Java進階11 IO流-功能流
一、字符緩沖流
字符緩沖流在源代碼中內置了字符數組,可以提高讀寫效率
1、構造方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| BufferedReader(new FileReader(文件路徑)) | 對傳入的字符輸入流進行包裝 |
| BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(文件路徑)) | 對傳入的字符輸出流進行包裝 |
注意:緩沖流不具備讀寫功能,它們只是對普通的流對象進行包裝,正真和文件建立關聯的,還是普通流對象
1.1 字符緩沖流的使用
public class BufferedStreamDemo1 {/*1、字符緩沖流的基本使用*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day10\\A.txt"));
?//單個讀取int i;while((i=br.read())!=-1){System.out.println((char)i);}
?//讀取字符數組的一部分int len;char[] chs = new char[1024];while((len=br.read())!=-1){String s = new String(chs,0,len);System.out.println(s);}
?br.close();
?//字符緩沖輸出流BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day10\\A.txt"));bw.write("寫入數據......")bw.close();}
}
1.2 拷貝文件Demo
public class BufferedStreamDemo {/*字符緩沖流+自定義數組 拷貝文件*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//字符流只能拷貝純文本文件BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day11\\FileReaderDemo1.java"));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day11\\copy.java"));
?int len;char[] chs = new char[1024];while((len=br.read())!=-1){bw.write(chs,0,len);}br.close();bw.close();}
}
2、成員方法(特有)
2.1 BufferedReader
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| public String readLine() | 一次性讀取整行字符串,讀取到末尾返回null |
2.2 BufferedWriter
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| public void newLine() | 寫出換行符(具有兼容性)兼容各個操作系統的換行符 |
2.3 特有方法使用Demo
public class BufferedStreamDemo2 {/*拷貝本項目中A.txt文件到本項目copy.txt;一整行一整行地拷貝*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day11\\A.txt"));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day11\\copy.txt"));
?String line;while((line=br.readLine())!=null){//readLine讀不到換行符bw.write(line);//寫出換行符bw.newLine();}br.close();bw.close();}
}
二、轉換流
1、按照指定的字符編碼讀寫操作
| 構造方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName) | 按照指定的字符編碼讀取 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName) | 按照指定的字符編碼寫出 |
public class ChangeStreamDemo {/*轉換流的使用Demo*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//使用GBK字符編碼向路徑D:\itheima\Resource\A.txt文件寫入你好呀OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\itheima\\Rescouce\\A.txt"),"GBK");osw.write("你好呀");osw.close();
?//使用gbk字符編碼從路徑D:\itheima\Resource\A.txt文件中讀取字符InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\Resource\\A.txt"),"gbk");//單個讀取int i;while((i=isr.read())!=-1){System.out.print((char)i);}isr.close();}
}
2、將字節流轉換為字符流進行操作
三、序列化流
可以在流中,以字節的形式直接讀寫對象
1、構造方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| public ObjectInuputStream(InputStream in) | 對象輸入流關聯文件,關聯方式使用字節輸入流 |
| public ObjectOutputStream(OutoutStream out) | 對象輸出流關聯文件,關聯方式使用字節輸出流 |
2、成員方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| Object readObject() | 從流中讀取對象(反序列化) |
| void writeObject(Object obj) | 在流中將對象寫出(序列化) |
3、方法使用案例
需求:現有3個學生對象,并將對象序列化到流中,隨后完成反序列化操作
public class ObjectStreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {readObject();
?//用流讀對象ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day11\\obj.txt"));ArrayList<Student> stuList ?= (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();System.out.println(stuList);ois.close();}
?//將對象寫入流private static void readObject() throws IOException {//為了一次讀寫三個學生對象,創建list集合存儲ArrayList<Student> stu = new ArrayList<>();stu.add(new Student("張三",23));stu.add(new Student("李四",24));stu.add(new Student("王五",25));
?ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day11\\obj.txt"));oos.writeObject(stu);oos.close();}
}
注意事項
-
類需要實現Serializable接口才可以序列化
-
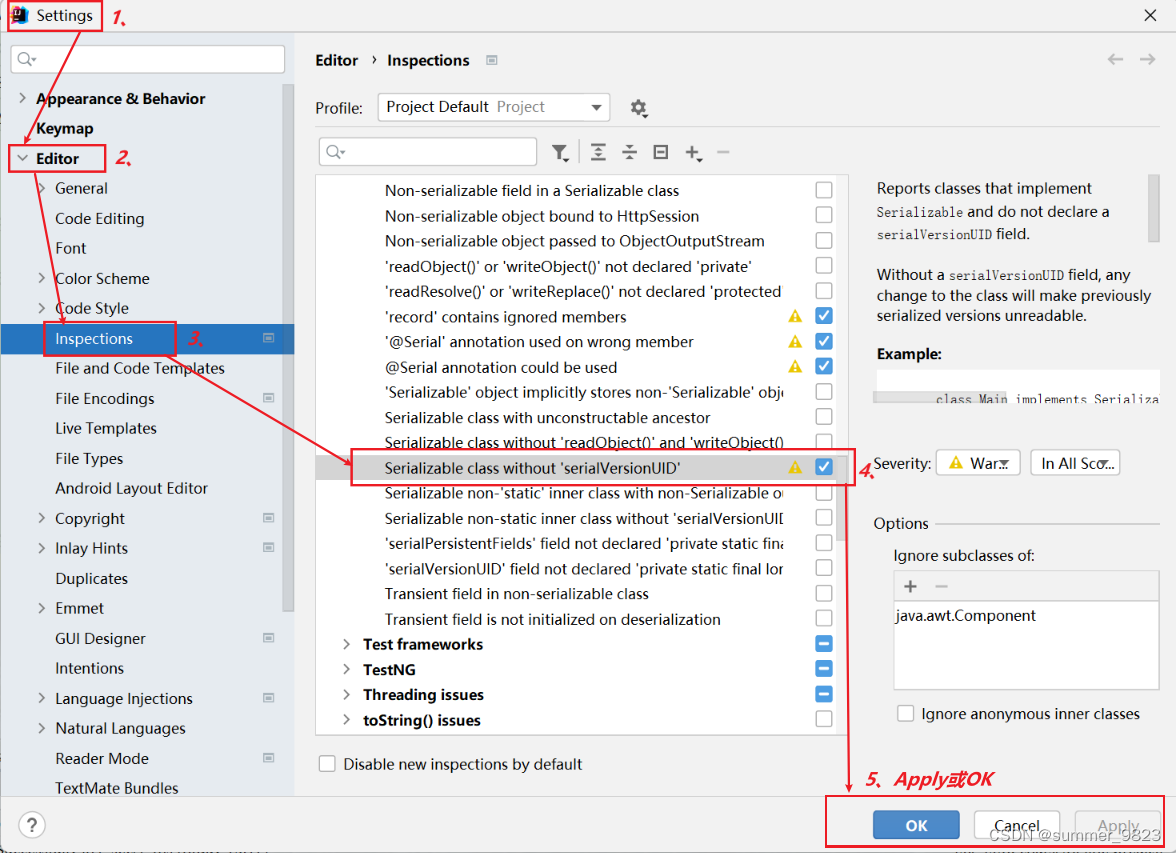
實現接口后,類就會自帶一份序列版本號。序列化操作的時候,會將對象信息和版本號一并保存到文件,反序列化的時候,會拿著版本號和流中的版本號進行對比,不一致就會拋異常,起到提醒作用。為了避免這個問題,推薦手動寫死serialVersionUID
在IDEA中設置快捷添加serialVersionUID的快捷鍵
-
-
如果類中的屬性被transient進行修飾,將不會參與序列化操作
-
建議:對象的讀寫操作只進行一次
四、打印流
打印流可以實現方便、高效的打印數據到文件中去(打印什么數據就是什么數據)
1、PrintStream字節打印流(重點)
| 構造器 | 說明 |
|---|
| public PrintStream(OutputStream os) | 打印流直接通向字節輸出流管道(想要追加時可在os對象的第二個參數位置打開append追加開關) |
| public PrintStream(File f) | 打印流直接通向文件對象 |
| public PrintStream(String filepath) | 打印流直接通向文件路徑 |
| 成員方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| public void print\println(Xxx xxx) | 打印任意類型的數據出去 |
2、PrintWriter字符打印流(了解即可)
| 構造器 | 說明 |
|---|
| public PrintWriter(OutputStream os) | 打印流直接通向字節輸出流管道 |
| public PrintWriter(Writer w) | 打印流直接通向字符輸出流管道 |
| public PrintWriter(File f) | 打印流直接通向文件對象 |
| public PrintWriter(String filepath) | 打印流直接通向文件路徑 |
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| public void print\println(Xxx xxx) | 打印任意類型的數據出去 |
五、Properties集合
1、Properties作為集合使用
| 構造器 | 說明 |
|---|
| Properties() | 創建一個沒有默認值的空屬性列表 |
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| Object setProperty(String key,String value) | 添加(修改)一個鍵值對 |
| String getPreperty(String key,String defaultValue) | 根據鍵獲取值 |
| Set<String> stringPropertyNames() | 獲取集合中所有的鍵 |
public class PropertiesDemo1 {/*properties作為集合的使用*/public static void main(String[] args) {//1、創建集合容器(不需要指定泛型,鍵和值都是String類)Properties prop = new Properties();//2、添加數據到集合(類似于put方法,當key相同時,新value會覆蓋舊value)prop.setProperty("username","admin");prop.setProperty("passward","123456");
?//3、獲取集合數據,根據鍵找值String username = prop.getProperty("username");String passward = prop.getProperty("passward");System.out.println(username+"----"+passward);
?System.out.println("-------------------------------");
?//4、類似Map集合中keySet方法,獲取所有的鍵Set<String> keySet = prop.stringPropertyNames();//5、遍歷集合+根據鍵找值拿到properties集合中的所有鍵值對for (String key : keySet) {System.out.println(key+"----"+prop.get(key));}}
}
2、Properties和IO有關的方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|
| void load(InputStream inStream) | 從輸入字節流讀取屬性列表(鍵和元素對) |
| void load(Reader reader) | 從輸入字符流讀取屬性列表(鍵和元素對) |
| void store(OutputStream out,String comments) | 將此屬性列表(鍵和元素對)寫入此Properties表中,以適合于使用load(InputStream)方法的格式寫入輸出字符流 |
| void store(Writer writer,String comments) | 將次屬性列表(鍵和元素對)寫入此Properties表中,以適合使用load(Reader)方法的格式寫入輸出字符流 |
public class PropertiesDemo2 {/*以字節輸入輸出流為例*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {store();load();}
?//讀取方法private static void load() throws IOException {Properties prop = new Properties();FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day11\\config.properties");//將讀取到的內容存入prop集合prop.load(fis);System.out.println(prop);fis.close();
?/**經常需要修改的值(如用戶名密碼、數據庫連接密碼等)寫在配置文件里,到時候只要執行這個代碼就能直接加載配置文件里的一些設置,免去了頻繁修改代碼的繁瑣*/String username = prop.getProperty("username");String password = prop.getProperty("password");
?System.out.println(username);System.out.println(password);}
?//寫入方法private static void store() throws IOException {Properties prop = new Properties();prop.setProperty("username","admin");prop.setProperty("password","123456");
?FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day11\\cpnfig.properties");
?//第二個參數為備注內容,可傳null,也可以傳入字符串值prop.store(fos,"null");
?fos.close();}
}






)












——方法與數組)
——模板的進階與繼承(一))
