藍橋杯Python B組練習——python復習2
一、簡介
復習python,參考書《Python編程從入門到實踐》,[美]Eric Mathes著。前一部分見專欄——藍橋杯Python B組練習
這一部分不全,不想寫了
二、字典
1.一個簡單的字典
來看一個游戲,其中包含一些外星人,這些外星人的顏色和點數各不相同。下面是一個簡單的字典,存儲了有關特定外星人的信息:
alien_0={'color':'green','points':5}
print(alien_0['color'])
print(alien_0['points'])運行結果:
green
5
2.使用字典
在Python中,字典是一系列鍵-值對。每個鍵都與一個值相關聯,你可以使用鍵來訪問與之相關聯的值。與鍵相關的值可以是數字、字符串、列表乃至字典。事實上,可將任何Python對象用作字典中的值。
在Python中,字典用放在花括號{}中的一系列鍵-值對表示,如下:
alien_0={'color':'green','points':5}
鍵值對是兩個相關聯的值。指定鍵是Python將返回與之相關聯的值。鍵和值之間用冒號分隔,而鍵值對之間用逗號分隔。
1)訪問鍵值對
print(alien_0['color'])
2)添加鍵值對
alien_0={'color':'green','points':5}
alien_0['x_position']=0
alien_0['y_position']=0
print(alien_0)運行結果:
{'color': 'green', 'points': 5, 'x_position': 0, 'y_position': 0}
3)先創建一個空字典
有時候,在空字典中添加鍵值對是為了方便,而有時候必須這樣做。
alien_0={}
alien_0['color']='green'
alien_0['points']=5
print(alien_0)運行結果:
{'color': 'green', 'points': 5}
4)修改字典中的值
alien_0={}
alien_0['color']='green'
alien_0['points']=5
print(alien_0)
alien_0['color']='yellow'
print(alien_0)運行結果:
{'color': 'green', 'points': 5}
{'color': 'yellow', 'points': 5}
5)刪除鍵值對
對于字典中不再需要的信息,可使用del語句將相應的鍵值對徹底刪除。使用del語句時,必須指定字典名和要刪除的鍵。
alien_0={'color':'green','points':5}
print(alien_0)del alien_0['points']
print(alien_0)運行結果:
{'color': 'green', 'points': 5}
{'color': 'green'}
3.遍歷字典
1)遍歷所有的鍵值對
user_0 = {'username':'efermi','first':'enrico','last':'fermi',
}for key,value in user_0.items():print("\nKey:"+key)print("Value:"+value)如上所示,編寫for循環,可聲明兩個變量,用于存儲鍵值對中的鍵和值。對于這兩個變量,可使用任何名稱。
如:for k,v in user_0.items()
運行結果:
Key:username
Value:efermi
Key:first
Value:enrico
Key:last
Value:fermi
2)遍歷字典中的所有鍵
user_0 = {'username':'efermi','first':'enrico','last':'fermi',
}for k in user_0.keys():print(k.title())
運行結果:
Username
First
Last
還可以使用keys()確定某個鍵是否在keys中。
user_0 = {'username':'efermi','first':'enrico','last':'fermi',
}if 'second_name' not in user_0.keys():方法keys()并非只能用于遍歷;實際上,它返回一個列表,其中包含字典中的所有鍵。
運行結果:
Please take out poll
3)按順序遍歷字典中的所有鍵
要以特定的順序返回元素,一種辦法是在for循環中返回的鍵進行排序。為此,可使用函數sorted()來獲得按特定順序排序的鍵列表的副本:
user_0 = {'username':'efermi','first':'enrico','last':'fermi',
}for k in sorted(user_0.keys()):print(k.title())運行結果:
First
Last
Username
4)遍歷字典中的所有值
如果你感興趣的主要是字典包含的值,可使用方法values(),它返回一個值列表,而不包含任何鍵。
user_0 = {'username':'efermi','first':'enrico','last':'fermi',
}for v in user_0.values():print(v.title())運行結果:
Efermi
Enrico
Fermi
?
這樣的做法提取字典的所有值,而沒有考慮是否重復。為剔除重復項,可使用集合(set)。集合類似于列表,但每一個元素都必須是獨一無二的:
favorite_languages={'jen':'python','sarah':'c','edward':'ruby','phil':'python',
}for language in set(favorite_languages.values()):print(language.title())運行結果:
C
Python
Ruby
4.嵌套
有時候,需要將一系列字典存儲在列表中,或者將列表作為值存儲在字典中,這稱為嵌套。
1)字典列表
alien_0 ={'color':'green','points':5}
alien_1 ={'color':'yellow','points':10}
alien_2 ={'color':'red','points':15}aliens=[alien_0,alien_1,alien_2]for alien in aliens:print(alien)運行結果:
{'color': 'green', 'points': 5}
{'color': 'yellow', 'points': 10}
{'color': 'red', 'points': 15}
2)在字典中存儲列表
有時候需要將列表存儲在字典中,而不是將字典存儲在列表中。
#存儲所點披薩的信息
pizza ={'crust':'thick','toppings':['mushrooms','extra cheese'],
}
#概述所點的披薩
print("You ordered a"+pizza['crust']+"-crust pizza"+"with the following toppings:")
for topping in pizza['toppings']:print("\t"+topping)運行結果:
You ordered athick-crust pizzawith the following toppings:
?? ?mushrooms
?? ?extra cheese
3)在字典中存儲字典
users = {'aeinstein':{'first':'albert','last':'einstein','location':'princeton',},'mcurie':{'first':'marie','last':'curie','location':'paris',},
}for username,user_info in users.items():print("\nUsername:"+username)full_name=user_info['first']+" "+user_info['last']location = user_info['location']print("\tFull name:"+full_name.title())print("\tLocation:"+location.title())運行結果:
Username:aeinstein
?? ?Full name:Albert Einstein
?? ?Location:Princeton
Username:mcurie
?? ?Full name:Marie Curie
?? ?Location:Paris
三、用戶輸入和while循環
1.函數input()的工作原理
函數input()讓程序暫停運行,等待用戶輸入一些文本。獲取用戶輸入后,Python將其存儲在一個變量中,以方便你使用。
name=input("Please enter your name:")
print("Hello,"+name+"!")運行結果:
Please enter your name:Eric
Hello,Eric!
1)使用int()來獲取數值輸入
age=input("How old are you?")
age>=18如上,用戶輸入的是數字21,但我們請求Python提供變量age時,它返回的是‘21’——用戶輸入的數值的字符串表示。如果試圖將輸入作為數字使用,就會引發錯誤:

為解決這個問題,可以用函數int()
age=input("How old are you?")
age=int(age)
if age>=18:print("True")運行結果:

2)求模運算符
處理數值信息時,求模運算符(%)是一個很有用的工具,它將兩個數相除并返回余數:
print(4%3)
print(5%3)
print(6%3)
print(7%3)運行結果:
1
2
0
1
2.while循環簡介
1)使用while循環
使用while循環來數數,例如,下面的while循環從1數到5:
current_number=1
while current_number <=5:print(current_number)current_number+=1運行結果:
1
2
3
4
5
2)讓用戶選擇何時退出
prompt = "\nTell me something,and I will repeat it back to you:"
prompt=prompt+"\nEnter 'quit' to end the program."
message=""
while message !='quit':message=input(prompt)print(message)
運行結果:
Python首次執行while語句時,需要將message的值與‘quit’進行比較,但此時用戶還沒有輸入。如果沒有可供比較的東西,Python將無法繼續運行程序。為解決這個問題,我們必須給變量message指定一個初始值。雖然這個初始值只是一個空字符串,但符合要求,讓Python能夠執行while循環所需的比較。只需要message的值不是‘quit’,這個循環就會不斷運行。
3)使用標志
在要求很多條件都滿足才繼續運行的程序中,可定義一個變量,用于判斷整個程序是否處于活動狀態。這個變量被稱為標志。充當了程序的交通信號燈。你可讓程序在標志為True時繼續運行,并在任何事件導致標志值為False時讓程序停止運行。
prompt = "\nTell me something,and I will repeat it back to you:"
prompt=prompt+"\nEnter 'quit' to end the program."
active = True
while active:message=input(prompt)if message == 'quit':active = Falseelse:print(message)
運行結果:
4)使用break退出循環
要立即退出while循環,不再運行循環中余下的代碼,也不管條件測試的結果如何,可使用break語句。
prompt = "\nPlease enter the name of a city you have visited:"
prompt += "\n(Enter 'quit' when you are finished.)"while True:city=input(prompt)if city == 'quit':breakelse:print("I'd love to go to"+city.title()+"!")運行結果:
注意:在任何循環中都可使用break語句。例如,可使用break語句來退出遍歷列表或字典的for循環。
5)在循環中使用continue
要返回到循環開頭,并根據條件測試結果決定是否繼續執行循環,可使用continue語句,它不像break語句那樣不再執行余下的代碼并退出整個循環。
prompt = "\nPlease enter the name of a city you have visited:"
prompt += "\n(Enter 'quit' when you are finished.)"while True:city=input(prompt)if city == 'quit':continueelse:print("I'd love to go to"+city.title()+"!")運行結果:
如運行結果顯示,陷入無限循環,無法跳出循環,我們應該避免無限循環。如果程序陷入無限循環,可按Ctrl+C,也可關閉顯示程序的終端窗口。
3.使用while循環來處理列表和字典
1)在列表之間移動元素
unconfirmed_users=['alice','brian','candace']
confirmed_users=[]while unconfirmed_users:current_user = unconfirmed_users.pop()print("Verifying user:"+ current_user.title())confirmed_users.append(current_user)print("\nThe following users have been confirmed:")
for confirmed_user in confirmed_users:print(confirmed_user.title())運行結果:

2)刪除包含特定值的所有列表元素
我們使用函數remove()來刪除列表中的特定值,這之所以可行,是因為要刪除的值在列表中值出現了一次。
假設你有一個寵物列表,其中包含多個值為’cat‘的元素。要刪除所有這些元素,可不斷運行一個while循環,直到列表中不再包含值’cat‘,如下所示:
pets = ['dog','cat','dog','goldfish','cat','rabbit','cat']
print(pets)while 'cat' in pets:pets.remove('cat')print(pets)運行結果:

3)使用用戶輸入來填充字典
responses = {}polling_active = Truewhile polling_active:name = input("\nWhat is your name?")response = input("Which mountain would you like to climb someday?")responses[name] = responserepeat = input("Would you like to let another person respond?(yes/no)")if repeat == 'no':polling_active = False
print("\n--------Poll Result------")
for name,response in responses.items():print(name+"would like to climb"+response+".")
運行結果:

四、函數
1.定義函數
下面是一個打印問候語的簡單函數,名為greet_user():
def greet_user():
? ? ? ? print("Hello!")
greet_user()
第一行的代碼使用關鍵字def來告訴Python你要定義一個函數。這是函數定義,向Python指出了函數名。第二行函數體,第三行執行函數,打印Hello!
1)向函數傳遞信息
def greet_user(username):print("Hello!"+username.title()+"!")greet_user('jesse')運行結果:
Hello!Jesse!
2.傳遞實參
向函數傳遞實參的方式很多,可使用位置實參,這要求實參的順序與形參順序相同;也可使用關鍵字實參,其中每個實參都由變量名和值組成。
1)位置實參
def descirbe_pet(animal_type,pet_name):print("\nI have a "+animal_type+".")print("My" + animal_type+"'s name is"+pet_name.title()+".")descirbe_pet('hamster','harry')
運行結果:

注意:位置實參的順序很重要
2)關鍵字實參
關鍵字實參是傳遞函數的名稱-值對。
def descirbe_pet(animal_type,pet_name):print("\nI have a "+animal_type+".")print("My" + animal_type+"'s name is"+pet_name.title()+".")descirbe_pet(animal_type='hamster',pet_name='harry')
運行結果:

3)默認值
編寫函數時,可給每個形參指定默認值。
def descirbe_pet(pet_name,animal_type='dog'):print("\nI have a "+animal_type+".")print("My" + animal_type+"'s name is"+pet_name.title()+".")descirbe_pet(pet_name='harry')運行結果:
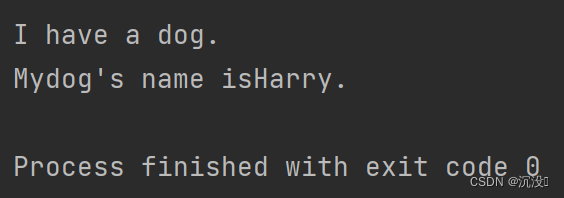
注意:使用默認值時,在形參列表中必須先列出沒有默認值的形參,再列出有默認值的形參。
這讓Python依然能夠正確地解讀位置實參。
3.返回值
函數并非總是直接顯示輸出,相反,它可以處理一些數據,并返回一個或一組值。函數返回的值被稱為返回值。
1)返回簡單值
def get_formatted_name(first_name,last_name):full_name=first_name+' '+last_namereturn full_name.title()musician = get_formatted_name('jimi','hendrix')
print(musician)? ? 運行結果:
Jimi Hendrix
2)讓實參變成可選的
并非所有人都有中間名,為讓中間名變成可選的,可采用如下:
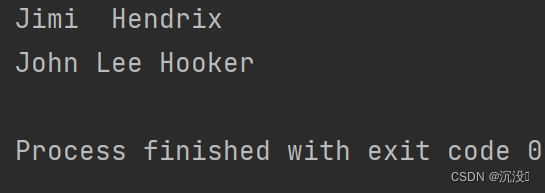
def get_formatted_name(first_name,last_name,middle_name=''):full_name=first_name+' '+middle_name+' '+last_namereturn full_name.title()musician = get_formatted_name('jimi','hendrix')
print(musician)musician = get_formatted_name('john','hooker','lee')
print(musician)? ? 給實參middle_name指定一個默認值——空字符串,并在用戶沒有提供中間名時不使用這個實參。為讓get_formatted_name()在沒有提供中間名時依然可以運行,可給實參middle_name指定一個默認——空字符串,并將其移到形參列表末尾。
運行結果:
3)返回字典
def build_person(first_name,last_name):person = {'first':first_name,'last':last_name}return personmusician = build_person('jimi','hendrix')
print(musician)運行結果:
{'first': 'jimi', 'last': 'hendrix'}
4)結合使用函數和while循環
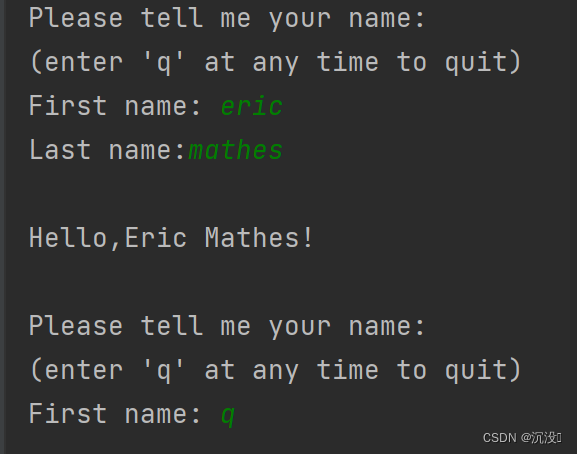
def get_formatted_name(first_name,last_name):full_name = first_name+' '+last_namereturn full_name.title()while True:print("\nPlease tell me your name:")print("(enter 'q' at any time to quit)")f_name = input("First name: ")if f_name == 'q':breakl_name = input("Last name:")if l_name == 'q':breakformatted_name = get_formatted_name(f_name,l_name)print("\nHello,"+ formatted_name+"!")運行結果:
4.傳遞列表
假設有一個用戶列表,我們要問候其中的每位用戶。下面示例將一個名字列表傳遞給一個名為greet_users()的函數,這個函數問候列表中的每個人:
def greet_uers(names):for name in names:msg = "Hello, "+name.title()+"!"print(msg)
usernames=['hannah','ty','margot']
greet_uers(usernames)運行結果:

5.傳遞任意數量的實參
函數只有一個形參*toppings,不管調用語句提供了多少實參,這個形參都將它們統統收入囊中:
def make_pizza(*toppings):print(toppings)make_pizza('pepperoni')
make_pizza('mushrooms','green peppers','extra cheese')運行結果:
('pepperoni',)
('mushrooms', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
1)結合使用位置實參和任意數量實參
如果要讓函數接受不同類型的實參,必須在函數定義中將接納任意數量實參的形參放在最后。
def make_pizza(size,*toppings):print("\nMaking a "+str(size)+"-inch pizza with the following toppings:")for topping in toppings:print("- "+topping)make_pizza(16,'pepperoni')
make_pizza(20,'mushrooms','green peppers','extra cheese')運行結果:

2)使用任意數量的關鍵字實參
有時候,需要接受任意數量的實參,但預先不知道傳遞給函數的是什么樣的信息。
在下面的實例中,函數build_profile()接受名和姓,同時還接受任意數量的關鍵字實參:
def build_profile(first,last,**user_info):profile={}profile['first_name']=firstprofile['last_name']=lastfor key,value in user_info.items():profile[key]=valuereturn profile
user_profile = build_profile('albert','einstein',location='princeton',field='physics')print(user_profile)運行結果:
{'first_name': 'albert', 'last_name': 'einstein', 'location': 'princeton', 'field': 'physics'}
6.將函數存儲在模塊中
略
五、類
1.創建和使用類
使用類幾乎可以模擬任何東西。
?1)創建Dog類
class Dog():def __init__(self,name,age):self.name=nameself.age=agedef sit(self):print(self.name.title()+"is now sitting.")def roll_over(self):print(self.name.title()+"rolled over!")類中的函數稱為方法;前面學的有關函數的一切都適用于方法,就目前而言,唯一重要的差別是調用方法的方式。__init__()是一個特殊的方法,每當你根據Dog類創建新實列時,Python都會自動運行它。在這個方法的名稱中,開頭和末尾各有兩個下劃線,這是一種約定,旨在避免Python默認方法與普通方法發生的名稱沖突。__init__()中包含了三個形參:self、name和age。在這個方法的定義中,形參self必不可少,還必須位于其他形參前面。
2)根據類創建實例
1.訪問屬性
my_dog.name
class Dog():def __init__(self,name,age):self.name=nameself.age=agedef sit(self):print(self.name.title()+"is now sitting.")def roll_over(self):print(self.name.title()+"rolled over!")my_dog = Dog('willie',6)print("My dog's name is"+my_dog.name.title()+'.')
print("My dog is"+str(my_dog.age)+"years old.")運行結果:
My dog's name isWillie.
My dog is6years old.
2.調用方法
my_dog.sit()






函數詳解上)






![[算法沉淀記錄] 分治法應用 —— 二分搜索(Binary Search)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[算法沉淀記錄] 分治法應用 —— 二分搜索(Binary Search))





