基本概念 | 官方定義
VFS(Virtual File System)是文件系統的虛擬層,它不是一個實際的文件系統,而是一個異構文件系統之上的軟件粘合層,為用戶提供統一的類Unix文件操作接口。由于不同類型的文件系統接口不統一,若系統中有多個文件系統類型,訪問不同的文件系統就需要使用不同的非標準接口。而通過在系統中添加VFS層,提供統一的抽象接口,屏蔽了底層異構類型的文件系統的差異,使得訪問文件系統的系統調用不用關心底層的存儲介質和文件系統類型,提高開發效率。
OpenHarmony內核中,VFS框架是通過在內存中的樹結構來實現的,樹的每個結點都是一個Vnode結構體,父子結點的關系以PathCache結構體保存。VFS最主要的兩個功能是:
- 查找節點。
- 統一調用(標準)。
VFS層具體實現包括四個方面:
- 通過三大函數指針操作接口,實現對不同文件系統類型調用不同接口實現標準接口功能;
- 通過
Vnode與PathCache機制,提升路徑搜索以及文件訪問的性能; - 通過掛載點管理進行分區管理;
- 通過FD管理進行進程間FD隔離等。
三大操作接口
VFS層通過函數指針的形式,將統一調用按照不同的文件系統類型,分發到不同文件系統中進行底層操作。各文件系統的各自實現一套Vnode操作(VnodeOps)、掛載點操作(MountOps)以及文件操作接口(file_operations_vfs),并以函數指針結構體的形式存儲于對應Vnode、掛載點、File結構體中,實現VFS層對下訪問。這三個接口分別為:
VnodeOps | 操作 Vnode 節點
struct VnodeOps {int (*Create)(struct Vnode *parent, const char *name, int mode, struct Vnode **vnode);//創建節點int (*Lookup)(struct Vnode *parent, const char *name, int len, struct Vnode **vnode);//查詢節點//Lookup向底層文件系統查找獲取inode信息int (*Open)(struct Vnode *vnode, int fd, int mode, int flags);//打開節點int (*Close)(struct Vnode *vnode);//關閉節點int (*Reclaim)(struct Vnode *vnode);//回收節點int (*Unlink)(struct Vnode *parent, struct Vnode *vnode, const char *fileName);//取消硬鏈接int (*Rmdir)(struct Vnode *parent, struct Vnode *vnode, const char *dirName);//刪除目錄節點int (*Mkdir)(struct Vnode *parent, const char *dirName, mode_t mode, struct Vnode **vnode);//創建目錄節點/*創建一個目錄時,實際做了3件事:在其“父目錄文件”中增加一個條目;分配一個inode;再分配一個存儲塊,用來保存當前被創建目錄包含的文件與子目錄。被創建的“目錄文件”中自動生成兩個子目錄的條目,名稱分別是:“.”和“..”。前者與該目錄具有相同的inode號碼,因此是該目錄的一個“硬鏈接”。后者的inode號碼就是該目錄的父目錄的inode號碼。所以,任何一個目錄的"硬鏈接"總數,總是等于它的子目錄總數(含隱藏目錄)加2。即每個“子目錄文件”中的“..”條目,加上它自身的“目錄文件”中的“.”條目,再加上“父目錄文件”中的對應該目錄的條目。*/int (*Readdir)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct fs_dirent_s *dir);//讀目錄節點int (*Opendir)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct fs_dirent_s *dir);//打開目錄節點int (*Rewinddir)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct fs_dirent_s *dir);//定位目錄節點int (*Closedir)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct fs_dirent_s *dir);//關閉目錄節點int (*Getattr)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct stat *st);//獲取節點屬性int (*Setattr)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct stat *st);//設置節點屬性int (*Chattr)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct IATTR *attr);//改變節點屬性(change attr)int (*Rename)(struct Vnode *src, struct Vnode *dstParent, const char *srcName, const char *dstName);//重命名int (*Truncate)(struct Vnode *vnode, off_t len);//縮減或擴展大小int (*Truncate64)(struct Vnode *vnode, off64_t len);//縮減或擴展大小int (*Fscheck)(struct Vnode *vnode, struct fs_dirent_s *dir);//檢查功能int (*Link)(struct Vnode *src, struct Vnode *dstParent, struct Vnode **dst, const char *dstName);int (*Symlink)(struct Vnode *parentVnode, struct Vnode **newVnode, const char *path, const char *target);ssize_t (*Readlink)(struct Vnode *vnode, char *buffer, size_t bufLen);
};MountOps | 掛載點操作
//掛載操作
struct MountOps {int (*Mount)(struct Mount *mount, struct Vnode *vnode, const void *data);//掛載int (*Unmount)(struct Mount *mount, struct Vnode **blkdriver);//卸載int (*Statfs)(struct Mount *mount, struct statfs *sbp);//統計文件系統的信息,如該文件系統類型、總大小、可用大小等信息
};file_operations_vfs | 文件操作接口
struct file_operations_vfs
{int (*open)(struct file *filep); //打開文件int (*close)(struct file *filep); //關閉文件ssize_t (*read)(struct file *filep, char *buffer, size_t buflen); //讀文件ssize_t (*write)(struct file *filep, const char *buffer, size_t buflen);//寫文件off_t (*seek)(struct file *filep, off_t offset, int whence);//尋找,檢索 文件int (*ioctl)(struct file *filep, int cmd, unsigned long arg);//對文件的控制命令int (*mmap)(struct file* filep, struct VmMapRegion *region);//內存映射實現<文件/設備 - 線性區的映射>/* The two structures need not be common after this point */#ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_POLLint (*poll)(struct file *filep, poll_table *fds); //輪詢接口
#endifint (*stat)(struct file *filep, struct stat* st); //統計接口int (*fallocate)(struct file* filep, int mode, off_t offset, off_t len);int (*fallocate64)(struct file *filep, int mode, off64_t offset, off64_t len);int (*fsync)(struct file *filep);ssize_t (*readpage)(struct file *filep, char *buffer, size_t buflen);int (*unlink)(struct Vnode *vnode);
};
PathCache | 路徑緩存
PathCache是路徑緩存,它通過哈希表存儲,利用父節點Vnode的地址和子節點的文件名,可以從PathCache中快速查找到子節點對應的Vnode。當前PageCache僅支持緩存二進制文件,在初次訪問文件時通過mmap映射到內存中,下次再訪問時,直接從PageCache中讀取,可以提升對同一個文件的讀寫速度。另外基于PageCache可實現以文件為基底的進程間通信。下圖展示了文件/目錄的查找流程。

LIST_HEAD g_pathCacheHashEntrys[LOSCFG_MAX_PATH_CACHE_SIZE]; //路徑緩存哈希表項
struct PathCache {//路徑緩存struct Vnode *parentVnode; /* vnode points to the cache */ struct Vnode *childVnode; /* vnode the cache points to */LIST_ENTRY parentEntry; /* list entry for cache list in the parent vnode */LIST_ENTRY childEntry; /* list entry for cache list in the child vnode */LIST_ENTRY hashEntry; /* list entry for buckets in the hash table */uint8_t nameLen; /* length of path component */
#ifdef LOSCFG_DEBUG_VERSIONint hit; /* cache hit count*/
#endifchar name[0]; /* path component name */
};
//路徑緩存初始化
int PathCacheInit(void)
{for (int i = 0; i < LOSCFG_MAX_PATH_CACHE_SIZE; i++) {LOS_ListInit(&g_pathCacheHashEntrys[i]);}return LOS_OK;
}掛載點管理
當前OpenHarmony內核中,對系統中所有掛載點通過鏈表進行統一管理。掛載點結構體中,記錄了該掛載分區內的所有Vnode。當分區卸載時,會釋放分區內的所有Vnode。
static LIST_HEAD *g_mountList = NULL;//掛載鏈表,上面掛的是系統所有掛載點
struct Mount {LIST_ENTRY mountList; /* mount list */ //通過本節點將Mount掛到全局Mount鏈表上const struct MountOps *ops; /* operations of mount */ //掛載操作函數 struct Vnode *vnodeBeCovered; /* vnode we mounted on */ //要被掛載的節點 即 /bin1/vs/sd 對應的 vnode節點struct Vnode *vnodeCovered; /* syncer vnode */ //要掛載的節點 即/dev/mmcblk0p0 對應的 vnode節點struct Vnode *vnodeDev; /* dev vnode */LIST_HEAD vnodeList; /* list of vnodes */ //鏈表表頭int vnodeSize; /* size of vnode list */ //節點數量LIST_HEAD activeVnodeList; /* list of active vnodes */ //激活的節點鏈表int activeVnodeSize; /* szie of active vnodes list *///激活的節點數量void *data; /* private data */ //私有數據,可使用這個成員作為一個指向它們自己內部數據的指針uint32_t hashseed; /* Random seed for vfs hash */ //vfs 哈希隨機種子unsigned long mountFlags; /* Flags for mount */ //掛載標簽char pathName[PATH_MAX]; /* path name of mount point */ //掛載點路徑名稱 /bin1/vs/sdchar devName[PATH_MAX]; /* path name of dev point */ //設備名稱 /dev/mmcblk0p0
};
//分配一個掛載點
struct Mount* MountAlloc(struct Vnode* vnodeBeCovered, struct MountOps* fsop)
{struct Mount* mnt = (struct Mount*)zalloc(sizeof(struct Mount));//申請一個mount結構體內存,小內存分配用 zallocif (mnt == NULL) {PRINT_ERR("MountAlloc failed no memory!\n");return NULL;}LOS_ListInit(&mnt->activeVnodeList);//初始化激活索引節點鏈表LOS_ListInit(&mnt->vnodeList);//初始化索引節點鏈表mnt->vnodeBeCovered = vnodeBeCovered;//設備將裝載到vnodeBeCovered節點上vnodeBeCovered->newMount = mnt;//該節點不再是虛擬節點,而作為 設備結點
#ifdef LOSCFG_DRIVERS_RANDOM //隨機值 驅動模塊HiRandomHwInit();//隨機值初始化(VOID)HiRandomHwGetInteger(&mnt->hashseed);//用于生成哈希種子HiRandomHwDeinit();//隨機值反初始化
#elsemnt->hashseed = (uint32_t)random(); //隨機生成哈子種子
#endifreturn mnt;
}fd管理 | 兩種描述符/句柄的關系
Fd(File Descriptor)是描述一個打開的文件/目錄的描述符。當前OpenHarmony內核中,fd總規格為896,分為三種類型:
- 普通文件描述符,系統總數量為512。
#define CONFIG_NFILE_DESCRIPTORS 512 // 系統文件描述符數量
- Socket描述符,系統總規格為128。
#define LWIP_CONFIG_NUM_SOCKETS 128 //socket鏈接數量#define CONFIG_NSOCKET_DESCRIPTORS LWIP_CONFIG_NUM_SOCKETS
- 消息隊列描述符,系統總規格為256。
#define CONFIG_NQUEUE_DESCRIPTORS 256請記住,在OpenHarmony內核中,在不同的層面會有兩種文件句柄::
-
系統文件描述符(
sysfd),由內核統一管理,和進程描述符形成映射關系,一個sysfd可以被多個profd映射,也就是說打開一個文件只會占用一個sysfd,但可以占用多個profd,即一個文件被多個進程打開. -
進程文件描述符(
profd),由進程管理的叫進程文件描述符,內核對不同進程中的fd進行隔離,即進程只能訪問本進程的fd.舉例說明之間的關系:
文件 sysfd profd吃個桃桃.mp4 10 13(A進程)吃個桃桃.mp4 10 3(B進程)容嬤嬤被冤枉.txt 12 3(A進程)容嬤嬤被冤枉.txt 12 3(C進程)-
不同進程的相同
fd往往指向不同的文件,但有三個fd例外STDIN_FILENO(fd = 0)標準輸入 接收鍵盤的輸入STDOUT_FILENO(fd = 1)標準輸出 向屏幕輸出STDERR_FILENO(fd = 2)標準錯誤 向屏幕輸出
sysfd和所有的profd的(0,1,2)號都是它們.熟知的printf就是向STDOUT_FILENO中寫入數據.
-
具體涉及結構體
struct file_table_s {//進程fd <--> 系統FD綁定intptr_t sysFd; /* system fd associate with the tg_filelist index */};//sysFd的默認值是-1struct fd_table_s {//進程fd表結構體unsigned int max_fds;//進程的文件描述符最多有256個struct file_table_s *ft_fds; /* process fd array associate with system fd *///系統分配給進程的FD數組 ,fd 默認是 -1fd_set *proc_fds; //進程fd管理位,用bitmap管理FD使用情況,默認打開了 0,1,2 (stdin,stdout,stderr)fd_set *cloexec_fds;sem_t ft_sem; /* manage access to the file table */ //管理對文件表的訪問的信號量};struct files_struct {//進程文件表結構體int count; //持有的文件數量struct fd_table_s *fdt; //持有的文件表unsigned int file_lock; //文件互斥鎖unsigned int next_fd; //下一個fd#ifdef VFS_USING_WORKDIRspinlock_t workdir_lock; //工作區目錄自旋鎖char workdir[PATH_MAX]; //工作區路徑,最大 256個字符#endif};typedef struct ProcessCB {#ifdef LOSCFG_FS_VFSstruct files_struct *files; /**< Files held by the process */ //進程所持有的所有文件,注者稱之為進程的文件管理器#endif //每個進程都有屬于自己的文件管理器,記錄對文件的操作. 注意:一個文件可以被多個進程操作}解讀
- 鴻蒙的每個進程
ProcessCB都有屬于自己的進程的文件描述符files_struct,該進程和文件系統有關的信息都由它表達. - 搞清楚
files_struct,fd_table_s,file_table_s三個結構體的關系就明白了進度描述符和系統描述符的關系. fd_table_s是由alloc_fd_table分配的一個結構體數組,用于存放進程的文件描述符
//分配進程文件表,初始化 fd_table_s 結構體中每個數據,包括系統FD(0,1,2)的綁定static struct fd_table_s * alloc_fd_table(unsigned int numbers){struct fd_table_s *fdt;void *data;fdt = LOS_MemAlloc(m_aucSysMem0, sizeof(struct fd_table_s));//申請內存if (!fdt){goto out;}fdt->max_fds = numbers;//最大數量if (!numbers){fdt->ft_fds = NULL;fdt->proc_fds = NULL;return fdt;}data = LOS_MemAlloc(m_aucSysMem0, numbers * sizeof(struct file_table_s));//這是和系統描述符的綁定if (!data){goto out_fdt;}fdt->ft_fds = data;//這其實是個 int[] 數組,for (int i = STDERR_FILENO + 1; i < numbers; i++){fdt->ft_fds[i].sysFd = -1;//默認的系統描述符都為-1,即還沒有和任何系統文件描述符綁定}data = LOS_MemAlloc(m_aucSysMem0, sizeof(fd_set));//管理FD的 bitmap if (!data){goto out_arr;}(VOID)memset_s(data, sizeof(fd_set), 0, sizeof(fd_set));fdt->proc_fds = data;alloc_std_fd(fdt);//分配標準的0,1,2系統文件描述符,這樣做的結果是任務進程都可以寫系統文件(0,1,2)(void)sem_init(&fdt->ft_sem, 0, 1);//互斥量初始化return fdt;out_arr:(VOID)LOS_MemFree(m_aucSysMem0, fdt->ft_fds);out_fdt:(VOID)LOS_MemFree(m_aucSysMem0, fdt);out:return NULL;}
file_table_s記錄sysfd和profd的綁定關系.fdt->ft_fds[i].sysFd中的i就是profd
鴻蒙全棧開發全新學習指南
也為了積極培養鴻蒙生態人才,讓大家都能學習到鴻蒙開發最新的技術,針對一些在職人員、0基礎小白、應屆生/計算機專業、鴻蒙愛好者等人群,整理了一套純血版鴻蒙(HarmonyOS Next)全棧開發技術的學習路線【包含了大廠APP實戰項目開發】。
本路線共分為四個階段:
第一階段:鴻蒙初中級開發必備技能

第二階段:鴻蒙南北雙向高工技能基礎:gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH

第三階段:應用開發中高級就業技術
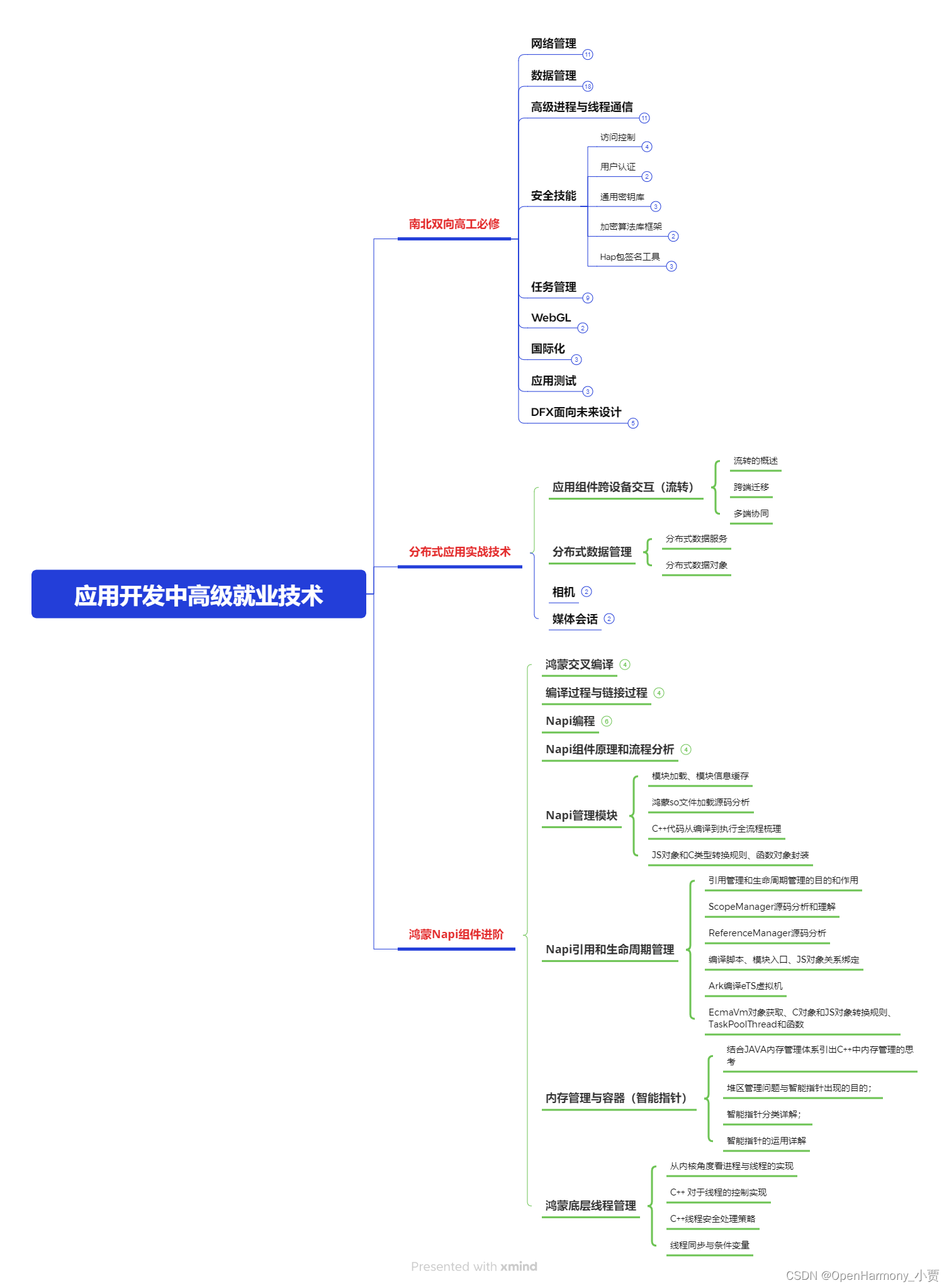
第四階段:全網首發-工業級南向設備開發就業技術:https://gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH

《鴻蒙 (Harmony OS)開發學習手冊》(共計892頁)
如何快速入門?
1.基本概念
2.構建第一個ArkTS應用
3.……

開發基礎知識:gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH
1.應用基礎知識
2.配置文件
3.應用數據管理
4.應用安全管理
5.應用隱私保護
6.三方應用調用管控機制
7.資源分類與訪問
8.學習ArkTS語言
9.……

基于ArkTS 開發
1.Ability開發
2.UI開發
3.公共事件與通知
4.窗口管理
5.媒體
6.安全
7.網絡與鏈接
8.電話服務
9.數據管理
10.后臺任務(Background Task)管理
11.設備管理
12.設備使用信息統計
13.DFX
14.國際化開發
15.折疊屏系列
16.……

鴻蒙開發面試真題(含參考答案):gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH

鴻蒙入門教學視頻:
美團APP實戰開發教學:gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH

寫在最后
- 如果你覺得這篇內容對你還蠻有幫助,我想邀請你幫我三個小忙:
- 點贊,轉發,有你們的 『點贊和評論』,才是我創造的動力。
- 關注小編,同時可以期待后續文章ing🚀,不定期分享原創知識。
- 想要獲取更多完整鴻蒙最新學習資源,請移步前往小編:
gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH


)


并不可怕,可怕的是...)

![[ACTF新生賽2020]SoulLike](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[ACTF新生賽2020]SoulLike)




。Javaee項目,ssm vue前后端分離項目)







)