背景介紹
接觸過大模型應用開發的研發同學應該都或多或少地聽過 Dify 這個大模型應用基礎服務,這個項目自從 2023 年上線以來,截止目前(2024-6)已經獲得了 35k 多的 star,是目前大模型應用基礎服務中最熱門的項目之一。這篇文章對 Dify 中核心的基礎模塊 RAG 服務進行深入解讀,后續可能會更新其他模塊的內容。
Dify 簡介
Dify 是一個 LLMOps 服務, 涵蓋了大語言模型(如GPT系列)開發、部署、維護和優化的一整套實踐和流程。可以大幅簡化大模型應用的開發。
基于 Dify 可以在不需要太多開發的情況下,快速搭建一個大模型應用。應用中可以調用 Dify 中內置的大量基礎能力,比如知識庫檢索 RAG,大模型調用。通過可插拔式的組合構建大模型應用。一個典型的應用如下所示:

上面的場景中使用分類場景,RAG 服務以及大模型調用的基礎模塊,組合生成一個大模型應用。
RAG 核心流程
RAG 服務的基礎流程在之前的 搭建離線私有大模型知識庫 文章中已經介紹過了。RAG 服務的開源框架 有道 QAnything 和 Ragflow 也都解讀過基礎的 RAG 流程了,這部分就不詳細展開了。一般情況下,RAG 服務會包含如下所示的功能模塊:
- 文件加載的支持;
- 文件的預處理策略;
- 文件檢索的支持;
- 檢索結果的重排;
- 大模型的處理;
因為 RAG 服務只是 Dify 中的一個基礎模塊,官方沒有過多強調 RAG 服務的獨特設計,但是依舊可以看到一個獨特點:
- 支持 Q&A 模式,與上述普通的「Q to P」(問題匹配文本段落)匹配模式不同,它是采用「Q to Q」(問題匹配問題)匹配工作;
- 豐富的召回模式,支持
N 選 1 召回和多路召回;
下面的部分會對獨特之處進行詳細展開。
核心模塊解讀
之前介紹過來自中科院的 RAG 服務 GoMate 采取的是模塊化設計,方便進行上層應用的組合。從目前的實現來看,Dify 的 RAG 設計也是采用模塊化設計,RAG 的代碼實現都在 api/core/rag 中,從代碼結構上也很容易理解各個模塊的作用:

深入來看代碼的實現質量也比較高,對 RAG 的模塊化設計感興趣的可以深入了解下實現細節。
文件加載
Dify 的文件加載都是在 api/core/rag/extractor/extract_processor.py 中實現的,主要的文件解析是基于 unstructured 實現,另外基于其他第三方庫實現了特定格式文件的處理
比如對于 pdf 文件,會基于 pypdfium2 進行解析,html 是基于 BeautifulSoup 進行解析,這部分代碼實現都比較簡單,就不展開介紹了。
文件預處理
加載的模型中的內容可能會存在一些問題,比如多余的無用字符,編碼錯誤或其他的一些問題,因此需要對文件解析的內容進行必要的清理,這部分代碼實現在 api/core/rag/cleaner 中。實際的清理都是基于 unstructured cleaning 實現的,Dify 主要就是將不同的清理策略封裝為同樣的接口,方便應用層自由選擇。這部分實現也比較簡單,感興趣可以自行了解下。
Q&A 模式
Q&A 分段模式功能,與上述普通的「Q to P」(問題匹配文本段落)匹配模式不同,它是采用「Q to Q」(問題匹配問題)匹配工作,在文檔經過分段后,經過總結為每一個分段生成 Q&A 匹配對,當用戶提問時,系統會找出與之最相似的問題,然后返回對應的分段作為答案,實際的流程如下所示:
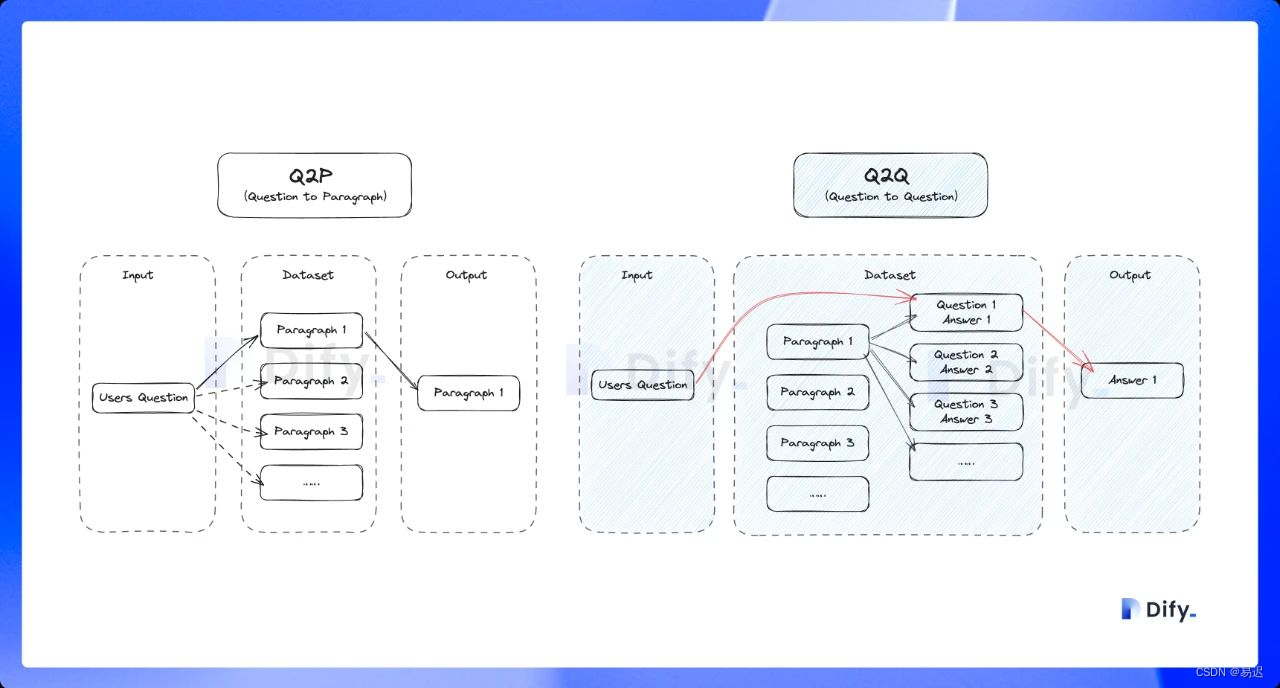
從上面的流程可以看到,Q&A 模式下會根據原始文檔生成問答對,實現實現是在 api/core/llm_generator/llm_generator.py 中:
# 構造 promptGENERATOR_QA_PROMPT = ('<Task> The user will send a long text. Generate a Question and Answer pairs only using the knowledge in the long text. Please think step by step.''Step 1: Understand and summarize the main content of this text.\n''Step 2: What key information or concepts are mentioned in this text?\n''Step 3: Decompose or combine multiple pieces of information and concepts.\n''Step 4: Generate questions and answers based on these key information and concepts.\n''<Constraints> The questions should be clear and detailed, and the answers should be detailed and complete. ''You must answer in {language}, in a style that is clear and detailed in {language}. No language other than {language} should be used. \n''<Format> Use the following format: Q1:\nA1:\nQ2:\nA2:...\n''<QA Pairs>'
)def generate_qa_document(cls, tenant_id: str, query, document_language: str):prompt = GENERATOR_QA_PROMPT.format(language=document_language)model_manager = ModelManager()model_instance = model_manager.get_default_model_instance(tenant_id=tenant_id,model_type=ModelType.LLM,)# 拼接出完整的調用 promptprompt_messages = [SystemPromptMessage(content=prompt),UserPromptMessage(content=query)]# 調用大模型直接生成問答對response = model_instance.invoke_llm(prompt_messages=prompt_messages,model_parameters={'temperature': 0.01,"max_tokens": 2000},stream=False)answer = response.message.contentreturn answer.strip()
可以看到就是通過一個 prompt 就完成了原始文檔到問答對的轉換,可以看到大模型確實可以幫助實現業務所需的基礎能力。
文件檢索
知識庫的檢索是在 api/core/workflow/nodes/knowledge_retrieval/knowledge_retrieval_node.py 中實現的,與常規的 RAG 存在明顯不同之處在于支持了豐富的召回模式。
豐富的召回模式
用戶可以自由選擇所需的召回模式:

N 選 1 召回:先根據用戶輸入的意圖選擇合適的知識庫,然后從知識庫檢索所需的文檔,適用于知識庫彼此隔離,不需要互相聯合查詢的場景;多路召回:此時會同時從多個知識庫檢索,然后進行重新排序,適用于知識庫需要聯合查詢的場景。
常規的 RAG 服務需要先手工選擇知識庫,然后從對應的知識庫進行檢索,無法支持跨庫檢索。相對而言,Dify 的這個設計還是要更方便一些。下面以 N 選 1 召回 為例介紹下文件的檢索,對應的流程如下所示:
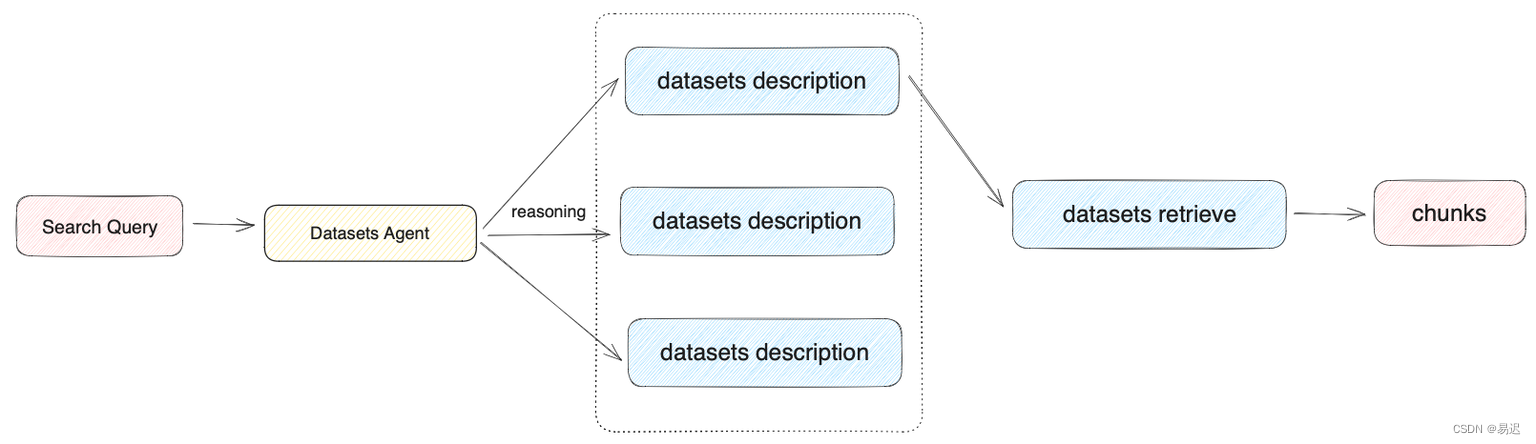
N 選 1 召回 的知識庫選擇是基于用戶問題與知識庫描述的語義匹配性來進行選擇,存在 Function Call/ReAct 兩種模式,實現代碼在 api/core/rag/retrieval/dataset_retrieval.py 中,具體如下所示:
tools = []
# 根據用戶輸入的意圖,使用知識庫的描述構造 promptfor dataset in available_datasets:description = dataset.descriptionif not description:description = 'useful for when you want to answer queries about the ' + dataset.namedescription = description.replace('\n', '').replace('\r', '')message_tool = PromptMessageTool(name=dataset.id,description=description,parameters={"type": "object","properties": {},"required": [],})tools.append(message_tool)# 支持 ReAct 模式if planning_strategy == PlanningStrategy.REACT_ROUTER:react_multi_dataset_router = ReactMultiDatasetRouter()dataset_id = react_multi_dataset_router.invoke(query, tools, model_config, model_instance,user_id, tenant_id)
# 支持 Function Call 模式elif planning_strategy == PlanningStrategy.ROUTER:function_call_router = FunctionCallMultiDatasetRouter()dataset_id = function_call_router.invoke(query, tools, model_config, model_instance)Function Call模式就是構造了一個 prompt,讓大模型根據描述選擇合適的知識庫,實現比較簡單ReAct模式則是基于 ReAct , 通過推理 + 任務的結合選擇正確的知識庫
知識庫檢索
在前面根據模式選擇了對應的知識庫之后,就可以在單個知識庫內進行檢索,目前支持的檢索方式包含下面三種:
向量檢索,通過生成查詢嵌入并查詢與其向量表示最相似的文本分段。全文檢索,索引文檔中的所有詞匯,從而允許用戶查詢任意詞匯,并返回包含這些詞匯的文本片段。混合檢索,同時執行全文檢索和向量檢索,并附加重排序步驟,從兩類查詢結果中選擇匹配用戶問題的最佳結果。
從實際的代碼來看,還有一個 關鍵詞檢索 的能力,但是沒有特別介紹,不確定是否是效果上還不夠穩定,可以關注下后續的進展。混合檢索的流程如下所示:

實際的實現在 api/core/rag/datasource/retrieval_service.py :
# 關鍵詞檢索if retrival_method == 'keyword_search':keyword_thread = threading.Thread(target=RetrievalService.keyword_search, kwargs={'flask_app': current_app._get_current_object(),'dataset_id': dataset_id,'query': query,'top_k': top_k,'all_documents': all_documents,'exceptions': exceptions,})threads.append(keyword_thread)keyword_thread.start()# 向量檢索(混合檢索中也會調用)if RetrievalMethod.is_support_semantic_search(retrival_method):embedding_thread = threading.Thread(target=RetrievalService.embedding_search, kwargs={'flask_app': current_app._get_current_object(),'dataset_id': dataset_id,'query': query,'top_k': top_k,'score_threshold': score_threshold,'reranking_model': reranking_model,'all_documents': all_documents,'retrival_method': retrival_method,'exceptions': exceptions,})threads.append(embedding_thread)embedding_thread.start()# 文本檢索(混合檢索中也會調用)if RetrievalMethod.is_support_fulltext_search(retrival_method):full_text_index_thread = threading.Thread(target=RetrievalService.full_text_index_search, kwargs={'flask_app': current_app._get_current_object(),'dataset_id': dataset_id,'query': query,'retrival_method': retrival_method,'score_threshold': score_threshold,'top_k': top_k,'reranking_model': reranking_model,'all_documents': all_documents,'exceptions': exceptions,})threads.append(full_text_index_thread)full_text_index_thread.start()for thread in threads:thread.join()# 混合檢索之后會執行向量和文本檢索結果合并后的重排序if retrival_method == RetrievalMethod.HYBRID_SEARCH:data_post_processor = DataPostProcessor(str(dataset.tenant_id), reranking_model, False)all_documents = data_post_processor.invoke(query=query,documents=all_documents,score_threshold=score_threshold,top_n=top_k)
檢索結果重排
檢索結果的重排也比較簡單,就是通過外部模型進行打分,之后基于打分的結果進行排序,實際的實現在 api/core/model_manager.py 中:
def invoke_rerank(self, query: str, docs: list[str], score_threshold: Optional[float] = None,top_n: Optional[int] = None,user: Optional[str] = None) \-> RerankResult:self.model_type_instance = cast(RerankModel, self.model_type_instance)# 輪詢調用重排序模型,獲得重排序得分,并基于得分進行排序return self._round_robin_invoke(function=self.model_type_instance.invoke,model=self.model,credentials=self.credentials,query=query,docs=docs,score_threshold=score_threshold,top_n=top_n,user=user)
總結
本文主要介紹了 Dify 的知識庫 RAG 服務,作為完整 Agent 中一個基礎模塊,Dify 沒有特別強調 RAG 獨特之處,但是依舊存在一些獨特的亮點:
- 多種召回模式,支持根據用戶意圖自動選擇合適的知識庫,也可以跨知識庫進行檢索,彌補了常規的 RAG 服務需要用戶手工選擇知識庫的不便之處;
- 獨特的 Q&A 模式,可以直接根據文本生成問答對,可以解決常規情況下用戶問題與文本匹配度不夠的問題,但是應該只適用于特定類型的場景,否則可能會因為轉換導致的信息損耗導致效果更差;
總體而言,Dify 中的 RAG 服務是一個設計完備的服務,模塊化的設計方便組合與拓展,一些獨特的設計也可以提升易用性,代碼質量也很高,感興趣的可以深入研究下。



















)