一、實戰
99島嶼數量 深搜
99. 島嶼數量
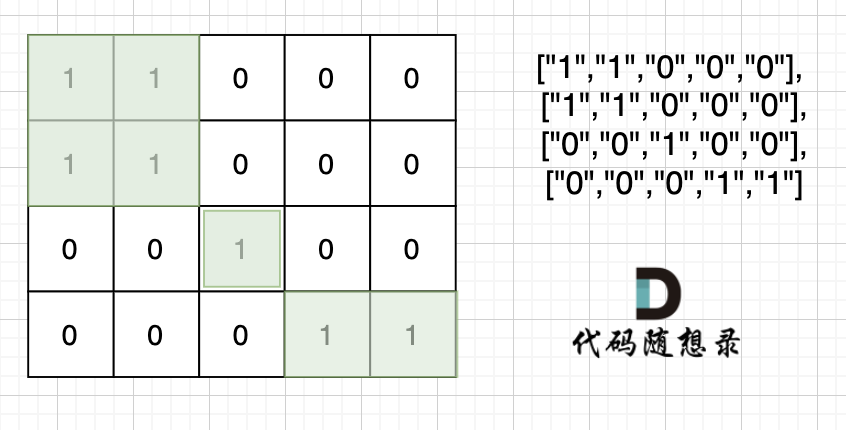
本題中每座島嶼只能由水平方向和/或豎直方向上相鄰的陸地連接形成,也就是說斜角度鏈接是不算的。思路是用遇到一個沒有遍歷過的節點陸地,計數器就加一,然后把該節點陸地所能遍歷到的陸地都標記上。在遇到標記過的陸地節點和海洋節點的時候直接跳過。 這樣計數器就是最終島嶼的數量。
深度優先搜索有兩個版本,一個是沒有終止條件,一個是有終止條件
沒有終止條件版本:
package org.example;//具體運行時去掉import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int m = scan.nextInt(); // 網格行數int n = scan.nextInt(); // 網格列數int[][] grid = new int[m][n]; // 存儲網格數據// 輸入網格for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {grid[i][j] = scan.nextInt();}}boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; // 標記是否已訪問int result = 0; // 記錄島嶼數量// 遍歷每個格子for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {// 如果當前格子是陸地(1)且未被訪問if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 發現新島嶼visited[i][j] = true; // 標記為已訪問dfs(visited, i, j, grid); // 深度優先搜索,標記整個連通區域}}}System.out.println(result); // 輸出島嶼總數scan.close();}// 四個方向:右、下、上、左(x, y 增量)public static int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};/*** 從坐標 (x, y) 開始進行深度優先搜索,標記所有相連的陸地*/private static void dfs(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int[][] grid) {// 向四個方向擴展for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextX = x + dir[i][0];int nextY = y + dir[i][1];// 越界檢查if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY >= grid[0].length) {continue;}// 如果下一個位置是未訪問的陸地if (!visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] == 1) {visited[nextX][nextY] = true; // 標記為已訪問dfs(visited, nextX, nextY, grid); // 繼續遞歸搜索}}}
}有終止條件版本,其實終止條件 就寫在了 調用dfs的地方,如果遇到不合法的方向,直接不會去調用dfs。:
package org.example;//具體運行時去掉import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int m = scan.nextInt(); // 網格行數int n = scan.nextInt(); // 網格列數int[][] grid = new int[m][n]; // 存儲網格數據// 輸入網格for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {grid[i][j] = scan.nextInt();}}boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; // 標記是否已訪問int result = 0; // 記錄島嶼數量// 遍歷每個格子for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {// 如果當前格子是陸地(1)且未被訪問if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 發現新島嶼visited[i][j] = true; // 標記為已訪問dfs(visited, i, j, grid); // 深度優先搜索,標記整個連通區域}}}System.out.println(result); // 輸出島嶼總數scan.close();}// 四個方向:右、下、上、左(x, y 增量)public static int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};/*** 從坐標 (x, y) 開始進行深度優先搜索,標記所有相連的陸地*/private static void dfs(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int[][] grid) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 終止條件:訪問過的節點 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 標記為已訪問// 向四個方向擴展for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextX = x + dir[i][0];int nextY = y + dir[i][1];// 越界檢查if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY >= grid[0].length) {continue;}dfs(visited, nextX, nextY, grid); // 繼續遞歸搜索}}
}99島嶼數量?廣搜
99. 島嶼數量
本題思路與深搜類似,遇到一個沒有遍歷過的節點陸地,計數器就加一,然后把該節點陸地所能遍歷到的陸地都標記上。再遇到標記過的陸地節點和海洋節點的時候直接跳過。 這樣計數器就是最終島嶼的數量。
用廣搜做這道題目的時候容易超時,因為已經入隊列的節點因為標記的時間太晚導致重復進入隊列,因此只要 加入隊列就代表 走過,就需要標記,而不是從隊列拿出來的時候再去標記走過。
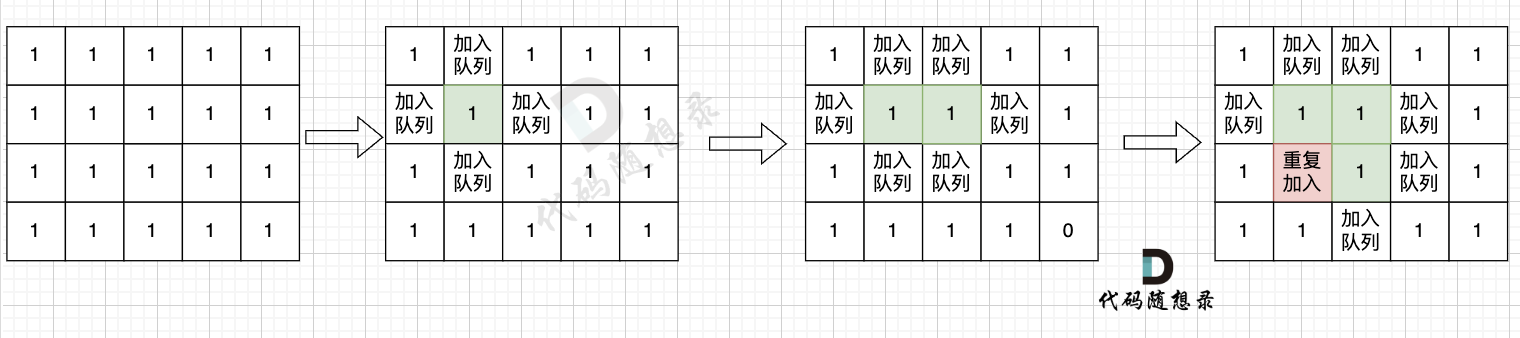
//超時寫法
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四個方向
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {queue<pair<int, int>> que;que.push({x, y});// 應在放入隊列的時候就進行標記while(!que.empty()) {pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();int curx = cur.first;int cury = cur.second;visited[curx][cury] = true; // 從隊列中取出在標記走過for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳過if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {que.push({nextx, nexty});}}}}具體代碼如下:
package org.example;//具體運行時去掉import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int m = scan.nextInt(); // 網格行數int n = scan.nextInt(); // 網格列數int[][] grid = new int[m][n]; // 存儲網格數據// 輸入網格for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {grid[i][j] = scan.nextInt();}}boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; // 標記是否已訪問int result = 0; // 記錄島嶼數量// 遍歷每個格子for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {// 如果當前格子是陸地(1)且未被訪問if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {result++; // 發現新島嶼visited[i][j] = true; // 標記為已訪問bfs(visited, i, j, grid); // 深度優先搜索,標記整個連通區域}}}System.out.println(result); // 輸出島嶼總數scan.close();}/*** 自定義 Pair 類,用于封裝坐標 (x, y)*/static class pair {int first;int second;public pair(int first, int second) {this.first = first;this.second = second;}}// 四個方向:右、下、上、左(x, y 增量)public static int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};private static void bfs(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int[][] grid) {Queue<pair> queue = new LinkedList<pair>();//定義坐標隊列,沒有現成的pair類,在下面自定義了queue.add(new pair(x, y));visited[x][y] = true;//遇到入隊直接標記為優先,// 否則出隊時才標記的話會導致重復訪問,比如下方節點會在右下順序的時候被第二次訪問入隊while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int curX = queue.peek().first;int curY = queue.poll().second;//當前橫縱坐標for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {//順時針遍歷新節點next,下面記錄坐標int nextX = curX + dir[i][0];int nextY = curY + dir[i][1];if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY < 0 || nextY >= grid[0].length) {continue;}//去除越界部分if (!visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] == 1) {queue.add(new pair(nextX, nextY));visited[nextX][nextY] = true;//邏輯同上}}}}/*** 從坐標 (x, y) 開始進行深度優先搜索,標記所有相連的陸地*/private static void dfs(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int[][] grid) {if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 終止條件:訪問過的節點 或者 遇到海水visited[x][y] = true; // 標記為已訪問// 向四個方向擴展for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextX = x + dir[i][0];int nextY = y + dir[i][1];// 越界檢查if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY >= grid[0].length) {continue;}dfs(visited, nextX, nextY, grid); // 繼續遞歸搜索}}
}100島嶼的最大面積(深搜-無結束條件版本)
100. 島嶼的最大面積
思路:如果是有結束條件版本,dfs處理當前節點,即在主函數遇到島嶼就計數為0,dfs處理接下來的全部陸地;如果是無結束條件版本,則dfs處理當前節點的相鄰節點,即在主函數遇到島嶼就計數為1,dfs處理接下來的相鄰陸地
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;public class Main {// 四個方向:右、下、左、上(順時針)static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};static int result = 0; // 記錄最大島嶼面積static int count = 0; // 記錄當前島嶼的面積(DFS過程中累加)public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt(); // 網格行數int m = scanner.nextInt(); // 網格列數int[][] map = new int[n][m]; // 存儲地圖// 輸入地圖數據for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {map[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();}}boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m]; // 標記是否已訪問// 遍歷每個格子for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {// 發現未訪問的陸地,開始新島嶼的DFSif (!visited[i][j] && map[i][j] == 1) {count = 0; // 重置當前島嶼面積計數器dfs(map, visited, i, j); // 深度優先搜索,統計該島嶼面積result = Math.max(count, result); // 更新最大面積}}}System.out.println(result); // 輸出最大島嶼面積scanner.close();}/*** DFS:從 (x, y) 開始遍歷整個連通的陸地,累加面積*/static void dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {count++; // 當前格子是陸地,面積+1visited[x][y] = true; // 標記為已訪問,防止重復計算// 向四個方向擴展for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextX = x + dir[i][0];int nextY = y + dir[i][1];// 跳過:越界、已訪問、海水if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 ||nextX >= map.length || nextY >= map[0].length ||visited[nextX][nextY] || map[nextX][nextY] == 0) {continue;}// 遞歸訪問相鄰陸地dfs(map, visited, nextX, nextY);}}
}

)





![[激光原理與應用-287]:理論 - 波動光學 - 電磁波既能承載能量,又能承載信息?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[激光原理與應用-287]:理論 - 波動光學 - 電磁波既能承載能量,又能承載信息?)




)




常用命令全解析:從基礎到進階)
