前言:
最近在大模型預測,簡單了解了lag-llama開源項目,網上也有很多講解原理的,這里就將如何快速上手使用說一下,只懂得一點點皮毛,有錯誤的地方歡迎大佬指出。
簡單介紹:
Lag-Llama?是一個開源的時間序列預測模型,基于?Transformer?架構設計,專注于利用?滯后特征(Lagged Features)?捕捉時間序列的長期依賴關系。其核心思想是將傳統時間序列分析中的滯后算子(Lags)與現代深度學習結合,實現對復雜時序模式的高效建模。
GitHup地址:GitHub - time-series-foundation-models/lag-llama: Lag-Llama: Towards Foundation Models for Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting
相關技術原理:...(搜一下很多文章講的都非常好)
實現模型預測:
1.下載模型文件
從?HuggingFace下載,如果網絡原因訪問不了,建議從魔搭社區下載(lag-Llama · 模型庫)
2.準備數據集
參考文檔:pandas.DataFrame based dataset - GluonTS documentation
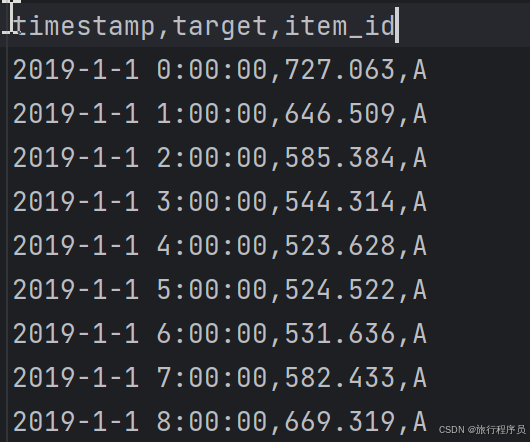
以我測試數據舉例:
3.完整代碼:(需要替換模型文件地址和數據集地址)
from itertools import islicefrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdatesimport torch
from gluonts.evaluation import make_evaluation_predictions, Evaluator
from gluonts.dataset.repository.datasets import get_datasetfrom gluonts.dataset.pandas import PandasDataset
import pandas as pdfrom lag_llama.gluon.estimator import LagLlamaEstimatordef get_lag_llama_predictions(dataset, prediction_length, device, num_samples, context_length=32, use_rope_scaling=False):# 模型文件地址ckpt = torch.load("/models/lag-Llama/lag-llama.ckpt", map_location=device, weights_only=False) # Uses GPU since in this Colab we use a GPU.estimator_args = ckpt["hyper_parameters"]["model_kwargs"]rope_scaling_arguments = {"type": "linear","factor": max(1.0, (context_length + prediction_length) / estimator_args["context_length"]),}estimator = LagLlamaEstimator(# 模型文件地址ckpt_path="/models/lag-Llama/lag-llama.ckpt",prediction_length=prediction_length,context_length=context_length,# Lag-Llama was trained with a context length of 32, but can work with any context length# estimator argsinput_size=estimator_args["input_size"],n_layer=estimator_args["n_layer"],n_embd_per_head=estimator_args["n_embd_per_head"],n_head=estimator_args["n_head"],scaling=estimator_args["scaling"],time_feat=estimator_args["time_feat"],rope_scaling=rope_scaling_arguments if use_rope_scaling else None,batch_size=1,num_parallel_samples=100,device=device,)lightning_module = estimator.create_lightning_module()transformation = estimator.create_transformation()predictor = estimator.create_predictor(transformation, lightning_module)forecast_it, ts_it = make_evaluation_predictions(dataset=dataset,predictor=predictor,num_samples=num_samples)forecasts = list(forecast_it)tss = list(ts_it)return forecasts, tssimport pandas as pd
from gluonts.dataset.pandas import PandasDataseturl = ("/lag-llama/history.csv"
)
df = pd.read_csv(url, index_col=0, parse_dates=True)# Set numerical columns as float32
for col in df.columns:# Check if column is not of string typeif df[col].dtype != 'object' and pd.api.types.is_string_dtype(df[col]) == False:df[col] = df[col].astype('float32')# Create the Pandas
dataset = PandasDataset.from_long_dataframe(df, target="target", item_id="item_id")backtest_dataset = dataset
# 預測長度
prediction_length = 24 # Define your prediction length. We use 24 here since the data is of hourly frequency
# 樣本數
num_samples = 1 # number of samples sampled from the probability distribution for each timestep
device = torch.device("cuda:1") # You can switch this to CPU or other GPUs if you'd like, depending on your environmentforecasts, tss = get_lag_llama_predictions(backtest_dataset, prediction_length, device, num_samples)# 提取第一個時間序列的預測結果
forecast = forecasts[0]
print('=================================')
# 概率預測的完整樣本(形狀: [num_samples, prediction_length])
samples = forecast.samples
print(samples)關鍵參數說明:
| 參數 | 說明 |
| prediction_length | 預測的未來時間步長 |
| context_length | 模型輸入的歷史時間步長(需 >= 季節性周期) |
| num_samples | 概率預測的采樣次數(值越大,概率區間越準) |
| checkpoint_path | 預訓練模型權重路徑(需提前下載) |
| freq | 時間序列頻率(如 "H" 小時、"D" 天) |
結果:
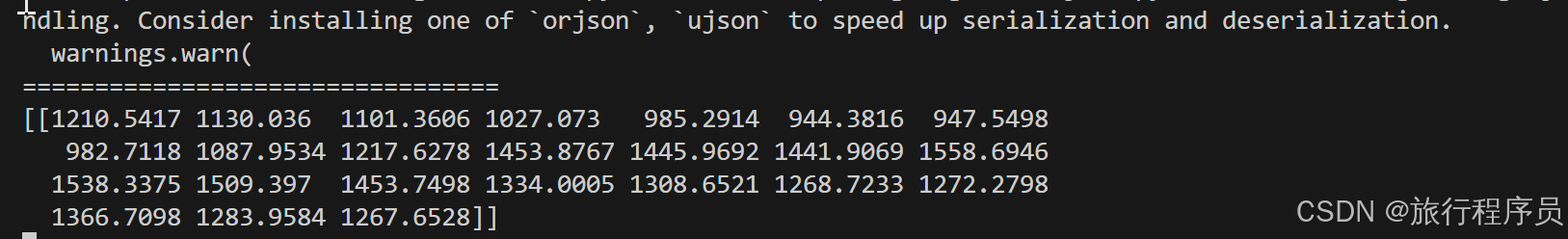
這里只是給出了簡單的代碼實現,想要更好的效果還需深入研究!!!



)















