?1.1if語句
//colddays.c --找出0攝氏度以下的天數占總天數的百分比
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{const int FREEZING = 0;float temperature;int cold_days = 0;int all_days = 0;printf("Enter the list of daily low temperature.\n");printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.\n");while (scanf("%f", &temperature) == 1){all_days++;if (temperature < FREEZING)cold_days++;}if (all_days != 0)printf("%d days total: %.1f%% were below freezing.\n", all_days, 100.0 * (float)cold_days / all_days);if (all_days == 0)printf("No data enterd!\n");return 0;
}
程序結果:

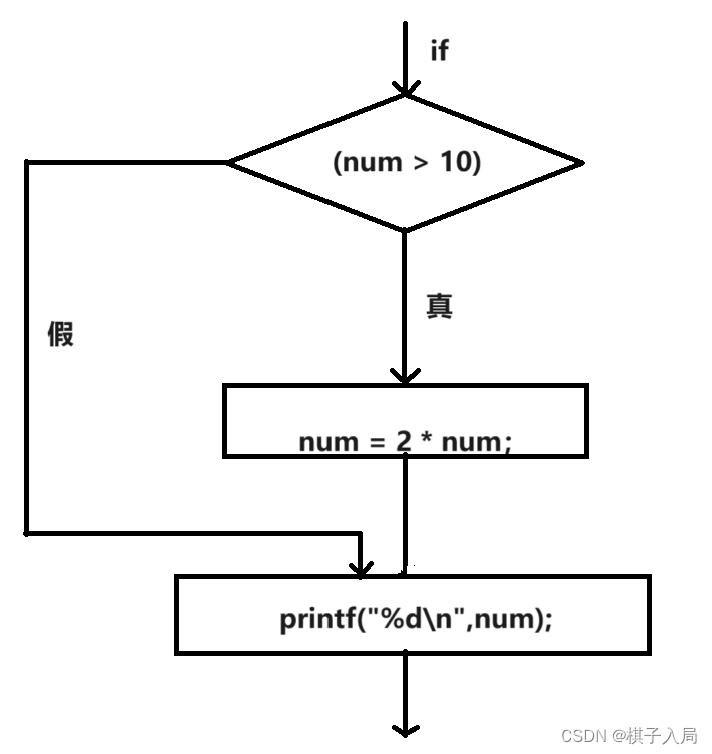
if語句被稱為分支語句或選擇語句,相當于一個交叉點,程序要在兩條分支中行選擇執。
通用形式:
? ? ? ? if(表達式)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 語句
表達式一般是關系表達式,如果對表達式求值,為真,執行語句;為假,跳過語句。
語句可以是一條簡單的語句,也可以是一個花括號里多條的復合語句。
if語句和while語句的區別:
? ? ? ? 當滿足條件語句可執行時,if語句只能測試和執行一次,但是while語句可以測試和執行多次。
注:即使if語句由復合語句構成,整個if語句也是一條語句。
1.2if else語句
//colddays.c --找出0攝氏度以下的天數占總天數的百分比
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{const int FREEZING = 0;float temperature;int cold_days = 0;int all_days = 0;printf("Enter the list of daily low temperature.\n");printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to quit.\n");while (scanf("%f", &temperature) == 1){all_days++;if (temperature < FREEZING)cold_days++;}if (all_days != 0)printf("%d days total: %.1f%% were below freezing.\n", all_days, 100.0 * (float)cold_days / all_days);elseprintf("No data enterd!\n");return 0;
}
程序結果:

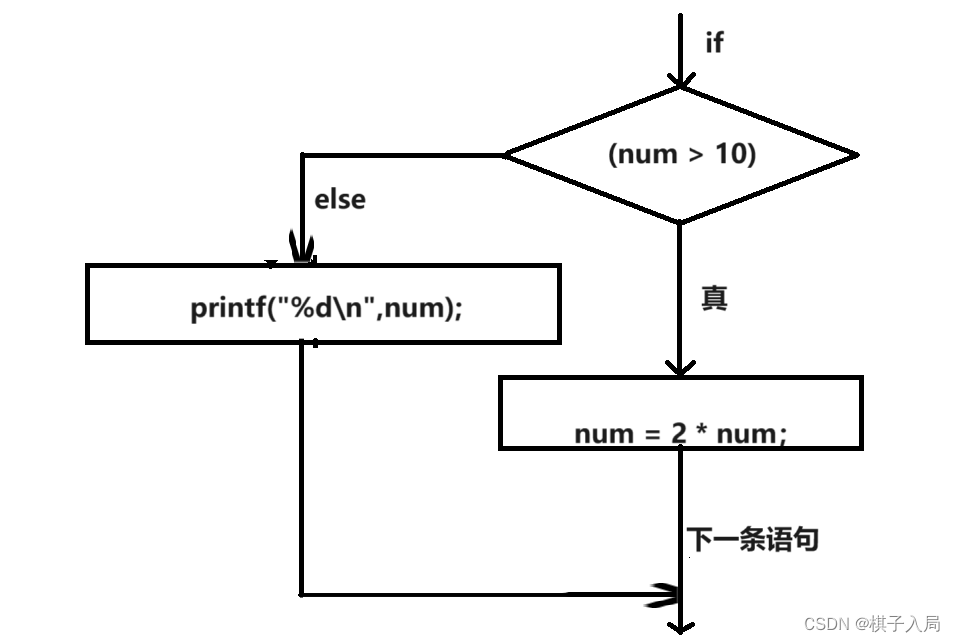
if else形式在兩條語句之間做選擇。
if else通用形式:
? ? ? ? if(表達式)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 語句1
? ? ? ? else
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?語句2
if else之間的多條語句必須用花括號括起來形成一個塊。
if和if else之間的區別:
if用于選擇是否執行一個行為,if else用于在兩個行為之間進行選擇。
1.2.1getchar()和putchar()
getchar()函數不帶任何參數,它從輸入隊列中返回下一個字符。
例:讀取下一個字符輸入,并把該字符的值賦給變量ch
ch = getchar();? ? ? ? ==? ? ? ? scanf("%c", &ch);
putchar()函數打印它的參數。
例:把之前賦給ch的值作為字符打印出來
putchar(ch);? ? ? ? ==? ? ? ? printf("%c",ch);
注:這兩個函數只處理字符,因此比scanf()和printf()函數更快,更簡潔。且這兩個函數不需要轉換說明,通常定義在頭文件stdio.h中,通常時預處理宏。
cypher1.c --更改輸入,空格不變
#include <stdio.h>
#define SPACE ' '
int main(void)
{char ch;ch = getchar(); //讀取一個字符while(ch != '\n'){if(ch == SPACE)putchar(ch);elseputchar(ch + 1); //獲取下一個字符ch = getchar();} putchar(ch); //打印換行符return 0;
}1.2.2多重選擇else if
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{int a = 0;scanf("%d", &a);if(a % 3 == 0)printf("余數是0\n");else if(a % 3 == 1)printf("余數是1\n");elseprintf("余數是2\n");return 0;
}它的另一種寫法是:
if(a % 3 == 0)
? ? ? ? printf("……");
else
? ? ? ? if(a % 3 == 1)
? ? ? ? ????????printf("……");
? ? ? ? else
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? printf("……");
該程序由一個if else語句組成,else部分包含了一個if else語句。
配對規則是在沒有花括號的前提下,else和最近的if配對。
1.2.3嵌套if語句?
for(div = 2; (div * div) <= num; div++)
{if(num % div == 0){if(div * div != num)printf("%d is divisible by %d and %d.\n", num, div, num / div);elseprintf("%d is divisible by %d.\n", num, div);}
}1.3邏輯運算符
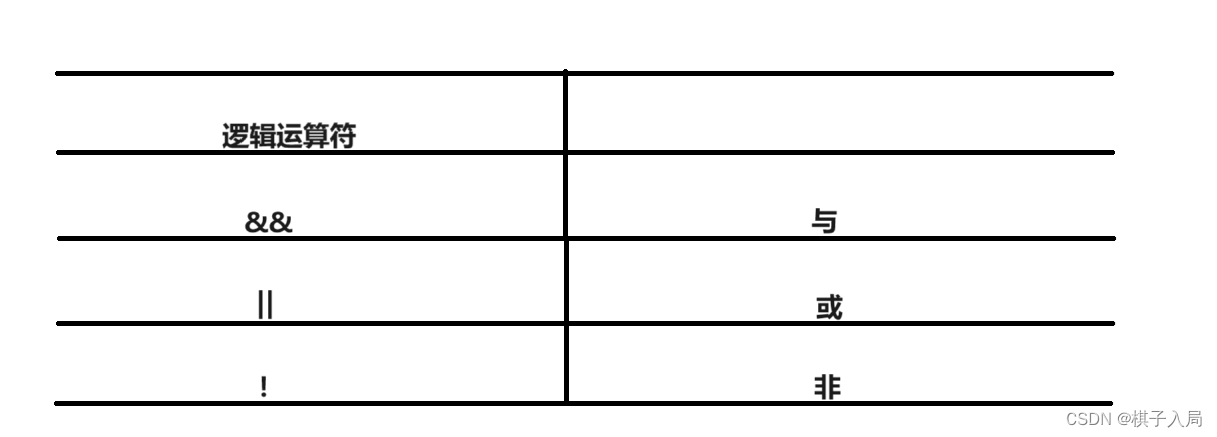
&&全真才為真;||全假才為假;!取反。
1.3.1優先級
!優先級最高,與遞增運算符相同,比()低;&&比||高,比關系運算符低,比賦值運算符高。
1.4條件運算符:?:
三元運算符,通式:
expression1?expression2:expression3
如果expression是真的,那么執行expression,否則執行expression3.。
例:max = (a > b)? a : b;
1.5continue和break
1.5.1continue語句
執行到該語句時,會跳過本次迭代的剩余部分,并開始下一輪迭代。如果continue語句嵌套在循環內,只會影響包含該語句的內層循環。
/*skippart.c --使用continue跳過部分循環*/
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
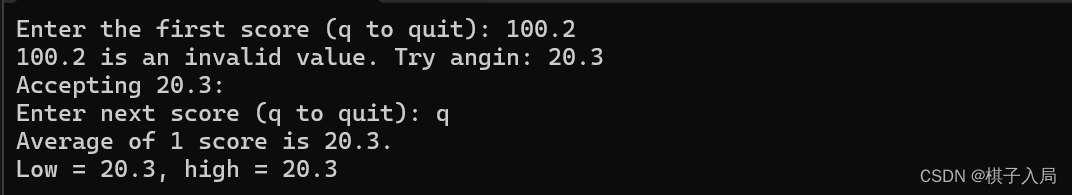
{const float MIN = 0.0f;const float MAX = 100.0f;float score;float total = 0.0f;int n = 0;float min = MAX;float max = MIN;printf("Enter the first score (q to quit): ");while (scanf("%f", &score) == 1){if (score < MIN || score > MAX){printf("%0.1f is an invalid value. Try angin: ", score);continue; //跳轉至while循環}printf("Accepting %0.1f:\n", score);min = (score < min) ? score : min;max = (score > max) ? score : max;total += score;n++;printf("Enter next score (q to quit): ");}if (n > 0){printf("Average of %d score is %0.1f.\n", n, total / n);printf("Low = %0.1f, high = %0.1f\n", min, max);}elseprintf("No valid scores were entered.\n");return 0;
}程序結果:
1.5.2break語句
當程序執行到break時,會終止包含它的循環。如果break位于嵌套循環內,只影響包含它的循環。

在for循環中的break和continue,執行beak后直接執行循環后面的第1條語句,連更新部分也跳過。嵌套循環內層的break只會讓程序跳出包含它當前循環
int p, q;scanf("%d", &p);
while(p > 0)
{printf("%d\n", p);scanf("%d", &q);while(q > 0){printf("%d\n", p * q);if(q > 100)break; //跳出內層循環scanf("%d", &q);}if(q > 100)break; //跳出外層循環scanf("%d", &p);
}1.6多重選擇:switch和break
int main()
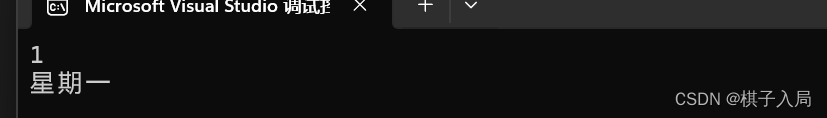
{int day = 0;scanf("%d", &day);switch (day){case 1:printf("星期一\n");break;case 2:printf("星期二\n");break; case 3:printf("星期三\n");break;case 4:printf("星期四\n");break;case 5:printf("星期五\n");break;case 6:printf("星期六\n");break;case 7:printf("星期日\n");break;default:printf("輸入錯誤: \n");break;}return 0;
}程序結果:
1.6.1switch語句
break作用是讓程序離開switch語句,跳至switch語句后的下一條語句。如果沒有break語句,就會從匹配標簽開始執行到switch末尾。break語句可用于switch和循環中,continue只能用于循環。
switch在圓括號中的測試表達式是一個整數值(包含char),case標簽必須是整數類型的常量或整型常量表達式。
switch構造:
switch(整形表達式)
{
case 常量1:
? ? ? ? 語句
case 常量2:
? ? ? ? 語句
default:
語句
}
1.7goto語句
goto語句兩部分:goto和標簽名。?
goto part2;
part2: printf("……");
可以快速跳出循環,但是慎用,可能會導致循環混亂。
真題解析)

)
】)










)
(200分))



