EventBus
簡介
EventBus:github
EventBus是Android和Java的發布/訂閱事件總線。
- 簡化組件之間的通信
-
解耦事件發送者和接收者
-
在 Activities, Fragments, background threads中表現良好
-
避免復雜且容易出錯的依賴關系和生命周期問題
-
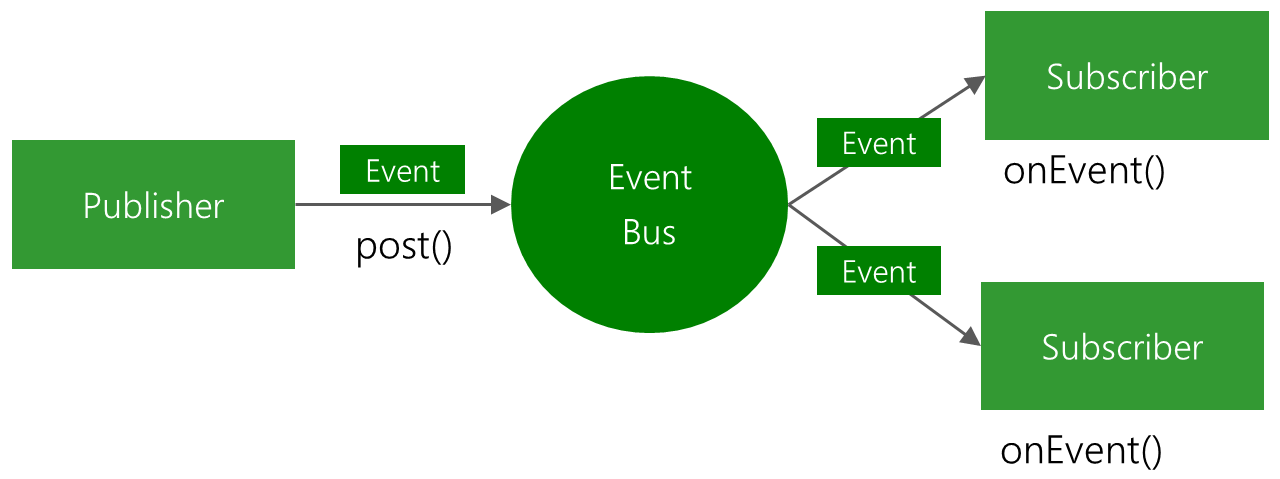
Publisher使用post發出一個Event事件,Subscriber在onEvent()函數中接收事件。
EventBus 是一款在 Android 開發中使用的發布/訂閱事件總線框架,基于觀察者模式,將事件的接收者和發送者分開,簡化了組件之間的通信,使用簡單、效率高、體積小!下邊是官方的 EventBus 原理圖:
導入
Android Projects:
implementation("org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.2.0")
Java Projects:
implementation("org.greenrobot:eventbus-java:3.2.0")
<dependency><groupId>org.greenrobot</groupId><artifactId>eventbus-java</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
配置
配置混淆文件
-keepattributes *Annotation*
-keepclassmembers class * {@org.greenrobot.eventbus.Subscribe <methods>;
}
-keep enum org.greenrobot.eventbus.ThreadMode { *; }# If using AsyncExecutord, keep required constructor of default event used.
# Adjust the class name if a custom failure event type is used.
-keepclassmembers class org.greenrobot.eventbus.util.ThrowableFailureEvent {<init>(java.lang.Throwable);
}# Accessed via reflection, avoid renaming or removal
-keep class org.greenrobot.eventbus.android.AndroidComponentsImpl
使用
簡單流程
- 創建事件類
public static class MessageEvent { /* Additional fields if needed */ }
- 在需要訂閱事件的地方,聲明訂閱方法并注冊EventBus。
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void onMessageEvent(MessageEvent event) {// Do something
}
public class EventBusActivity extends AppCompatActivity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);}@Overrideprotected void onStart() {super.onStart();//注冊EventBusEventBus.getDefault().register(this);}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.POSTING, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_POSTING: " + message.toString());}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg1(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_MAIN: " + message.toString());}//接收事件@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN_ORDERED, sticky = true, priority = 1)public void onReceiveMsg2(MessageEvent message){Log.e("EventBus_Subscriber", "onReceiveMsg_MAIN_ORDERED: " + message.toString());}@Overrideprotected void onDestroy() {super.onDestroy();//取消事件EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);}
}
- 提交訂閱事件
@OnClick(R2.id.send_event_common)
public void clickCommon(){MessageEvent message = new MessageEvent(1, "這是一條普通事件");EventBus.getDefault().post(message);
}@OnClick(R2.id.send_event_sticky)
public void clickSticky(){MessageEvent message = new MessageEvent(1, "這是一條黏性事件");EventBus.getDefault().postSticky(message);
}
Subcribe注解
Subscribe是EventBus自定義的注解,共有三個參數(可選):threadMode、boolean sticky、int priority。 完整的寫法如下:
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN,sticky = true,priority = 1)
public void onReceiveMsg(MessageEvent message) {Log.e(TAG, "onReceiveMsg: " + message.toString());
}
priority
priority是優先級,是一個int類型,默認值為0。值越大,優先級越高,越優先接收到事件。
值得注意的是,只有在post事件和事件接收處理,處于同一個線程環境的時候,才有意義。
sticky
sticky是一個boolean類型,默認值為false,默認不開啟黏性sticky特性,那么什么是sticky特性呢?
上面的例子都是對訂閱者 (接收事件) 先進行注冊,然后在進行post事件。
那么sticky的作用就是:訂閱者可以先不進行注冊,如果post事件已經發出,再注冊訂閱者,同樣可以接收到事件,并進行處理。
ThreadMode 模式
POSITING:訂閱者將在發布事件的同一線程中被直接調用。這是默認值。事件交付意味著最少的開銷,因為它完全避免了線程切換。因此,對于已知可以在很短時間內完成而不需要主線程的簡單任務,推薦使用這種模式。使用此模式的事件處理程序必須快速返回,以避免阻塞發布線程(可能是主線程)。
MAIN:在Android上,訂閱者將在Android的主線程(UI線程)中被調用。如果發布線程是主線程,將直接調用訂閱者方法,阻塞發布線程。否則,事件將排隊等待交付(非阻塞)。使用此模式的訂閱者必須快速返回以避免阻塞主線程。如果不是在Android上,行為與POSITING相同。
MAIN_ORDERED:在Android上,訂閱者將在Android的主線程(UI線程)中被調用。與MAIN不同的是,事件將始終排隊等待交付。這確保了post調用是非阻塞的。
BACKGROUND:在Android上,訂閱者將在后臺線程中被調用。如果發布線程不是主線程,訂閱者方法將在發布線程中直接調用。如果發布線程是主線程,EventBus使用一個后臺線程,它將按順序傳遞所有事件。使用此模式的訂閱者應盡量快速返回,以避免阻塞后臺線程。如果不是在Android上,總是使用一個后臺線程。
ASYNC:訂閱服務器將在單獨的線程中調用。這始終獨立于發布線程和主線程。使用此模式發布事件從不等待訂閱者方法。如果訂閱者方法的執行可能需要一些時間,例如網絡訪問,則應該使用此模式。避免同時觸發大量長時間運行的異步訂閱者方法,以限制并發線程的數量。EventBus使用線程池來有效地重用已完成的異步訂閱者通知中的線程。
/*** Each subscriber method has a thread mode, which determines in which thread the method is to be called by EventBus.* EventBus takes care of threading independently from the posting thread.* * @see EventBus#register(Object)* @author Markus*/
public enum ThreadMode {/*** Subscriber will be called directly in the same thread, which is posting the event. This is the default. Event delivery* implies the least overhead because it avoids thread switching completely. Thus this is the recommended mode for* simple tasks that are known to complete in a very short time without requiring the main thread. Event handlers* using this mode must return quickly to avoid blocking the posting thread, which may be the main thread.*/POSTING,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in Android's main thread (UI thread). If the posting thread is* the main thread, subscriber methods will be called directly, blocking the posting thread. Otherwise the event* is queued for delivery (non-blocking). Subscribers using this mode must return quickly to avoid blocking the main thread.* If not on Android, behaves the same as {@link #POSTING}.*/MAIN,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in Android's main thread (UI thread). Different from {@link #MAIN},* the event will always be queued for delivery. This ensures that the post call is non-blocking.*/MAIN_ORDERED,/*** On Android, subscriber will be called in a background thread. If posting thread is not the main thread, subscriber methods* will be called directly in the posting thread. If the posting thread is the main thread, EventBus uses a single* background thread, that will deliver all its events sequentially. Subscribers using this mode should try to* return quickly to avoid blocking the background thread. If not on Android, always uses a background thread.*/BACKGROUND,/*** Subscriber will be called in a separate thread. This is always independent from the posting thread and the* main thread. Posting events never wait for subscriber methods using this mode. Subscriber methods should* use this mode if their execution might take some time, e.g. for network access. Avoid triggering a large number* of long running asynchronous subscriber methods at the same time to limit the number of concurrent threads. EventBus* uses a thread pool to efficiently reuse threads from completed asynchronous subscriber notifications.*/ASYNC
}
相關文檔
- EventBus詳解 (詳解 + 原理)
- 三幅圖弄懂EventBus核心原理

【應用啟動框架AppStartup】)












)
是什么)



