學習數據結構重要的三個部分:指針、結構體、動態內存管理(malloc、calloc、realloc、free)。
1.為什么存在動態內存分配?
1.空間開辟大小是固定的;
2.數組在聲明時,必須指定數組的長度,它所需要的內存在編譯時分配。
int main()
{int a = 10; //4個字節int arr[10]; //40個字節return 0;
}
2.動態內存函數的介紹
2.1malloc和free
C語言提供了一個動態內存開辟的函數:malloc()
這個函數向內存申請一塊連續可用的空間,并返回指向這塊空間的指針。
- 如果開辟成功,則返回一個指向開辟好的空間的指針;
- 如果開辟失敗,則返回一個NULL指針。因此malloc的返回值一定要做檢查;
- 返回值的類型是void*,所以malloc函數并不知道開辟空間的類型,具體在使用的時候使用者自己來決定。
- 如果參數size為0,malloc的行為是標準未定義的,取決于編譯器。

#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int arr[10] = {0};//動態內存開辟int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (p == NULL){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){*(p+i) = i;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", *(p+i)); //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 }return 0;
}

#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int arr[10] = {0};//動態內存開辟int* p = (int*)malloc(INT_MAX);if (p == NULL){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){*(p+i) = i;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", *(p+i)); //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 }return 0;
}
free(動態內存的釋放和回收)
void free(void* ptr)
- 如果參數ptr指向的空間不是動態開辟的,那么free函數的行為是未定義的;
- 如果參數ptr是NULL指針,則函數什么事情也不做。
沒有free,并不是說內存空間就不回收了。當程序退出時,系統會自動回收內存空間。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int arr[10] = {0};//動態內存開辟int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (p == NULL){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){*(p+i) = i;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", *(p+i)); //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 }free(p);p = NULL; //最好的做法,free釋放后,賦值為NULLreturn 0;
}
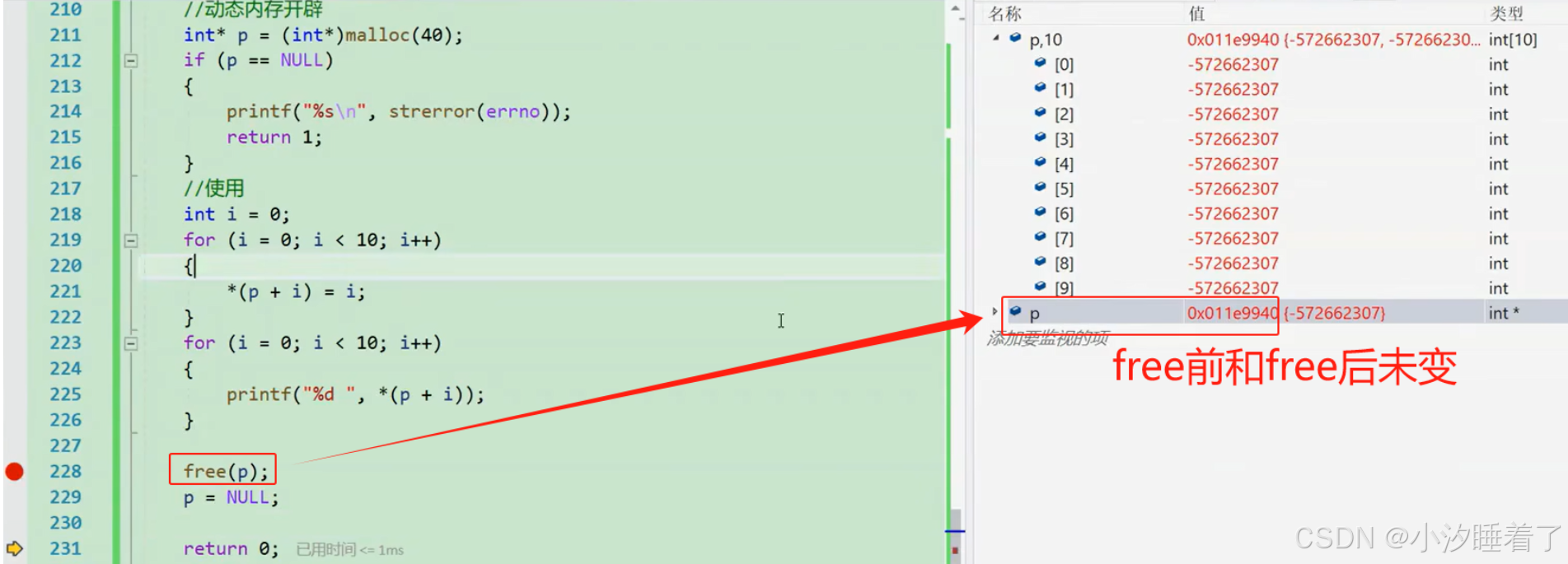
//error,必須釋放動態開辟的空間
int main()
{int a = 10;int* p = &a;//···free(p); p = NULL;return 0;
}
int main()
{int* p = NULL;free(p); //啥事也不干return 0;
}
2.2calloc

#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>//開辟10個整型的空間
int main()
{int* p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int));if (p == NULL){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//打印int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", *(p+i)); //calloc會初始化為全0}//釋放free(p);p = NULL;return 0;
}
可以理解為:calloc=malloc+memset
2.3realloc


#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (NULL == p){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//使用1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){*(p+i) = i+1;}//擴容int* ptr = (int*)realloc(p, 80);if (ptr != NULL) //擴容成功{p = ptr;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%s\n", *(p+i)); //1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10}//釋放free(p);p = NULL;return 0;
}
第一種情況:
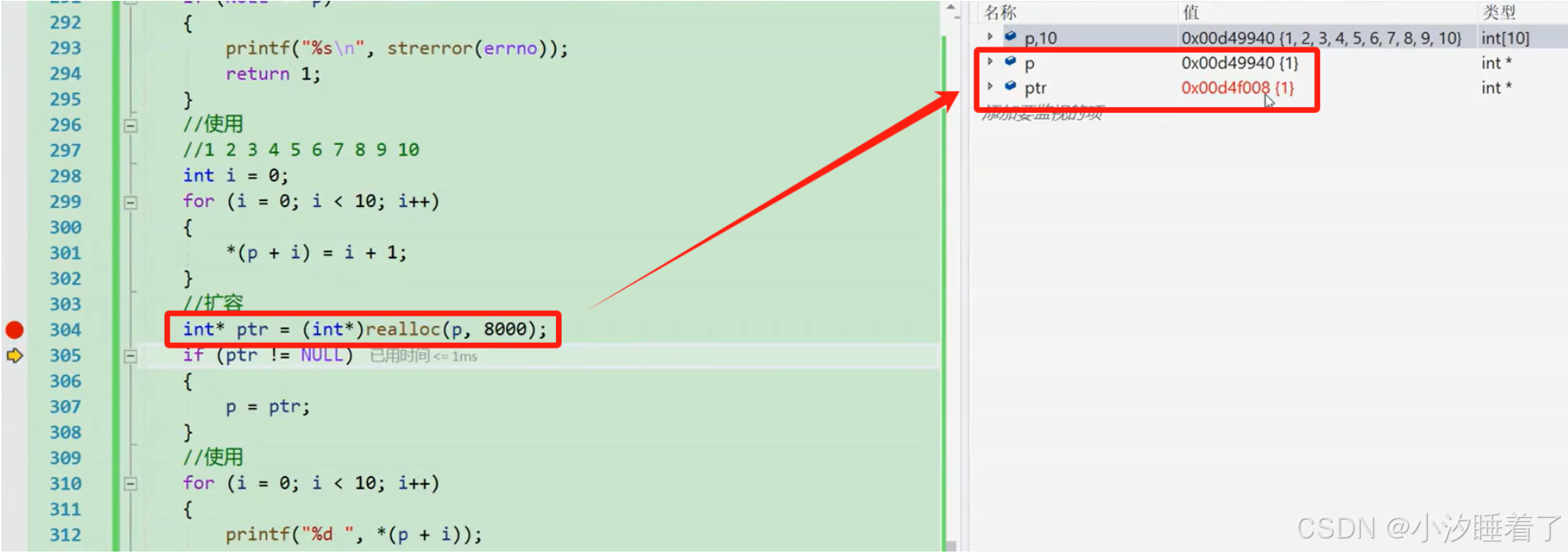
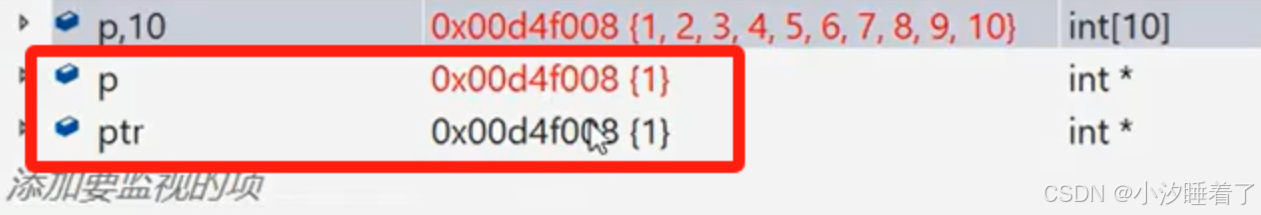
第二種情況:

int main()
{realloc(NULL, 40); //等價于malloc(40);return 0;
}
練習:動態版本的通訊錄
動態版本的通訊錄:
1.通訊錄默認能存放3個人的信息
2.如果空間不夠了,就增加空間,每次增加2個人的空間
//test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include "contact.h"void menu()
{printf("*************************************************\n");printf("************1.add 2.del**********************\n");printf("************3.search 4.modify*******************\n");printf("************5.show 6.sort*********************\n");printf("************ 0.exit **********************\n");printf("*************************************************\n");
}
int main()
{int input = 0;Contact con; //通訊錄InitContact(&con); //初始化通訊錄do{menu();printf("請選擇:>");scanf("%d", &input);switch (input){case 1:AddContact(&con);break;case 2:DelContact(&con);break;case 3:SearchContact(&con);break;case 4:ModifyContact(&con);break;case 5:ShowContact(&con);break;case 6:SortContact(&con);break;case 0:DestroyContact(&con); //動態版本,銷毀通訊錄printf("退出通訊錄\n");break;default:printf("選擇錯誤\n");break;}} while (input);return 0;
}
//contact.h
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define DEFAULT_SZ 3
#define INC_SZ 2#define MAX 100
#define MAX_NAME 20
#define MAX_SEX 10
#define MAX_TELE 12
#define MAX_ADDR 30//類型的聲明
typedef struct PeoInfo //人的信息
{char name[MAX_NAME];int age;char sex[MAX_SEX];char tele[MAX_TELE];char addr[MAX_ADDR];
}PeoInfo;//靜態版本
//typedef struct Contact //通訊錄的信息
//{
// PeoInfo data[MAX]; //存放人的信息
// int count; //記錄當前通訊錄中實際人的個數
//}Contact;//動態版本
typedef struct Contact //通訊錄的信息
{PeoInfo* data; //存放人的信息int count; //記錄當前通訊錄中實際人的個數int capacity;//記錄當前通訊錄的容量
}Contact;int InitContact(Contact* pc); //初始化通訊錄void DestroyContact(Contact* pc); //動態版本,銷毀通訊錄void AddContact(Contact* pc); //添加聯系人的通訊錄void ShowContact(const Contact* pc); //打印通訊錄的信息void DelContact(Contact* pc); //刪除指定聯系人void SearchContact(Contact* pc); //查找指定聯系人void ModifyContact(Contact* pc); //修改指定聯系人void SortContact(Contact* pc); //排序通訊錄中的內容,可以按照名字來排序,按照年齡來排序···
//contact.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include "contact.h"//靜態版本
//void InitContact(Contact* pc)
//{
// assert(pc);
// pc->count = 0;
// memset(pc->data, 0, sizeof(pc->data));
//}//動態版本
int InitContact(Contact* pc)
{assert(pc);pc->count = 0;pc->data = (PeoInfo*)calloc(3, sizeof(PeoInfo));if (pc->data == NULL){printf("InitContact::%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}pc->capacity = DEFAULT_SZ;return 0;
}void DestroyContact(Contact* pc) //動態版本,銷毀通訊錄
{assert(pc);free(pc->data);pc->data = NULL;
}//靜態版本
//void AddContact(Contact* pc)
//{
// assert(pc);
// if (pc->count == MAX)
// {
// printf("通訊錄已滿,無法添加\n");
// return;
// }
// printf("請輸入名字:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].name);
// printf("請輸入年齡:>");
// scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pc->count].age));
// printf("請輸入性別:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].sex);
// printf("請輸入電話:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].tele);
// printf("請輸入地址:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].addr);
//
// pc->count++;
// printf("添加成功\n");
//}//動態版本
void CheckCapacity(Contact* pc)
{if (pc->count == pc->capacity){PeoInfo* ptr = (PeoInfo*)realloc(pc->data, (pc->capacity + INC_SZ)*sizeof(PeoInfo));if (ptr == NULL){printf("AddContact::%s\n", strerror(errno));return;}else{pc->data = ptr;pc->capacity += INC_SZ;printf("擴容成功\n");}}
}
void AddContact(Contact* pc)
{assert(pc);//擴容CheckCapacity(pc);printf("請輸入名字:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].name);printf("請輸入年齡:>");scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pc->count].age));printf("請輸入性別:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].sex);printf("請輸入電話:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].tele);printf("請輸入地址:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->count].addr);pc->count++;printf("添加成功\n");
}void ShowContact(const Contact* pc)
{assert(pc);int i = 0;printf("%-20s\t%-5s\t%-5s\t%-12s\t%-30s\n", "名字", "年齡", "性別", "電話", "地址");for (i = 0; i < pc->count; i++){printf("%-20s\t%-5d\t%-5s\t%-12s\t%-30s\n", pc->data[i].name,pc->data[i].age,pc->data[i].sex,pc->data[i].tele,pc->data[i].addr);}
}static int FindByName(Contact* pc, char name[])
{assert(pc);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < pc->count; i++){if (0 == strcmp(pc->data[i].name, name)){return i;}}return -1;
}void DelContact(Contact* pc)
{char name[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };assert(pc);int i = 0;if (pc->count == 0){printf("通訊錄為空,沒有信息可以刪除\n");return;}printf("請輸入要刪除人的名字:>");scanf("%s", name);//刪除//1.查找int pos = FindByName(pc, name);if (pos == -1){printf("要刪除的人不存在\n");return;}//2.刪除for (i = pos; i < pc->count - 1; i++){pc->data[i] = pc->data[i + 1];}pc->count--;printf("刪除成功\n");}void SearchContact(Contact* pc)
{assert(pc);char name[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };printf("請輸入要查找人的名字:>");scanf("%s", name);//1.查找int pos = FindByName(pc, name);if (pos == -1){printf("要查找的人不存在\n");return;}//2.打印printf("%-20s\t%-5s\t%-5s\t%-12s\t%-30s\n", "名字", "年齡", "性別", "電話", "地址");printf("%-20s\t%-5d\t%-5s\t%-12s\t%-30s\n", pc->data[pos].name,pc->data[pos].age,pc->data[pos].sex,pc->data[pos].tele,pc->data[pos].addr);}void ModifyContact(Contact* pc)
{assert(pc);char name[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };printf("請輸入要修改人的名字:>");scanf("%s", name);//1.查找int pos = FindByName(pc, name);if (pos == -1){printf("要修改的人不存在\n");return;}printf("要修改的人的信息已經找到,接下來開始修改\n");//2.修改printf("請輸入名字:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].name);printf("請輸入年齡:>");scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pos].age));printf("請輸入性別:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].sex);printf("請輸入電話:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].tele);printf("請輸入地址:>");scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].addr);printf("修改成功\n");
}int cmp_peo_by_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{return strcmp(((PeoInfo*)e1)->name, ((PeoInfo*)e2)->name);
}
void SortContact(Contact* pc) //按照名字來排序
{assert(pc);qsort(pc->data, pc->count, sizeof(PeoInfo), cmp_peo_by_name);printf("排序成功\n");
}
3.常見的動態內存錯誤
3.1對NULL指針的解引用操作
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);*p = 20; //如果p的值是NULL,就會出現問題return 0;
}
修正:
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (p == NULL){return 1;}*p = 20;free(p);p = NULL;return 0;
}
3.2對動態開辟空間的越界訪問
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (p == NULL){printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {p[i] = i;}free(p);p = NULL;return 0;
}
3.3對非動態開辟內存使用free釋放
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{int a = 10;int* p = &a;//···free(p);p = NULL;return 0;
}

3.4使用free釋放一塊動態開辟內存的一部分
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);if (p == NULL){return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){*p = i;p++;}//釋放free(p); //此時p的地址早已不是起始位置,必須指向開辟空間的起始位置p = NULL;return 0;
}
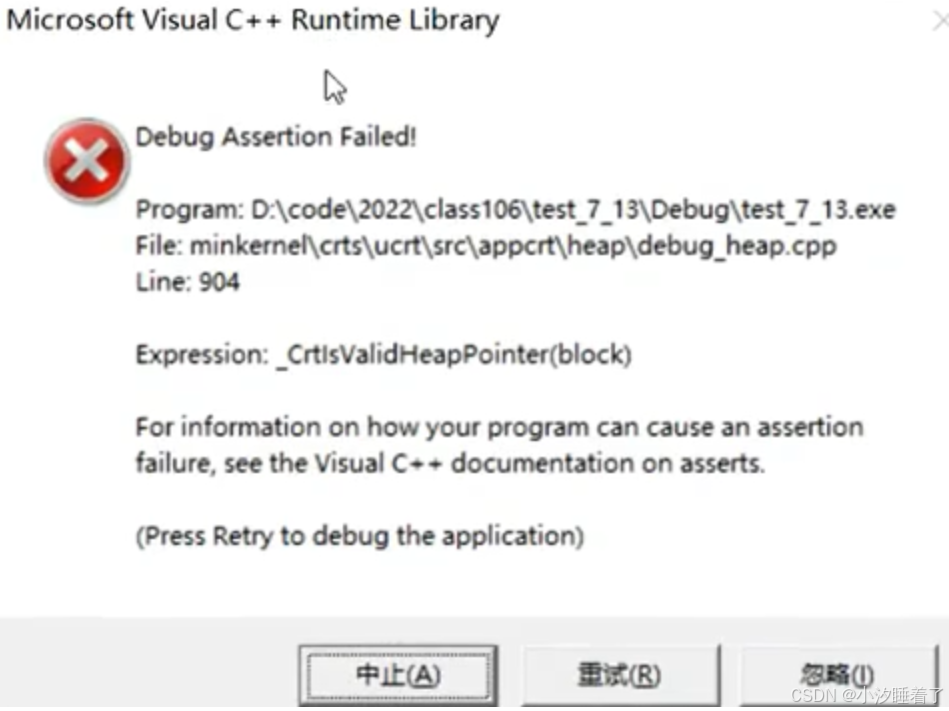
3.5對同一塊動態內存多次釋放
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);//···free(p);//···free(p);return 0;
}

修正:
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(40);//···free(p);p = NULL;//···free(p);return 0;
}
3.6動態開辟內存忘記釋放(內存泄漏)
#include <stdlib.h>void test()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(100);//···int flag = 0;scanf("%d", &flag); //5if (flag == 5)return;free(p);p = NULL;
}int main()
{test();//···return 0;
}
場景2:
#include <stdlib.h>int* test()
{int* p = (int*)malloc(100); //開辟空間if (p == NULL){return p;}//···return p;
}int main()
{int* ret = test();//忘記釋放了return 0;
}
4.經典筆試題(出自《高質量的C-C++編程》)

修改版本2:(有點別扭)

#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{printf("hello world\n"); //hello worldchar* p = "hello world";printf(p); //hello worldprintf("%s\n", p); //hello worldreturn 0;
}//要理解底層原理,傳遞的是h字符的地址
返回棧空間地址的問題。
#include <stdio.h>int* test()
{//返回棧空間地址的問題int a = 10;return &a;
}int main()
{int* p = test();printf("%d\n", *p); //10return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>int* test()
{int a = 10;return &a;
}int main()
{int* p = test();printf("hehe\n"); //heheprintf("%d\n", *p); //5return 0;
}
5.C/C++程序的內存開辟
自行學習。
書籍《深入理解計算機系統》
6.柔性數組(flexible array)
C99中,結構中的最后一個元素允許是未知大小的數組,這就叫做柔性數組成員。
typedef struct st_type
{int i;int a[0]; //柔性數組成員
}type_a;
有些編譯器會報錯無法編譯可以寫成:
typedef struct st_type
{int i;int a[]; //柔性數組成員
}type_a;
6.1柔性數組的特點
結構中的柔性數組成員前面必須至少一個其它成員;
sizeof返回的這種結構大小不包括柔性數組的內存;
包含柔性數組成員的結構用malloc()函數進行內存的動態分配,并且分配的內存應該大于結構的大小,以上適應柔性數組的預期大小。
#include <stdio.h>struct S
{int n;int arr[]; //柔性數組成員
};int main()
{int sz = sizeof(struct S);printf("%d\n", sz); //4 return 0;
}
6.2柔性數組的使用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>struct S
{int n;int arr[]; //柔性數組成員
};int main()
{//柔性數組的使用struct S* ps = (struct S*)malloc(sizeof(struct S) + 40);if (ps == NULL){//···return 1;}ps->n = 100;int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){ps->arr[i] = i;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}//調整struct S* ptr = (struct S*)realloc(ps, sizeof(struct S) + 80);if (ptr != NULL){ps = ptr;ptr = NULL;}//···//釋放free(ps);ps = NULL;return 0;
}
方案二:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct S
{int n;int* arr;
};int main()
{struct S* ps =(struct S*)malloc(sizeof(struct S));if (ps == NULL){return 1;}ps->n = 100;ps->arr = (int*)malloc(40);if (ps->arr == NULL){return 1;}//使用int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){ps->arr[i] = i;}//打印for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}//調整int* ptr = (int*)realloc(ps->arr, 80);if (ptr == NULL){return 1;}//釋放free(ps->arr);free(ps);ps = NULL;return 0;
}
方案二:釋放時容易忘記導致內存泄漏;多次開辟空間,碎片化嚴重,導致內存利用率下降。
6.3柔性數組的優勢
方便內存釋放;
理論上有利于訪問速度(連續的內存有利于訪問速度,減少內存碎片)。
總結
今天就暫且更新至此吧,期待下周再會。如有錯誤還請不吝賜教。希望對您學習有所幫助,翻頁前留下你的支持,以防下次失蹤了嗷。
作者更新不易,免費關注別手軟。





)


)










