olap 多維分析
In the previous article of OLAP, we have seen various applications of OLAP, Various types of OLAP, advantages, and disadvantages of OLAP. In this article, we will learn about the,
在OLAP的上一篇文章中,我們了解了OLAP的各種應用,各種類型的OLAP,OLAP的優缺點 。 在本文中,我們將了解
OLAP Cube
OLAP多維數據集
OLAP Cube Operations
OLAP多維數據集操作
1)OLAP多維數據集 (1) OLAP Cube)
An OLAP cube may be a multi-dimensional array of knowledge. The online analytical process (OLAP) may be a computer-based technique of analyzing knowledge to appear for insights. The term cube here refers to a multi-dimensional dataset, that is additionally known as a Hypercube if the quantity of dimensions is larger than three. A cube is also thought of as a multi-dimensional generalization of a two- or three-dimensional program. For instance, a corporation may like to summarize monetary knowledge by product, by time-period, and by the town to check actual and budget expenses. Product, time, cities and situation (actual and budget) are the data's dimensions as shown in the figure. A cube isn't a "cube" within the strict mathematical sense, as all the edges aren't essentially equal.
OLAP多維數據集可以是知識的多維數組。 在線分析過程(OLAP)可能是一種基于計算機的技術,用于分析知識以獲取見解。 術語“多維數據集”在這里是指多維數據集,如果維的數量大于3,則又稱為“超多維數據集”。 多維數據集也被認為是二維或三維程序的多維概括。 例如,公司可能希望按產品,時間段和鎮來匯總貨幣知識,以檢查實際和預算支出。 產品,時間,城市和情況(實際和預算)是數據的尺寸,如圖所示。 在嚴格的數學意義上,多維數據集不是“多維數據集”,因為所有的邊實際上都不相等。
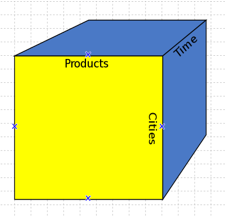
Fig 1: OLAP Cube
圖1:OLAP多維數據集
2)OLAP多維數據集操作 (2) OLAP Cube Operations)
Since OLAP servers work on data of multidimensional view, we are going to discuss OLAP operations in multidimensional information.
由于OLAP服務器可以處理多維視圖的數據,因此我們將在多維信息中討論OLAP操作。
Here is the list of OLAP operations,
這是OLAP操作的列表,
Roll-up
卷起
Drill-down
下鉆
Slice
片
Dice
骰子
Pivot (rotate)
樞軸旋轉
2.1。 卷起 (2.1. ROLL UP)
Roll-up is performed by rising up a planning hierarchy for the dimension location. Initially the conception hierarchy was "street < town < province < country". On rolling up, aggregation of data is done by ascending the hierarchy of location from the level of street to the level of the country. A roll-up involves summarizing the information on a dimension. The summarization rule may be Associate in Nursing mixture operate, like computing totals on a hierarchy or applying a collection of formulas like "profit = sales - expenses". General aggregation functions are also pricey to cipher once rolling up: if they can not be determined from the cells of the cube, they need to be computed from the bottom information, either computing them on-line (slow) or precomputing them for attainable rollouts (large space). Aggregation functions that will be determined from the cells square measure referred to as complex aggregation functions, and permit economical computation.
匯總是通過提升維度位置的計劃層次結構來執行的。 最初,概念層次是“街道<城鎮<省<國家”。 匯總時,數據的匯總是通過將位置層次結構從街道級別提升到國家/地區級別來完成的。 匯總涉及匯總有關維度的信息。 匯總規則可以是“護理中的助理人員”混合操作,例如在層次結構上計算總計或應用諸如“利潤=銷售-費用”之類的公式集合。 通用聚合函數一旦匯總就需要付出昂貴的代價:如果無法從多維數據集的單元中確定它們,則需要從底層信息中進行計算,要么在線(緩慢)計算它們,要么對其進行預先計算以實現可擴展性(大空間)。 由單元平方確定的聚合函數稱為復雜聚合函數,可以經濟地進行計算。
For example, it is easy to calculate COUNT, MAX, MIN, and SUM in OLAP, as this can be computed for each cell of the OLAP cube and then rolled up, since on overall sum (or count, etc.) is the sum of sub-sums, but it is difficult to support MEDIAN, as that must be computed for every view separately: the median of a collection isn't the median of medians of subsets.
例如,很容易在OLAP中計算COUNT,MAX,MIN和SUM,因為可以對OLAP多維數據集的每個單元格進行計算,然后匯總,因為總和(或計數等)是總和子和,但很難支持MEDIAN,因為必須分別針對每個視圖進行計算:集合的中位數不是子集的中位數。
Let us understand it with a diagrammatic flow,
讓我們以圖解流程了解它,
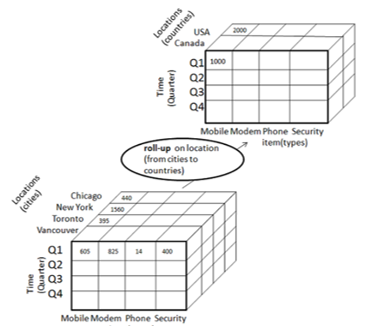
Fig 2.1 : Roll up Operation
圖2.1:匯總操作
2.2。 向下鉆取 (2.2. DRILL DOWN)
Drill-down is performed by stepping down the hierarchy for the dimension time. Initially, the conception hierarchy was "day < month < quarter < year." On drilling down, the dimension of time exists in descended from i.e. from the extent of the quarter to the extent of the month. When drill-down is performed, one or additional dimensions from the information cube are supplemental. It navigates knowledge from less elaborate information to extremely elaborate data.
通過在維度時間上降低層次結構來執行向下鉆取。 最初,概念層次結構是“天<月<季度<年”。 在向下鉆取時,時間的維數是從四分之一的范圍降到一個月的范圍。 執行向下鉆取時,信息多維數據集中的一個或其他維度是補充。 它可以將知識從不太復雜的信息導航到極其復雜的數據。
Fig 2.2 : Drill Down Operation
圖2.2:下鉆操作
2.3。 OLAP切片 (2.3. OLAP SLICING)
The slice operation selects one specific dimension from a given cube and provides a replacement sub-cube.
切片操作從給定的多維數據集中選擇一個特定的維度,并提供替換子多維數據集。
Slice is that the act of selecting an oblong set of a cube by selecting one worth for one in all its dimensions, making a replacement cube with one fewer dimension.
切片是指通過在其所有維度中為一個立方體選擇一個值來選擇一個長方形的立方體的動作,從而使替換的立方體的尺寸減少了一個。
The picture shows a slicing operation.
圖片顯示了切片操作。
Slicing is performed for the dimension "time" using the criteria time = "Q1".
使用標準時間=“ Q1”對維“時間”執行切片。
Subcube is formed by using or selecting one or two dimensions.
通過使用或選擇一維或二維來形成子多維數據集。
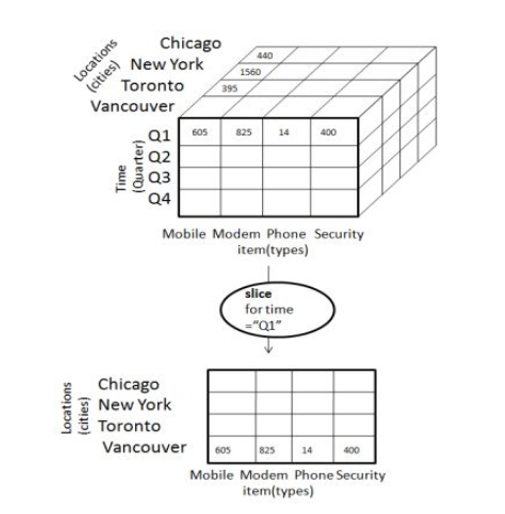
Fig 2.3 : OLAP Slicing
圖2.3:OLAP切片
2.4。 OLAP骰子 (2.4. OLAP DICING)
Dice selects 2 or additional dimensions from a given cube and provides a brand new sub-cube. think about the subsequent diagram that shows the dice operation. The dice operation produces a subcube by permitting the analyst to choose specific values of multiple dimensions. the image shows a dicing operation. The dicing operation on the cube which involves three dimensions is based on the following selection criteria,
Dice從給定的多維數據集中選擇2個或其他維度,并提供一個全新的子多維數據集。 考慮下面顯示骰子操作的圖。 骰子操作通過允許分析人員選擇多維的特定值來生成子多維數據集。 該圖顯示了切塊操作。 涉及三個維度的多維數據集上的切塊操作基于以下選擇標準,
(location = "Toronto" or "Vancouver")
(位置=“多倫多”或“溫哥華”)
(time = "Q1" or "Q2")
(時間=“ Q1”或“ Q2”)
(item =" Mobile" or "Modem")
(項目=“移動”或“調制解調器”)

Fig 2.4 : Cube Dicing
圖2.4:立方體切丁
2.5。 OLAP PIVOT (2.5. OLAP PIVOT)
The pivot operation is additionally referred to as rotation. It rotates the info axes seeable to produce an alternate presentation of knowledge. take into account the subsequent diagram that shows the pivot operation. Pivot permits AN analyst to rotate the cube in the area to check its varied faces. As an example, cities may well be organized vertically and product horizontally whereas viewing information for a selected quarter. Pivoting may replace the product with periods to check information across time for one product. The picture shows a pivoting operation: the full cube is turned, giving another perspective on the data.
樞轉操作另外稱為旋轉。 它旋轉可見的信息軸以產生替代的知識表示。 請考慮以下顯示樞軸操作的圖表。 Pivot允許分析人員旋轉該區域中的多維數據集以檢查其變化的面。 例如,在查看選定季度的信息時,很可能垂直組織城市,水平組織產品。 數據透視可能會用句點替換產品,以跨時間檢查一種產品的信息。 該圖顯示了樞軸操作:旋轉了整個立方體,從而為數據提供了另一個視角。
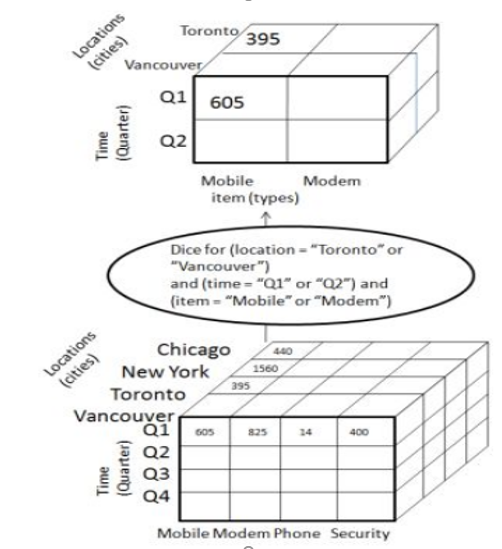
Fig 2.5 : Olap Pivot
圖2.5:Olap樞軸
翻譯自: https://www.includehelp.com/basics/olap-online-analytical-processing-olap-cube-and-operations.aspx
olap 多維分析








)

)


——柵格以及方程數值解估算)
算法)




