最小生成樹 kruskal
In Electronic Circuit we often required less wiring to connect pins together. We can model this wiring problem with a connected, undirected graph G=(V, E), where V is the set of pins, E is the set of possible interconnections between pair of pins, and for each edge we have a weight w(u,v) specifying the cost (amount of wire needed) to connect u and v. We then wish to find an acyclic subset T that connects all of the vertices and whose total weight w(T)= sum of all the weights in T is minimized . Since T is acyclic and connects all of the vertices, it must form a tree, which we call a spanning tree since it spans the graph G. We call this problem minimum spanning tree problem.
在電子電路中,我們通常需要較少的接線來將引腳連接在一起。 我們可以使用連接的無向圖G =(V,E)來建模此布線問題,其中V是引腳組, E是引腳對之間可能的互連集,對于每個邊,我們都有權重w( u,v)指定連接u和v的成本(所需的電線數量)。 然后,我們希望找到一個無環子集T ,它連接所有頂點,并且總權重w(T)= T中所有權重的總和最小 。 由于T是無環的并且連接所有頂點,因此它必須形成一棵樹,由于它跨越了圖G ,因此我們將其稱為生成樹 。 我們稱這個問題為最小生成樹問題 。
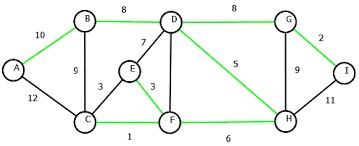
MST Green color edges are the selected edges for MST.
MST綠色邊緣是MST的選定邊緣。
There are two algorithm to solve this problem: Kruskal's Algorithm and Prim's Algorithm. Each of them run in O(E lg V )
有兩種算法可以解決此問題: Kruskal算法和Prim算法 。 它們每個都以O(E lg V)運行
Here we are discussing Kruskal's Algorithm...
在這里,我們討論的是Kruskal算法...
克魯斯卡爾算法 (Kruskal's Algorithm)
This Algorithm first makes the forest of each vertex and then sorts the edges according to their weights, and in each step, it adds the minimum weight edge in the tree that connects two distinct vertexes that do not belong to the same tree in the forest.
該算法首先創建每個頂點的森林,然后根據其權重對邊緣進行排序,然后在每個步驟中,在連接兩個不屬于該森林中同一棵樹的不同頂點的樹中添加最小權重邊緣。
It uses a disjoint set data structure to maintain several disjoint sets of elements. Each set contains the vertices in one tree of the current forest.
它使用不連續集數據結構來維護幾個不連續元素集。 每一組包含當前森林的一棵樹中的頂點。
Example: Here we are finding the cost of MST.
示例:在這里我們發現MST的成本。
Program:
程序:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class MST{
static class set{
int parent,rank;
}
//find set which represents vertex i
static int find(set subsets[],int i ){
if(subsets[i].parent==i)
return i;
return find(subsets,subsets[i].parent);
}
//function for adding edges whose vertex belongs
//to the different tree ie. UNION
static void UNION(set subsets[],int x,int y){
int xroot=find(subsets,x);
int yroot=find(subsets,y);
if(subsets[xroot].rank>subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent=xroot;
else if(subsets[xroot].rank<subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent=yroot;
else{
subsets[yroot].parent=xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
static int mst(int n, Integer[][] edges) {
set subsets[]=new set[n];
//Create forest of vrtices that is separate tree for each vertex
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
subsets[i]=new set();
subsets[i].parent=i; // Each vertex is its own parent
subsets[i].rank=0; //Having no child
}
int e=0,i=0,count=0;
//Create graph having exactly vertex-1 ie. n-1 edges
while(e<n-1){
//find set from which current vertex belongs
int x=find(subsets,edges[i][0]-1);
//find set from which current vertex belongs
int y=find(subsets,edges[i][1]-1);
if(x!=y){
count+=edges[i][2];
e++;
// union the two vertex in the same tree
//if they belong to the different set
UNION(subsets,x,y);
}
i++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt(); //number of nodes
int m = in.nextInt(); //number of edges
Integer [][]edges = new Integer[m][3];
for(int edges_i = 0; edges_i < m; edges_i++){
for(int edges_j = 0; edges_j < 3; edges_j++){
edges[edges_i][edges_j] = in.nextInt();
}
}
//Sort edges two dimensional array according to
//its third column i.e. weight
Arrays.sort(edges,new Comparator<Integer[]>(){
@Override
public int compare(Integer[] i1,Integer[] i2){
//Comparing third column having index 2
return i1[2].compareTo(i2[2]);
}
});
int result=mst(n,edges);
System.out.println(result);
in.close();
}
}
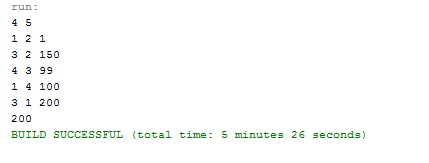
Output
輸出量
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/java/minimum-spanning-tree-problem-using-kruskals-algorithm.aspx
最小生成樹 kruskal




)



)的輸出結果是)

...)
 如何用Apache POI操作Excel文件-----POI-3.10的一個和注解(comment)相關的另外一個bug...)

)




)
