1.存儲映射
存儲映射 I/O (Memory-mapped I/O) 使一個磁盤文件與存儲空間中的一個緩沖區相映射。于是當從緩沖區中取數據,就相當于讀文件中的相應字節。于此類似,將數據存入緩沖區,則相應的字節就自動寫入文件。這樣,就可在不適用 read 和 write 函數的情況下,使用地址(指針)完成 I/O 操作。 使用存儲映射這種方法,首先應通知內核,將一個指定文件映射到存儲區域中。這個映射工作可以通過mmap 函數來實現。
? ? ?這個文件僅僅是用來進程間通信的橋梁。

1.1mmap函數映射
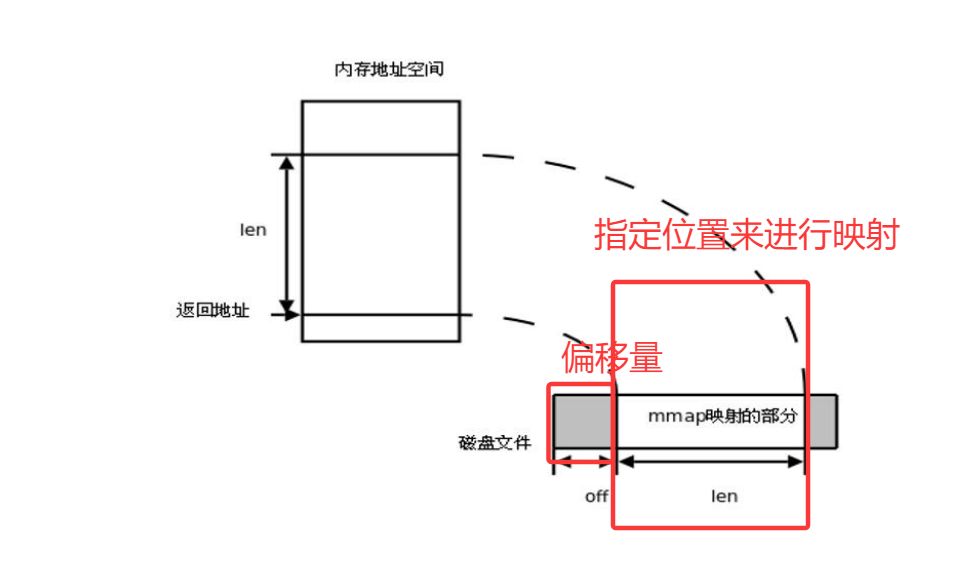
mmap函數:建立映射區
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags,int fd, off_t offset);參數解釋
addr 地址,填 NULL(讓系統自己找一個合理的地址)
length 長度 要申請的映射區的長度
prot 權限(讀還是寫)
????????PROT_READ 可讀
????????PROT_WRITE 可寫
flags 標志位
????????MAP_SHARED 共享的 -- 對映射區的修改會影響源文件(一般是這個)
????????MAP_PRIVATE 私有的
fd 文件描述符 需要打開一個文件
offset 指定一個偏移位置 ,從該位置開始映射(一般寫0,不偏移)
返回值
????????成功 返回映射區的首地址
????????失敗 返回 MAP_FAILED ((void *) -1)
1.2munmap函數
munmap函數:解除映射(斷開當前進程和磁盤文件的映射關系,不影響其他進程的映射)
int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);參數解釋
????????addr 映射區的首地址
????????length 映射區的長度
返回值
????????成功 返回 0
????????失敗 返回 -1
1.3truncate函數
truncate函數:拓展文件的大小
一般磁盤映射是新建一個文件,這個文件新建的時候,大小是0,因此里面無法存儲數據,所以需要拓展文件的大小
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);參數解釋
????????path 要拓展的文件
????????length 要拓展的長度
1.4代碼案例
不相關的進程間通信
寫代碼:
#define _POSIX_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//1.通過open打開文件int fd = open("temp",O_RDWR |O_CREAT,0666);//新建的文件無大小//2.拓展文件的大小truncate("temp",16);//3.建立映射char *buff = (char *)mmap(NULL,16,PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED ,fd,0);//4.使用內存區域strcpy(buff,"hello mmap");//5.斷開映射munmap(buff,16);close(fd);return 0;
}
讀代碼:
#define _POSIX_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//1.通過open打開文件int fd = open("temp",O_RDWR |O_CREAT,0666);//新建的文件無大小//2.拓展文件的大小truncate("temp",16);//3.建立映射char *buff = (char *)mmap(NULL,16,PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED ,fd,0);//4.使用內存區域printf("收到數據%s\n",buff);printf("收到數據%s\n",buff);//5.斷開映射munmap(buff,16);close(fd);return 0;
}

除非被覆蓋,否則數據一直在
2.共享內存
2.1共享內存理論
共享內存允許兩個或者多個進程共享給定的存儲區域。(進程間通信的最快的方式)
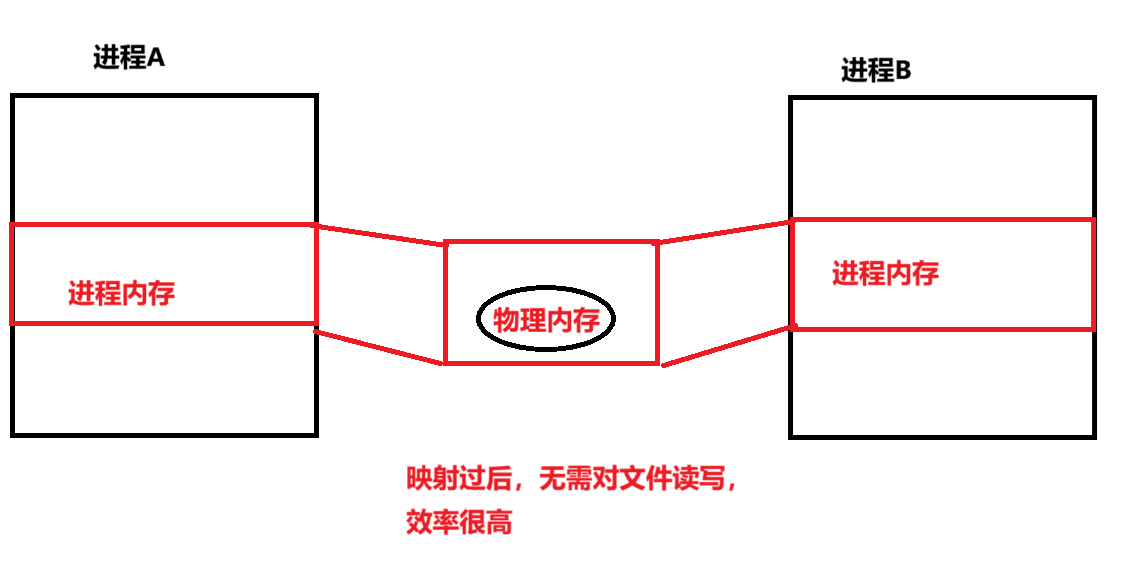
共享內存的特點
1、 共享內存是進程間共享數據的一種最快的方法。 一個進程向共享的內存區域寫入了數據, 共享這個內存區域的所有進程就可以立刻看到其中的內容。
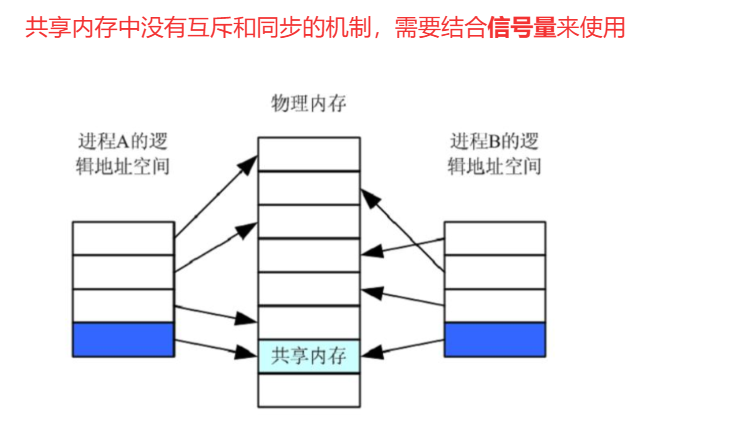
2、 使用共享內存要注意的是多個進程之間對一個給定存儲區訪問的互斥。 若一個進程正在向共享內存區寫數據, 則在它做完這一步操作前, 別的進程不應當去讀、 寫這些數據。
在 ubuntu 部分版本中共享內存限制值如下 共享存儲區的最小字節數:
1 共享存儲區的最大字節數: 32M
共享存儲區的最大個數: 4096
每個進程最多能映射的共享存儲區的個數: 4096
2.2共享內存的API
shmget函數:創建或打開一塊共享內存區,即獲得一個共享內存標識符
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size,int shmflg);功能:
????????創建或打開一塊共享內存區
參數:
????????key:IPC 鍵值(需要ftok函數)
????????size:該共享存儲段的長度(字節)
????????shmflg:標識函數的行為及共享內存的權限。
????????????????參數:shmflg:
????????????????????????IPC_CREAT:如果不存在就創建
????????????????????????IPC_EXCL:如果已經存在則返回失敗
????????????????????????位或權限位:共享內存位或權限位后可以設置共享內存的訪問權限,格式 和 open 函數的 mode_t 一樣,但可執行權限未使用。
返回值:
????????成功:返回共享內存標識符。
????????失敗:返回-1。
使用 shell 命令操作共享內存
查看共享內存
ipcs -m --內存
ipcs -q --隊列
ipcrm -m shmid --刪除shmid的共享內存
代碼案例:
創建一個共享內存,獲取標識符:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{ // 1.獲取唯一key值key_t key = ftok("/home/qf/桌面", 2504);// 2.得到唯一共享內存標識(分配物理內存)int shm_id = shmget(key,16,IPC_CREAT | 0666) ; printf("%d\n",shm_id);return 0;
}
shmat函數:將一個共享內存段映射到調用進程的數據段中,即建立進程與物理內存的映射
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr,int shmflg);
函數功能:
????????將一個共享內存段映射到調用進程的數據段中。
參數:
????????shmid:共享內存標識符。
????????shmaddr:共享內存映射地址(若為 NULL 則由系 統自動指 定),推薦使用 NULL。
????????shmflg:共享內存段的訪問權限和映射條件(映射時的讀寫關系)
????????????????0:共享內存具有可讀可寫權限。
????????????????SHM_RDONLY:只讀。
????????????????SHM_RND:(shmaddr 非空時才有效)(自己申請的虛擬地址來進行映射(例如malloc來的),建議shmaddr選NUMM)
????????????????沒有指定 SHM_RND 則此段連接到 shmaddr 所指定的地址上(shmaddr 必需 頁對齊)。 指定了 SHM_RND 則此段連接到 shmaddr- shmaddr%SHMLBA 所表示的地址 上。
返回值:
成功:返回共享內存段映射地址
失敗:返回 -1
代碼案例:建立內存與進程間的映射
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{ // 1.獲取唯一key值key_t key = ftok("/home/qf/桌面", 2504);// 2.得到唯一共享內存標識(分配物理內存)int shm_id = shmget(key,16,IPC_CREAT | 0666) ; printf("%d\n",shm_id);//3.建立進程和物理內存間的映射char *p = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,0);//4.斷開映射,只斷開自己return 0;
}
shmdt函數:將共享內存和當前進程分離(僅僅是斷開聯系并不刪除共享內存)。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);功能:
????????將共享內存和當前進程分離(僅僅是斷開聯系并不刪除共享內存)。
參數:
????????shmaddr:共享內存映射地址。
返回值:
成功返回 0
失敗返回 -1
shmctl:共享內存控制函數
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd,struct shmid_ds *buf);功能:
????????共享內存空間的控制。
參數:
????????shmid:共享內存標識符。
????????cmd:函數功能的控制。
????????buf:shmid_ds 數據類型的地址,用來存放或修改共享內存的屬性。
????????????????cmd:函數功能的控制
????????????????????????IPC_RMID:刪除。
????????????????????????IPC_SET:設置 shmid_ds 參數。
????????????????????????IPC_STAT:保存 shmid_ds 參數。
????????????????????????SHM_LOCK:鎖定共享內存段(超級用戶)。
????????????????????????SHM_UNLOCK:解鎖共享內存段。
返回值:
成功返回 0
失敗返回 -1
注意:
SHM_LOCK 用于鎖定內存,禁止內存交換。并不代表共享內存被鎖定后,禁止其它進程訪問。其真正的意義是:被鎖定的內存不允許被交換到虛擬內存中(即只針對當前進程)。這樣做的優勢在于讓共享內存一直處于內存中,從而提高程序性能
讀寫代碼案例:
寫:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{ // 1.獲取唯一key值key_t key = ftok("/home/qf/桌面", 2504);// 2.得到唯一共享內存標識(分配物理內存)int shm_id = shmget(key,16,IPC_CREAT | 0666) ; printf("%d\n",shm_id);//3.建立進程和物理內存間的映射char *p = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,0);strcpy(p,"hello world!");//4.斷開映射,只斷開自己shmdt(p);return 0;
}
讀:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{ // 1.獲取唯一key值key_t key = ftok("/home/qf/桌面", 2504);// 2.得到唯一共享內存標識(分配物理內存)int shm_id = shmget(key,16,IPC_CREAT | 0666) ; printf("%d\n",shm_id);//3.建立進程和物理內存間的映射char *p = (char *)shmat(shm_id,NULL,SHM_RDONLY);printf("收到數據:%s\n",p);//4.斷開映射,只斷開自己return 0;
}
)

)






:『可觀測性的定義與實踐』)




抽象工廠模式)




