一,設備驅動模型
1,概述
在前面寫的驅動中,我們發現編寫驅動有個固定的模式只有往里面套代碼就可以了,它們之間的大致流程可以總結如下:
-
實現入口函數xxx_init()和卸載函數xxx_exit()
-
申請設備號 register_chrdev_region()
-
初始化字符設備,cdev_init函數、cdev_add函數
-
硬件初始化,如時鐘寄存器配置使能,GPIO設置為輸入輸出模式等。
-
構建file_operation結構體內容,實現硬件各個相關的操作
-
在終端上使用mknod根據設備號來進行創建設備文件(節點) (也可以在驅動使用class_create創建設備類、在類的下面device_create創建設備節點)
因此,在Linux開發驅動,只要能夠掌握了這些“套路”,開發一個驅動便不是難事。但是,如果我們將硬件的信息都寫進了驅動里了, 根據某個硬件編寫的驅動只要修改了一下引腳接口,這個驅動代碼就得重新修改才能使用,這顯然是不合理的。
那有沒有合適的解決方案呢?答案是肯定的:
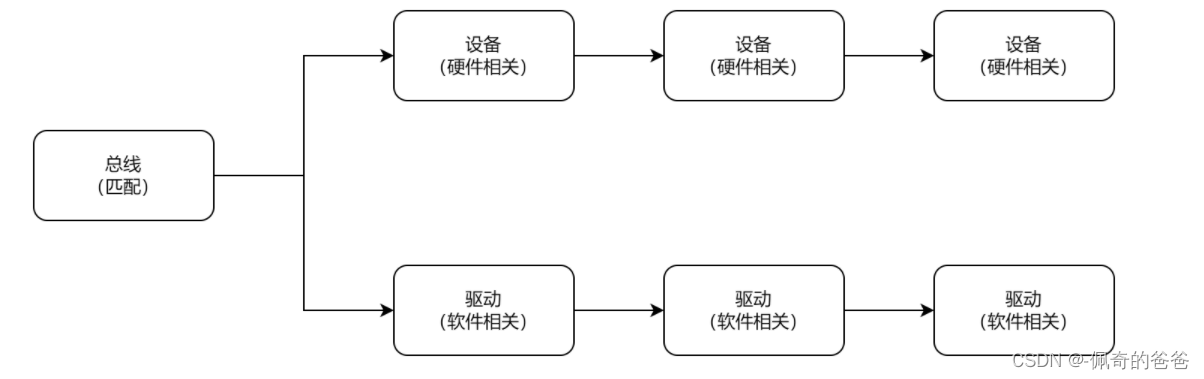
Linux引入了設備驅動模型分層的概念, 將我們編寫的驅動代碼分成:設備與驅動。
-
設備負責提供硬件資源
-
驅動代碼負責去使用這些設備提供的硬件資源
-
總線將它們聯系起來
這樣子就構成以下圖形中的關系:

在實際操作上:
-
每次有新設備device添加時,bus就會去匹配合適的驅動
-
每次有新驅動driver添加時,bus就會去匹配合適的設備
-
這樣device代表的硬件設置就和driver代表的軟件設計解耦了
當然實際中,同一總線下的設備有很多,驅動也有很多,在總線上管理著兩個鏈表,分別管理著設備和驅動,當我們向系統注冊一個驅動時,便會向驅動的管理鏈表插入我們的新驅動, 同樣當我們向系統注冊一個設備時,便會向設備的管理鏈表插入我們的新設備。
在插入的同時總線會執行一個匹配方法對新插入的設備/驅動進行匹配,在匹配成功的時候會調用驅動中的初始化方法,在移除設備或驅動時會調用注銷方法。
以上只是設備驅動模型的機制 。
2,設備驅動模型初始化
從內核啟動到driver_init()的流程:
start_kernel(void) // msm_kernel\init\main.carch_call_rest_init();rest_init();kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);kernel_init_freeable();do_basic_setup();driver_init();driver_init()調用流程:
msm_kernel\drivers\base\init.c
/**
* driver_init - initialize driver model.
*
* Call the driver model init functions to initialize their
* subsystems. Called early from init/main.c.
*/
void __init driver_init(void)
{/* These are the core pieces */devtmpfs_init();devices_init(); //初始化 devices_kset, /sys/devices/buses_init(); //初始化bus_kset, /sys/bus/classes_init(); //初始化class_kset, /sys/class firmware_init();hypervisor_init();/* These are also core pieces, but must come after the* core core pieces.*/of_core_init(); //初始化of_ksetplatform_bus_init(); //注冊platform_bus device和platform_bus_type buscpu_dev_init();memory_dev_init();container_dev_init();
}二,總線的注冊
在Linux設備模型中,Bus(總線)是一類特殊的設備,它是連接處理器和其它設備之間的通道(channel)。為了方便設備模型的實現,內核規定,系統中的每個設備都要連接在一個Bus上,這個Bus可以是一個內部Bus、虛擬Bus或者Platform Bus。內核通過struct bus_type結構,抽象Bus。
1,struct bus_type結構體
/**
* struct bus_type - The bus type of the device
*
* @name: The name of the bus.
* @dev_name: Used for subsystems to enumerate devices like ("foo%u", dev->id).
* @dev_root: Default device to use as the parent.
* @bus_groups: Default attributes of the bus.
* @dev_groups: Default attributes of the devices on the bus.
* @drv_groups: Default attributes of the device drivers on the bus.
* @match: Called, perhaps multiple times, whenever a new device or driver
* is added for this bus. It should return a positive value if the
* given device can be handled by the given driver and zero
* otherwise. It may also return error code if determining that
* the driver supports the device is not possible. In case of
* -EPROBE_DEFER it will queue the device for deferred probing.
* @uevent: Called when a device is added, removed, or a few other things
* that generate uevents to add the environment variables.
* @probe: Called when a new device or driver add to this bus, and callback
* the specific driver's probe to initial the matched device.
* @sync_state: Called to sync device state to software state after all the
* state tracking consumers linked to this device (present at
* the time of late_initcall) have successfully bound to a
* driver. If the device has no consumers, this function will
* be called at late_initcall_sync level. If the device has
* consumers that are never bound to a driver, this function
* will never get called until they do.
* @remove: Called when a device removed from this bus.
* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.
*
* @online: Called to put the device back online (after offlining it).
* @offline: Called to put the device offline for hot-removal. May fail.
*
* @suspend: Called when a device on this bus wants to go to sleep mode.
* @resume: Called to bring a device on this bus out of sleep mode.
* @num_vf: Called to find out how many virtual functions a device on this
* bus supports.
* @dma_configure: Called to setup DMA configuration on a device on
* this bus.
* @pm: Power management operations of this bus, callback the specific
* device driver's pm-ops.
* @iommu_ops: IOMMU specific operations for this bus, used to attach IOMMU
* driver implementations to a bus and allow the driver to do
* bus-specific setup
* @p: The private data of the driver core, only the driver core can
* touch this.
* @lock_key: Lock class key for use by the lock validator
* @need_parent_lock: When probing or removing a device on this bus, the
* device core should lock the device's parent.
*
* A bus is a channel between the processor and one or more devices. For the
* purposes of the device model, all devices are connected via a bus, even if
* it is an internal, virtual, "platform" bus. Buses can plug into each other.
* A USB controller is usually a PCI device, for example. The device model
* represents the actual connections between buses and the devices they control.
* A bus is represented by the bus_type structure. It contains the name, the
* default attributes, the bus' methods, PM operations, and the driver core's
* private data.
*/
struct bus_type {const char *name; //總線的名字,在syfs中以目錄的形式存在例如,/sys/bus/i2cconst char *dev_name; //子系統枚舉設備時的名字struct device *dev_root;const struct attribute_group **bus_groups; //bus屬性集const struct attribute_group **dev_groups; //device屬性集const struct attribute_group **drv_groups; //driver屬性集int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv); /* bus提供的match函數, 一個由具體的bus driver實現的回調函數。當任何屬于該Bus的device或者device_driver添加到內核時,內核都會調用該接口 */int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env); /* 一個由具體的bus driver實現的回調函數。當任何屬于該Bus的device,發生添加、移除或者其它動作時,Bus模塊的核心邏輯就會調用該接口,以便bus driver能夠修改環境變量 */int (*probe)(struct device *dev); /* bus提供的probe函數, 如果需要probe(其實就是初始化)指定的device話,需要保證該device所在的bus是被初始化過、確保能正確工作的。這就要就在執行device_driver的probe前,先執行它的bus的probe */void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);int (*remove)(struct device *dev);void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);int (*online)(struct device *dev);int (*offline)(struct device *dev);int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);int (*resume)(struct device *dev);int (*num_vf)(struct device *dev);int (*dma_configure)(struct device *dev);const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;struct subsys_private *p; //bus的私有成員struct lock_class_key lock_key;bool need_parent_lock;ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
};bus私有成員結構體,這個結構就是集合了一些bus模塊需要使用的私有數據:
/**
* struct subsys_private - structure to hold the private to the driver core portions of the bus_type/class structure.
*
* @subsys - the struct kset that defines this subsystem
* @devices_kset - the subsystem's 'devices' directory
* @interfaces - list of subsystem interfaces associated
* @mutex - protect the devices, and interfaces lists.
*
* @drivers_kset - the list of drivers associated
* @klist_devices - the klist to iterate over the @devices_kset
* @klist_drivers - the klist to iterate over the @drivers_kset
* @bus_notifier - the bus notifier list for anything that cares about things
* on this bus.
* @bus - pointer back to the struct bus_type that this structure is associated
* with.
*
* @glue_dirs - "glue" directory to put in-between the parent device to
* avoid namespace conflicts
* @class - pointer back to the struct class that this structure is associated
* with.
*
* This structure is the one that is the actual kobject allowing struct
* bus_type/class to be statically allocated safely. Nothing outside of the
* driver core should ever touch these fields.
*/
struct subsys_private {struct kset subsys; //bus內嵌的kset,代表其自身 eg: /sys/bus/i2c,kset是一個特殊的kobject,用來集合相似的kobject,它在sysfs中也會以目錄的形式體現struct kset *devices_kset; //屬于subsys kset, eg: /sys/bus/i2c/devicesstruct list_head interfaces;struct mutex mutex;struct kset *drivers_kset; //屬于subsys kset, eg: /sys/bus/i2c/driversstruct klist klist_devices; //本bus包含的所有設備struct klist klist_drivers; //本bus包含的所有driverstruct blocking_notifier_head bus_notifier;unsigned int drivers_autoprobe:1; //device與driver是否自動probestruct bus_type *bus; //回指到bus_typestruct kset glue_dirs;struct class *class;
};2,bus_register()流程
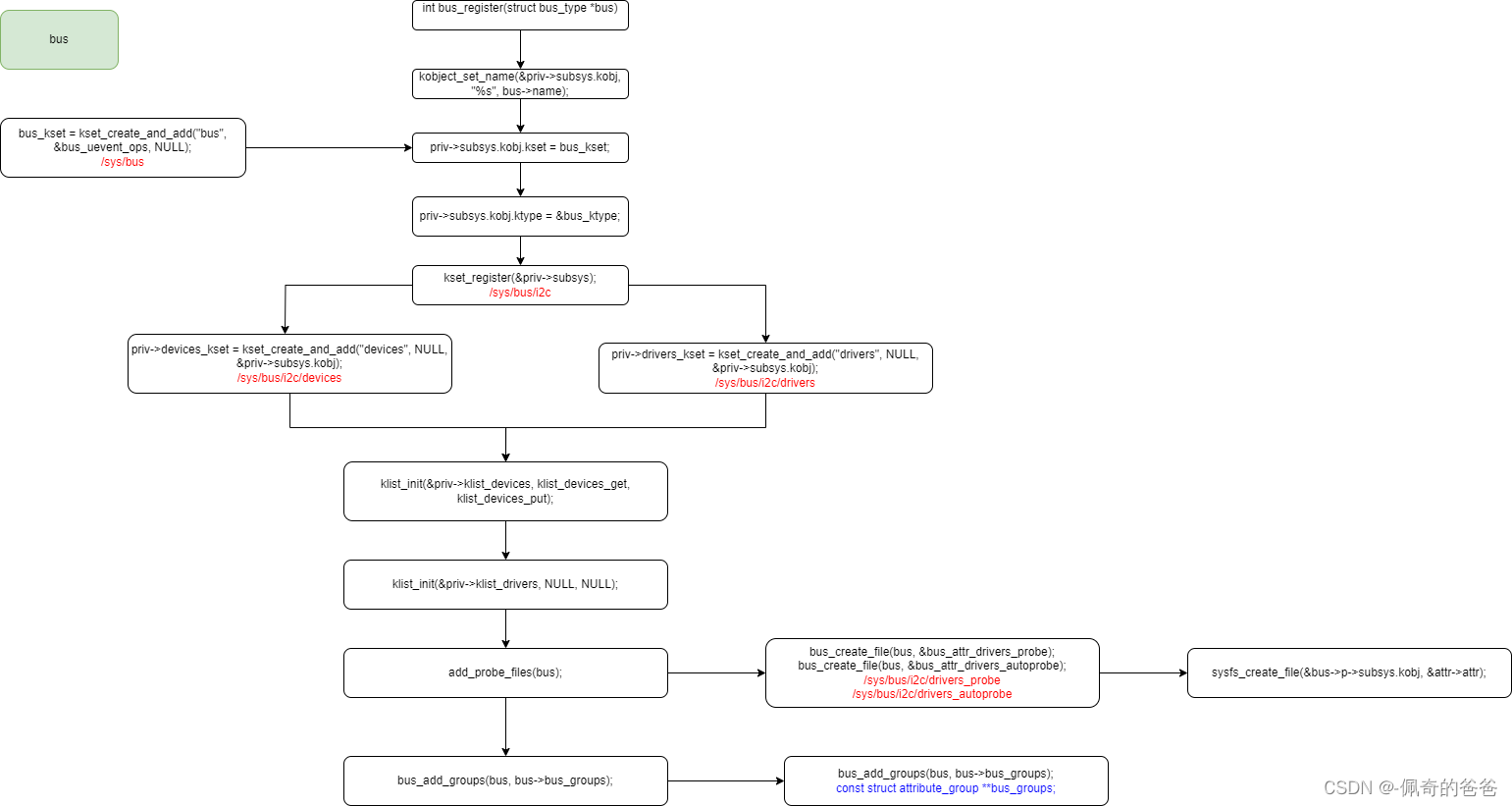
3,關鍵代碼流程分析
int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus)
{int retval;struct subsys_private *priv;struct lock_class_key *key = &bus->lock_key;priv = kzalloc(sizeof(struct subsys_private), GFP_KERNEL); //為struct subsys_private分配空間if (!priv)return -ENOMEM;priv->bus = bus; //私有成員的bus回指該busbus->p = priv; //初始化bus->p,即其私有屬性BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&priv->bus_notifier);retval = kobject_set_name(&priv->subsys.kobj, "%s", bus->name); //設置該bus的名字,bus是kset的封裝if (retval)goto out;priv->subsys.kobj.kset = bus_kset; //bus_ket即為所有bus的總起始端點,本bus從屬于bus_ket,/sys/bus/priv->subsys.kobj.ktype = &bus_ktype; //屬性操作級別統一為bus_ktypepriv->drivers_autoprobe = 1; //device與driver自動進行proberetval = kset_register(&priv->subsys); //注冊kset,創建目錄結構以及層級關系 /sys/bus/i2c/if (retval)goto out;retval = bus_create_file(bus, &bus_attr_uevent); //當前bus下生成uevent attribute文件 /sys/bus/i2c/ueventif (retval)goto bus_uevent_fail;priv->devices_kset = kset_create_and_add("devices", NULL, //初始化bus目錄下的devices目錄,里面級聯了該bus下的設備,仍然以ket為原型&priv->subsys.kobj); // /sys/bus/i2c/devicesif (!priv->devices_kset) {retval = -ENOMEM;goto bus_devices_fail;}priv->drivers_kset = kset_create_and_add("drivers", NULL, //初始化bus目錄下的drivers目錄,里面級聯了該bus下設備的driver&priv->subsys.kobj); // /sys/bus/i2c/driversif (!priv->drivers_kset) {retval = -ENOMEM;goto bus_drivers_fail;}INIT_LIST_HEAD(&priv->interfaces);__mutex_init(&priv->mutex, "subsys mutex", key);klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, klist_devices_get, klist_devices_put); //初始化klist_devices里的操作函數成員 klist_init(&priv->klist_drivers, NULL, NULL); //klist_drivers里的操作函數置空retval = add_probe_files(bus); /* 增加drivers_autoprobe和drivers_probe屬性文件,/sys/bus/i2c/drivers_probe, /sys/bus/i2c/drivers_autoprobe */if (retval)goto bus_probe_files_fail;retval = bus_add_groups(bus, bus->bus_groups); //增加bus默認的屬性文件, const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;if (retval)goto bus_groups_fail;pr_debug("bus: '%s': registered\n", bus->name);return 0;bus_groups_fail:remove_probe_files(bus);
bus_probe_files_fail:kset_unregister(bus->p->drivers_kset);
bus_drivers_fail:kset_unregister(bus->p->devices_kset);
bus_devices_fail:bus_remove_file(bus, &bus_attr_uevent);
bus_uevent_fail:kset_unregister(&bus->p->subsys);
out:kfree(bus->p);bus->p = NULL;return retval;
}由此可見,bus又是kset的封裝,bus_register主要完成了其私有成員priv的初始化,并初始化了其下的兩個目錄devices和drivers,及其屬性文件,bus有個自己的根目錄也就是bus有個起始端點,是bus_kset,經過此番的注冊,bus目錄下將會出現我們注冊的bus,并且其下會有device和driver兩個子目錄,代表它下面的driver和device鏈表。
三,設備的注冊
1,struct device 結構體
/**
* struct device - The basic device structure
* @parent: The device's "parent" device, the device to which it is attached.
* In most cases, a parent device is some sort of bus or host
* controller. If parent is NULL, the device, is a top-level device,
* which is not usually what you want.
* @p: Holds the private data of the driver core portions of the device.
* See the comment of the struct device_private for detail.
* @kobj: A top-level, abstract class from which other classes are derived.
* @init_name: Initial name of the device.
* @type: The type of device.
* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific
* information.
* @mutex: Mutex to synchronize calls to its driver.
* @lockdep_mutex: An optional debug lock that a subsystem can use as a
* peer lock to gain localized lockdep coverage of the device_lock.
* @bus: Type of bus device is on.
* @driver: Which driver has allocated this
* @platform_data: Platform data specific to the device.
* Example: For devices on custom boards, as typical of embedded
* and SOC based hardware, Linux often uses platform_data to point
* to board-specific structures describing devices and how they
* are wired. That can include what ports are available, chip
* variants, which GPIO pins act in what additional roles, and so
* on. This shrinks the "Board Support Packages" (BSPs) and
* minimizes board-specific #ifdefs in drivers.
* @driver_data: Private pointer for driver specific info.
* @links: Links to suppliers and consumers of this device.
* @power: For device power management.
* See Documentation/driver-api/pm/devices.rst for details.
* @pm_domain: Provide callbacks that are executed during system suspend,
* hibernation, system resume and during runtime PM transitions
* along with subsystem-level and driver-level callbacks.
* @em_pd: device's energy model performance domain
* @pins: For device pin management.
* See Documentation/driver-api/pinctl.rst for details.
* @msi_list: Hosts MSI descriptors
* @msi_domain: The generic MSI domain this device is using.
* @numa_node: NUMA node this device is close to.
* @dma_ops: DMA mapping operations for this device.
* @dma_mask: Dma mask (if dma'ble device).
* @coherent_dma_mask: Like dma_mask, but for alloc_coherent mapping as not all
* hardware supports 64-bit addresses for consistent allocations
* such descriptors.
* @bus_dma_limit: Limit of an upstream bridge or bus which imposes a smaller
* DMA limit than the device itself supports.
* @dma_range_map: map for DMA memory ranges relative to that of RAM
* @dma_parms: A low level driver may set these to teach IOMMU code about
* segment limitations.
* @dma_pools: Dma pools (if dma'ble device).
* @dma_mem: Internal for coherent mem override.
* @cma_area: Contiguous memory area for dma allocations
* @archdata: For arch-specific additions.
* @of_node: Associated device tree node.
* @fwnode: Associated device node supplied by platform firmware.
* @devt: For creating the sysfs "dev".
* @id: device instance
* @devres_lock: Spinlock to protect the resource of the device.
* @devres_head: The resources list of the device.
* @knode_class: The node used to add the device to the class list.
* @class: The class of the device.
* @groups: Optional attribute groups.
* @release: Callback to free the device after all references have
* gone away. This should be set by the allocator of the
* device (i.e. the bus driver that discovered the device).
* @iommu_group: IOMMU group the device belongs to.
* @iommu: Per device generic IOMMU runtime data
*
* @offline_disabled: If set, the device is permanently online.
* @offline: Set after successful invocation of bus type's .offline().
* @of_node_reused: Set if the device-tree node is shared with an ancestor
* device.
* @state_synced: The hardware state of this device has been synced to match
* the software state of this device by calling the driver/bus
* sync_state() callback.
* @dma_coherent: this particular device is dma coherent, even if the
* architecture supports non-coherent devices.
* @dma_ops_bypass: If set to %true then the dma_ops are bypassed for the
* streaming DMA operations (->map_* / ->unmap_* / ->sync_*),
* and optionall (if the coherent mask is large enough) also
* for dma allocations. This flag is managed by the dma ops
* instance from ->dma_supported.
*
* At the lowest level, every device in a Linux system is represented by an
* instance of struct device. The device structure contains the information
* that the device model core needs to model the system. Most subsystems,
* however, track additional information about the devices they host. As a
* result, it is rare for devices to be represented by bare device structures;
* instead, that structure, like kobject structures, is usually embedded within
* a higher-level representation of the device.
*/
struct device {struct kobject kobj; //該數據結構對應的struct kobject,代表自身struct device *parent; //該設備的父設備,一般是該設備所從屬的bus、controller等設備struct device_private *p; //一個用于struct device的私有數據結構指針const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */ /* 任何注冊到內核中的設備,都必須有一個合法的名稱,可以在初始化時給出,也可以由內核根據“bus name + device ID”的方式創造 */const struct device_type *type;struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated thisdevice */void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, devicecore doesn't touch it */void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get withdev_set_drvdata/dev_get_drvdata */
#ifdef CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKINGstruct mutex lockdep_mutex;
#endifstruct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to* its driver.*/struct dev_links_info links;struct dev_pm_info power;struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;#ifdef CONFIG_ENERGY_MODELstruct em_perf_domain *em_pd;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAINstruct irq_domain *msi_domain;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRLstruct dev_pin_info *pins;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQstruct list_head msi_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPSconst struct dma_map_ops *dma_ops;
#endifu64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma'able device) */u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but foralloc_coherent mappings asnot all hardware supports64 bit addresses for consistentallocations such descriptors. */u64 bus_dma_limit; /* upstream dma constraint */const struct bus_dma_region *dma_range_map;struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_DECLARE_COHERENTstruct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent memoverride */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMAstruct cma *cma_area; /* contiguous memory area for dmaallocations */
#endif/* arch specific additions */struct dev_archdata archdata;struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; /* firmware device node */#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAint numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
#endifdev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */ /* 該變量主要用于在sys文件系統中,為每個具有設備號的device,創建/sys/dev/* 下的對應目錄 */u32 id; /* device instance */spinlock_t devres_lock;struct list_head devres_head;struct class *class; //該設備屬于哪個classconst struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */ /* 該設備的默認attribute集合。將會在設備注冊時自動在sysfs中創建對應的文件 */void (*release)(struct device *dev);struct iommu_group *iommu_group;struct dev_iommu *iommu;bool offline_disabled:1;bool offline:1;bool of_node_reused:1;bool state_synced:1;
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_DEVICE) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU_ALL)bool dma_coherent:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_OPS_BYPASSbool dma_ops_bypass : 1;
#endifANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(5);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(6);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(7);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(8);
};設備的私有屬性結構:
/**
* struct device_private - structure to hold the private to the driver core portions of the device structure.
*
* @klist_children - klist containing all children of this device
* @knode_parent - node in sibling list
* @knode_driver - node in driver list
* @knode_bus - node in bus list
* @knode_class - node in class list
* @deferred_probe - entry in deferred_probe_list which is used to retry the
* binding of drivers which were unable to get all the resources needed by
* the device; typically because it depends on another driver getting
* probed first.
* @async_driver - pointer to device driver awaiting probe via async_probe
* @device - pointer back to the struct device that this structure is
* associated with.
* @dead - This device is currently either in the process of or has been
* removed from the system. Any asynchronous events scheduled for this
* device should exit without taking any action.
*
* Nothing outside of the driver core should ever touch these fields.
*/
struct device_private {struct klist klist_children; //包含的子設備struct klist_node knode_parent; //父級掛接點struct klist_node knode_driver; //driver list掛接點struct klist_node knode_bus; //bus list掛接點struct klist_node knode_class; //class list掛接點struct list_head deferred_probe;struct device_driver *async_driver;char *deferred_probe_reason;struct device *device; //回指向該設備u8 dead:1;
};2,device_register()流程
清晰分解圖:

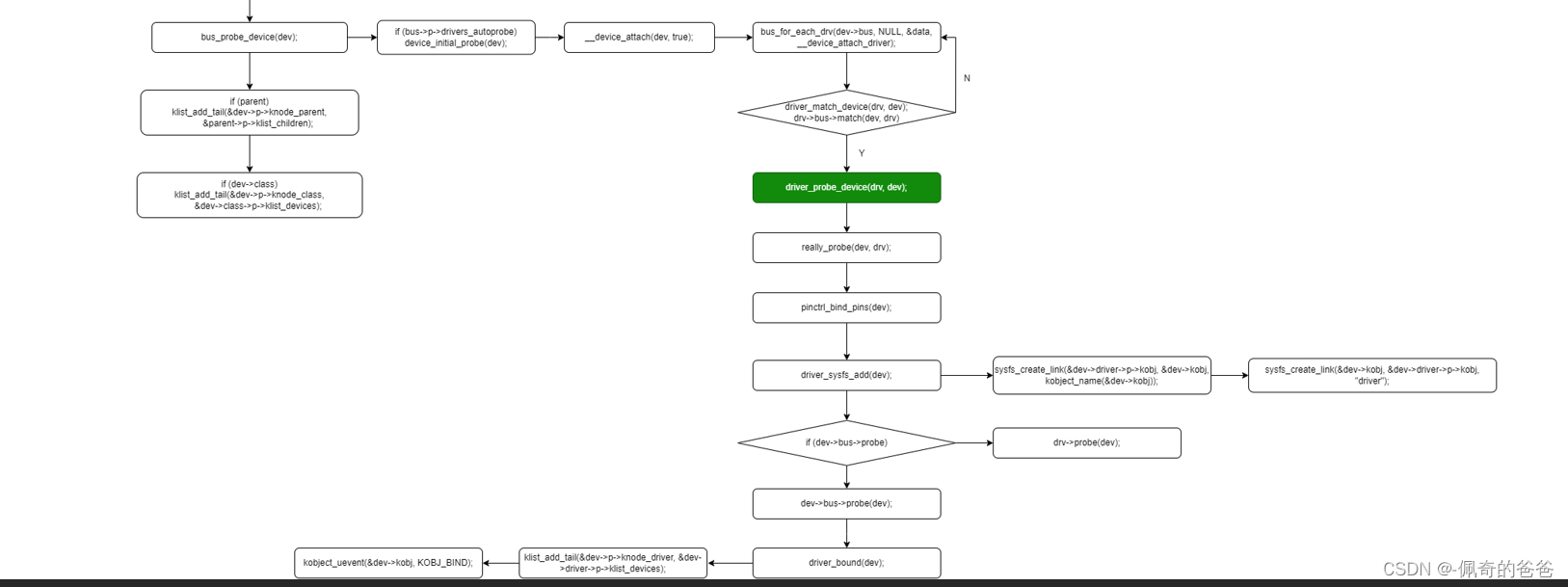
3,關鍵代碼流程分析
/* device_initialize */
void device_initialize(struct device *dev)
{dev->kobj.kset = devices_kset; //device kobject屬于devices_ksetkobject_init(&dev->kobj, &device_ktype); //初始化這個kobj并建立層次關系以及屬性文件,此時是放到了總的device文件目錄下面INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->dma_pools);mutex_init(&dev->mutex);
#ifdef CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKINGmutex_init(&dev->lockdep_mutex);
#endiflockdep_set_novalidate_class(&dev->mutex);spin_lock_init(&dev->devres_lock);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->devres_head);device_pm_init(dev);set_dev_node(dev, -1);
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQINIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->msi_list);
#endifINIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->links.consumers);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->links.suppliers);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->links.defer_sync);dev->links.status = DL_DEV_NO_DRIVER;
}/* device_add */
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{struct device *parent;struct kobject *kobj;struct class_interface *class_intf;int error = -EINVAL;struct kobject *glue_dir = NULL;dev = get_device(dev);if (!dev)goto done;if (!dev->p) {error = device_private_init(dev); //初始化dev的私有成員及其鏈表操作函數if (error)goto done;}/** for statically allocated devices, which should all be converted* some day, we need to initialize the name. We prevent reading back* the name, and force the use of dev_name()*/if (dev->init_name) {dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name); //設置kobject的名字,kobj->name = sdev->init_name = NULL;}/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id); //如果kobj的名字為空,則使用總線名字+設備的ID組合當做設備名字if (!dev_name(dev)) {error = -EINVAL;goto name_error; //如果dev的名字還是空則退出,必須有正確的設備名字才能被注冊}pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);parent = get_device(dev->parent);kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent); //獲取父親節點if (IS_ERR(kobj)) {error = PTR_ERR(kobj);goto parent_error;}if (kobj)dev->kobj.parent = kobj;/* use parent numa_node */if (parent && (dev_to_node(dev) == NUMA_NO_NODE))set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));/* first, register with generic layer. *//* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL); //初始化kobj與其父親節點的連接,在父親dev的目錄下會創建該device的sysfs path,并設置kobj->state_in_sysfs為1,表示該設備已被注冊if (error) {glue_dir = get_glue_dir(dev);goto Error;}/* notify platform of device entry */error = device_platform_notify(dev, KOBJ_ADD);if (error)goto platform_error;error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent); //產生uevent屬性文件,/sys/devices/llcc-pmu/ueventif (error)goto attrError;error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev); //在dev的path創建一些符號鏈接,具體鏈接上述流程圖中有示例if (error)goto SymlinkError;error = device_add_attrs(dev); //在dev的path添加一些屬性文件if (error)goto AttrsError;error = bus_add_device(dev); //把設備添加到busif (error)goto BusError;error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);if (error)goto DPMError;device_pm_add(dev);if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);if (error)goto DevAttrError;error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);if (error)goto SysEntryError;devtmpfs_create_node(dev);}/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().*/if (dev->bus)blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD); //發送該設備被ADD的uevent消息 KOBJ_ADD/** Check if any of the other devices (consumers) have been waiting for* this device (supplier) to be added so that they can create a device* link to it.** This needs to happen after device_pm_add() because device_link_add()* requires the supplier be registered before it's called.** But this also needs to happen before bus_probe_device() to make sure* waiting consumers can link to it before the driver is bound to the* device and the driver sync_state callback is called for this device.*/if (dev->fwnode && !dev->fwnode->dev) {dev->fwnode->dev = dev;fw_devlink_link_device(dev);}bus_probe_device(dev); //為一個新的device探測driverif (parent)klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,&parent->p->klist_children); //如果該設備有關聯的父設備,將該設備掛接到父設備的children listif (dev->class) {mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->mutex);/* tie the class to the device */klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_class,&dev->class->p->klist_devices); //如果設備跟class關聯,將設備掛接到class list/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */list_for_each_entry(class_intf,&dev->class->p->interfaces, node)if (class_intf->add_dev)class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->mutex);}
done:put_device(dev); //減少device的引用計數return error;
SysEntryError:if (MAJOR(dev->devt))device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
DevAttrError:device_pm_remove(dev);dpm_sysfs_remove(dev);
DPMError:bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
attrError:device_platform_notify(dev, KOBJ_REMOVE);
platform_error:kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);glue_dir = get_glue_dir(dev);kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:cleanup_glue_dir(dev, glue_dir);
parent_error:put_device(parent);
name_error:kfree(dev->p);dev->p = NULL;goto done;
}/* bus_add_device */
int bus_add_device(struct device *dev)
{struct bus_type *bus = bus_get(dev->bus);int error = 0;if (bus) {pr_debug("bus: '%s': add device %s\n", bus->name, dev_name(dev));error = device_add_groups(dev, bus->dev_groups); //在該設備的sysfs目錄中創建bus上默認的屬性文件if (error)goto out_put;error = sysfs_create_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj,&dev->kobj, dev_name(dev)); /* 調用sysfs_create_link接口,將該device在sysfs中的目錄,鏈接到該bus的device目錄下,eg: /sys/bus/platform/devices/soc:gpio_keys -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/soc:gpio_keys */if (error)goto out_groups;error = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj,&dev->bus->p->subsys.kobj, "subsystem"); /* 調用sysfs_create_link接口,在該device的sysfs中創建一個指向該設備所在bus目錄的鏈接,取名為subsystem eg: /sys/devices/platform/soc/soc:gpio_keys/subsystem -> ../../../../bus/platform */if (error)goto out_subsys;klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_devices); //將該設備掛接到bus的device list鏈表}return 0;out_subsys:sysfs_remove_link(&bus->p->devices_kset->kobj, dev_name(dev));
out_groups:device_remove_groups(dev, bus->dev_groups);
out_put:bus_put(dev->bus);return error;
}/*__device_attach */
static int __device_attach(struct device *dev, bool allow_async)
{int ret = 0;bool async = false;device_lock(dev);if (dev->p->dead) {goto out_unlock; //如果設備已經dead直接退出} else if (dev->driver) { //默認指定了driver就直接綁定if (device_is_bound(dev)) { //判斷該設備是否已經driver綁定,這一點很重要,通過它,可以使同一個Driver,驅動相同名稱的多個設備ret = 1;goto out_unlock; //如果設備已經綁定過驅動直接退出}ret = device_bind_driver(dev); //將一個driver與一個device綁定if (ret == 0)ret = 1;else {dev->driver = NULL;ret = 0;}} else {struct device_attach_data data = {.dev = dev,.check_async = allow_async,.want_async = false,};if (dev->parent)pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);ret = bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data,__device_attach_driver); //沒有給設備指定driver就進行遍歷匹配if (!ret && allow_async && data.have_async) {/** If we could not find appropriate driver* synchronously and we are allowed to do* async probes and there are drivers that* want to probe asynchronously, we'll* try them.*/dev_dbg(dev, "scheduling asynchronous probe\n");get_device(dev);async = true;} else {pm_request_idle(dev);}if (dev->parent)pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);}
out_unlock:device_unlock(dev);if (async)async_schedule_dev(__device_attach_async_helper, dev);return ret;
}/*?bus_for_each_drv */
int bus_for_each_drv(struct bus_type *bus, struct device_driver *start,void *data, int (*fn)(struct device_driver *, void *))
{struct klist_iter i;struct device_driver *drv;int error = 0;if (!bus)return -EINVAL;klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_drivers, &i,start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL); /* 從頭開始遍歷bus的driver鏈表,發現一個driver就調用fn即__device_attach_driver進行匹配 */while ((drv = next_driver(&i)) && !error)error = fn(drv, data);klist_iter_exit(&i);return error;
}/*?__device_attach_driver */
static int __device_attach_driver(struct device_driver *drv, void *_data)
{struct device_attach_data *data = _data;struct device *dev = data->dev;bool async_allowed;int ret;ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev); /* drv->bus->match(dev, drv)調用bus的match函數,檢查device與driver是否匹配,device和device_driver必須具備相同的名稱,內核才能完成匹配操作,進而調用device_driver中的相應接口。這里的同名,作用范圍是同一個bus下的所有device和device_driver */if (ret == 0) {/* no match */return 0;} else if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {dev_dbg(dev, "Device match requests probe deferral\n");driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);/** Device can't match with a driver right now, so don't attempt* to match or bind with other drivers on the bus.*/return ret;} else if (ret < 0) {dev_dbg(dev, "Bus failed to match device: %d\n", ret);return ret;} /* ret > 0 means positive match */async_allowed = driver_allows_async_probing(drv);if (async_allowed)data->have_async = true;if (data->check_async && async_allowed != data->want_async)return 0;return driver_probe_device(drv, dev); //device與driver匹配成功,將device與driver綁定
}/*?really_probe */
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{int ret = -EPROBE_DEFER;int local_trigger_count = atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count);bool test_remove = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_TEST_DRIVER_REMOVE) &&!drv->suppress_bind_attrs;ret = device_links_check_suppliers(dev);if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER)driver_deferred_probe_add_trigger(dev, local_trigger_count);if (ret)return ret;atomic_inc(&probe_count);pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: probing driver %s with device %s\n",drv->bus->name, __func__, drv->name, dev_name(dev));if (!list_empty(&dev->devres_head)) {dev_crit(dev, "Resources present before probing\n");ret = -EBUSY;goto done;}re_probe:dev->driver = drv; //將綁定的driver賦值給dev->driver/* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);if (ret)goto pinctrl_bind_failed;if (dev->bus->dma_configure) {ret = dev->bus->dma_configure(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;}ret = driver_sysfs_add(dev); //創建driver與device之間的符號鏈接if (ret) {pr_err("%s: driver_sysfs_add(%s) failed\n",__func__, dev_name(dev));goto probe_failed;}if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->activate) {ret = dev->pm_domain->activate(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;}if (dev->bus->probe) { //如果bus有probe函數優先執行bus的probe函數,如果沒有則執行驅動的probe函數ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;} else if (drv->probe) {ret = drv->probe(dev);if (ret)goto probe_failed;}ret = device_add_groups(dev, drv->dev_groups); //創建屬性文件,const struct attribute_group **dev_groupsif (ret) {dev_err(dev, "device_add_groups() failed\n");goto dev_groups_failed;}if (dev_has_sync_state(dev)) {ret = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_state_synced);if (ret) {dev_err(dev, "state_synced sysfs add failed\n");goto dev_sysfs_state_synced_failed;}}pinctrl_init_done(dev);if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->sync)dev->pm_domain->sync(dev);driver_bound(dev); //將該設備掛接到driver的device list,一個driver可以對應于幾個設備,因此driver同樣有其設備鏈表,用于掛接可以操作的設備ret = 1;pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: bound device %s to driver %s\n",drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);goto done;dev_sysfs_state_synced_failed:device_remove_groups(dev, drv->dev_groups);
dev_groups_failed:if (dev->bus->remove)dev->bus->remove(dev);else if (drv->remove)drv->remove(dev);
probe_failed:if (dev->bus)blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,BUS_NOTIFY_DRIVER_NOT_BOUND, dev);
pinctrl_bind_failed:device_links_no_driver(dev);devres_release_all(dev);arch_teardown_dma_ops(dev);kfree(dev->dma_range_map);dev->dma_range_map = NULL;driver_sysfs_remove(dev);dev->driver = NULL;dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);pm_runtime_reinit(dev);dev_pm_set_driver_flags(dev, 0);switch (ret) {case -EPROBE_DEFER:/* Driver requested deferred probing */dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s requests probe deferral\n", drv->name);driver_deferred_probe_add_trigger(dev, local_trigger_count);break;case -ENODEV:case -ENXIO:pr_debug("%s: probe of %s rejects match %d\n",drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);break;default:/* driver matched but the probe failed */pr_warn("%s: probe of %s failed with error %d\n",drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);}/** Ignore errors returned by ->probe so that the next driver can try* its luck.*/ret = 0;
done:atomic_dec(&probe_count);wake_up_all(&probe_waitqueue);return ret;
}/*?driver_sysfs_add */
static int driver_sysfs_add(struct device *dev)
{int ret;if (dev->bus)blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,BUS_NOTIFY_BIND_DRIVER, dev);ret = sysfs_create_link(&dev->driver->p->kobj, &dev->kobj,kobject_name(&dev->kobj)); /* 在該設備綁定的bus下的driver目錄中創建一個指向該device在sysfs下的目錄,名字為設備的名字 eg: /sys/bus/platform/drivers/gpio-keys/soc:gpio_keys -> ../../../../devices/platform/soc/soc:gpio_keys */if (ret)goto fail;ret = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj, &dev->driver->p->kobj,"driver"); /* 在該device的sysfs目錄下創建一個指向該設備綁定的bus下的driver目錄的鏈接,名字為"driver", eg: /sys/devices/platform/soc/soc:gpio_keys/driver -> ../../../../bus/platform/drivers/gpio-keys */if (ret)goto rm_dev;if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEV_COREDUMP) || !dev->driver->coredump ||!device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_coredump))return 0;sysfs_remove_link(&dev->kobj, "driver");rm_dev:sysfs_remove_link(&dev->driver->p->kobj,kobject_name(&dev->kobj));fail:return ret;
}/*?driver_bound */
static void driver_bound(struct device *dev)
{if (device_is_bound(dev)) {pr_warn("%s: device %s already bound\n",__func__, kobject_name(&dev->kobj));return;}pr_debug("driver: '%s': %s: bound to device '%s'\n", dev->driver->name,__func__, dev_name(dev));klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_driver, &dev->driver->p->klist_devices); //將該設備掛接到driver的device listdevice_links_driver_bound(dev);device_pm_check_callbacks(dev);/** Make sure the device is no longer in one of the deferred lists and* kick off retrying all pending devices*/driver_deferred_probe_del(dev);driver_deferred_probe_trigger();if (dev->bus)blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,BUS_NOTIFY_BOUND_DRIVER, dev);kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_BIND); //device與driver已經綁定,發出該設備的KOBJ_BIND uevent消息
}device注冊主要是在devices_kset的目錄中創建了屬于該設備的目錄結構,并將該設備掛接在bus的device list中,然后遍歷bus的driver list,為該設備查找匹配的驅動,當匹配成功之后將device與driver綁定,一個device只能與一個driver對應,一個driver能驅動多個device,整個過程中還伴隨著一些屬性文件的創建,通過這些屬性文件可以直接讀寫設備的信息,以及一些符號鏈接的創建,通過這些符號鏈接class/bus/device/driver可以關聯在一起,bus下的device會指向實際的sysfs下的device,bus下的driver也會指向實際的sysfs下的device,sysfs下的device也會有名字為driver指向bus下driver的軟鏈接,class下也有指向實際的sysfs下的device的鏈接。







)












