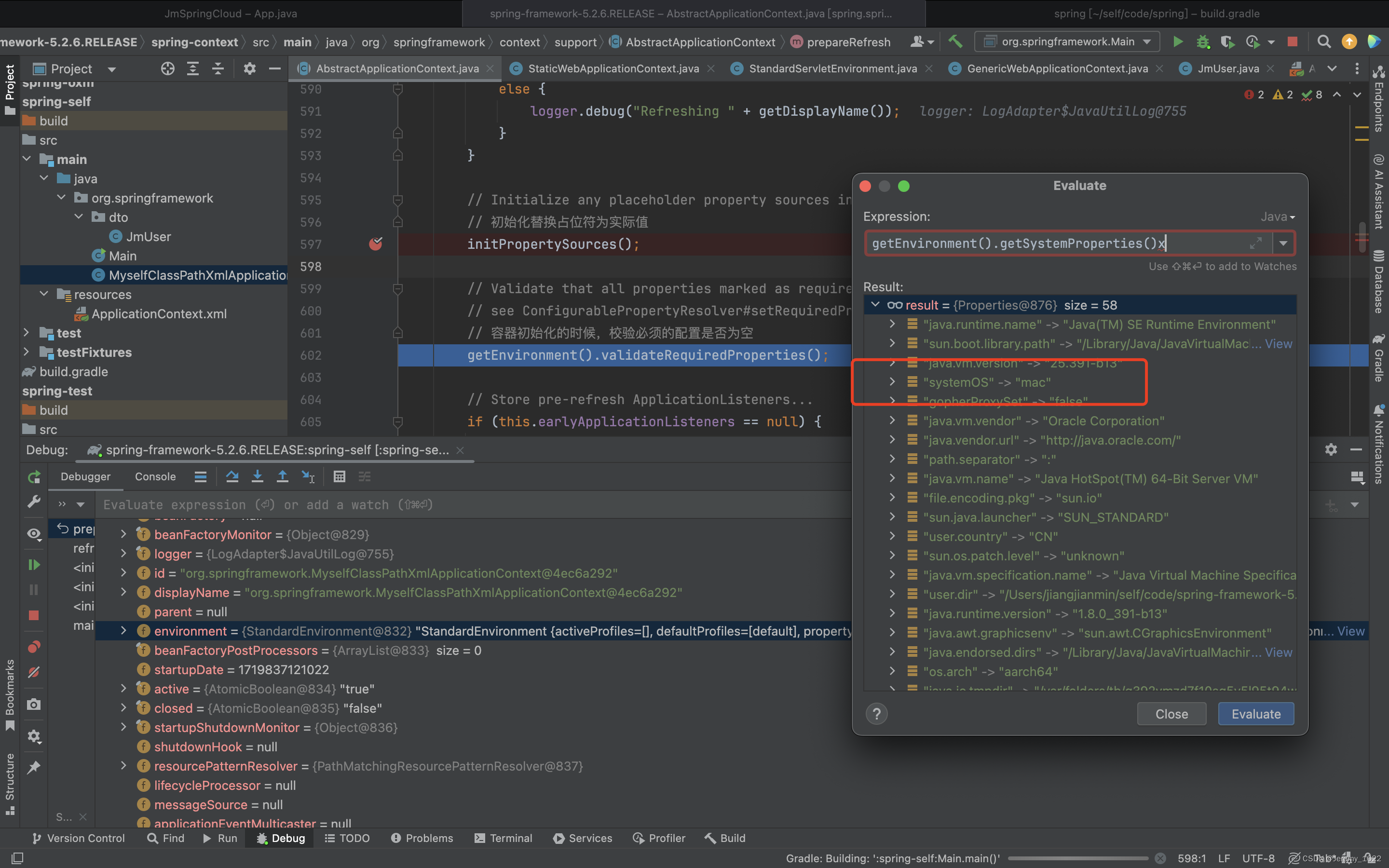
說完這個方法的設計,下面再來看看這個方法具體干了什么。看注釋說是為了替換占位符。既然這樣我們自己來重寫這個方法試試看就知道啦。重寫代碼如下:
public class MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends ClassPathXmlApplicationContext {/*** Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.* @param configLocations resource location* @throws BeansException if context creation failed*/public MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {super(configLocations);}@Overrideprotected void initPropertySources() {System.out.println("自定義 initPropertySources");getEnvironment().getSystemProperties().put("systemOS", "mac");}public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");JmUser jmUser = (JmUser)context.getBean("jmUser");System.out.println(jmUser.getName());System.out.println(jmUser.getAge());}
}執行完initPropertySources方法以后,發現環境變量多了我們設置的代碼systemOS,后續在需要的地方可以替換成我們所需要的值。
 接著我們來看prepareRefresh下一個方法:
接著我們來看prepareRefresh下一個方法:
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
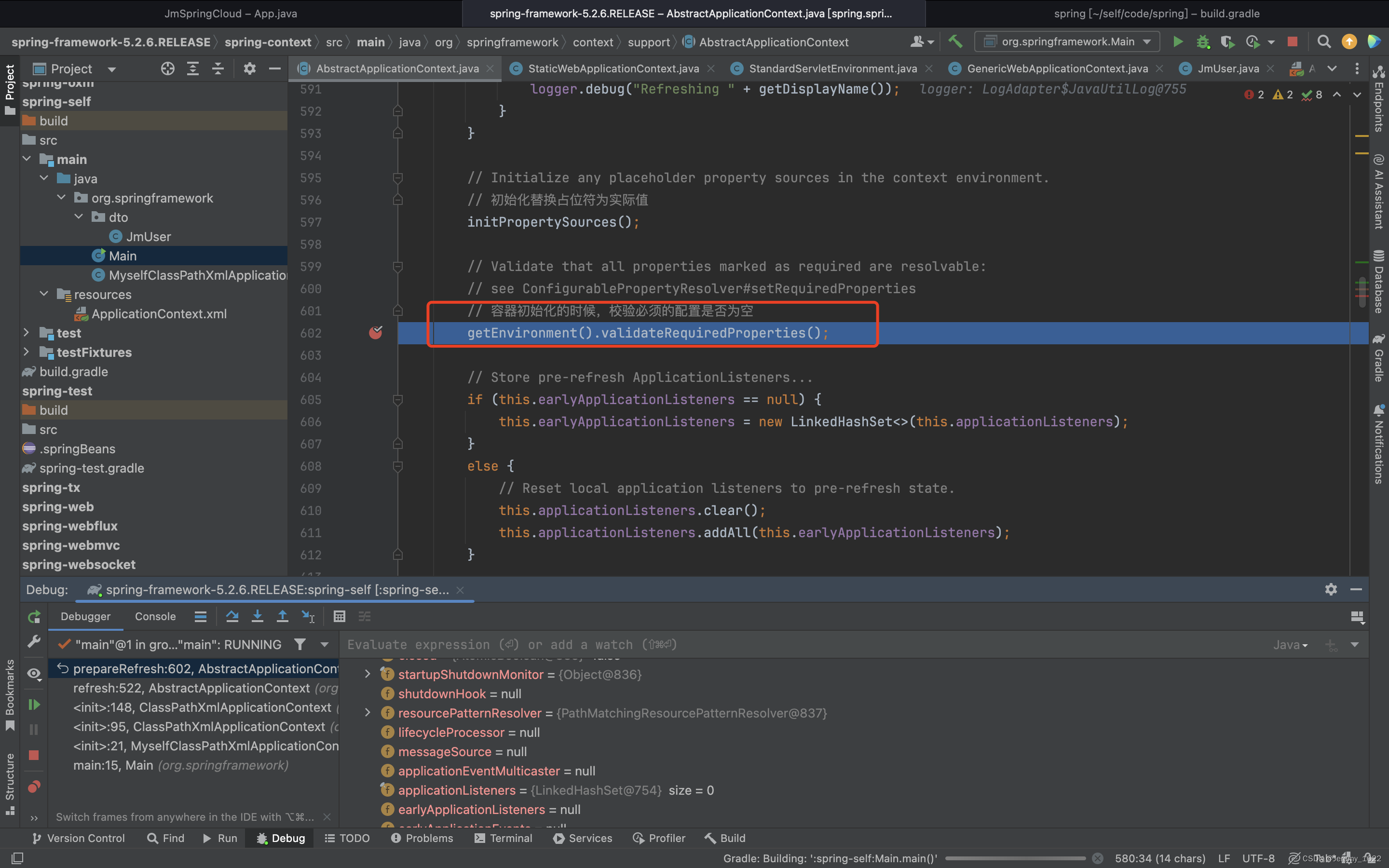
老樣子根據注釋和方法名稱簡答猜測一下,應該是用來校驗是否需要檢驗某個必須的屬性。猜測后進入代碼驗證一波。
看代碼是自己的成員屬性propertyResolver進行調用的,在進入方法看下:
@Overridepublic void validateRequiredProperties() {MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();for (String key : this.requiredProperties) {if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);}}if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {throw ex;}}
上述代碼主要是遍歷requirePrpperties屬性,將不存在的key存入ex中,待循環結束以后拋出異常。目前我們的代碼屬性為空。我們再改寫下上述代碼看看。
package org.springframework;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;/*** @author Jeremy* @version 1.0* @description: 自定義容器* @date 2024/7/1 20:17*/
public class MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends ClassPathXmlApplicationContext {/*** Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.* @param configLocations resource location* @throws BeansException if context creation failed*/public MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {super(configLocations);}@Overrideprotected void initPropertySources() {System.out.println("自定義 initPropertySources");
// getEnvironment().getSystemProperties().put("systemOS", "mac");getEnvironment().setRequiredProperties("systemOS");}
}
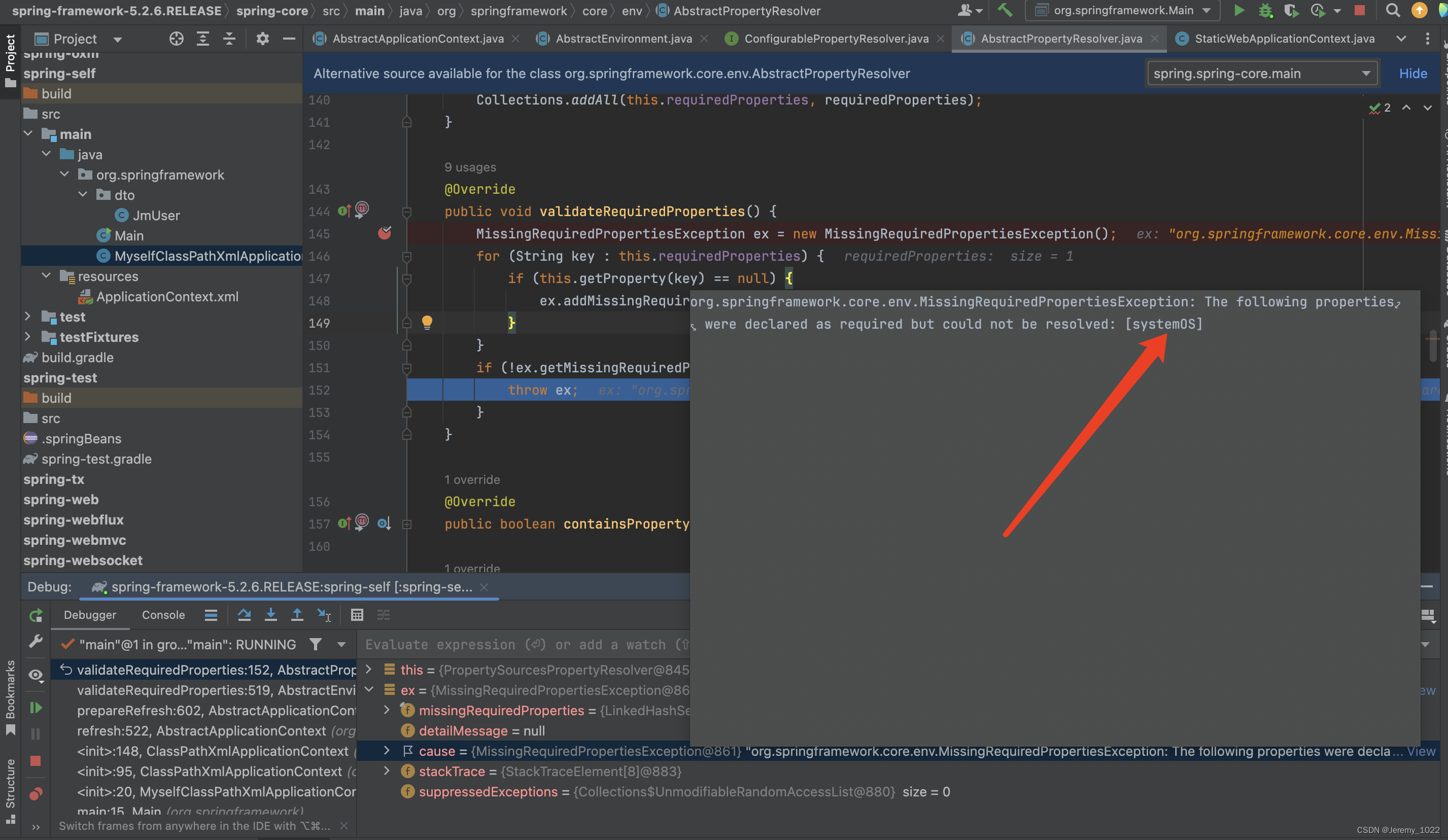
堆棧日志如下
自定義 initPropertySources
Disconnected from the target VM, address: 'localhost:50403', transport: 'socket'
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.core.env.MissingRequiredPropertiesException: The following properties were declared as required but could not be resolved: [systemOS]
?? ?at org.springframework.core.env.AbstractPropertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties(AbstractPropertyResolver.java:145)
?? ?at org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment.validateRequiredProperties(AbstractEnvironment.java:519)
?? ?at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.prepareRefresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:602)
?? ?at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:522)
?? ?at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:148)
?? ?at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:95)
?? ?at org.springframework.MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(MyselfClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:20)
?? ?at org.springframework.Main.main(Main.java:15)
放開上面注釋:正常運行。通過上述兩個簡單的實例我們可以通過重寫上述代碼為我們Spring容器提供基礎的校驗和設置對應的值。方便后續開發。到這里我們初始化容器上下文prepareRefresh方法告一段落。
總結
目前我們代碼進程如下圖所示:
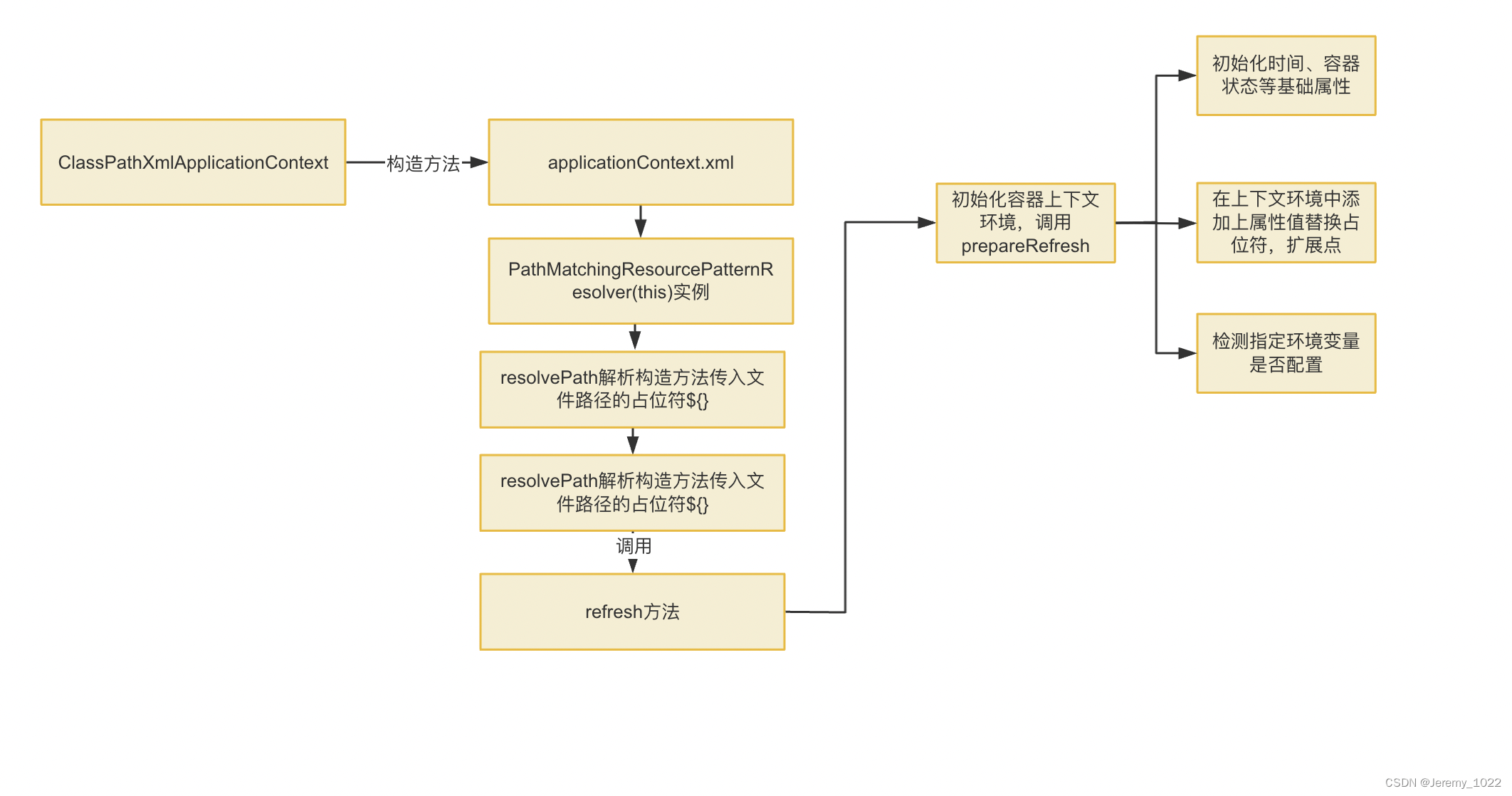
下一節我們正式進入初始化容器,看看眾所周知的Bean Factory到底怎么來的。



)


)
)











