接前一篇文章:QEMU源碼全解析 —— virtio(21)
前幾回講解了virtio驅動的加載。本回開始講解virtio驅動的初始化。
在講解virtio驅動的初始化之前,先要介紹virtio配置的函數集合變量virtio_pci_config_ops。實際上前文書也有提到,如下圖的右上角:

virtio_pci_config_ops的初始化有兩處,分別在Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_legacy.c和Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中。代碼分別如下:
- legacy
static const struct virtio_config_ops virtio_pci_config_ops = {.get = vp_get,.set = vp_set,.get_status = vp_get_status,.set_status = vp_set_status,.reset = vp_reset,.find_vqs = vp_find_vqs,.del_vqs = vp_del_vqs,.synchronize_cbs = vp_synchronize_vectors,.get_features = vp_get_features,.finalize_features = vp_finalize_features,.bus_name = vp_bus_name,.set_vq_affinity = vp_set_vq_affinity,.get_vq_affinity = vp_get_vq_affinity,
};- modern
static const struct virtio_config_ops virtio_pci_config_ops = {.get = vp_get,.set = vp_set,.generation = vp_generation,.get_status = vp_get_status,.set_status = vp_set_status,.reset = vp_reset,.find_vqs = vp_modern_find_vqs,.del_vqs = vp_del_vqs,.synchronize_cbs = vp_synchronize_vectors,.get_features = vp_get_features,.finalize_features = vp_finalize_features,.bus_name = vp_bus_name,.set_vq_affinity = vp_set_vq_affinity,.get_vq_affinity = vp_get_vq_affinity,.get_shm_region = vp_get_shm_region,.disable_vq_and_reset = vp_modern_disable_vq_and_reset,.enable_vq_after_reset = vp_modern_enable_vq_after_reset,
};在此以Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中的virtio_pci_config_ops為例進行講解。
在前文書講到的virtio_pci_modern_probe函數(Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c)中:
/* the PCI probing function */
int virtio_pci_modern_probe(struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev)
{struct virtio_pci_modern_device *mdev = &vp_dev->mdev;struct pci_dev *pci_dev = vp_dev->pci_dev;int err;mdev->pci_dev = pci_dev;err = vp_modern_probe(mdev);if (err)return err;if (mdev->device)vp_dev->vdev.config = &virtio_pci_config_ops;elsevp_dev->vdev.config = &virtio_pci_config_nodev_ops;vp_dev->config_vector = vp_config_vector;vp_dev->setup_vq = setup_vq;vp_dev->del_vq = del_vq;vp_dev->isr = mdev->isr;vp_dev->vdev.id = mdev->id;return 0;
}virtio_pci_config_ops變量被賦值給了virtio_device結構的config成員。struct virtio_device的定義在Linux內核源碼/include/linux/virtio.h中,代碼如下:
/*** struct virtio_device - representation of a device using virtio* @index: unique position on the virtio bus* @failed: saved value for VIRTIO_CONFIG_S_FAILED bit (for restore)* @config_enabled: configuration change reporting enabled* @config_change_pending: configuration change reported while disabled* @config_lock: protects configuration change reporting* @vqs_list_lock: protects @vqs.* @dev: underlying device.* @id: the device type identification (used to match it with a driver).* @config: the configuration ops for this device.* @vringh_config: configuration ops for host vrings.* @vqs: the list of virtqueues for this device.* @features: the features supported by both driver and device.* @priv: private pointer for the driver's use.*/
struct virtio_device {int index;bool failed;bool config_enabled;bool config_change_pending;spinlock_t config_lock;spinlock_t vqs_list_lock;struct device dev;struct virtio_device_id id;const struct virtio_config_ops *config;const struct vringh_config_ops *vringh_config;struct list_head vqs;u64 features;void *priv;
};其中的struct?virtio_config_ops的定義在Linux內核源碼/include/linux/virtio_config.h中,代碼如下:
/*** struct virtio_config_ops - operations for configuring a virtio device* Note: Do not assume that a transport implements all of the operations* getting/setting a value as a simple read/write! Generally speaking,* any of @get/@set, @get_status/@set_status, or @get_features/* @finalize_features are NOT safe to be called from an atomic* context.* @get: read the value of a configuration field* vdev: the virtio_device* offset: the offset of the configuration field* buf: the buffer to write the field value into.* len: the length of the buffer* @set: write the value of a configuration field* vdev: the virtio_device* offset: the offset of the configuration field* buf: the buffer to read the field value from.* len: the length of the buffer* @generation: config generation counter (optional)* vdev: the virtio_device* Returns the config generation counter* @get_status: read the status byte* vdev: the virtio_device* Returns the status byte* @set_status: write the status byte* vdev: the virtio_device* status: the new status byte* @reset: reset the device* vdev: the virtio device* After this, status and feature negotiation must be done again* Device must not be reset from its vq/config callbacks, or in* parallel with being added/removed.* @find_vqs: find virtqueues and instantiate them.* vdev: the virtio_device* nvqs: the number of virtqueues to find* vqs: on success, includes new virtqueues* callbacks: array of callbacks, for each virtqueue* include a NULL entry for vqs that do not need a callback* names: array of virtqueue names (mainly for debugging)* include a NULL entry for vqs unused by driver* Returns 0 on success or error status* @del_vqs: free virtqueues found by find_vqs().* @synchronize_cbs: synchronize with the virtqueue callbacks (optional)* The function guarantees that all memory operations on the* queue before it are visible to the vring_interrupt() that is* called after it.* vdev: the virtio_device* @get_features: get the array of feature bits for this device.* vdev: the virtio_device* Returns the first 64 feature bits (all we currently need).* @finalize_features: confirm what device features we'll be using.* vdev: the virtio_device* This sends the driver feature bits to the device: it can change* the dev->feature bits if it wants.* Note that despite the name this can be called any number of* times.* Returns 0 on success or error status* @bus_name: return the bus name associated with the device (optional)* vdev: the virtio_device* This returns a pointer to the bus name a la pci_name from which* the caller can then copy.* @set_vq_affinity: set the affinity for a virtqueue (optional).* @get_vq_affinity: get the affinity for a virtqueue (optional).* @get_shm_region: get a shared memory region based on the index.* @disable_vq_and_reset: reset a queue individually (optional).* vq: the virtqueue* Returns 0 on success or error status* disable_vq_and_reset will guarantee that the callbacks are disabled and* synchronized.* Except for the callback, the caller should guarantee that the vring is* not accessed by any functions of virtqueue.* @enable_vq_after_reset: enable a reset queue* vq: the virtqueue* Returns 0 on success or error status* If disable_vq_and_reset is set, then enable_vq_after_reset must also be* set.*/
struct virtio_config_ops {void (*get)(struct virtio_device *vdev, unsigned offset,void *buf, unsigned len);void (*set)(struct virtio_device *vdev, unsigned offset,const void *buf, unsigned len);u32 (*generation)(struct virtio_device *vdev);u8 (*get_status)(struct virtio_device *vdev);void (*set_status)(struct virtio_device *vdev, u8 status);void (*reset)(struct virtio_device *vdev);int (*find_vqs)(struct virtio_device *, unsigned nvqs,struct virtqueue *vqs[], vq_callback_t *callbacks[],const char * const names[], const bool *ctx,struct irq_affinity *desc);void (*del_vqs)(struct virtio_device *);void (*synchronize_cbs)(struct virtio_device *);u64 (*get_features)(struct virtio_device *vdev);int (*finalize_features)(struct virtio_device *vdev);const char *(*bus_name)(struct virtio_device *vdev);int (*set_vq_affinity)(struct virtqueue *vq,const struct cpumask *cpu_mask);const struct cpumask *(*get_vq_affinity)(struct virtio_device *vdev,int index);bool (*get_shm_region)(struct virtio_device *vdev,struct virtio_shm_region *region, u8 id);int (*disable_vq_and_reset)(struct virtqueue *vq);int (*enable_vq_after_reset)(struct virtqueue *vq);
};再回過頭來看一下Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中的virtio_pci_config_ops,對照著上邊 struct virtio_config_ops的定義。
static const struct virtio_config_ops virtio_pci_config_ops = {.get = vp_get,.set = vp_set,.generation = vp_generation,.get_status = vp_get_status,.set_status = vp_set_status,.reset = vp_reset,.find_vqs = vp_modern_find_vqs,.del_vqs = vp_del_vqs,.synchronize_cbs = vp_synchronize_vectors,.get_features = vp_get_features,.finalize_features = vp_finalize_features,.bus_name = vp_bus_name,.set_vq_affinity = vp_set_vq_affinity,.get_vq_affinity = vp_get_vq_affinity,.get_shm_region = vp_get_shm_region,.disable_vq_and_reset = vp_modern_disable_vq_and_reset,.enable_vq_after_reset = vp_modern_enable_vq_after_reset,
};virtio_pci_config_ops結構中的成員函數通常是virtio PCI代理設備的IO操作,包括讀寫virtio PCI代理設備的PIO和MMIO,如get_status和set_status成員對應的vp_get_status函數和vp_set_status函數。分別來看:
- get_status
根據struct virtio_config_ops中的說明:
@get_status: read the status byte
?*?? ?vdev: the virtio_device
?*?? ?Returns the status byte
get_status的作用是讀取狀態字節。有一個參數vdev,代表了virtio device。返回值為讀取到的狀態字節。
get_status所指向的vp_get_status函數也在Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中,代碼如下:
/* config->{get,set}_status() implementations */
static u8 vp_get_status(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev = to_vp_device(vdev);return vp_modern_get_status(&vp_dev->mdev);
}vp_modern_get_status函數在Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern_dev.c中,代碼如下:
/** vp_modern_get_status - get the device status* @mdev: the modern virtio-pci device** Returns the status read from device*/
u8 vp_modern_get_status(struct virtio_pci_modern_device *mdev)
{struct virtio_pci_common_cfg __iomem *cfg = mdev->common;return vp_ioread8(&cfg->device_status);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(vp_modern_get_status);- set_status
?@set_status: write the status byte
?*?? ?vdev: the virtio_device
?*?? ?status: the new status byte
set_status的作用是寫入狀態字節。有兩個參數:vdev代表了virtio device;status為新的要寫入的狀態字節。
set_status所指向的vp_set_status函數也在Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern.c中,代碼如下:
static void vp_set_status(struct virtio_device *vdev, u8 status)
{struct virtio_pci_device *vp_dev = to_vp_device(vdev);/* We should never be setting status to 0. */BUG_ON(status == 0);vp_modern_set_status(&vp_dev->mdev, status);
}vp_modern_set_status函數在Linux內核源碼/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci_modern_dev.c中,代碼如下:
/** vp_modern_set_status - set status to device* @mdev: the modern virtio-pci device* @status: the status set to device*/
void vp_modern_set_status(struct virtio_pci_modern_device *mdev,u8 status)
{struct virtio_pci_common_cfg __iomem *cfg = mdev->common;/** Per memory-barriers.txt, wmb() is not needed to guarantee* that the cache coherent memory writes have completed* before writing to the MMIO region.*/vp_iowrite8(status, &cfg->device_status);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(vp_modern_set_status);vp_modern_get_status和vp_modern_set_status函數直接讀寫vp_dev->mdev->common->device_status。從前文書(QEMU源碼全解析 —— virtio(14))的講解可知,vp_dev->common對應的是virtio PCI代理設備第四個BAR表示的地址中的一段空間。

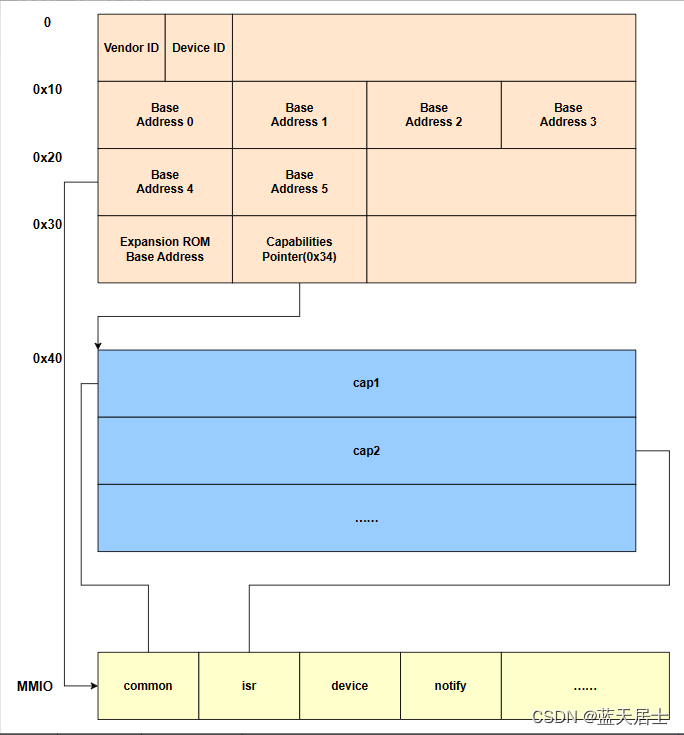
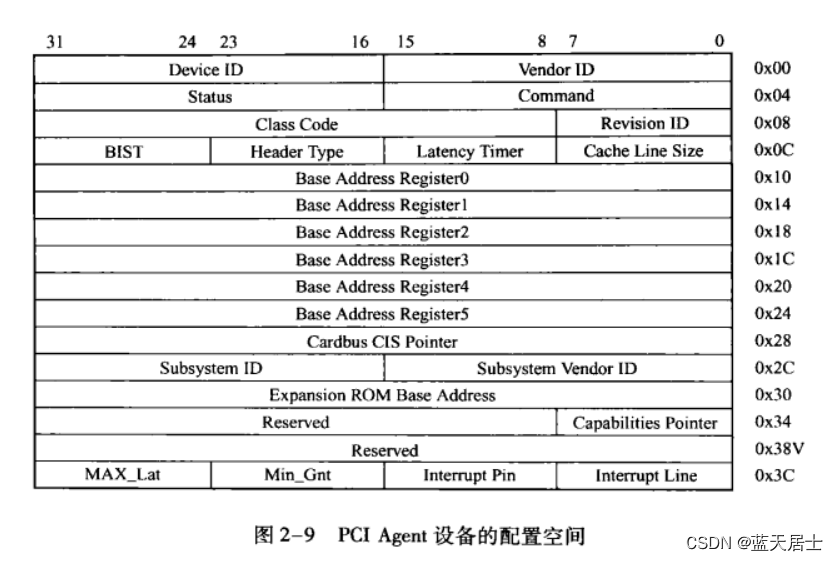
vp_dev->mdev->common的類型為struct virtio_pci_common_cfg,該結構的定義在Linux內核源碼/include/uapi/linux/virtio_pci.h中,代碼如下:
/* Fields in VIRTIO_PCI_CAP_COMMON_CFG: */
struct virtio_pci_common_cfg {/* About the whole device. */__le32 device_feature_select; /* read-write */__le32 device_feature; /* read-only */__le32 guest_feature_select; /* read-write */__le32 guest_feature; /* read-write */__le16 msix_config; /* read-write */__le16 num_queues; /* read-only */__u8 device_status; /* read-write */__u8 config_generation; /* read-only *//* About a specific virtqueue. */__le16 queue_select; /* read-write */__le16 queue_size; /* read-write, power of 2. */__le16 queue_msix_vector; /* read-write */__le16 queue_enable; /* read-write */__le16 queue_notify_off; /* read-only */__le32 queue_desc_lo; /* read-write */__le32 queue_desc_hi; /* read-write */__le32 queue_avail_lo; /* read-write */__le32 queue_avail_hi; /* read-write */__le32 queue_used_lo; /* read-write */__le32 queue_used_hi; /* read-write */
};struct virtio_pci_common_cfg的每一個成員都表示一個virtio PCI代理設備modern MMIO地址空間中對應的值,讀寫這寫成員都會陷入到QEMU中。比如上面的讀取或者設置設備狀態的device_status成員,其地址從virtio_pci_common_cfg結構開始的偏移20字節處(4+4+4+4+2+2=20),所以讀寫該地址的時候會陷入到QEMU中,并且地址是virtio設備的common MemoryRegion偏移20字節處。該MemoryRegion對應的回調操作結構是common_ops,類型為MemoryRegionOps。
common_ops在hw/virtio/virtio-pci.c中初始化,代碼如下:
static void virtio_pci_modern_regions_init(VirtIOPCIProxy *proxy,const char *vdev_name)
{static const MemoryRegionOps common_ops = {.read = virtio_pci_common_read,.write = virtio_pci_common_write,.impl = {.min_access_size = 1,.max_access_size = 4,},.endianness = DEVICE_LITTLE_ENDIAN,};……
}回到struct_pci_config_ops。
static const struct virtio_config_ops virtio_pci_config_ops = {.get = vp_get,.set = vp_set,.generation = vp_generation,.get_status = vp_get_status,.set_status = vp_set_status,.reset = vp_reset,.find_vqs = vp_modern_find_vqs,.del_vqs = vp_del_vqs,.synchronize_cbs = vp_synchronize_vectors,.get_features = vp_get_features,.finalize_features = vp_finalize_features,.bus_name = vp_bus_name,.set_vq_affinity = vp_set_vq_affinity,.get_vq_affinity = vp_get_vq_affinity,.get_shm_region = vp_get_shm_region,.disable_vq_and_reset = vp_modern_disable_vq_and_reset,.enable_vq_after_reset = vp_modern_enable_vq_after_reset,
};virtio_pci_config_ops的各個函數封裝了這些I/O操作,不僅是MMO操作,還有PIO操作。virtio設備可以通過此結構中的各個回調函數來驅動設備。
本回就講到這里。下一回以virtio balloon設備的初始化過程為例,分析virtio設備的初始化過程,即上一回講到的virtio驅動初始化設備的過程中的“執行設備相關的初始化操作”一步。
欲知后事如何,且看下回分解。





函數)

)

)






)


