背景
? ? ? ? c++中智能指針shared_ptr用于自動管理資源,通過引用計數來記錄資源被多少出地方使用。在不使用資源時,減少引用計數,如果引用計數為0,表示資源不會再被使用,此時會釋放資源。本文記錄對c++中std::shared_ptr的源碼學習。
為什么需要“智能”指針
? ? ? ?當我們需要在堆上分配對象時,可以通過new來創建,在不需要使用對象時,需要使用delete來釋放對象占用的資源,如下所示:
void foo() {...int *pi = new int(0);...delete pi;...
}? ? ? ? 如果在delete之前,函數提前return,則new出來的內存不會被釋放,導致內存泄露。另外,如果一個對象在函數中被new出來,并作為返回值返回,但是使用者如果不清楚函數內部實現,也可能忘記delete調new出來的對象,導致內存泄露,如下所示:
int* foo() {return new int(0);
}void bar() {int *pi = foo();...return; // 因為不知道foo返回的int*是new出來的,所以沒有delete pi
}? ? ? ? 對上面這種場景,還可能會出現一個指針被多處使用。為了確保指針在使用過程中沒有被delete,還需要關注指針使用的先后順序。但在迭代的過程中,這會導致指針的使用變得很難維護。為此,我們需要有一個“智能”的指針,維護我們new出來的對象,并在不需要的時候自動delete,釋放資源。
智能指針如何“智能”
? ? ? ? c++智能指針利用class的構造函數和析構函數來對指針管理,構造函數中將new出來的指針傳入,在析構函數中判斷如果沒人再使用,則會釋放指針。
? ? ? ? 如何判斷指針還被使用呢?答案是使用引用計數。只要指針被引用了,引用計數加1,當某一個引用不再使用(析構之后),則引用計數減1,如果指針不再被使用時,引用計數為0,此時即可delete指針,釋放資源。
? ? ? ? 那如何知道一個指針被引用了呢?答案就是復制構造和賦值構造。如果不知道什么是復制構造和賦值構造,可以先去學習下,以下是個簡單的例子:
class A {
public:// 構造函數A() {x = 0;}// 析構函數~A() {}// 復制構造A(const A &a) {x = a.x;}// 賦值構造A& operate=(cosnt A &a) {x = a.x;return *this;}
private:int x;
}int main() {A a1; // 構造函數A a2(a1); // 復制構造A a3 = a1; // 賦值構造
}
// 離開作用域,a1, a2, a3析構shared_ptr概覽
? ? ? ? shared_ptr定義如下:
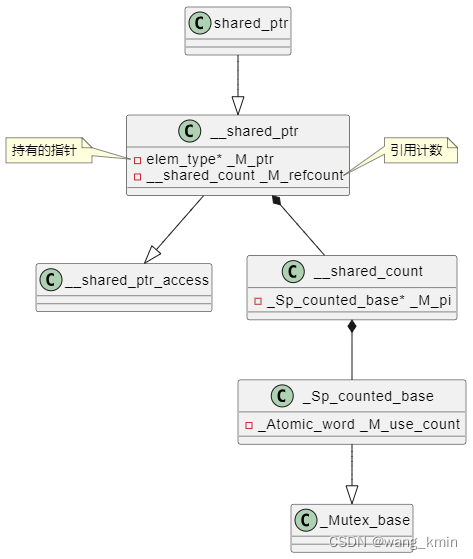
/*** @brief A smart pointer with reference-counted copy semantics.** The object pointed to is deleted when the last shared_ptr pointing to* it is destroyed or reset.*/template<typename _Tp>class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>{...}即shared_ptr繼承__shared_ptr,__shared_ptr定義如下:
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr: public __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;...private:element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.}? ? ? ? 從注釋中可以看出,__shared_ptr中有兩個成員變量:_M_ptr和_M_refcount。_M_ptr是智能指針管理的資源,_M_refcount是引用計數。再看下_M_refcount的類型定義,即__shared_count:
template<_Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_count{...private:_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;};template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>class _Sp_counted_base: public _Mutex_base<_Lp>{...private:_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared...};typedef int _Atomic_word;? ? ? ? 可以看出,引用計數本質是一個int值:_M_use_count。
? ? ? ? shared_ptr簡單的類圖示意如下:
? ? ? ? 根據智能指針實現方式,我們主要考慮構造函數、析構函數、復制構造函數、賦值構造函數。
構造函數
? ? ? ? 用以下代碼作為示例說明智能指針構造過程:
class A {
public:A() {cout << "construct A" << endl;}~A() {cout << "deconstruct A" << endl;}
};void test_init() {shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);
}? ? ? ? 當test函數被調用是,創建了一個A指針,該指針作為shared_ptr入參傳入構造函數,shared_ptr構造函數調用過程如下:
// shared_ptr構造函數/*** @brief Construct a %shared_ptr that owns the pointer @a __p.* @param __p A pointer that is convertible to element_type*.* @post use_count() == 1 && get() == __p* @throw std::bad_alloc, in which case @c delete @a __p is called.*/template<typename _Yp, typename = _Constructible<_Yp*>>explicitshared_ptr(_Yp* __p) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p) { }// __shared_ptr構造函數,本文考慮指針不是數組指針,即is_array<_Tp>::type() == false_typetemplate<typename _Yp, typename = _SafeConv<_Yp>>explicit__shared_ptr(_Yp* __p): _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p, typename is_array<_Tp>::type()){...}// 引用計數__shared_ptr::_M_refcount(__shared_count類型)構造函數template<typename _Ptr>__shared_count(_Ptr __p, /* is_array = */ false_type): __shared_count(__p){ }template<typename _Ptr>explicit__shared_count(_Ptr __p) : _M_pi(0){__try{_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_ptr<_Ptr, _Lp>(__p);}__catch(...){delete __p;__throw_exception_again;}}// __shared_count::_M_pi構造函數// Counted ptr with no deleter or allocator supporttemplate<typename _Ptr, _Lock_policy _Lp>class _Sp_counted_ptr final : public _Sp_counted_base<_Lp>{public:explicit_Sp_counted_ptr(_Ptr __p) noexcept: _M_ptr(__p) { }...private:_Ptr _M_ptr;};_Sp_counted_base() noexcept: _M_use_count(1), _M_weak_count(1) { }
? ? ? ?可以看到,new創建的指針被存在__shared_ptr::_M_ptr中,同時,__shared_ptr::_M_refcount構造函數中,new創建了_M_refcount::_M_pi,這樣,引用計數才不會因為__shared_ptr析構而消失,引用計數的生命周期應該與指針的生命周期一致,才能記錄指針被引用的次數。__Sp_counted_base構造函數中,初始化引用計數_M_use_count為1,表示當前只有1處在使用該指針。
????????構造函數調用結束之后,shared_ptr數據可簡單表示為:

? ? ? ? (為什么內存布局是這樣?可查看附錄中的測試代碼。)
復制構造
? ? ? ? 以下代碼被調用時,智能指針的復制構造函數被調用:
int test_copy() {shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);shared_ptr<A> pa_copy(pa); // 復制構造
}? ? ? ? 復制構造主要實現代碼如下:
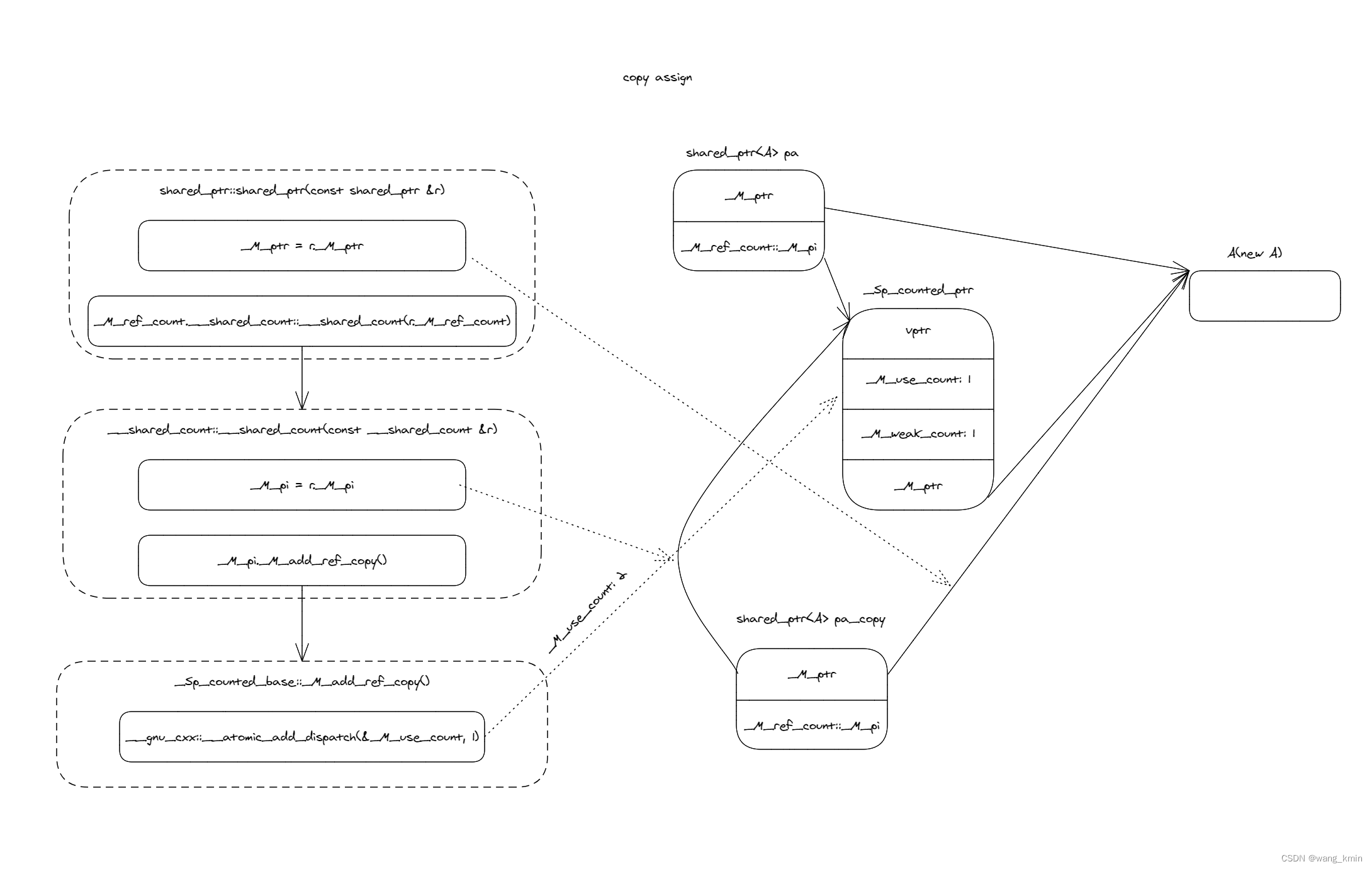
template<typename _Tp>class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>{...public:...shared_ptr(const shared_ptr&) noexcept = default; // 默認復制構造...}template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr: public __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;...__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr&) noexcept = default; // 默認復制構造...private:...element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.}? ? ? ? 復制構造使用編譯器生成的默認復制構造函數,偽代碼可以表示成:
template<typename _Tp>class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>{...public:...shared_ptr(const shared_ptr& ptr) noexcept {_M_ptr = __ptr._M_ptr;_M_refcount.__shared_count::__shared_count(__ptr._M_refcount);}...}? ? ? ? 繼續看__shared_count的復制構造函數:
template<_Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_count{...public:__shared_count(const __shared_count& __r) noexcept: _M_pi(__r._M_pi){if (_M_pi != 0)_M_pi->_M_add_ref_copy();}...private:..._Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;}template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>class _Sp_counted_base: public _Mutex_base<_Lp>{public:...void_M_add_ref_copy(){ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1); }...private:_Sp_counted_base(_Sp_counted_base const&) = delete;_Sp_counted_base& operator=(_Sp_counted_base const&) = delete;_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared_Atomic_word _M_weak_count; // #weak + (#shared != 0)};namespace __gnu_cxx _GLIBCXX_VISIBILITY(default)
{
_GLIBCXX_BEGIN_NAMESPACE_VERSION// Functions for portable atomic access.// To abstract locking primitives across all thread policies, use:// __exchange_and_add_dispatch// __atomic_add_dispatch
#ifdef _GLIBCXX_ATOMIC_BUILTINSstatic inline _Atomic_word __exchange_and_add(volatile _Atomic_word* __mem, int __val){ return __atomic_fetch_add(__mem, __val, __ATOMIC_ACQ_REL); }...static inline void__attribute__ ((__unused__))__atomic_add_dispatch(_Atomic_word* __mem, int __val){
#ifdef __GTHREADSif (__gthread_active_p())__atomic_add(__mem, __val);else__atomic_add_single(__mem, __val);
#else__atomic_add_single(__mem, __val);
#endif}_GLIBCXX_END_NAMESPACE_VERSION
} // namespace
? ? ? ? 可以看到,復制構造函數最終就是將引用計數加1,且是通過原子操作來進行加1的,由此可見:智能指針是線程安全的!至于如何實現的線程安全,本文暫不深究。
賦值構造
? ? ? ? 類似地,以下函數調用時,智能指針的賦值構造函數被調用:
int test_assgin() {shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);shared_ptr<A> pa_assign(new A);pa_assign = pa; // 賦值構造
}? ? ? ? 比復制構造稍微復雜一點,賦值構造的實現如下:
template<typename _Tp>class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>{...public:...shared_ptr& operator=(const shared_ptr&) noexcept = default;...}template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr: public __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;...__shared_ptr& operator=(const __shared_ptr&) noexcept = default;...private:...element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.}template<_Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_count{...public:...__shared_count&operator=(const __shared_count& __r) noexcept{_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;if (__tmp != _M_pi){if (__tmp != 0)__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy();if (_M_pi != 0)_M_pi->_M_release();_M_pi = __tmp;}return *this;}...private:..._Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;}template<typename _Ptr, _Lock_policy _Lp>class _Sp_counted_ptr final : public _Sp_counted_base<_Lp>{public:...virtual void_M_dispose() noexcept{ delete _M_ptr; }virtual void_M_destroy() noexcept{ delete this; }...}template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>class _Sp_counted_base: public _Mutex_base<_Lp>{public:...void_M_add_ref_copy(){ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1); }...void_M_release() noexcept{// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config._GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_use_count);if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, -1) == 1){_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_use_count);_M_dispose();// There must be a memory barrier between dispose() and destroy()// to ensure that the effects of dispose() are observed in the// thread that runs destroy().// See http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/libstdc++/2005-11/msg00136.htmlif (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers){__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);}// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config._GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count,-1) == 1){_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);_M_destroy();}}}...private:_Sp_counted_base(_Sp_counted_base const&) = delete;_Sp_counted_base& operator=(_Sp_counted_base const&) = delete;_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared_Atomic_word _M_weak_count; // #weak + (#shared != 0)};namespace __gnu_cxx _GLIBCXX_VISIBILITY(default)
{
_GLIBCXX_BEGIN_NAMESPACE_VERSION...static inline _Atomic_word__attribute__ ((__unused__))__exchange_and_add_dispatch(_Atomic_word* __mem, int __val){
#ifdef __GTHREADSif (__gthread_active_p())return __exchange_and_add(__mem, __val);elsereturn __exchange_and_add_single(__mem, __val);
#elsereturn __exchange_and_add_single(__mem, __val);
#endif}..._GLIBCXX_END_NAMESPACE_VERSION
} // namespace? ? ? ? 賦值構造會將被復制的對象引用計數加1,同時,將自身的引用計數減1,如果減1之前,自身的引用計數已經為1,則將釋放持有的指針:_M_dispose(),并且weak_count=1時,也會將自身delete掉:_M_destroy()。整個操作也是線程安全的。

析構函數
? ? ? ? 當類離開其作用域時,析構函數會被調用:
int test_destroy() {{shared_ptr<A> pa(new A);}// 此時, pa的析構函數已經被調用
}? ? ? ? 析構函數的實現如下:
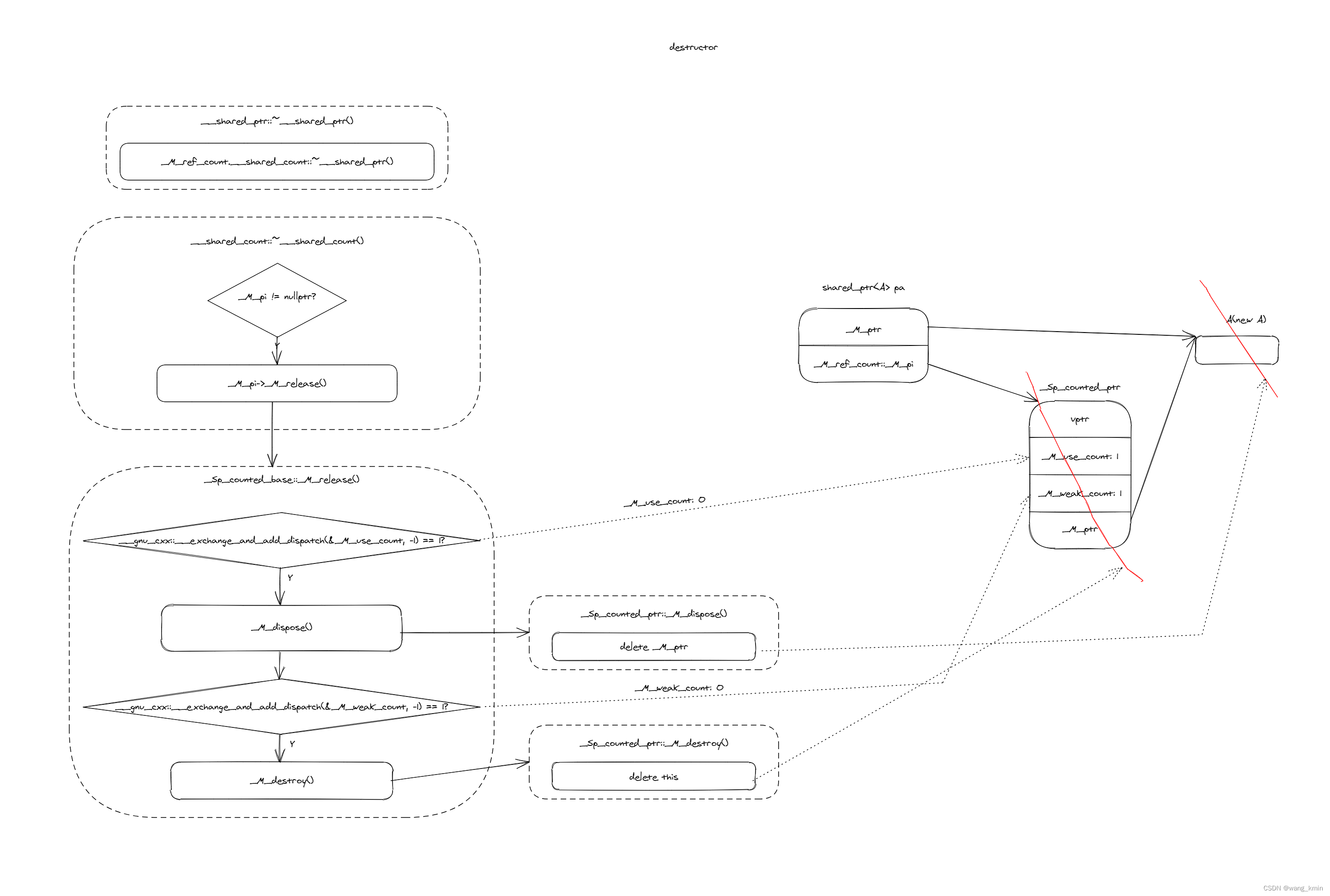
// shared_ptr沒有顯式定義析構函數template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr: public __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;...~__shared_ptr() = default;...private:...element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.}template<_Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_count{...public:...~__shared_count() noexcept{if (_M_pi != nullptr)_M_pi->_M_release();}...private:..._Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;}
? ? ? ? 析構函數調用引用計數的_M_release(),即引用計數減1,且如果資源不再使用,則釋放資源。
像使用指針一樣
? ? ? ? 在使用智能指針時,為了能像使用指針一樣,智能指針對操作符*、->進行了重載,我們就能像下面這樣使用智能指針了:
struct B {int b;
};void test() {B *pb = new B;shared_ptr<B> shared_pb(pb);shared_pb->b = 1; // 類似于pb->b = 1B b = *shared_pb; // 類似于B b = *pb;
}? ? ? ? 重載操作符的實現如下:
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp, true, false>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;#if __cplusplus <= 201402L[[__deprecated__("shared_ptr<T[]>::operator* is absent from C++17")]]element_type&operator*() const noexcept{__glibcxx_assert(_M_get() != nullptr);return *_M_get();}[[__deprecated__("shared_ptr<T[]>::operator-> is absent from C++17")]]element_type*operator->() const noexcept{_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_PEDASSERT(_M_get() != nullptr);return _M_get();}
#endif...private:element_type*_M_get() const noexcept{ return static_cast<const __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>*>(this)->get(); }};template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>class __shared_ptr: public __shared_ptr_access<_Tp, _Lp>{public:using element_type = typename remove_extent<_Tp>::type;...element_type*get() const noexcept{ return _M_ptr; }...private:element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.};總結
? ? ? ? 總結一下,智能指針,就是申請資源(本文中的例子是指針)之后,將資源交給智能指針,智能指針復制、賦值時原子增加、減少引用計數,并在引用計數為0,即沒有人再使用資源時,釋放資源,并將引用計數釋放掉(引用計數也是new申請出來的),以此來實現“智能”管理資源。
附錄
shared_ptr內存布局測試
? ? ? ? 測試代碼如下:
# include <memory>
# include <iostream>
# include <stdint.h>using namespace std;class A {
public:A() {cout << "construct A" << endl;}~A() {cout << "deconstruct A" << endl;}
};/*__shared_ptr:element_type* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.__shared_count:_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;_Sp_counted_ptr:void *vptr;_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared_Atomic_word _M_weak_count; // #weak + (#shared != 0)_Ptr _M_ptr;*/int main() {{A *pa = new A();shared_ptr<A> shared_pa(pa);char *addr = (char*)&shared_pa;void *shared_pa_addr = *((void**)addr);void *_M_pi = *((void**)(addr+8));printf("pa: 0x%X, shared_pa_addr: 0x%X, _M_pi: 0x%X\n", pa, shared_pa_addr, _M_pi);addr = (char*)_M_pi;void *vptr = *((void**)addr);int _M_use_count = *((int*)(addr+8));int _M_weak_count = *((int*)(addr+12));void *_M_ptr = *((void**)(addr+16));printf("vptr: 0x%X, _M_use_count: %d, _M_weak_count: %d, _M_ptr: 0x%X\n", vptr, _M_use_count, _M_weak_count, _M_ptr);}cout << "move scope" << endl;
}
面試要求寫一個智能指針
? ? ? ? 面試中可能會被要求實現一個智能指針,先不考慮線程安全、各種場景的兼容,可以對上面代碼進行精簡,僅對核心邏輯做實現:
#ifndef M_SMART_POINTER_H
#define M_SMART_POINTER_Htemplate<typename T>
class MSmartPointer {
public:MSmartPointer(T *ptr_) {ptr = ptr_;ref_count_ptr = new int(1);}MSmartPointer(const MSmartPointer &r) {Copy(r);}MSmartPointer& operator=(const MSmartPointer &r) {if (r.ptr != ptr) {Release();Copy(r);}return *this;}~MSmartPointer() {Release();}T& operator*() {return *ptr;}T* operator->() {return ptr;}int ref_count() {return *ref_count_ptr;}
private:void Copy(const MSmartPointer &r) {ptr = r.ptr; // 持有指針ref_count_ptr = r.ref_count_ptr; // 持有指針對應的引用計數if (ref_count_ptr)(*ref_count_ptr)++; // 引用計數加1}void Release() {if (!ref_count_ptr) return;if (--(*ref_count_ptr) <= 0) { // 引用計數減1,如果引用計數小于等于0,代表沒人用了,需要釋放資源delete ref_count_ptr; // 釋放引用計數ref_count_ptr = nullptr;delete ptr; // 釋放持有的指針ptr = nullptr;}}private:T *ptr;int *ref_count_ptr;
};#endif? ? ? ? 附上測試代碼:
void test_m_smart_pointer() {cout << "test_m_smart_pointer" << endl;{MSmartPointer<Test> p(new Test);cout << "1. ref_count: " << p.ref_count() << endl;p->t = 1;cout << "1. t: " << p->t << endl;{MSmartPointer<Test> p1(p);cout << "2. ref_count: " << p.ref_count() << endl; (*(p1)).t = 2;cout << "2. t: " << p->t << endl;MSmartPointer<Test> p2(new Test);p2 = p;cout << "3. ref_count: " << p.ref_count() << endl; }cout << "4. ref_count: " << p.ref_count() << endl; }cout << "move scope" << endl;
}線程安全思考
? ? ? ? 在對智能指針的引用計數進行修改時,都使用額原子操作,因此引用計數的加減都是現成安全的。但是,在釋放資源時,其整個釋放的操作為非原子的。如果在釋放資源的過程,發生了復制、賦值,則就可能出現資源被釋放,但是還有地方在引用的問題。不考慮多線程場景,以下面的代碼舉例:
void test_atomic_thread_safe() {A *pa = new A;shared_ptr<A> shared_pa(pa);shared_pa.__shared_ptr<A>::~__shared_ptr<A>();shared_ptr<A> shared_pb(pa);cout << "test call deconstruct: " << shared_pb.use_count() << endl;
}? ? ? ? ?這段代碼運行結果如下:
construct A
deconstruct A
test call deconstruct: 1
deconstruct A
deconstruct A
free(): double free detected in tcache 2
[1] 6372 abort (core dumped) ./output/main? ? ? ? 可以看到,在shared_pa被析構之后,再去對其復制,將導致持有的指針不再有效。但是,正常情況下,誰會主動掉析構函數呢?如果我們不主動調析構函數,則析構函數被調用時,我們也取不到對象了,更別提對其引用。所以總體看來,智能指針還是線程安全的。


—封裝頭部導航組件)




-KDE巡檢報告(模板)











