學習目標:掌握Python程序性能分析和優化的通用方法,建立工程化開發的規范意識,為后續AI項目開發奠定堅實的編程基礎
在數據科學和AI開發中,代碼性能往往決定了項目的可行性。一個處理時間從幾小時縮短到幾分鐘的優化,可能意味著從實驗室概念到生產應用的跨越。本課將系統性地講解Python性能優化的核心方法和工程化開發的最佳實踐。
8.1 性能分析:發現代碼瓶頸的科學方法
> 性能分析的基本原理
性能分析(Performance Profiling) 是通過測量程序運行時的各項指標來識別性能瓶頸的過程。在優化之前,我們必須先知道程序的時間都花在了哪里,這就是"測量優于猜測"的工程原則。
Python提供了多種性能分析工具,每種工具都有其特定的應用場景:
- cProfile:Python內置的函數級性能分析器,適合整體性能概覽
- line_profiler:行級分析工具,能夠精確定位到具體代碼行
- memory_profiler:內存使用分析器,監控內存消耗模式
- py-spy:采樣式分析器,對運行中的程序影響最小
pip install memory-profiler
import cProfile
import pstats
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
from memory_profiler import profile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 創建測試函數來演示性能分析
def inefficient_data_processing():"""低效的數據處理函數:演示常見性能問題"""# 問題1:重復計算data = []for i in range(10000):# 每次循環都重新計算相同的值result = sum(range(100)) * np.sqrt(i)data.append(result)# 問題2:低效的數據結構操作processed_data = []for item in data:processed_data.append(item * 2) # 應該使用列表推導式或NumPy# 問題3:不必要的數據復制df = pd.DataFrame({'values': processed_data})df_copy1 = df.copy()df_copy2 = df.copy()df_copy3 = df.copy()return df_copy3def optimized_data_processing():"""優化后的數據處理函數"""# 優化1:預計算常量constant_sum = sum(range(100))# 優化2:使用NumPy向量化操作indices = np.arange(10000)data = constant_sum * np.sqrt(indices)# 優化3:避免不必要的中間步驟processed_data = data * 2# 優化4:直接創建最終結果df = pd.DataFrame({'values': processed_data})return dfprint("=== 使用cProfile進行性能分析 ===")# 分析低效函數
profiler = cProfile.Profile()
profiler.enable()
result1 = inefficient_data_processing()
profiler.disable()# 保存分析結果
stats = pstats.Stats(profiler)
stats.sort_stats('cumulative')
print("低效函數的性能分析(前10個最耗時的函數):")
stats.print_stats(10)# 分析優化后的函數
profiler2 = cProfile.Profile()
profiler2.enable()
result2 = optimized_data_processing()
profiler2.disable()stats2 = pstats.Stats(profiler2)
stats2.sort_stats('cumulative')
print("\n優化后函數的性能分析(前10個最耗時的函數):")
stats2.print_stats(10)# 簡單的時間對比
import timeittime_inefficient = timeit.timeit(inefficient_data_processing, number=3)
time_optimized = timeit.timeit(optimized_data_processing, number=3)print(f"\n=== 性能對比結果 ===")
print(f"低效版本平均時間: {time_inefficient/3:.4f} 秒")
print(f"優化版本平均時間: {time_optimized/3:.4f} 秒")
print(f"性能提升倍數: {time_inefficient/time_optimized:.2f}x")

> 內存使用分析
內存優化在處理大數據集時尤為重要。Python的內存管理機制決定了我們需要特別關注內存使用模式。
# 內存使用分析示例
@profile # 需要安裝memory_profiler:pip install memory_profiler
def memory_intensive_function():"""內存密集型函數示例"""# 創建大型數據結構large_list = list(range(1000000))# 數據轉換(會創建新的內存副本)squared_list = [x**2 for x in large_list]# 轉換為DataFrame(又一次內存復制)df = pd.DataFrame({'values': squared_list})# 添加計算列(更多內存使用)df['values_sqrt'] = np.sqrt(df['values'])return dfdef memory_efficient_function():"""內存優化版本"""# 直接使用NumPy創建和計算values = np.arange(1000000, dtype=np.int32) # 指定更小的數據類型values_squared = values ** 2values_sqrt = np.sqrt(values_squared)# 一次性創建DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame({'values': values_squared,'values_sqrt': values_sqrt})return dfprint("\n=== 內存使用對比 ===")
print("運行memory_intensive_function時的內存使用情況:")
# 注意:需要在命令行運行:python -m memory_profiler your_script.py
print("(需要使用命令行工具查看詳細內存分析)")# 簡單的內存使用估算
import sys# 比較不同數據結構的內存效率
list_data = list(range(100000))
array_data = np.array(range(100000))print(f"Python列表內存使用: {sys.getsizeof(list_data) / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
print(f"NumPy數組內存使用: {array_data.nbytes / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")
print(f"內存效率提升: {sys.getsizeof(list_data) / array_data.nbytes:.2f}x")
8.2 算法復雜度:從理論到實踐的性能分析
> 時間復雜度的實際意義
時間復雜度(Time Complexity) 描述了算法運行時間如何隨輸入規模增長而變化。理解復雜度不僅有助于選擇合適的算法,更能幫助我們預測代碼在大規模數據下的表現。
常見復雜度等級及其實際含義:
- O(1):常數時間,如字典查找、數組索引
- O(log n):對數時間,如二分查找、平衡樹操作
- O(n):線性時間,如列表遍歷、簡單查找
- O(n log n):線性對數時間,如高效排序算法
- O(n2):平方時間,如嵌套循環、冒泡排序
- O(2^n):指數時間,如遞歸斐波那契數列
import time
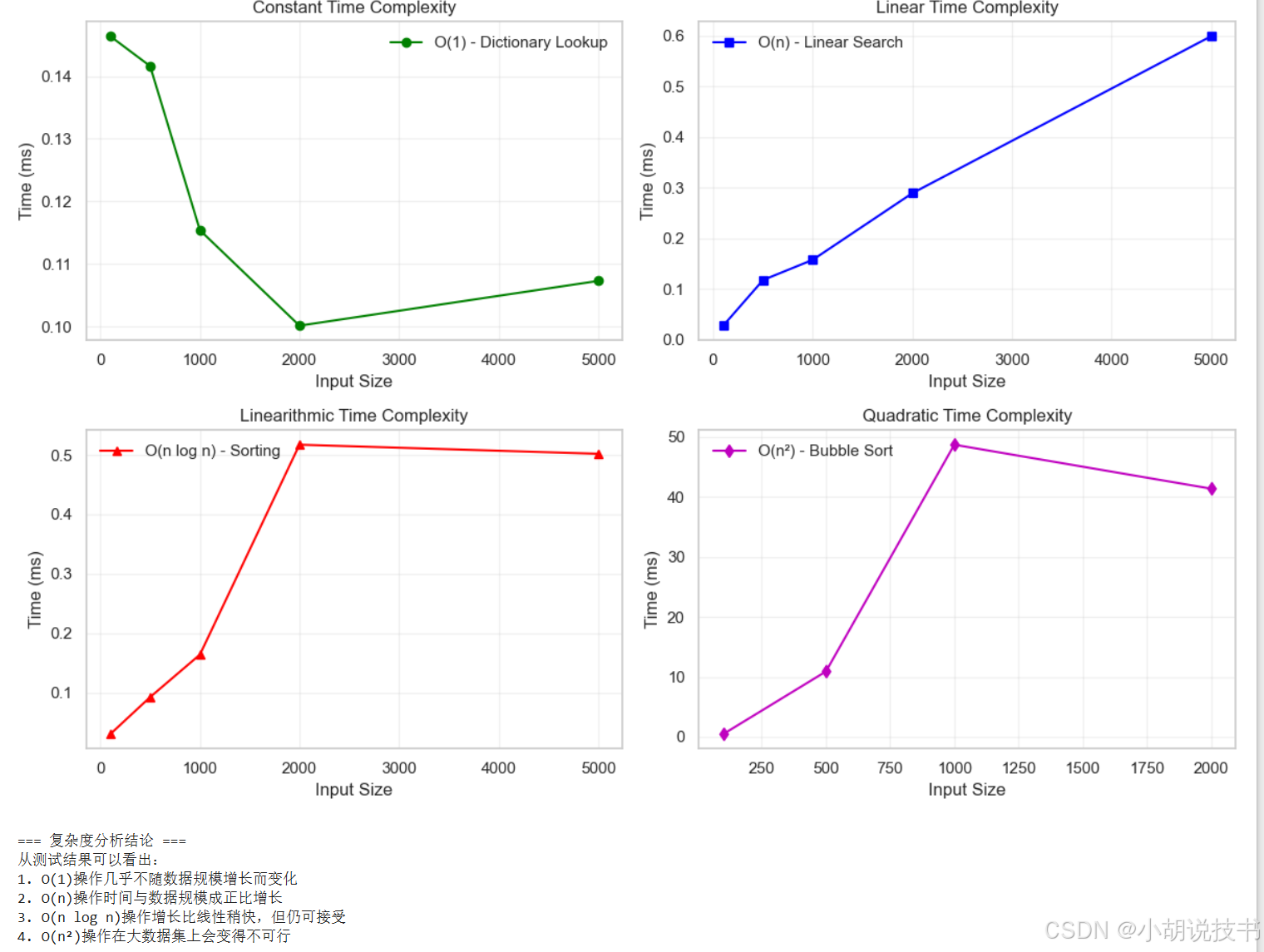
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef complexity_comparison():"""不同算法復雜度的實際性能對比"""# 測試不同規模的輸入sizes = [100, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000]# 存儲各算法的執行時間times_o1 = [] # O(1) - 常數時間times_on = [] # O(n) - 線性時間 times_onlogn = [] # O(n log n) - 線性對數時間times_on2 = [] # O(n2) - 平方時間for size in sizes:data = list(range(size))# O(1) 操作:字典查找lookup_dict = {i: i for i in data}start = time.time()for _ in range(1000): # 重復測試以獲得穩定結果_ = lookup_dict.get(size//2, 0)times_o1.append((time.time() - start) * 1000) # 轉換為毫秒# O(n) 操作:線性搜索start = time.time()for _ in range(10): # 減少重復次數因為較慢target = size // 2for item in data:if item == target:breaktimes_on.append((time.time() - start) * 1000)# O(n log n) 操作:排序start = time.time()for _ in range(10):_ = sorted(data[::-1]) # 對逆序數據排序times_onlogn.append((time.time() - start) * 1000)# O(n2) 操作:冒泡排序(僅對小數據集測試)if size <= 2000: # 避免過長等待時間start = time.time()test_data = data[:min(size, 1000)] # 限制數據規模# 簡化的冒泡排序for i in range(len(test_data)):for j in range(len(test_data) - 1 - i):if test_data[j] > test_data[j + 1]:test_data[j], test_data[j + 1] = test_data[j + 1], test_data[j]times_on2.append((time.time() - start) * 1000)else:times_on2.append(None) # 對大數據集跳過測試# 可視化復雜度差異plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)plt.plot(sizes, times_o1, 'g-o', label='O(1) - Dictionary Lookup')plt.xlabel('Input Size')plt.ylabel('Time (ms)')plt.title('Constant Time Complexity')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)plt.plot(sizes, times_on, 'b-s', label='O(n) - Linear Search')plt.xlabel('Input Size')plt.ylabel('Time (ms)')plt.title('Linear Time Complexity')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)plt.plot(sizes, times_onlogn, 'r-^', label='O(n log n) - Sorting')plt.xlabel('Input Size')plt.ylabel('Time (ms)')plt.title('Linearithmic Time Complexity')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)# 過濾掉None值valid_sizes = [s for s, t in zip(sizes, times_on2) if t is not None]valid_times = [t for t in times_on2 if t is not None]plt.plot(valid_sizes, valid_times, 'm-d', label='O(n2) - Bubble Sort')plt.xlabel('Input Size')plt.ylabel('Time (ms)')plt.title('Quadratic Time Complexity')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()return {'sizes': sizes,'O(1)': times_o1,'O(n)': times_on,'O(n log n)': times_onlogn,'O(n2)': times_on2}# 運行復雜度對比
print("=== 算法復雜度實際性能測試 ===")
complexity_results = complexity_comparison()# 分析結果
print("\n=== 復雜度分析結論 ===")
print("從測試結果可以看出:")
print("1. O(1)操作幾乎不隨數據規模增長而變化")
print("2. O(n)操作時間與數據規模成正比增長")
print("3. O(n log n)操作增長比線性稍快,但仍可接受")
print("4. O(n2)操作在大數據集上會變得不可行")
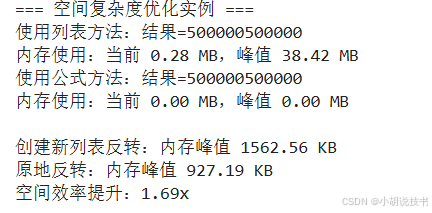
> 空間復雜度優化實例
空間復雜度(Space Complexity) 描述算法使用的額外內存空間如何隨輸入規模變化。在內存受限的環境中,空間優化同樣重要。
def space_complexity_examples():"""空間復雜度優化示例"""print("=== 空間復雜度優化實例 ===")# 示例1:計算數列和 - O(n) vs O(1) 空間復雜度def sum_with_list(n):"""O(n)空間復雜度:存儲所有中間結果"""numbers = list(range(1, n + 1)) # 需要O(n)空間return sum(numbers)def sum_without_list(n):"""O(1)空間復雜度:使用數學公式"""return n * (n + 1) // 2 # 只需要O(1)空間# 測試空間效率n = 1000000import tracemalloc# 測量第一種方法的內存使用tracemalloc.start()result1 = sum_with_list(n)current, peak = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()print(f"使用列表方法:結果={result1}")print(f"內存使用:當前 {current / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB,峰值 {peak / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")# 測量第二種方法的內存使用tracemalloc.start()result2 = sum_without_list(n)current, peak = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()print(f"使用公式方法:結果={result2}")print(f"內存使用:當前 {current / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB,峰值 {peak / 1024 / 1024:.2f} MB")# 示例2:原地算法 vs 創建新數據結構def reverse_create_new(arr):"""創建新列表進行反轉:O(n)額外空間"""return arr[::-1]def reverse_in_place(arr):"""原地反轉:O(1)額外空間"""left, right = 0, len(arr) - 1while left < right:arr[left], arr[right] = arr[right], arr[left]left += 1right -= 1return arr# 空間效率對比test_data = list(range(100000))tracemalloc.start()reversed1 = reverse_create_new(test_data.copy())current1, peak1 = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()tracemalloc.start()reversed2 = reverse_in_place(test_data.copy())current2, peak2 = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()print(f"\n創建新列表反轉:內存峰值 {peak1 / 1024:.2f} KB")print(f"原地反轉:內存峰值 {peak2 / 1024:.2f} KB")print(f"空間效率提升:{peak1/peak2:.2f}x")space_complexity_examples()
8.3 內存優化:高效數據處理的關鍵技術
> 生成器和迭代器模式
生成器(Generator) 是Python中實現惰性求值的重要工具。它允許我們處理無法完全裝入內存的大數據集,這在數據科學應用中極為重要。
def memory_optimization_techniques():"""內存優化技術演示"""print("=== 生成器vs列表:內存使用對比 ===")# 傳統列表方式:一次性創建所有數據def process_data_with_list(n):"""使用列表存儲所有數據"""data = [x**2 for x in range(n)] # 一次性創建所有平方數processed = [x * 2 for x in data if x % 2 == 0] # 再次創建新列表return sum(processed)# 生成器方式:按需生成數據def process_data_with_generator(n):"""使用生成器按需處理數據"""# 生成器表達式:不會立即創建所有數據squares = (x**2 for x in range(n))even_doubles = (x * 2 for x in squares if x % 2 == 0)return sum(even_doubles)# 自定義生成器函數def fibonacci_generator():"""斐波那契數列生成器:無限序列,但只占用常數內存"""a, b = 0, 1while True:yield aa, b = b, a + b# 數據處理管道生成器def data_pipeline(data_source):"""數據處理管道:每次只處理一個元素"""for item in data_source:# 清洗數據if item is not None and item > 0:# 轉換數據processed = item * 2 + 1# 過濾數據if processed < 1000:yield processed# 內存使用對比import tracemallocn = 100000# 測試列表方式tracemalloc.start()result1 = process_data_with_list(n)current1, peak1 = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()# 測試生成器方式tracemalloc.start()result2 = process_data_with_generator(n)current2, peak2 = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()tracemalloc.stop()print(f"列表方式:結果={result1},內存峰值={peak1/1024:.2f} KB")print(f"生成器方式:結果={result2},內存峰值={peak2/1024:.2f} KB")print(f"內存節省:{peak1/peak2:.2f}x")# 演示無限序列處理print(f"\n=== 生成器處理無限序列 ===")fib = fibonacci_generator()first_10_fibs = [next(fib) for _ in range(10)]print(f"前10個斐波那契數:{first_10_fibs}")# 演示數據管道print(f"\n=== 數據處理管道 ===")sample_data = [1, -2, 3, None, 5, 1000, 7, 8, 999]pipeline_result = list(data_pipeline(sample_data))print(f"原始數據:{sample_data}")print(f"管道處理結果:{pipeline_result}")memory_optimization_techniques()# 高級內存優化技術
def advanced_memory_techniques():"""高級內存優化技術"""print("\n=== 高級內存優化技術 ===")# 1. 使用__slots__減少內存開銷class RegularClass:"""普通類:使用字典存儲屬性"""def __init__(self, x, y):self.x = xself.y = yclass OptimizedClass:"""優化類:使用__slots__固定屬性"""__slots__ = ['x', 'y'] # 限制屬性,節省內存def __init__(self, x, y):self.x = xself.y = y# 內存使用對比import sysregular_obj = RegularClass(1, 2)optimized_obj = OptimizedClass(1, 2)print(f"普通類對象大小:{sys.getsizeof(regular_obj)} 字節")print(f"優化類對象大小:{sys.getsizeof(optimized_obj)} 字節")print(f"內存節省:{sys.getsizeof(regular_obj)/sys.getsizeof(optimized_obj):.2f}x")# 2. 使用array模塊替代列表(同類型數據)import array# Python列表(存儲對象引用)python_list = list(range(10000))# array數組(直接存儲值)int_array = array.array('i', range(10000)) # 'i'表示有符號整數print(f"\nPython列表大小:{sys.getsizeof(python_list)} 字節")print(f"Array數組大小:{int_array.buffer_info()[1] * int_array.itemsize} 字節")print(f"內存效率提升:{sys.getsizeof(python_list)/(int_array.buffer_info()[1] * int_array.itemsize):.2f}x")# 3. 內存映射文件處理大數據import mmapimport tempfileimport os# 創建大文件用于演示with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False) as tmp_file:# 寫入大量數據data = b"Hello World! " * 100000tmp_file.write(data)tmp_file_path = tmp_file.nametry:# 傳統方式:將整個文件讀入內存with open(tmp_file_path, 'rb') as f:file_data = f.read()# 內存映射方式:按需讀取with open(tmp_file_path, 'rb') as f:with mmap.mmap(f.fileno(), 0, access=mmap.ACCESS_READ) as mmapped_file:# 只讀取文件的一部分partial_data = mmapped_file[0:100]print(f"\n內存映射讀取前100字節:{partial_data[:50]}...")print(f"文件總大小:{len(mmapped_file)} 字節")print("內存映射允許處理比可用內存更大的文件")finally:# 清理臨時文件os.unlink(tmp_file_path)advanced_memory_techniques()

8.4 并發編程:充分利用多核處理器
> 并發編程模式選擇
Python提供了多種并發編程模式,每種都有其適用場景。理解何時使用哪種模式是提升程序性能的關鍵。
并發編程選擇指南:
- 多線程(Threading):適用于I/O密集型任務(文件讀寫、網絡請求)
- 多進程(Multiprocessing):適用于CPU密集型任務(數值計算、圖像處理)
- 異步編程(Asyncio):適用于高并發I/O任務(Web服務器、API調用)
import threading
import multiprocessing
import asyncio
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, ProcessPoolExecutor
import sys# 將函數移到模塊級別,避免多進程序列化問題
def is_prime(n):"""判斷質數的CPU密集型函數"""if n < 2:return Falsefor i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):if n % i == 0:return Falsereturn Truedef simulate_io_task(task_id):"""模擬I/O操作(如網絡請求、文件讀取)"""time.sleep(0.1) # 模擬I/O等待時間return f"Task {task_id} completed"def concurrent_programming_demo():"""并發編程模式對比演示"""print("=== 并發編程模式對比 ===")def find_primes_sequential(numbers):"""串行方式查找質數"""return [n for n in numbers if is_prime(n)]def find_primes_threaded(numbers, num_threads=4):"""多線程方式查找質數"""with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=num_threads) as executor:results = list(executor.map(is_prime, numbers))return [n for n, is_p in zip(numbers, results) if is_p]def find_primes_multiprocess_safe(numbers, num_processes=4):"""安全的多進程方式查找質數"""try:# 在Jupyter或某些環境中,多進程可能不工作if 'ipykernel' in sys.modules:print("檢測到Jupyter環境,跳過多進程測試")return Nonewith ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=num_processes) as executor:results = list(executor.map(is_prime, numbers))return [n for n, is_p in zip(numbers, results) if is_p]except Exception as e:print(f"多進程執行失敗: {e}")print("這在Jupyter環境中是常見現象,使用備選方案...")return None# 測試CPU密集型任務test_numbers = list(range(10000, 10050)) # 減少數據量以加快演示# 串行執行start_time = time.time()primes_seq = find_primes_sequential(test_numbers)seq_time = time.time() - start_time# 多線程執行start_time = time.time()primes_thread = find_primes_threaded(test_numbers)thread_time = time.time() - start_time# 多進程執行(帶異常處理)start_time = time.time()primes_mp = find_primes_multiprocess_safe(test_numbers)mp_time = time.time() - start_time if primes_mp is not None else Noneprint(f"CPU密集型任務(查找質數)結果:")print(f"串行執行時間:{seq_time:.4f} 秒")print(f"多線程執行時間:{thread_time:.4f} 秒(提升 {seq_time/thread_time:.2f}x)")if mp_time is not None:print(f"多進程執行時間:{mp_time:.4f} 秒(提升 {seq_time/mp_time:.2f}x)")else:print("多進程執行:在當前環境中不可用")print("說明:在標準Python腳本中,多進程通常比多線程更適合CPU密集型任務")print(f"找到質數數量:{len(primes_seq)}")# I/O密集型任務演示def run_io_sequential(num_tasks):"""串行執行I/O任務"""results = []for i in range(num_tasks):results.append(simulate_io_task(i))return resultsdef run_io_threaded(num_tasks, num_threads=4):"""多線程執行I/O任務"""with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=num_threads) as executor:results = list(executor.map(simulate_io_task, range(num_tasks)))return results# 測試I/O密集型任務num_io_tasks = 10 # 減少任務數以加快演示# 串行I/Ostart_time = time.time()io_seq_results = run_io_sequential(num_io_tasks)io_seq_time = time.time() - start_time# 多線程I/Ostart_time = time.time()io_thread_results = run_io_threaded(num_io_tasks)io_thread_time = time.time() - start_timeprint(f"\nI/O密集型任務結果:")print(f"串行執行時間:{io_seq_time:.4f} 秒")print(f"多線程執行時間:{io_thread_time:.4f} 秒(提升 {io_seq_time/io_thread_time:.2f}x)")# 異步編程示例
async def async_task(task_id, duration):"""異步任務:模擬異步I/O操作"""print(f"任務 {task_id} 開始執行")await asyncio.sleep(duration) # 模擬異步等待print(f"任務 {task_id} 執行完成")return f"Task {task_id} result"async def run_async_tasks():"""并發執行多個異步任務"""tasks = [async_task(1, 0.3),async_task(2, 0.2),async_task(3, 0.4),async_task(4, 0.1)]# 并發執行所有任務results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)return resultsasync def async_programming_demo():"""異步編程演示"""print(f"\n=== 異步編程演示 ===")# 運行異步任務start_time = time.time()results = await run_async_tasks()async_time = time.time() - start_timeprint(f"異步執行時間:{async_time:.4f} 秒")print(f"所有任務都是并發執行的,總時間約等于最長任務的時間")print(f"異步執行結果:{results}")# 運行演示
try:concurrent_programming_demo()# 運行異步演示print("\n正在運行異步編程演示...")asyncio.run(async_programming_demo())except Exception as e:print(f"演示過程中發生錯誤:{e}")# 添加并發編程總結
print(f"\n=== 并發編程總結 ===")
print("1. CPU密集型任務:多進程 > 串行 > 多線程(由于GIL限制)")
print("2. I/O密集型任務:多線程 ≈ 異步編程 > 串行")
print("3. 在Jupyter環境中,多進程功能可能受限")
print("4. 異步編程特別適合高并發的網絡I/O操作")
print("5. 選擇并發模式時要考慮任務類型和運行環境")

8.5 代碼質量保證:構建可靠的軟件系統
> 單元測試框架
單元測試(Unit Testing) 是確保代碼質量的基礎工具。它不僅能幫助發現bug,更重要的是促進良好的代碼設計,提高代碼的可維護性。
import unittest
import doctest
from typing import List, Optionalclass DataProcessor:"""數據處理類:演示測試驅動開發"""def __init__(self):self.data = []def add_data(self, value: float) -> None:"""添加數據點Args:value: 要添加的數值Raises:TypeError: 當value不是數字類型時Examples:>>> processor = DataProcessor()>>> processor.add_data(10.5)>>> len(processor.data)1"""if not isinstance(value, (int, float)):raise TypeError("Value must be a number")self.data.append(float(value))def calculate_mean(self) -> Optional[float]:"""計算平均值Returns:數據的平均值,如果沒有數據則返回NoneExamples:>>> processor = DataProcessor()>>> processor.add_data(10)>>> processor.add_data(20)>>> processor.calculate_mean()15.0"""if not self.data:return Nonereturn sum(self.data) / len(self.data)def find_outliers(self, threshold: float = 2.0) -> List[float]:"""查找異常值(超出平均值±threshold*標準差的值)Args:threshold: 異常值判斷的標準差倍數Returns:異常值列表"""if len(self.data) < 2:return []mean = self.calculate_mean()variance = sum((x - mean) ** 2 for x in self.data) / len(self.data)std_dev = variance ** 0.5outliers = []for value in self.data:if abs(value - mean) > threshold * std_dev:outliers.append(value)return outliersclass TestDataProcessor(unittest.TestCase):"""DataProcessor類的單元測試"""def setUp(self):"""測試前的準備工作"""self.processor = DataProcessor()def test_add_data_valid_input(self):"""測試添加有效數據"""self.processor.add_data(10.5)self.assertEqual(len(self.processor.data), 1)self.assertEqual(self.processor.data[0], 10.5)def test_add_data_invalid_input(self):"""測試添加無效數據"""with self.assertRaises(TypeError):self.processor.add_data("invalid")with self.assertRaises(TypeError):self.processor.add_data([1, 2, 3])def test_calculate_mean_empty_data(self):"""測試空數據的平均值計算"""result = self.processor.calculate_mean()self.assertIsNone(result)def test_calculate_mean_valid_data(self):"""測試有效數據的平均值計算"""test_data = [10, 20, 30]for value in test_data:self.processor.add_data(value)result = self.processor.calculate_mean()self.assertEqual(result, 20.0)def test_find_outliers(self):"""測試異常值檢測"""# 添加正常數據和一個明顯的異常值normal_data = [10, 12, 11, 13, 9, 10, 12]outlier = 100for value in normal_data:self.processor.add_data(value)self.processor.add_data(outlier)outliers = self.processor.find_outliers(threshold=2.0)self.assertIn(outlier, outliers)self.assertEqual(len(outliers), 1)def test_integration_workflow(self):"""集成測試:完整的工作流程"""# 模擬真實的使用場景sample_data = [1.0, 2.0, 1.5, 2.5, 1.8, 2.2, 10.0] # 10.0是異常值for value in sample_data:self.processor.add_data(value)mean = self.processor.calculate_mean()outliers = self.processor.find_outliers()self.assertIsNotNone(mean)self.assertTrue(len(outliers) > 0)self.assertIn(10.0, outliers)def run_tests():"""運行所有測試"""print("=== 運行單元測試 ===")# 運行unittest測試unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity=2).run(unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(TestDataProcessor))# 運行doctest(文檔字符串中的測試)print("\n=== 運行文檔測試 ===")doctest.testmod(verbose=True)# 運行測試
run_tests()
> 代碼質量工具
代碼質量不僅包括功能正確性,還包括可讀性、可維護性和一致性。Python生態系統提供了豐富的代碼質量工具。
def code_quality_examples():"""代碼質量最佳實踐示例"""print("\n=== 代碼質量最佳實踐 ===")# 1. 類型注解:提高代碼可讀性和IDE支持from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Uniondef process_user_data(user_id: int,user_info: Dict[str, Union[str, int]],preferences: List[str]) -> Tuple[bool, str]:"""處理用戶數據的函數,使用類型注解提高代碼清晰度Args:user_id: 用戶IDuser_info: 用戶信息字典preferences: 用戶偏好列表Returns:處理結果元組:(是否成功, 結果消息)"""try:# 驗證必要字段required_fields = ['name', 'email', 'age']for field in required_fields:if field not in user_info:return False, f"Missing required field: {field}"# 驗證數據類型if not isinstance(user_info['age'], int) or user_info['age'] < 0:return False, "Invalid age value"# 處理用戶偏好processed_preferences = [pref.lower().strip() for pref in preferences]return True, f"User {user_id} processed successfully"except Exception as e:return False, f"Processing error: {str(e)}"# 2. 錯誤處理最佳實踐class DataValidationError(Exception):"""自定義數據驗證異常"""passdef validate_and_process_data(data: List[Dict]) -> List[Dict]:"""數據驗證和處理的最佳實踐展示了:- 自定義異常- 早期錯誤檢測- 詳細的錯誤信息- 數據清洗"""if not data:raise DataValidationError("No data provided")processed_data = []for i, record in enumerate(data):try:# 驗證必要字段if 'value' not in record:raise DataValidationError(f"Record {i}: missing 'value' field")# 數據類型轉換和驗證try:value = float(record['value'])except (ValueError, TypeError):raise DataValidationError(f"Record {i}: invalid value '{record['value']}'")# 業務邏輯驗證if value < 0:raise DataValidationError(f"Record {i}: negative values not allowed")# 數據清洗和標準化cleaned_record = {'value': value,'timestamp': record.get('timestamp', 'unknown'),'source': record.get('source', 'default').lower()}processed_data.append(cleaned_record)except DataValidationError as e:print(f"警告:{e}")continue # 跳過有問題的記錄,繼續處理其他數據return processed_data# 3. 日志記錄最佳實踐import logging# 配置日志logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)def robust_data_processor(data_file: str) -> bool:"""健壯的數據處理函數,演示完整的錯誤處理和日志記錄"""logger.info(f"開始處理數據文件: {data_file}")try:# 模擬數據處理過程logger.debug("正在驗證文件格式...")# 這里應該是實際的文件處理邏輯sample_data = [{'value': '10.5', 'source': 'sensor1'},{'value': 'invalid', 'source': 'sensor2'}, # 無效數據{'value': '25.0', 'source': 'sensor3'},]logger.info(f"開始處理 {len(sample_data)} 條記錄")processed = validate_and_process_data(sample_data)logger.info(f"成功處理 {len(processed)} 條記錄")logger.warning(f"跳過 {len(sample_data) - len(processed)} 條無效記錄")return Trueexcept DataValidationError as e:logger.error(f"數據驗證錯誤: {e}")return Falseexcept Exception as e:logger.critical(f"未預期的錯誤: {e}")return Falsefinally:logger.info("數據處理完成")# 運行示例print("1. 類型注解示例:")result = process_user_data(user_id=123,user_info={'name': 'Alice', 'email': 'alice@example.com', 'age': 25},preferences=['Python', 'Data Science', 'Machine Learning'])print(f"處理結果:{result}")print("\n2. 數據驗證示例:")robust_data_processor("sample_data.txt")print("\n3. 代碼文檔化示例:")help(process_user_data) # 顯示函數文檔code_quality_examples()
8.6 實戰項目:高性能數據處理流水線
現在讓我們將所有學到的技能整合到一個完整的高性能數據處理項目中。
import asyncio
import multiprocessing as mp
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor, ThreadPoolExecutor
import time
import logging
from pathlib import Path
import json
from typing import List, Dict, Iterator, Optional
from dataclasses import dataclass
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys@dataclass
class ProcessingConfig:"""數據處理配置類"""batch_size: int = 1000num_workers: int = mp.cpu_count()chunk_size: int = 10000output_format: str = 'parquet'enable_parallel: bool = Trueuse_threading: bool = False # 新增:是否使用線程而非進程log_level: str = 'INFO'class HighPerformanceDataPipeline:"""高性能數據處理流水線"""def __init__(self, config: ProcessingConfig):self.config = configself.setup_logging()self.processed_count = 0self.error_count = 0# 檢測運行環境self.is_jupyter = 'ipykernel' in sys.modulesif self.is_jupyter and not self.config.use_threading:self.logger.warning("檢測到Jupyter環境,將使用線程代替進程進行并行處理")self.config.use_threading = Truedef setup_logging(self):"""配置日志系統"""logging.basicConfig(level=getattr(logging, self.config.log_level),format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)def generate_sample_data(self, num_records: int = 100000) -> Iterator[Dict]:"""生成示例數據的生成器"""self.logger.info(f"生成 {num_records} 條示例數據")np.random.seed(42)for i in range(num_records):yield {'id': i,'timestamp': f"2024-01-{(i % 30) + 1:02d} {(i % 24):02d}:{(i % 60):02d}:00",'user_id': np.random.randint(1, 10000),'product_id': np.random.choice(['P001', 'P002', 'P003', 'P004', 'P005']),'amount': np.random.exponential(100),'quantity': np.random.poisson(2) + 1,'category': np.random.choice(['A', 'B', 'C'], p=[0.5, 0.3, 0.2]),'region': np.random.choice(['North', 'South', 'East', 'West']),'is_premium': np.random.choice([True, False], p=[0.2, 0.8])}@staticmethoddef process_data_chunk(chunk_data: List[Dict]) -> Dict:"""處理數據塊的靜態方法"""processed_records = []error_count = 0for record in chunk_data:try:# 數據驗證if record['amount'] < 0:raise ValueError("負金額")# 數據轉換和計算processed_record = {'id': record['id'],'user_id': record['user_id'],'total_value': record['amount'] * record['quantity'],'category': record['category'],'region': record['region'],'is_premium': record['is_premium'],'processed_timestamp': time.time()}# 業務邏輯處理if record['is_premium']:processed_record['total_value'] *= 1.1processed_records.append(processed_record)except Exception as e:error_count += 1continuereturn {'processed_records': processed_records,'processed_count': len(processed_records),'error_count': error_count}def process_parallel_safe(self, data_generator: Iterator[Dict]) -> pd.DataFrame:"""安全的并行處理數據"""parallel_type = "線程" if self.config.use_threading else "進程"self.logger.info(f"開始并行數據處理,使用 {self.config.num_workers} 個{parallel_type}")start_time = time.time()# 將數據分塊chunks = []current_chunk = []for record in data_generator:current_chunk.append(record)if len(current_chunk) >= self.config.chunk_size:chunks.append(current_chunk)current_chunk = []if current_chunk:chunks.append(current_chunk)self.logger.info(f"數據分為 {len(chunks)} 個塊進行并行處理")# 選擇執行器all_processed = []try:if self.config.use_threading:# 使用線程池with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.config.num_workers) as executor:future_to_chunk = {executor.submit(self.process_data_chunk, chunk): chunk for chunk in chunks}for future in future_to_chunk:try:result = future.result()all_processed.extend(result['processed_records'])self.processed_count += result['processed_count']self.error_count += result['error_count']except Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"處理塊時發生錯誤: {e}")self.error_count += len(future_to_chunk[future])else:# 使用進程池(僅在非Jupyter環境)with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.config.num_workers) as executor:future_to_chunk = {executor.submit(self.process_data_chunk, chunk): chunk for chunk in chunks}for future in future_to_chunk:try:result = future.result()all_processed.extend(result['processed_records'])self.processed_count += result['processed_count']self.error_count += result['error_count']except Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"處理塊時發生錯誤: {e}")self.error_count += len(future_to_chunk[future])except Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"并行處理完全失敗: {e}")self.logger.info("回退到串行處理")return self.process_serial(self.generate_sample_data(len(chunks) * self.config.chunk_size))processing_time = time.time() - start_timeself.logger.info(f"并行處理完成,耗時 {processing_time:.2f} 秒")return pd.DataFrame(all_processed)def process_serial(self, data_generator: Iterator[Dict]) -> pd.DataFrame:"""串行處理數據"""self.logger.info("開始串行數據處理")start_time = time.time()all_processed = []chunk = []for record in data_generator:chunk.append(record)if len(chunk) >= self.config.chunk_size:result = self.process_data_chunk(chunk)all_processed.extend(result['processed_records'])self.processed_count += result['processed_count']self.error_count += result['error_count']chunk = []# 處理最后一個塊if chunk:result = self.process_data_chunk(chunk)all_processed.extend(result['processed_records'])self.processed_count += result['processed_count']self.error_count += result['error_count']processing_time = time.time() - start_timeself.logger.info(f"串行處理完成,耗時 {processing_time:.2f} 秒")return pd.DataFrame(all_processed)def save_results(self, df: pd.DataFrame, output_path: str):"""保存處理結果"""try:output_file = Path(output_path)if self.config.output_format == 'csv':df.to_csv(output_file.with_suffix('.csv'), index=False)elif self.config.output_format == 'parquet':df.to_parquet(output_file.with_suffix('.parquet'), index=False)elif self.config.output_format == 'json':df.to_json(output_file.with_suffix('.json'), orient='records')self.logger.info(f"結果已保存到 {output_file}")except Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"保存結果失敗: {e}")def generate_performance_report(self, processing_time: float, total_records: int) -> Dict:"""生成性能報告"""return {'total_records': total_records,'processed_records': self.processed_count,'error_records': self.error_count,'processing_time_seconds': processing_time,'records_per_second': self.processed_count / processing_time if processing_time > 0 else 0,'success_rate': (self.processed_count / total_records * 100) if total_records > 0 else 0,'configuration': {'batch_size': self.config.batch_size,'num_workers': self.config.num_workers,'chunk_size': self.config.chunk_size,'parallel_enabled': self.config.enable_parallel,'using_threading': self.config.use_threading}}def run_pipeline(self, num_records: int = 100000, output_path: str = "processed_data") -> Dict:"""運行完整的數據處理流水線"""self.logger.info("=== 開始高性能數據處理流水線 ===")# 重置計數器self.processed_count = 0self.error_count = 0start_time = time.time()try:# 生成數據data_gen = self.generate_sample_data(num_records)# 選擇處理模式if self.config.enable_parallel:processed_df = self.process_parallel_safe(data_gen)else:processed_df = self.process_serial(data_gen)# 保存結果self.save_results(processed_df, output_path)# 生成報告total_time = time.time() - start_timereport = self.generate_performance_report(total_time, num_records)self.logger.info("=== 數據處理流水線完成 ===")return reportexcept Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"流水線執行失敗: {e}")raisedef benchmark_pipeline_performance():"""性能基準測試"""print("=== 高性能數據處理流水線性能測試 ===")test_configs = [ProcessingConfig(enable_parallel=False, chunk_size=5000),ProcessingConfig(enable_parallel=True, num_workers=2, chunk_size=5000, use_threading=True),ProcessingConfig(enable_parallel=True, num_workers=4, chunk_size=5000, use_threading=True),]test_data_size = 20000 # 減少數據量以加快測試results = []for i, config in enumerate(test_configs):print(f"\n--- 測試配置 {i+1} ---")parallel_type = "線程并行" if config.use_threading and config.enable_parallel else "串行"if config.enable_parallel and not config.use_threading:parallel_type = "進程并行"print(f"處理模式: {parallel_type}")print(f"工作單元數: {config.num_workers if config.enable_parallel else 1}")print(f"數據塊大小: {config.chunk_size}")pipeline = HighPerformanceDataPipeline(config)try:report = pipeline.run_pipeline(num_records=test_data_size,output_path=f"test_output_{i+1}")results.append(report)print(f"處理時間: {report['processing_time_seconds']:.2f} 秒")print(f"處理速度: {report['records_per_second']:.0f} 條/秒")print(f"成功率: {report['success_rate']:.1f}%")except Exception as e:print(f"測試失敗: {e}")continue# 性能對比分析if len(results) > 1:print(f"\n=== 性能對比分析 ===")baseline_time = results[0]['processing_time_seconds']for i, result in enumerate(results):speedup = baseline_time / result['processing_time_seconds']print(f"配置 {i+1} 相對于串行的性能提升: {speedup:.2f}x")print(f"配置 {i+1} 成功處理: {result['processed_records']} 條記錄")return results# 運行性能測試
try:performance_results = benchmark_pipeline_performance()except Exception as e:print(f"測試過程中發生錯誤: {e}")
8.7 學習總結與工程化開發指導
> 性能優化的系統性方法
通過本課學習,我們建立了完整的Python性能優化方法論。性能優化不是孤立的技巧收集,而是需要遵循科學的分析和改進流程:
分析階段:使用性能分析工具準確定位瓶頸,避免過早優化和盲目猜測。
算法層面:從復雜度角度評估和選擇合適的算法和數據結構。
實現層面:運用Python特定的優化技術,如生成器、向量化、內存優化等。
系統層面:合理使用并發和并行技術,充分利用硬件資源。
> 工程化開發的核心理念
代碼質量先于性能:可讀、可維護的代碼是長期項目成功的基礎。性能優化應該在保證代碼質量的前提下進行。
測試驅動開發:完善的測試體系不僅保證功能正確性,更為重構和優化提供安全保障。
漸進式優化:從可工作的簡單版本開始,通過測量和分析逐步優化,避免過度工程化。
文檔和日志:良好的文檔和日志系統是團隊協作和問題診斷的重要工具。
> 實際項目應用指導
在實際的數據科學和AI項目中,性能優化往往決定了解決方案的可行性:
數據預處理階段:運用內存優化和并行處理技術處理大規模數據集。
模型訓練階段:合理利用GPU加速和分布式計算框架。
模型服務階段:優化推理性能,確保實時響應需求。
監控和維護:建立完善的性能監控體系,及時發現和解決性能問題。
> 與后續課程的連接
本課程建立的工程化開發基礎將在機器學習項目中發揮重要作用。從數據處理流水線的構建,到模型訓練的性能優化,再到生產環境的部署和監控,每個環節都需要本課所學的技能。
特別是在處理大規模數據和復雜模型時,性能優化能力往往是區分業余項目和專業解決方案的關鍵因素。
附錄:專業術語表
性能分析(Performance Profiling):通過測量程序運行時的各項指標來識別性能瓶頸的系統性方法
時間復雜度(Time Complexity):描述算法運行時間如何隨輸入規模增長而變化的數學表示
空間復雜度(Space Complexity):描述算法使用的額外內存空間如何隨輸入規模變化的度量
生成器(Generator):Python中實現惰性求值的機制,能夠按需生成數據而不需要一次性存儲所有結果
向量化操作(Vectorization):將操作應用于整個數組而不是逐個元素的編程技術,通常能顯著提升性能
并發編程(Concurrent Programming):設計程序使多個任務能夠在重疊的時間段內執行的編程范式
多進程(Multiprocessing):利用多個獨立進程并行執行任務的并發方式,適用于CPU密集型任務
多線程(Multithreading):在單個進程內使用多個執行線程的并發方式,適用于I/O密集型任務
異步編程(Asynchronous Programming):基于事件循環和協程的非阻塞編程模式,特別適合高并發I/O操作
單元測試(Unit Testing):對程序中最小可測試單元進行檢查和驗證的軟件測試方法
代碼覆蓋率(Code Coverage):衡量測試代碼執行覆蓋程度的指標,包括行覆蓋率、分支覆蓋率等
內存映射(Memory Mapping):將文件或設備的內容映射到進程地址空間的技術,允許高效訪問大文件
惰性求值(Lazy Evaluation):延遲計算直到真正需要結果時才執行的求值策略
GIL(Global Interpreter Lock):Python解釋器中的全局鎖,限制了多線程在CPU密集型任務中的效果

總結(89))
-圖像修復與編輯)


)









![[react] react-router-dom是啥?](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[react] react-router-dom是啥?)



深入無鎖并發演進,AtomicInteger核心API詳解與典型場景舉例)