Redisson獲取鎖過程?
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("lock:order" + userId);
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);調用tyrLock其實就是下面的方法,如果說沒有指定鎖的過期時間,可以看到這邊設置為了-1
@Overridepublic boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {return tryLock(waitTime, -1, unit);}再往下追,,只需要先看tryAcquire就行,這是獲取鎖的核心,tryLock后面還有一堆東西現在先不用管
這里將等待時間轉化為毫秒,獲取了當前線程id,當前時間
@Overridepublic boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);long current = System.currentTimeMillis();long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
再往下追,可以看到會根據有沒有設置鎖的超時時間,調用不同的方法,沒有設置的話調用的話會進入下面的代碼設置看門狗時間getLockWatchdogTimeout,默認是30秒這里也是30*1000化為了毫秒
這里傳入的參數分別是 獲取鎖的等待時間,鎖的過期時間,時間單位,線程id
調用 tryLockInnerAsync 傳入的參數是?獲取鎖的等待時間,鎖的過期時間,時間單位,線程id,?Redis 命令(如?EVAL),用于執行 Lua 腳本
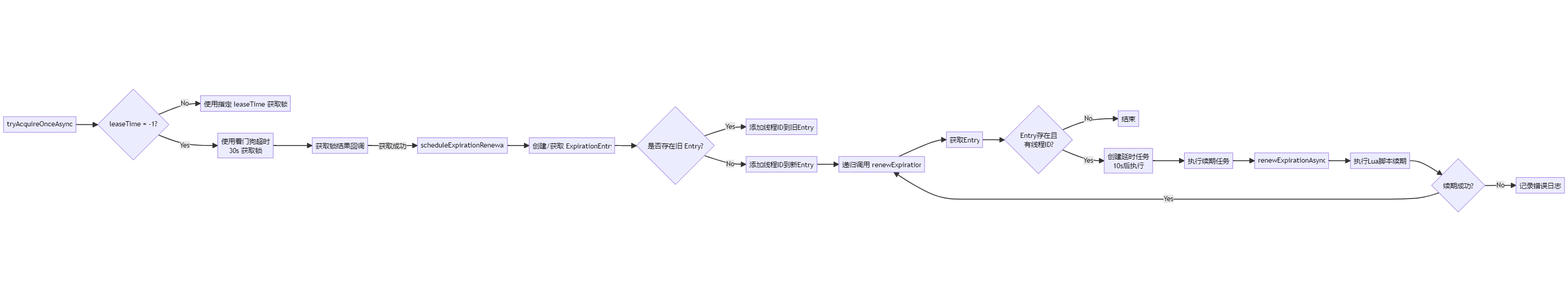
private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {if (leaseTime != -1) {return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);}
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {if (e != null) {return;}// lock acquiredif (ttlRemaining) {scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);}});核心步驟?
getName(): 獲取鎖在 Redis 中的鍵名(KEYS[1])。internalLockLeaseTime: 將傳入的鎖租約時間?leaseTime?轉換為毫秒。getLockName(threadId): 生成一個唯一標識當前線程(或客戶端)的字符串(ARGV[2])。command: 通常是一個 Redis 命令(如?EVAL),用于執行 Lua 腳本。
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +"return nil; " +"end; " +"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +"return nil; " +"end; " +"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",Collections.singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));}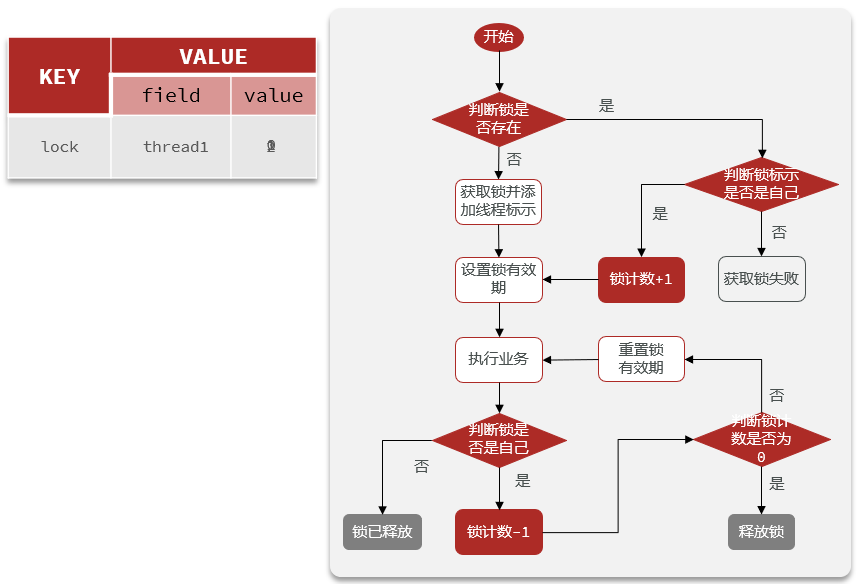
執行 Lua 腳本:?腳本邏輯是原子性的,確保并發安全。它包含三個主要分支:
分支 1:鎖不存在(首次獲取)
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1](@ref) == 0) thenredis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); -- 創建Hash,字段ARGV[2]的值設為1(計數)redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1](@ref); -- 設置整個鎖Key的過期時間return nil; -- 返回nil表示獲取成功 end;- 檢查鎖 Key (
KEYS[1]) 是否存在。 - 如果不存在(
exists == 0):- 使用?
HINCRBY?命令創建一個 Hash 結構,Key 是?KEYS[1],字段(field)是當前線程標識?ARGV[2],值初始化為?1(表示鎖計數)。 - 使用?
PEXPIRE?命令為整個鎖 Key (KEYS[1]) 設置過期時間(毫秒),值為?ARGV[1](即?internalLockLeaseTime)。 - 返回?
nil,表示獲取鎖成功。
- 使用?
- 檢查鎖 Key (
分支 2:鎖已存在且當前線程持有(鎖重入)
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2](@ref) == 1) thenredis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); -- 字段ARGV[2]的值加1(增加重入計數)redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1](@ref); -- 刷新整個鎖Key的過期時間return nil; -- 返回nil表示獲取成功(重入) end;- 檢查鎖 Key (
KEYS[1]) 對應的 Hash 中,是否存在字段?ARGV[2](即當前線程標識)。 - 如果存在(
hexists == 1):- 使用?
HINCRBY?命令將字段?ARGV[2]?的值加?1(實現可重入鎖,計數增加)。 - 使用?
PEXPIRE?命令刷新整個鎖 Key (KEYS[1]) 的過期時間(續租)。 - 返回?
nil,表示獲取鎖成功(重入成功)。
- 使用?
- 檢查鎖 Key (
分支 3:鎖已存在但被其他線程持有(獲取失敗)
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1](@ref); -- 返回鎖Key的剩余生存時間(毫秒)- 如果前兩個分支都不滿足(鎖存在但不是當前線程持有):
- 使用?
PTTL?命令獲取鎖 Key (KEYS[1]) 的剩余生存時間(毫秒)。 - 將這個剩余時間返回給調用者。
- 使用?
- 如果前兩個分支都不滿足(鎖存在但不是當前線程持有):
嘗試獲取鎖之后的邏輯
@Overridepublic boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);long current = System.currentTimeMillis();long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);//這里獲取到
的依舊是以毫秒為單位,如果獲取到鎖返回null,沒有獲取到鎖返回該鎖的剩余時間// lock acquiredif (ttl == null) {return true;//獲取成功直接返回true}time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; //time-上面代碼所消耗的時間if (time <= 0) { time是等待鎖的時間,判斷如果上面代碼消耗的時間過長,其實就是獲取鎖的時間太長大于了鎖的等待時間返回falseacquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);return false;}//如果還能等鎖釋放,繼續執行下面的代碼current = System.currentTimeMillis();//這里無需立即重新去獲取鎖了,因為你知道獲取鎖的那個人還在執行自己的業務//這里訂閱別人釋放鎖的信息, Redisson釋放鎖的時候會發布一條通知,這個后面會說RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);// 阻塞當前線程,等待 subscribeFuture 代表的異步訂閱操作完成(成功、失敗或取消)
,但最多只等待指定的 time 毫秒,超時返回falseif (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {if (e == null) {unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);//超時直接取消訂閱}});}acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);return false;}try {//再次獲取剩余時間time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;if (time <= 0) {acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);return false;}while (true) {//依舊和上面的邏輯一樣,先嘗試獲取鎖,為空代表成功,返回true//判斷剩余時間,不夠返回falselong currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);// lock acquiredif (ttl == null) {return true;}time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;if (time <= 0) {acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);return false;}// waiting for messagecurrentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//和上面一樣不要立刻嘗試獲取鎖if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {//ttl就是鎖的過期時間,而time則是我們可以等待的時間//哪個小等待哪個時間就行,因為一個到時了另一個也沒用了subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);} else {subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}//判斷是否超時time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;if (time <= 0) {acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);return false;}//沒有超時繼續循環重新嘗試獲取鎖}} finally {unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);}
// return get(tryLockAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit));}初始化時間與線程ID:
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);: 將用戶指定的最大等待時間?waitTime?轉換為毫秒?time。long current = System.currentTimeMillis();: 記錄當前時間戳?current。long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();: 獲取當前線程的唯一ID?threadId。
首次嘗試獲取鎖:
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);: 調用核心方法嘗試獲取鎖。- 成功 (
ttl == null): 直接返回?true。 - 失敗 (
ttl >= 0):?ttl?表示鎖當前的剩余生存時間(毫秒)。
- 成功 (
扣除首次嘗試耗時 & 檢查剩余等待時間:
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;: 計算首次嘗試獲取鎖花費的時間,并從總等待時間?time?中扣除。if (time <= 0) { ... return false; }: 如果扣除后剩余等待時間?time <= 0,說明等待時間已耗盡,調用?acquireFailed(記錄失敗指標)并返回?false。
訂閱鎖釋放通知頻道:
RFuture subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);:?異步發起訂閱操作,訂閱與當前鎖關聯的頻道,用于接收鎖釋放通知。返回?RFuture?對象?subscribeFuture。if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { ... }:?阻塞等待訂閱操作完成,最多等待剩余的?time?毫秒。- 訂閱超時 (
!await(...)):if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) { ... }: 嘗試取消訂閱操作。如果取消失敗(通常意味著訂閱在取消瞬間完成了),則注冊一個?onComplete?回調。這個回調的作用是:如果訂閱最終成功完成 (e == null),則立即執行?unsubscribe?清理資源。acquireFailed(...); return false;: 標記獲取失敗并返回?false。
- 訂閱成功 (
await(...)?返回?true): 繼續執行后續流程。
- 訂閱超時 (
扣除訂閱耗時 & 再次檢查剩余等待時間:
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;: 計算訂閱操作花費的時間,并從剩余等待時間?time?中扣除。if (time <= 0) { ... return false; }: 如果剩余時間耗盡,標記失敗并返回?false。
循環嘗試獲取鎖(核心重試邏輯):
while (true) { ... }: 進入一個無限循環,直到成功獲取鎖、等待超時或發生異常。- 記錄循環開始時間:?
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); - 再次嘗試獲取鎖:?
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);- 成功 (
ttl == null): 直接返回?true。 - 失敗 (
ttl >= 0): 繼續后續步驟。
- 成功 (
- 扣除本次嘗試耗時 & 檢查剩余時間:
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;if (time <= 0) { ... return false; }: 時間耗盡則失敗返回。
- 基于 TTL 的智能等待(關鍵優化):
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();: 記錄等待開始時間。if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) { ... } else { ... }:ttl < time?(鎖快過期): 調用?semaphore.tryAcquire(ttl, MILLISECONDS)。只等待鎖剩余生存時間?ttl。?期望鎖因過期自動釋放或收到通知。ttl >= time?(鎖活很久或無效): 調用?semaphore.tryAcquire(time, MILLISECONDS)。只等待剩余的?time。?期望在耐心耗盡前收到鎖釋放通知。
tryAcquire?行為:- 如果收到鎖釋放通知 (
semaphore.release()?被調用),tryAcquire?會立刻返回?true?(獲取到"許可"),然后循環會再次嘗試?tryAcquire?獲取鎖。 - 如果超時?(未收到通知),
tryAcquire?返回?false。
- 如果收到鎖釋放通知 (
- 扣除等待耗時 & 最終檢查剩余時間:
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;: 計算等待花費的時間。if (time <= 0) { ... return false; }: 時間耗盡則失敗返回。- 如果時間還有剩余,且?
tryAcquire?超時返回?false?(未收到通知),循環會再次執行,重新嘗試獲取鎖 (ttl = tryAcquire(...))。這提供了主動重試的機會,即使沒收到通知(比如通知丟失或鎖自動過期但通知未觸發)。
finally?塊 - 資源清理 (至關重要):unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);:?無論?tryLock?方法最終是成功返回 (true)、失敗返回 (false) 還是拋出異常 (InterruptedException?等),這段代碼都會被執行。- 目的:?釋放步驟 4 中建立的訂閱關系。
- 為什么必須放在?
finally?里?- 防止資源泄漏:?如果不取消訂閱,Redis 服務器會持續維護這個訂閱連接和頻道監聽,消耗服務器資源(內存、連接數)。
- 避免無效通知:?鎖釋放時,消息會發送到這個頻道,但客戶端線程已經不再關心(它要么獲得了鎖,要么放棄了),造成不必要的網絡流量和處理。
- 保證健壯性:?即使循環內部出現異常(雖然代碼中未顯式拋出,但理論上可能),也能確保訂閱被清理。
- 客戶端資源管理:?Redisson 客戶端也需要管理其內部的訂閱狀態,及時清理不再需要的訂閱。
看門狗”(Watchdog)機制核心作用
到這里其實還是有點問題,考慮一個問題
線程一 (Thread1):
- 成功調用?
tryLock?獲取鎖。 - 開始執行臨界區業務代碼。
- 業務代碼執行時間過長,超過了鎖的租約時間?
leaseTime。 - 鎖在 Redis 中因?TTL 到期而被自動刪除(超時釋放)。
- 成功調用?
線程二 (Thread2):
- 在 Thread1 持有鎖期間嘗試獲取鎖。
- 首次?
tryAcquire?失敗,返回?ttl(鎖的剩余時間)。 - 成功訂閱鎖釋放頻道。
- 在信號量上調用?
tryAcquire(ttl, ...)?進行等待。 - 當 Thread1 的鎖因超時被 Redis 自動刪除后:
- 可能情況一:?Redis 的?
expire?機制刪除鎖時,不會主動發布鎖釋放消息。(這是關鍵!Redis 的 Key 過期是惰性刪除+定期刪除,刪除事件不一定觸發發布訂閱通知)。 - 可能情況二:?即使 Redis 有?
__keyevent@<db>__:expired?這樣的 Keyspace 通知,Redisson 默認的鎖釋放監聽是基于特定頻道的普通發布訂閱,通常不會監聽 Key 過期事件。
- 可能情況一:?Redis 的?
- Thread2 的?
tryAcquire(ttl, ...)?超時返回?false(因為它沒收到鎖釋放的通知)。 - Thread2?跳出等待,再次調用?
tryAcquire。 - 此時鎖已被 Redis 刪除(超時釋放),Thread2?成功獲取鎖。
- Thread2 進入臨界區執行業務。
問題發生:
- Thread1 仍在執行它的業務代碼!?它以為自己還持有鎖(因為它沒有主動釋放,也不知道鎖被 Redis 強制移除了)。
- Thread2 也開始執行相同的業務代碼
- 結果:兩個線程同時進入了臨界區,破壞了鎖的互斥性,導致線程安全問題(如數據不一致)。
為什么單看上面的?tryLock?代碼有安全隱患
- 鎖的持有時間 (
leaseTime) 是固定的:?在?tryLock?方法中,leaseTime?是由調用者指定的。一旦設置,鎖在 Redis 中的 TTL 就是固定的。 - 業務執行時間不可控:?業務代碼的執行時間可能因為各種原因(GC、網絡延遲、復雜計算、死循環等)超出預期的?
leaseTime。 - 鎖超時釋放是靜默的:?Redis 在 Key 過期被刪除時,默認不會向 Redisson 訂閱的鎖釋放頻道發送消息。等待鎖的線程(Thread2)感知不到鎖是因為超時而被刪除的。它只能通過:
- 被動等待通知:?這通常只在鎖被主動釋放(調用?
unlock)時才會觸發。 - 主動重試:?在信號量等待超時后,Thread2 會再次嘗試?
tryAcquire。此時它才發現鎖已經被刪除了(超時釋放),從而成功獲取。但這發生在 Thread1 的業務還在執行期間。
- 被動等待通知:?這通常只在鎖被主動釋放(調用?
- 線程無法感知鎖丟失:?Thread1 在執行超長的業務時,完全不知道?Redis 上的鎖已經因為 TTL 到期而被刪除了。它仍然認為自己持有鎖,并繼續執行對共享資源的操作。
?我們再來看看下面的這段代碼
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {if (leaseTime != -1) {return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);}RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {if (e != null) {return;//發生異常,直接返回}// lock acquiredif (ttlRemaining == null) {//獲取鎖成功scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);//啟動鎖的自動續期任務}});return ttlRemainingFuture;}- 這里調用?
tryLockInnerAsync?嘗試獲取鎖,但傳入的租約時間不是?-1,而是配置的?lockWatchdogTimeout(默認 30,000 毫秒) - 返回一個?
RFuture<Long>?對象?ttlRemainingFuture,代表這個異步獲取鎖操作的結果
注冊回調函數
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {if (e != null) {return;}if (ttlRemaining == null) {scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);} });- 在?
ttlRemainingFuture?上注冊一個完成時觸發的回調函數 - 這個回調函數會在?
tryLockInnerAsync?操作完成時(無論成功或失敗)被調用
- 在?
最后看看鎖的自動續期相關代碼?
getEntryName返回的就是線程的id和鎖名稱拼接起來的字符串,這里的EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP是個靜態MAP?,一個鎖對應一個entry對象
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {// 1. 創建新的續期記錄ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();// 2. 嘗試將續期記錄放入全局管理MapExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);// 3. 處理續期記錄if (oldEntry != null) {// 3a. 如果已有記錄存在:添加當前線程IDoldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);} else {// 3b. 如果是新記錄:添加線程ID并啟動續期任務entry.addThreadId(threadId);renewExpiration(); // 啟動看門狗定時任務}
}
創建續期記錄
- 創建一個新的?
ExpirationEntry?實例 - 這個對象將用于跟蹤當前鎖的續期狀態
- 創建一個新的?
管理全局續期狀態
- 使用?
putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry)?嘗試將新記錄放入全局映射 - 這個方法原子性地執行:
- 如果映射中不存在指定鍵的條目,則添加新條目并返回?
null - 如果已存在,則返回現有條目
- 如果映射中不存在指定鍵的條目,則添加新條目并返回?
- 使用?
處理續期記錄
情況A:已有記錄存在 (
oldEntry != null)- 表示這個鎖已經啟動了續期任務
- 只需將當前線程ID添加到現有記錄:
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId) - 這支持鎖的可重入性(同一線程多次獲取同一鎖)
情況B:新記錄 (
oldEntry == null)- 表示這是第一次為此鎖啟動續期任務
- 將當前線程ID添加到新記錄:
entry.addThreadId(threadId) - 啟動續期任務:
renewExpiration()
加油就剩最后一點了,我們可以看到看門狗的核心機制
private void renewExpiration() {//獲取當前鎖的續期記錄ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());if (ee == null) {return; // 如果記錄不存在(鎖已被釋放),直接返回}//創建定時任務,再delay時間到期以后才會執行,這個delay也是作為newTimeout的第二個參數Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());if (ent == null) {return;}//從entry中取出線程Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();if (threadId == null) {return;}//調用函數刷新有效期RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);future.onComplete((res, e) -> {if (e != null) {log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);return;}if (res) {// reschedule itself//續期成功遞歸調用renewExpiration();}});}}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);//這里就是之前的看門狗時間ee.setTimeout(task);}也就是這個定時任務十秒之后才會執行
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +"return 1; " +"end; " +"return 0;",Collections.singletonList(getName()),internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));}可以看到這里的刷新有效期還是通過lua腳本來實現的,作用就是重置鎖的有效期
時,報404異常,下載失敗的問題解決)

:多傳感器融合定位系統中的標定與時間同步方案】)

—DHT11 溫濕度傳感器的硬件與軟件系統設計)





![命令執行漏洞和[GXYCTF2019]Ping Ping Ping](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/命令執行漏洞和[GXYCTF2019]Ping Ping Ping)
![[LeetCode]每日溫度](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[LeetCode]每日溫度)







