It is during our darkest moments that we must focus to see the light
???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????—— 24.5.24
一、第一種方式_繼承extends Thread方法
1.定義一個類,繼承Thread
2.重寫run方法,在run方法中設置線程任務(所謂的線程任務指的是此線程要干的具體的事兒,具體執行的代碼)
3.創建自定義線程類的對象
4.調用Thread中的start方法,開啟線程,jvm自動調用run方法package S64thread;public class Demo195Mythread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println("Mythread執行了"+i);}} }package S64thread;public class Demo196Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建線程對象Demo195Mythread t1 = new Demo195Mythread();// 調用start方法,開啟線程,jvm自動調用run方法,只有調用start才會開啟線程,二者一同執行// t1.run();t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println("main線程執行了"+i);}} }
二、多線程在內存中的運行原理?
????????注意:同一個線程對象不能連續調用多次start,如果想要再次調用start,那么咱們就new一個新的線程對象
三、Thread類中的方法
package S65threadMethod;public class Demo197Mythread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(getName()+"執行了"+i);}} }package S65threadMethod;public class Demo198Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建線程對象Demo197Mythread t1 = new Demo197Mythread();// 給線程設置名字t1.setName("趙四");// 調用start方法,開啟線程,jvm自動調用run方法,只有調用start才會開啟線程,二者一同執行// t1.run();t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println("main線程執行了"+i);}} }void start() -> 開啟線程,jvm自動調用run方法
void run() -> 設置線程任務,這個run方法是Thread重寫的接口Runnable中的run方法
String getName()?-> 獲取線程名字
void setName(string name) -> 給線程設置名字
static Thread currentThread() -> 獲取正在執行的線程對象(此方法在哪個線程中使用,獲取的就是哪個線程對象static void sleep(long millis) -> 線程睡眠,超時后會自動醒來繼續執行,傳遞的是毫秒值,睡眠時不會影響其他線程,其他線程會直接運行完,不會等待
package S65threadMethod;public class Demo197Mythread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// 線程睡眠try{// 線程sleep后一頓一頓的執行Thread.sleep(1000L);}catch (InterruptedException e){throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 鏈式調用 currentThread 獲取正在執行的線程對象System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"線程執行了"+i);}} }package S65threadMethod;public class Demo198Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建線程對象Demo197Mythread t1 = new Demo197Mythread();// 給線程設置名字 線程一頓一頓的執行t1.setName("趙四");// 調用start方法,開啟線程,jvm自動調用run方法,只有調用start才會開啟線程,二者一同執行// t1.run();t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// 鏈式調用System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"線程執行了"+i);}} }
問題:為啥在重寫的run方法中有異常只能try,不能throws
原因:繼承的 Thread中的run方法 沒有拋異常,所以在子類中重寫完run方法之后就不能拋,只能try…catch
四、thread中的其他方法
1.線程優先級
? ? ? ? ① void setPriority(int newPriority) —— 設置線程優先級,優先級越高的線程,搶到CPU使用權的幾率越大,但是不是每次都先搶到
? ? ? ? ② int getPriority() —— 獲取線程優先級
package S66thread;import S65threadMethod.Demo197Mythread;public class Demo200Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建兩個線程對象Demo199Mythread1 t1 = new Demo199Mythread1();t1.setName("金蓮");Demo199Mythread1 t2 = new Demo199Mythread1();t2.setName("阿慶");// 獲取兩個線程的優先級 5是一個默認優先級/*獲取兩個線程的優先級MIN_PRIORITY=1 最小優先級 1NORM_PRIORITY=5 默認優先級 5MAX_PRIORITY=10 最大優先級 10*/System.out.println(t1.getPriority());System.out.println(t2.getPriority());// 設置優先級t1.setPriority(1);t2.setPriority(10);System.out.println(t1.getPriority());System.out.println(t2.getPriority());t1.start();t2.start();} }
2.守護線程
????????③ void setDaemon(boolean on) —— 設置為守護線程,當非守護線程執行完畢,守護線程就要結束,但是守護線程也不是立馬結束,當非守護線程結束之后,系統會告訴守護線程人家結束了,你也結束吧,在告知的過程中,守護線程會執行,只不過執行到半路就結束了
package S67ProtectThread;public class Demo201MyThread1 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"執行了......"+i);}} }package S67ProtectThread;public class Demo203MyThread2 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 99; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"執行了..."+i);}} }package S67ProtectThread;public class Demo202Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建兩個線程對象Demo201MyThread1 t1 = new Demo201MyThread1();t1.setName("金蓮");Demo203MyThread2 t2 = new Demo203MyThread2();t2.setName("阿慶");// 將t2設置為守護線程t2.setDaemon(true);t1.start();t2.start();} }
使用場景:
3.禮讓線程
讓兩個線程盡可能的平衡一點->盡量讓兩個線程交替執行
????????④ static void yield() ——?禮讓線程,讓當前線程讓出CPU使用權
場景說明:如果兩個線程一起執行,可能會執行一會兒線程A,再執行一會線程B,或可能線程A執行完畢了,線程B在執行注意:只是盡可能的平衡,不是絕對的平衡,有可能在禮讓線程之后又搶到了CPU使用權
package S68PoliteThread;public class Demo204MyThread1 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了..."+i);// 禮讓線程Thread.yield();}} }package S68PoliteThread;public class Demo205Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建兩個線程對象Demo204MyThread1 t1 = new Demo204MyThread1();t1.setName("金蓮");Demo204MyThread1 t2 = new Demo204MyThread1();t2.setName("阿慶");// 禮讓線程Thread.yield();t1.start();t2.start();} }
?????
4.插入線程? ? ??
⑤ void join() ——?插入線程或者叫做插隊線程
package S69InsertThread;public class Demo206MyThread1 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了..."+i);// 插入線程}} }package S69InsertThread;public class Demo207Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 創建兩個線程對象Demo206MyThread1 t1 = new Demo206MyThread1();t1.setName("金蓮");t1.start();// 插入線程 表示把t1插入到當前線程之前t1.join();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了..."+i);// 插入線程}t1.start();} }
五、第二種方式_實現Thread中的Runnable接口
Thread中的run方法重寫的Runnable中的接口,可以直接實現Runnable接口
1.創建類,實現Runnable接口
2.重寫run方法,設置線程任務
3.利用Thread類的構造方法:Thread(Runnable target),創建Thread對象(線程對象),將自定義的類當參數傳遞到Thread構造中 —> 這一步是讓我們自己定義的類成為一個真正的線程類對象4.調用Thread中的start方法,開啟線程,jvm虛擬機自動調用run方法
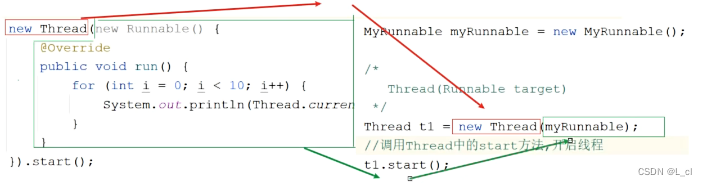
package S70ThreadRunnable;public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了"+i);}} }package S70ThreadRunnable;public class Demo208Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();// Thread(Runnable target)Thread t1 = new Thread(myRunnable);// 調用Thread中的start方法,開啟線程t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了"+i);}} }
六、兩種實現多線程的方式區別
1.繼承Thread:繼承只支持單繼承,有繼承的局限性
2.實現Runnable:沒有繼承的局限性,MyThread extends Fu implements Runnable
七、匿名內部類方式創建多線程
????????嚴格意義上來說,匿名內部類方式不屬于創建多線程方式其中之一,因為匿名內部類形式建立在實現Runnable接口的基礎上完成的
????????匿名內部類回顧:
????????????????1.new 接口/抽象類(){????????????????????????重寫方法
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }.重寫的方法();
????????????????2.接口名/類名對象名 = new 接口/抽象類(){????????????????????????重寫方法
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }????????
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 對象名.重寫的方法();匿名內部類給線程取名
Thread(Runnable target,string name)????????name指的是給匿名內部類中的線程設置名字
package S70ThreadRunnable;public class Demo209Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*Thread(Runnable r)*/new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了"+i);}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"...執行了"+i);}}}).start();} }









回歸預測)






![[實例] Unity Shader 逐像素漫反射與半蘭伯特光照](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[實例] Unity Shader 逐像素漫反射與半蘭伯特光照)











