1 Title
????????Deep Attention Diffusion Graph Neural Networks for Text Classification(Yonghao Liu、Renchu Guan、Fausto Giunchiglia、Yanchun Liang、Xiaoyue Feng)【EMnlp?2021】
2 Conclusion
????????Text classification is a fundamental task with broad applications in natural language processing. Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have attracted much attention due to their powerful representation ability. However, most existing methods for text classification based on GNNs consider only one-hop neighborhoods and low-frequency information within texts, which cannot fully utilize the rich context information of documents. Moreover, these models suffer from over-smoothing issues if many graph layers are stacked. In this paper, a Deep Attention Diffusion Graph Neural Network (DADGNN) model is proposed to learn text representations, bridging the chasm of interaction difficulties between a word and its distant neighbors.
3 Good Sentences
? ? ? ? 1、Previous shallow learning-based text classification approaches mainly use hand-crafted sparse lexical features, such as bag-of-words (BoW) or n-grams, for representing texts (Li et al., 2020). Since these features are predefined, the models do not take full advantage of the large amount of training data.(The disadvantages of previous methods)
? ? ? ? 2、?Theoretically, we can capture long-range dependencies between words with a large number of layers. However, a common challenge faced by most GNNs is that performance degrades severely when stacking multiple layers to exploit larger receptive fields. Some researchers attribute this phenomenon to over-smoothing indistinguishable representation of different classes of nodes.(The challenges of GNNs meet and its probably reason)
? ? ? ? 3、One crucial reason why our model achieves more significant improvements is that the receptive field of the target node is enhanced by attention diffusion, which incorporates more informative messages (i.e., both low-frequency and high-frequency information) in the text.(The reason why this method have an advantage)
? ? ? ?
-
問題背景:文本分類是自然語言處理中的基礎任務,圖神經網絡(GNNs)因其強大的表示能力而受到關注。然而,現有的基于GNN的文本分類方法通常只考慮單跳鄰域和文本中的低頻信息,無法充分利用文檔的豐富上下文信息。
-
現有方法的局限性:
- 受限的感受野:大多數方法只允許圖中的詞訪問直接鄰域,無法實現長距離詞交互。
- 較淺的層數:當前基于圖的模型通常采用較淺的設置,因為它們在兩層圖中表現最佳,但無法提取超過兩跳鄰居的信息。
- 非精確的文檔級表示:大多數模型使用簡單的池化操作(如求和或平均)來獲取文檔級表示,這會削弱一些關鍵節點的影響。
- 低通濾波器:現有的基于圖的方法主要是固定系數的低通濾波器,主要保留節點特征的共性,忽略了它們之間的差異。
-
DADGNN模型:為了克服上述限制,提出了DADGNN模型,該模型使用注意力擴散技術擴大每個詞的感受野,并解耦GNNs的傳播和轉換過程以訓練更深層的網絡。此外,通過計算每個節點的權重來獲得精確的文檔級表示。
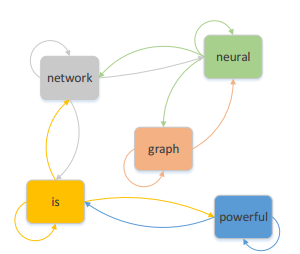
DADGNN有三個主要組成部分:文本圖構建、關鍵組件和圖級表示。
文本圖構建:

這樣構造的圖的優點是圖是有向的,其轉移矩陣就是對稱的,
Key Components:
為了獲得深層網絡中節點的判別特征表示,本文解耦了GNN的傳播和轉換過程。具體表述為:
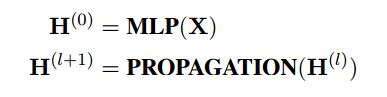

? ? ? ? 與傳統GNN不同,對于直接相連的節點對,本文使用公式3和4計算它們之間的注意力權重,并進行歸一化處理:

其中為權重矩陣,
為權重向量,是第
層共享的可訓練參數。
是第
層的圖注意矩陣。另外,σ是ReLU激活函數。
 后續可以通過擴散機制計算復雜網絡中不直接連接的節點之間的注意力。
后續可以通過擴散機制計算復雜網絡中不直接連接的節點之間的注意力。
????????根據注意矩陣A,得到圖的注意擴散矩陣T如下: ,其中ζn是可學習的系數,依賴于所構建的圖網絡所展示的屬性。
,其中ζn是可學習的系數,依賴于所構建的圖網絡所展示的屬性。
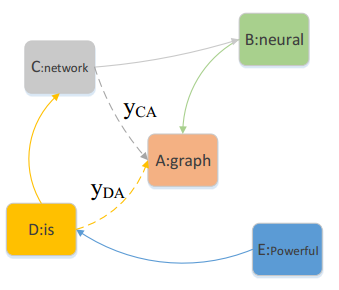 如圖所示,模型通過一個單層的注意力擴散過程來考慮節點之間的所有路徑,從而捕獲斷開節點的信息。例如(目標節點是“graph”,為簡潔起見,刪除(a)的不相關邊),
如圖所示,模型通過一個單層的注意力擴散過程來考慮節點之間的所有路徑,從而捕獲斷開節點的信息。例如(目標節點是“graph”,為簡潔起見,刪除(a)的不相關邊),![]() ,
,![]() 。
。
????????在實際應用中,考慮到現實世界網絡中小世界現象的特點,即任意兩個節點之間的最短路徑通常不會太長(最多四或六個跳),![]()
為了進一步提高注意擴散層的表達能力,本文部署了一個多頭注意擴散機制。具體來說,先獨立計算每個頭k的注意力擴散,然后將它們聚合。輸出特征表示如下:
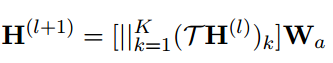
其中||是連接操作和表示轉換維度的權重矩陣
?Graph-Level Representation:
????????在傳播模型的第層之后,就可以計算每個文本圖上所有節點的最終表示。為了衡量圖中每個節點的不同作用,與使用一般池化的基于圖的文本分類模型相比,采用了節點級關注機制。具體可以用下式表示:
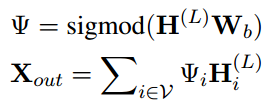 其中,
其中,是可訓練的權重矩陣,
表示圖中節點 i 的注意力系數。為了獲得每個類別的概率,進一步執行
![]() 。
。
最后,使用交叉熵損失作為目標函數來優化用于文本分類的神經網絡。
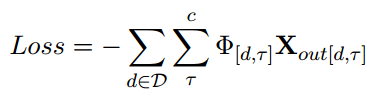 其中,D 是訓練數據集,Φ 是指標矩陣。需要注意的是,我們的模型可直接用于歸納學習任務,對于未見過的測試文檔,相應構建的圖可直接輸入訓練好的模型進行預測。此外,它是以端到端的方式進行訓練的,這意味著在優化網絡時會同時考慮可學習的參數。
其中,D 是訓練數據集,Φ 是指標矩陣。需要注意的是,我們的模型可直接用于歸納學習任務,對于未見過的測試文檔,相應構建的圖可直接輸入訓練好的模型進行預測。此外,它是以端到端的方式進行訓練的,這意味著在優化網絡時會同時考慮可學習的參數。





)






小紅叕戰小紫,小紅的數組移動,小紅的素數合并,小紅的子序列求和)






