SpringAOP
AOP為Aspect Oriented Programming的縮寫,意為:面向切面編程。他是一種可以在不修改原來核心代碼的情況俠給程序動態統一進行增強的一種技術
SpringAOP:批量對Spring容器中的bean方法做增強,并且這種增強不會與原來方法中的代碼耦合
1.快速入門
1.1需求
要求讓08_SpringAOP模塊中service包下所有類的所有方法在調用前都輸出:方法被調用了
1.2準備工作
第一步:引入依賴
<!--SpringIOC相關依賴--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><!--AOP相關依賴--><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.8.13</version></dependency>
第二步:開啟組件掃描
<context:component-scan base-package="com.sangeng"></context:component-scan>
第三步:相關bean注入容器中
@Service
public class PhoneService {public void deleteAll(){System.out.println("PhoneService中deleteAll的核心代碼");}
}
@Service
public class UserService {public void deleteAll(){System.out.println("UserService中deleteAll的核心代碼");}
}
1.3實現AOP
①開啟AOP注解支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!--開啟組件掃描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.sangeng"></context:component-scan><!--開啟aop注解支持--><aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy></beans>
②創建切面類
創建一個類,在類上加上@Component和@Aspect
使用@Pointcut注解來指定要被增強的方法
使用@Before注解來給我們的增強代碼所在的方法進行標識,并且指定了增強代碼是在被增強方法執行之前執行的
package com.sangeng.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {//寫一個pt方法,作用是用來承載PointCut//PointCut注解來聲明要對哪些方法進行增強@Pointcut("execution(* com.sangeng.service.*.*(..))")public void pt(){}//用@Before注解來指定該方法中是增強的代碼,并且指定被哪個切點表達式指定的方法前執行前執行的//@Before的屬性寫上加了@Pointcut注解的方法: 方法名()@Before("pt()")public void methodBefore(){System.out.println("方法被調用了");}}
③測試
package com.sangeng;import com.sangeng.service.PhoneService;
import com.sangeng.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");UserService userService = app.getBean(UserService.class);PhoneService phoneService = app.getBean(PhoneService.class);userService.deleteAll();phoneService.deleteAll();}
}
2.AOP核心概念
-
Jointpoint(連接點):所謂連接點是指那些可以被增強的點。在spring中,這些點指的的方法,因為spring只支持方法類型的連接點
-
Pointcut(切入點):所謂切入點是指被增強的連接點(方法)
-
Advice(通知/ 增強):所謂通知是指具體增強的代碼
-
Target(目標對象):被增強的對象就是目標對象
-
Aspect(切面):是切入點和通知(引介)的結合
-
Proxy (代理):一個類被 AOP 增強后,就產生一個結果代理類
3.切點確定
3.1切點表達式
可以使用切點表達式來表示要對哪些方法進行增強
寫法:execution([修飾符] 返回值類型 包名.類名.方法名(參數))
- 訪問修飾符可以省略,大部分情況下省略
- 返回值類型、包名、類名、方法名可以使用星號* 代表任意
- 包名與類名之間一個點 . 代表當前包下的類,兩個點 … 表示當前包及其子包下的類
- 參數列表可以使用兩個點 … 表示任意個數,任意類型的參數列表
execution(* com.sangeng.service.*.*(..)) 表示com.sangeng.service包下任意類,方法名任意,參數列表任意,返回值類型任意execution(* com.sangeng.service..*.*(..)) 表示com.sangeng.service包及其子包下任意類,方法名任意,參數列表任意,返回值類型任意execution(* com.sangeng.service.*.*()) 表示com.sangeng.service包下任意類,方法名任意,要求方法不能有參數,返回值類型任意execution(* com.sangeng.service.*.delete*(..)) 表示com.sangeng.service包下任意類,參數列表任意,返回值類型任意,方法名要求已delete開頭
3.2切點函數@annotation
我們也可以在要增強的方法上加上注解。然后使用@annotation來表示對加了什么注解的方法進行增強
寫法:@annotation(注解的全類名)
第一步:自定義注解如下
package com.sangeng.aspect;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target({ElementType.METHOD})//該注解可以加在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface KekeAnnotation {
}
切面類中使用@annotation來確定要增強的方法
package com.sangeng.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {@Pointcut("@annotation(com.sangeng.aspect.KekeAnnotation)")public void pt(){}//用@Before注解來指定該方法中是增強的代碼,并且指定被哪個切點表達式指定的方法前執行前執行的//@Before的屬性寫上加了@Pointcut注解的方法: 方法名()@Before("pt()")public void methodBefore(){System.out.println("方法被調用了");}}
給需要增強的方法增加注解
package com.sangeng.service;import com.sangeng.aspect.KekeAnnotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class PhoneService {@KekeAnnotationpublic void deleteAll(){System.out.println("PhoneService中deleteAll的核心代碼");}
}
測試
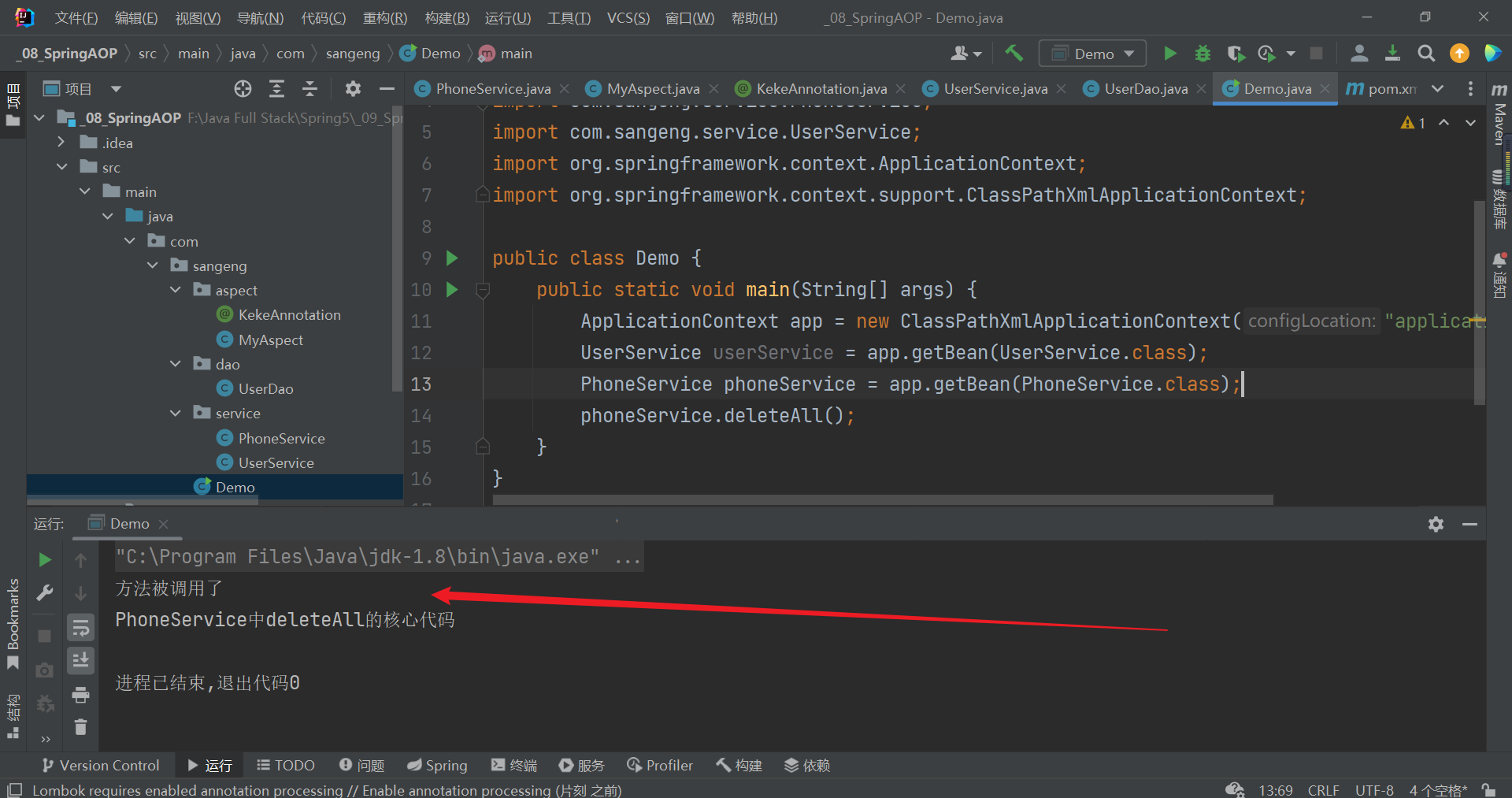
4.通知分類
-
@Before:前置通知,在目標方法執行前執行
-
@AfterReturning: 返回后通知,在目標方法執行后執行,如果出現異常不會執行
-
@After:后置通知,在目標方法之后執行,無論是否出現異常都會執行
-
@AfterThrowing:異常通知,在目標方法拋出異常后執行
-
@Around:環繞通知,圍繞著目標方法執行
環繞通知非常特殊,它可以對目標方法進行全方位的增強,我們重點學習@Around環繞通知
package com.sangeng.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {@Pointcut("@annotation(com.sangeng.aspect.KekeAnnotation)")public void pt(){}@Around("pt()")public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){System.out.println("目標方法執行前");try {pjp.proceed(); //目標方法執行System.out.println("目標方法執行后");} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("目標方法出現異常");} finally {System.out.println("finally代碼塊");}}}
5.獲取被增強方法相關信息
我們實際對方法進行增強時往往還需要獲取到被增強代碼的相關信息,比如方法名,參數,返回值,異常對象等
我們可以在除了環繞通知外的所有通知方法中增加一個JoinPoint類型的參數。這個參數封裝了被增強方法的相關信息。**我們可以通過這個參數獲取到除了異常對象和返回值之外的所有信息
@Before("pt()")public void methodbefore(JoinPoint jp){Object[] args = jp.getArgs();//方法調用時傳入的參數Object target = jp.getTarget();//被代理對象MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) jp.getSignature();//獲取被被增強方法簽名封裝的對象System.out.println("Before方法被調用了");}
案例:
需求:要求讓所有service包下類的所有方法被調用前都輸出全類名,方法名,以及調用時傳入的參數
package com.sangeng.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {@Pointcut("execution(* com.sangeng.service..*.*(..))")public void pt(){}@Before("pt()")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint jp){MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) jp.getSignature();//獲取參數Object[] args = jp.getArgs();Method method = signature.getMethod();//獲取方法名String methodName = method.getName();//獲取全類名String declaringTypeName = signature.getDeclaringTypeName();System.out.println("全類名:" + declaringTypeName);System.out.println("方法名:" + methodName);System.out.println("參數:" + Arrays.toString(args));}
}
如果需要獲取被增強方法中的異常對象或者返回值則需要在方法參數上增加一個對應類型的參數,并且使用注解的屬性進行配置。這樣Spring會把你想獲取的數據賦值給對應的方法參數
但是上述的方法比較麻煩,直接在環繞通知方法中增加一個ProceedingJoinPoint類型的參數。這個參數封裝了被增強方法的相關信息
該參數的proceed()方法被調用相當于被增強方法被執行,調用后的返回值就相當于被增強方法的返回值
@Around(value = "pt()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();//方法調用時傳入的參數Object target = pjp.getTarget();//被代理對象MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature();//獲取被被增強方法簽名封裝的對象Object ret = null;try {ret = pjp.proceed();//ret就是目標方法執行后的返回值} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();//throwable就是出現異常時的異常對象}return ret;}
6.多切面順序問題
在實際項目中我們可能會存在配置了多個切面的情況。這種情況下我們很可能需要控制切面的順序
我們在默認情況下Spring有它自己的排序規則。(按照類名排序)
默認排序規則往往不符合我們的要求,我們需要進行特殊控制
如果是注解方式配置的AOP可以在切面類上加**@Order注解來控制順序。@Order中的屬性越小優先級越高**
如果是XML方式配置的AOP,可以通過調整配置順序來控制
例如:
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class APrintLogAspect {//省略無關代碼
}
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class CryptAspect {//省略無關代碼
}
7.動態代理
實際上Spring的AOP其實底層就是使用動態代理來完成的。并且使用了兩種動態代理分別是JDK的動態代理和Cglib動態代理。所以我們接下去來學習下這兩種動態代理,理解下它們的不同點
7.1JDK動態代理
JDK的動態代理使用的java.lang.reflect.Proxy這個類來進行實現的。要求被代理(被增強)的類需要實現了接口。并且JDK動態代理也只能對接口中的方法進行增強
public static void main(String[] args) {AIControllerImpl aiController = new AIControllerImpl();//使用動態代理增強getAnswer方法//1.JDK動態代理//獲取類加載器ClassLoader cl = Demo.class.getClassLoader();//被代理類所實現接口的字節碼對象數組Class<?>[] interfaces = AIControllerImpl.class.getInterfaces();AIController proxy = (AIController) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {//使用代理對象的方法時 會調用到invokepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//proxy 是代理對象//method 是當前被調用的方法封裝的Method對象//args 是調用方法時傳入的參數//調用被代理對象的對應方法//判斷 當前調用的是否是getAnswer方法if(method.getName().equals("getAnswer")){System.out.println("增強");}Object ret = method.invoke(aiController, args);return ret;}});String answer = proxy.getAnswer("三連了嗎?");System.out.println(answer);}
7.2Cglib動態代理
使用的是org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer類進行實現的
public class CglibDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();//設置父類的字節碼對象enhancer.setSuperclass(AIControllerImpl.class);enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {//使用代理對象執行方法是都會調用到intercept方法@Overridepublic Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {//判斷當前調用的方法是不是getAnswer方法 如果是進行增強if ("getAnswer".equals(method.getName())){System.out.println("被增強了");}//調用父類中對應的方法Object ret = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);return ret;}});//生成代理對象AIControllerImpl proxy = (AIControllerImpl) enhancer.create();
// System.out.println(proxy.getAnswer("你好嗎?"));System.out.println(proxy.fortuneTelling("你好嗎?"));}
}
7.3兩種動態代理方案總結
? JDK動態代理要求被代理(被增強)的類必須要實現接口,生成的代理對象相當于是被代理對象的兄弟
? Cglib的動態代理不要求被代理(被增強)的類要實現接口,生成的代理對象相當于被代理對象的子類對象
? Spring的AOP默認情況下優先使用的是JDK的動態代理,如果使用不了JDK的動態代理才會使用Cglib的動態代理
7.4切換默認動態代理方式
如果我們是采用注解方式配置AOP的話:
設置aop:aspectj-autoproxy標簽的proxy-target-class屬性為true,代理方式就會修改成Cglib
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
8.Spring聲明式事務
8.1配置事務管理器和事務注解驅動
在spring的配置文件中添加如下配置:
<!--把事務管理器注入Spring容器,需要配置一個連接池--><bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/></bean><!--開啟事務注解驅動,配置使用的事務管理器--><tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
8.2添加注解
在需要進行事務控制的方法或者類上添加@Transactional注解就可以實現事務控制。
@Transactionalpublic void transfer(Integer outId, Integer inId, Double money) {//增加accoutDao.updateMoney(inId,money);
// System.out.println(1/0);//減少accoutDao.updateMoney(outId,-money);}
注意:如果加在類上,這個類的所有方法都會受事務控制,如果加在方法上,就是那一個方法受事務控制。
注意,因為聲明式事務底層是通過AOP實現的,所以最好把AOP相關依賴都加上。
<dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.9.6</version></dependency>
9.屬性配置
9.1事務傳播行為propagation
測試案例:
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl {@AutowiredAccountService accountService;@Transactionalpublic void test(){accountService.transfer(1,2,10D);accountService.log();}
}
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {//...省略其他不相關代碼@Transactionalpublic void log() {System.out.println("打印日志");int i = 1/0;}}
當事務方法嵌套調用時,需要控制是否開啟新事務,可以使用事務傳播行為來控制
| 屬性值 | 行為 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED(必須要有,默認值) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法就加入。外層沒有,內層就新建 |
| REQUIRES_NEW(必須要有新事務,其實就是創建了一個新的連接) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法新建。外層沒有,內層也新建 |
| SUPPORTS(支持有) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法就加入。外層沒有,內層就也沒有 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED(支持沒有) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法沒有。外層沒有,內層也沒有 |
| MANDATORY(強制要求外層有) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法加入。外層沒有。內層就報錯 |
| NEVER(絕不允許有) | 外層方法有事務,內層方法就報錯。外層沒有。內層就也沒有 |
上述案例中,test()方法里面有兩個業務1.轉賬操作 2.打印日志,并且該方法加了聲明式事務注解。這兩個業務也都加了事務注解。那么測試的時候轉賬是成功的,但是打印r日志的時候出現了除0異常,事務就會回滾,注意這里是回滾所有的業務,因為@Transactional注解的默認傳播行為,只建立一個連接c1
但我們并不希望這樣,因為轉賬業務是成功的,僅僅由于日志打印出現異常就導致轉賬業務回滾,顯然得不償失,日志記錄可以少記錄一天,但是轉賬無需回滾
如何解決這一問題?可以修改轉賬業務的事務傳播行為@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW),即創建了一個新的連接c2,開啟了一個新的事務,當執行到轉賬業務的時候,轉賬業務成功,這個連接就會提交事務,即使日志打印的業務出現異常回滾,也是只回滾c1,轉賬業務并不會回滾
代碼修改如下:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)public void transfer(Integer outId, Integer inId, Double money) {//增加accoutDao.updateMoney(inId,money);//減少accoutDao.updateMoney(outId,-money);}
9.2隔離級別isolation
Isolation.DEFAULT 使用數據庫默認隔離級別
Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED
Isolation.READ_COMMITTED
Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ
Isolation.SERIALIZABLE
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)public void transfer(Integer outId, Integer inId, Double money) {//增加accoutDao.updateMoney(inId,money);//減少accoutDao.updateMoney(outId,-money);}
9.3只讀readOnly
如果事務中的操作都是讀操作,沒涉及到對數據的寫操作可以設置readOnly為true。這樣可以提高效率
@Transactional(readOnly = true)public void log() {System.out.println("打印日志");int i = 1/0;}
Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED
Isolation.READ_COMMITTED
Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ
Isolation.SERIALIZABLE
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)public void transfer(Integer outId, Integer inId, Double money) {//增加accoutDao.updateMoney(inId,money);//減少accoutDao.updateMoney(outId,-money);}
9.3只讀readOnly
如果事務中的操作都是讀操作,沒涉及到對數據的寫操作可以設置readOnly為true。這樣可以提高效率
@Transactional(readOnly = true)public void log() {System.out.println("打印日志");int i = 1/0;}










-模塊化)





FPGA代碼篇)

)
