目錄
102.二叉樹的層序遍歷
107.二叉樹的層次遍歷II
199.二叉樹的右視圖
637.二叉樹的層平均值
429.N叉樹的層序遍歷
515.在每個樹行中找最大值
116.填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針
117.填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針II
104.二叉樹的最大深度
111.二叉樹的最小深度
參考:代碼隨想錄
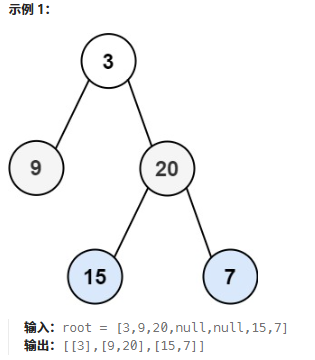
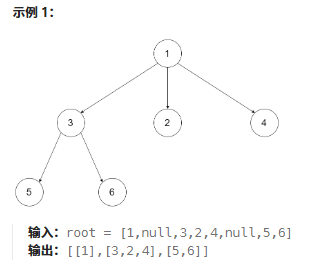
102.二叉樹的層序遍歷
鏈接:102. 二叉樹的層序遍歷 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:給你二叉樹的根節點?
root?,返回其節點值的?層序遍歷?。 (即逐層地,從左到右訪問所有節點)。
題解:隊列驅動+逐層收集節點值
?在二叉樹遍歷中,"迭代法"指的是使用循環結構(如 while/for)和顯式的數據結構(如隊列)?來實現遍歷,而不是通過函數遞歸調用(遞歸法)
工作流程
1.在每層開始時:記錄隊列當前長度len
????????這個值就是當前層所有節點的數量,此時隊列中的節點全部屬于同一層
2.處理當前層:執行len次循環
????????每次循環處理一個節點節點出隊時,將其子節點加入隊列 (這些子節點屬于下一層)
3.自然切換層級:當1en減到0時
????????當前層所有節點處理完畢,隊列中剩下的全是新加入的子節點(即下一層節點),自動切換到下一層的處理
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {checkFun02(root);return resList;}public void checkFun02(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) return;//頭出尾入的雙端隊列Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();//根節點入隊que.offer(node);//外層循環:處理每一層while (!que.isEmpty()) {//存儲當前層所有節點值List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<Integer>();//當前層節點的數量int len = que.size();//內層循環:處理當前層所有的節點while (len > 0) {//1.隊頭出隊TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();//2.記錄節點值itemList.add(tmpNode.val);//3.子節點入隊(先左后右)if (tmpNode.left != null) que.offer(tmpNode.left);if (tmpNode.right != null) que.offer(tmpNode.right);//當前層節點計數器減去1len--;}//整層節點值存入結果resList.add(itemList);}
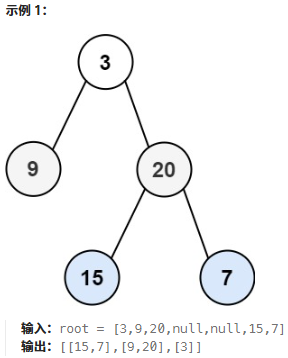
}107.二叉樹的層次遍歷II
鏈接:107. 二叉樹的層序遍歷 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:給你二叉樹的根節點?
root?,返回其節點值?自底向上的層序遍歷?。 (即按從葉子節點所在層到根節點所在的層,逐層從左向右遍歷)
題解:
public class N0107 {/*** 解法:隊列,迭代。* 層序遍歷,再翻轉數組即可。*/public List<List<Integer>> solution1(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return list;}que.offerLast(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();int levelSize = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {TreeNode peek = que.peekFirst();levelList.add(que.pollFirst().val);if (peek.left != null) {que.offerLast(peek.left);}if (peek.right != null) {que.offerLast(peek.right);}}list.add(levelList);}List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i-- ) {result.add(list.get(i));}return result;}
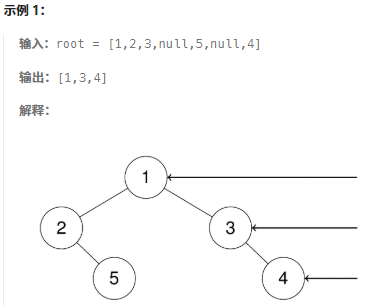
}199.二叉樹的右視圖
鏈接:199. 二叉樹的右視圖 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:給定一個二叉樹的?根節點?
root,想象自己站在它的右側,按照從頂部到底部的順序,返回從右側所能看到的節點值。
題解:層序遍歷的時候,判斷是否遍歷到單層的最后面的元素,如果是,放入result數組種,隨后返回result.
public class N0199 {/*** 解法:隊列,迭代。* 每次返回每層的最后一個字段即可。** 小優化:每層右孩子先入隊。代碼略。*/public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return list;}que.offerLast(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {int levelSize = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {TreeNode poll = que.pollFirst();if (poll.left != null) {que.addLast(poll.left);}if (poll.right != null) {que.addLast(poll.right);}if (i == levelSize - 1) {list.add(poll.val);}}}return list;}
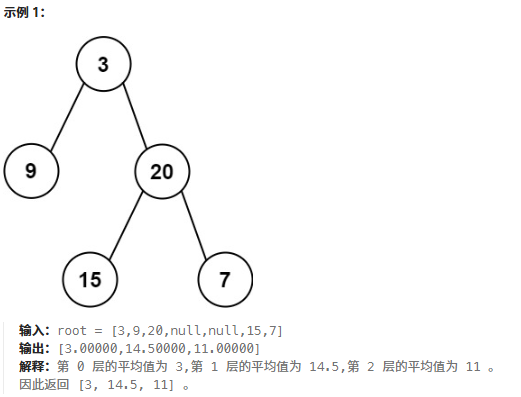
}637.二叉樹的層平均值
鏈接:637. 二叉樹的層平均值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:給定一個非空二叉樹的根節點?
root?, 以數組的形式返回每一層節點的平均值。與實際答案相差?10-5?以內的答案可以被接受。
題解:層序遍歷的時候把一層求個總和再取個均值。
public class N0637 {/*** 解法:隊列,迭代。* 每次返回每層的最后一個字段即可。*/public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return list;}que.offerLast(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {int levelSize = que.size();double levelSum = 0.0;for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {TreeNode poll = que.pollFirst();levelSum += poll.val;if (poll.left != null) {que.addLast(poll.left);}if (poll.right != null) {que.addLast(poll.right);}}list.add(levelSum / levelSize);}return list;}
}429.N叉樹的層序遍歷
鏈接:429. N 叉樹的層序遍歷 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:
????????給定一個 N 叉樹,返回其節點值的層序遍歷。(即從左到右,逐層遍歷)。
樹的序列化輸入是用層序遍歷,每組子節點都由 null 值分隔(參見示例)。
題解:一個節點有多個孩子
public class N0429 {/*** 解法1:隊列,迭代。*/public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();Deque<Node> que = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return list;}que.offerLast(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {int levelSize = que.size();List<Integer> levelList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {Node poll = que.pollFirst();levelList.add(poll.val);List<Node> children = poll.children;if (children == null || children.size() == 0) {continue;}for (Node child : children) {if (child != null) {que.offerLast(child);}}}list.add(levelList);}return list;}class Node {public int val;public List<Node> children;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}}
}515.在每個樹行中找最大值
鏈接:515. 在每個樹行中找最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:給定一棵二叉樹的根節點?
root?,請找出該二叉樹中每一層的最大值。
題解:層序遍歷,取每層的最大值。
class Solution {public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return Collections.emptyList();}List<Integer> result = new ArrayList();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--){TreeNode node = queue.poll();max = Math.max(max, node.val);if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);}result.add(max);}return result;}
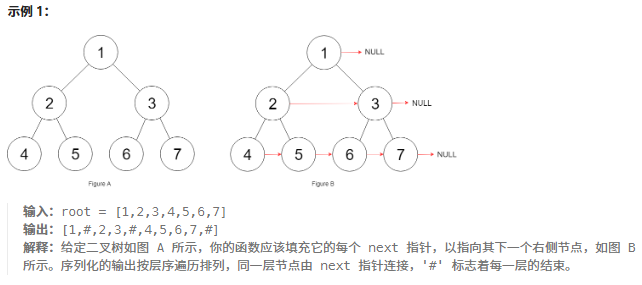
}116.填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針
鏈接:116. 填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:
???????
給定一個?完美二叉樹?,其所有葉子節點都在同一層,每個父節點都有兩個子節點。二叉樹定義如下:
struct Node {int val;Node *left;Node *right;Node *next; }填充它的每個 next 指針,讓這個指針指向其下一個右側節點。如果找不到下一個右側節點,則將 next 指針設置為?
NULL。初始狀態下,所有?next 指針都被設置為?
NULL。
題解:依然是層序遍歷,只不過在單層遍歷的時候記錄一下本層的頭部節點,然后在遍歷的時候讓前一個節點指向本節點就可以了
class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {Queue<Node> tmpQueue = new LinkedList<Node>();if (root != null) tmpQueue.add(root);while (tmpQueue.size() != 0){int size = tmpQueue.size();Node cur = tmpQueue.poll();if (cur.left != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.left);if (cur.right != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.right);for (int index = 1; index < size; index++){Node next = tmpQueue.poll();if (next.left != null) tmpQueue.add(next.left);if (next.right != null) tmpQueue.add(next.right);cur.next = next;cur = next;}}return root;}
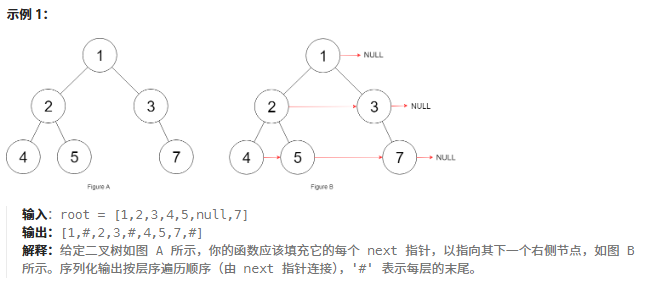
}117.填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針II
鏈接:117. 填充每個節點的下一個右側節點指針 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:
給定一個二叉樹:
struct Node {int val;Node *left;Node *right;Node *next; }填充它的每個 next 指針,讓這個指針指向其下一個右側節點。如果找不到下一個右側節點,則將 next 指針設置為?
NULL?。初始狀態下,所有?next 指針都被設置為?
NULL?。
題解:
class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();if (root != null) {queue.add(root);}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();Node node = null;Node nodePre = null;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {if (i == 0) {nodePre = queue.poll(); // 取出本層頭一個節點node = nodePre;} else {node = queue.poll();nodePre.next = node; // 本層前一個節點 next 指向當前節點nodePre = nodePre.next;}if (node.left != null) {queue.add(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.add(node.right);}}nodePre.next = null; // 本層最后一個節點 next 指向 null}return root;}
}104.二叉樹的最大深度
鏈接:104. 二叉樹的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:
????????給定一個二叉樹?
root?,返回其最大深度。二叉樹的?最大深度?是指從根節點到最遠葉子節點的最長路徑上的節點數。
題解:二叉樹的深度為根節點到最遠葉子節點的最長路徑上的節點數。最大的深度就是二叉樹的層數。
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();que.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.isEmpty()){int len = que.size();while (len > 0){TreeNode node = que.poll();if (node.left != null) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) que.offer(node.right);len--;}depth++;}return depth;}
}111.二叉樹的最小深度
鏈接:111. 二叉樹的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
題目:
????????給定一個二叉樹,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是從根節點到最近葉子節點的最短路徑上的節點數量。
說明:葉子節點是指沒有子節點的節點。
題解:當左右孩子都為空的時候,說明遍歷到最低點了。
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root){if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();depth++;TreeNode cur = null;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {cur = queue.poll();//如果當前節點的左右孩子都為空,直接返回最小深度if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null){return depth;}if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);}}return depth;}
}



)












![AI翻唱實戰:用[靈龍AI API]玩轉AI翻唱 – 第6篇](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/AI翻唱實戰:用[靈龍AI API]玩轉AI翻唱 – 第6篇)


