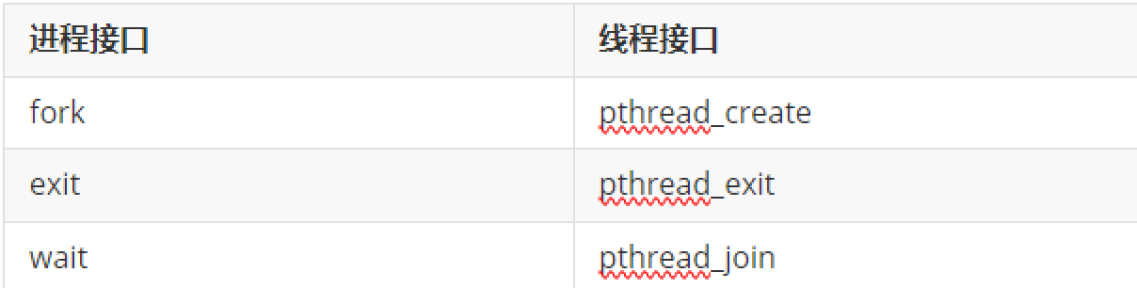
exec函數族
exec函數族
????????利用進程空間執行另一份代碼

#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{char *parg[5] = {"./hello","how","are","you",NULL,};printf("execl-up\n");//execl("./hello", "./hello", "how", "are", "you", NULL);execv(parg[0], parg);printf("execl-error\n");printf("execl-down\n");return 0;}主函數傳參
主函數形式

#include "../head.h"int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{int i = 0;printf("hello world\n");printf("==========\n");for(i = 0; i < argc; i++){printf("%s\n", argv[i]);}//for(i = 0; argv[i] != NULL; i++){printf("%s\n", argv[i]);}return 0;
}system

#include "../head.h"void mysystem(void)
{pid_t pid;pid = fork();if(-1 == pid){perror("fail to fork");return;}if(0 == pid){execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);}wait(NULL); //父子進程同步return;
}int main(void)
{printf("systen-up\n");mysystem();printf("system-down\n");return 0;
}線程
概念
- 線程是一個輕量級的進程
- 線程本質就是一個進程
- 線程和進程不完全一致,輕量指的是內存空間,進程空間和線程空間管理方法不同
進程和線程區別
- 線程本質是進程,線程是任務創建、調度、回收的過程
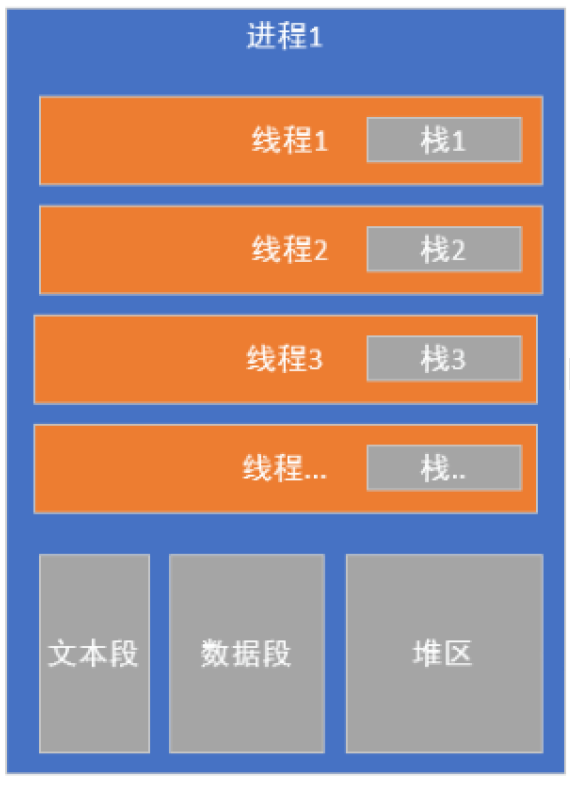
- 進程空間:文本段、數據段、系統數據段共同構成
- 線程空間:
- 線程必須位于進程內部,沒有進程,線程無法獨立存在
- 一個進程中的所有線程共享文本段+數據段+堆區,獨享棧區
- 線程獨享的棧區默認8M
- 一個進程中的多個線程切換調度任務時,資源開銷比較小
區別總結:
- 線程是CPU任務調度的最小單元,和進程一樣都是獨立執行的任務
- 進程是操作系統資源分配的最小單元,線程無法獨立存在,不是一個獨立的空間,只是任務的獨立。
多進程和多線程的優缺點
多線程和多進程對比

線程的調度
- 與進程調度保持一致
- 宏觀并行,微觀串行
線程的消亡
- 線程結束需要回收線程空間,否則產生僵尸線程
線程的函數接口
函數接口
pthread_create(創建線程)

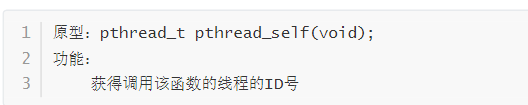
pthread_self(獲得線程的ID號)
pthread_exit(結束線程任務)

pthread_join(回收線程空間)

#include "../head.h"void *thread1(void *arg)
{printf("線程1(TID:%#lx)開始執行\n", pthread_self());pthread_exit("線程1退出");return NULL;
}
void *thread2(void *arg)
{printf("線程2(TID:%#lx)開始執行\n", pthread_self());pthread_exit("線程2退出");return NULL;
}
void *thread3(void *arg)
{printf("線程3(TID:%#lx)開始執行\n", pthread_self());pthread_exit("線程3退出");return NULL;
}int main(void)
{pthread_t tid[3];int i = 0;void *pret = NULL;void *(*p[3])(void *) = {thread1, thread2, thread3}; //函數指針數組for(i = 0; i < 3; i++){pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, p[i], NULL);}for(i = 0; i < 3; i++){pthread_join(tid[i], &pret); //回收狀態傳&pret,不回收狀態直接傳NULLprintf("線程退出狀態:%s\n", (char *)pret);}/*int ret = 0;pthread_t tid1;pthread_t tid2;pthread_t tid3;*//*ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread1, NULL);if(ret != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create");return -1;}printf("線程1(TID:%#lx)創建成功\n", tid1);ret = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread2, NULL);if(ret != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create\n");return -1;}printf("線程2(TID:%#lx)創建成功\n", tid2);ret = pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, thread3, NULL);if(ret != 0){perror("fail to pthread_create\n");return -1;}printf("線程3(TID:%#lx)創建成功\n", tid3);pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_join(tid3, NULL);*/return 0;
}





)
)



)




:事件總線、setState的細節、PureComponent、ref)


