一、JDK8新特性(Stream流)
接下來學習一個全新的知識,叫做Stream流(也叫Stream API)。它是從JDK8以后才有的一個新特性,是專業用于對集合或者數組進行便捷操作的。有多方便呢?我們用一個案例體驗一下,然后再詳細學習。
1.1 Stream流體驗
案例需求:有一個List集合,元素有"張三豐","張無忌","周芷若","趙敏","張強",找出姓張,且是3個字的名字,存入到一個新集合中去。
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "張三豐","張無忌","周芷若","趙敏","張強");
System.out.println(names);
- 用傳統方式來做,代碼是這樣的
// 找出姓張,且是3個字的名字,存入到一個新集合中去。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {if(name.startsWith("張") && name.length() == 3){list.add(name);}
}
System.out.println(list);
- 用Stream流來做,代碼是這樣的(ps: 是不是想流水線一樣,一句話就寫完了)
List<String> list2 = names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("張")).filter(a -> a.length()==3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list2);
先不用知道這里面每一句話是什么意思,具體每一句話的含義,待會再一步步學習。現在只是體驗一下。
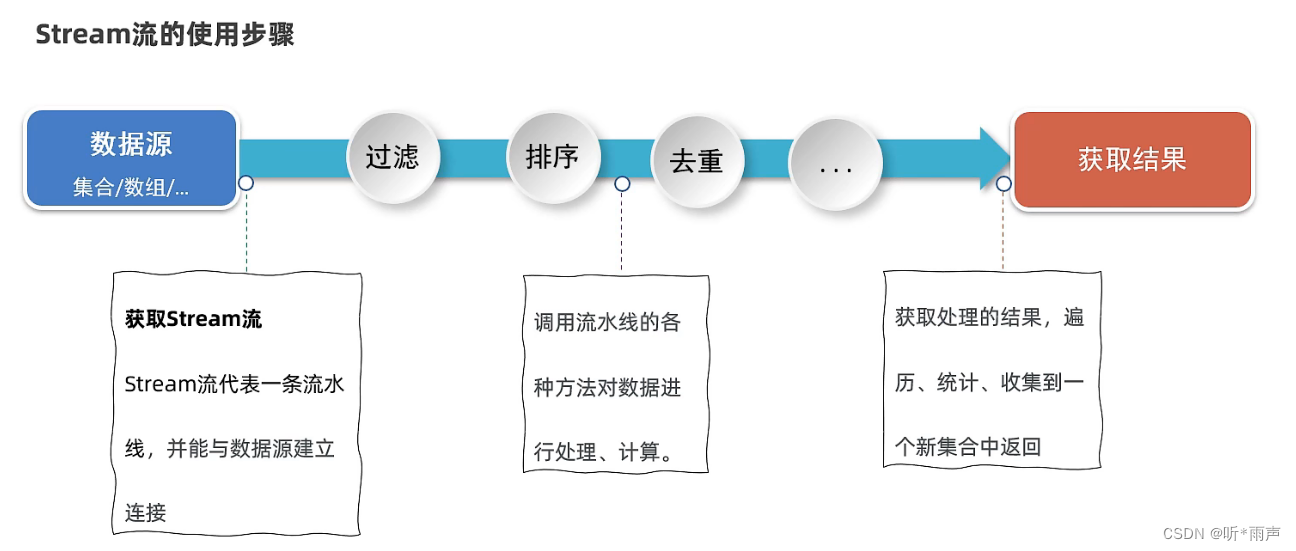
學習Stream流我們接下來,會按照下面的步驟來學習。
1.2 Stream流的創建
好,接下來我們正式來學習Stream流。先來學習如何創建Stream流、或者叫獲取Stream流。

主要掌握下面四點:1、如何獲取List集合的Stream流?2、如何獲取Set集合的Stream流?3、如何獲取Map集合的Stream流?4、如何獲取數組的Stream流?
直接上代碼演示
/*** 目標:掌握Stream流的創建。*/
public class StreamTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1、如何獲取List集合的Stream流?List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(names, "張三豐","張無忌","周芷若","趙敏","張強");Stream<String> stream = names.stream();// 2、如何獲取Set集合的Stream流?Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();Collections.addAll(set, "劉德華","張曼玉","蜘蛛精","馬德","德瑪西亞");Stream<String> stream1 = set.stream();stream1.filter(s -> s.contains("德")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));// 3、如何獲取Map集合的Stream流?Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("古力娜扎", 172.3);map.put("迪麗熱巴", 168.3);map.put("馬爾扎哈", 166.3);map.put("卡爾扎巴", 168.3);Set<String> keys = map.keySet();Stream<String> ks = keys.stream();Collection<Double> values = map.values();Stream<Double> vs = values.stream();Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();Stream<Map.Entry<String, Double>> kvs = entries.stream();kvs.filter(e -> e.getKey().contains("巴")).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey()+ "-->" + e.getValue()));// 4、如何獲取數組的Stream流?String[] names2 = {"張翠山", "東方不敗", "唐大山", "獨孤求敗"};Stream<String> s1 = Arrays.stream(names2);Stream<String> s2 = Stream.of(names2);}
}1.3 Stream流中間方法
中間方法指的是:調用完方法之后其結果是一個新的Stream流,于是可以繼續調用方法,這樣一來就可以支持鏈式編程(或者叫流式編程)。

話不多說,直接上代碼演示
/*** 目標:掌握Stream流提供的常見中間方法。*/
public class StreamTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Double> scores = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(scores, 88.5, 100.0, 60.0, 99.0, 9.5, 99.6, 25.0);// 需求1:找出成績大于等于60分的數據,并升序后,再輸出。scores.stream().filter(s -> s >= 60).sorted().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);// 需求2:找出年齡大于等于23,且年齡小于等于30歲的學生,并按照年齡降序輸出.students.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() >= 23 && s.getAge() <= 30).sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge()).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));// 需求3:取出身高最高的前3名學生,并輸出。students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight())).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");// 需求4:取出身高倒數的2名學生,并輸出。 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight())).skip(students.size() - 2).forEach(System.out::println);// 需求5:找出身高超過168的學生叫什么名字,要求去除重復的名字,再輸出。students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).map(Student::getName).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);// distinct去重復,自定義類型的對象(希望內容一樣就認為重復,重寫hashCode,equals)students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);Stream<String> st1 = Stream.of("張三", "李四");Stream<String> st2 = Stream.of("張三2", "李四2", "王五");Stream<String> allSt = Stream.concat(st1, st2);allSt.forEach(System.out::println);}
}
1.4 Stream流終結方法
最后,我們再學習Stream流的終結方法。這些方法的特點是,調用完方法之后,其結果就不再是Stream流了,所以不支持鏈式編程。
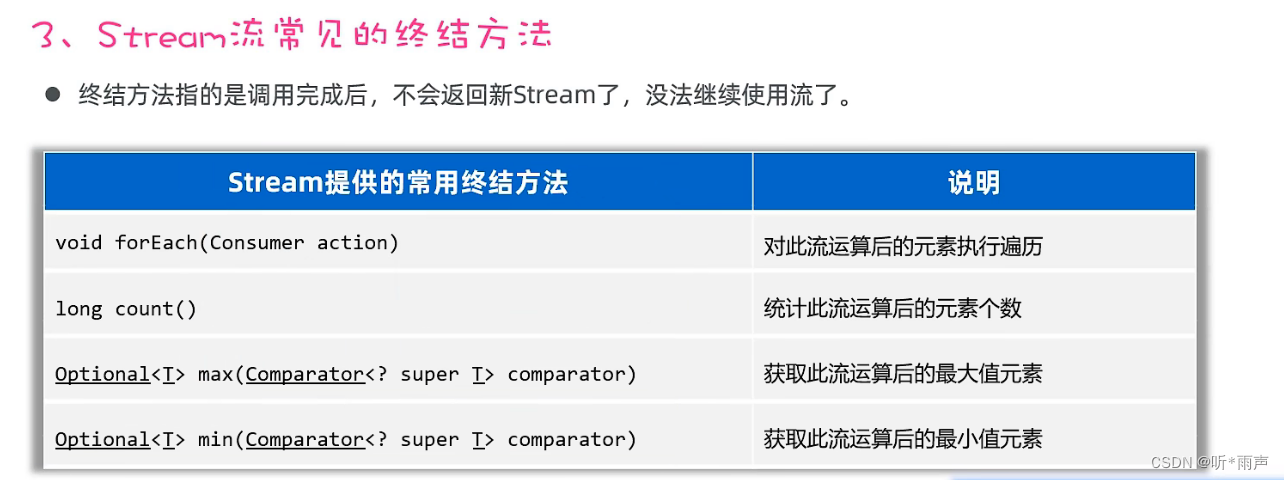
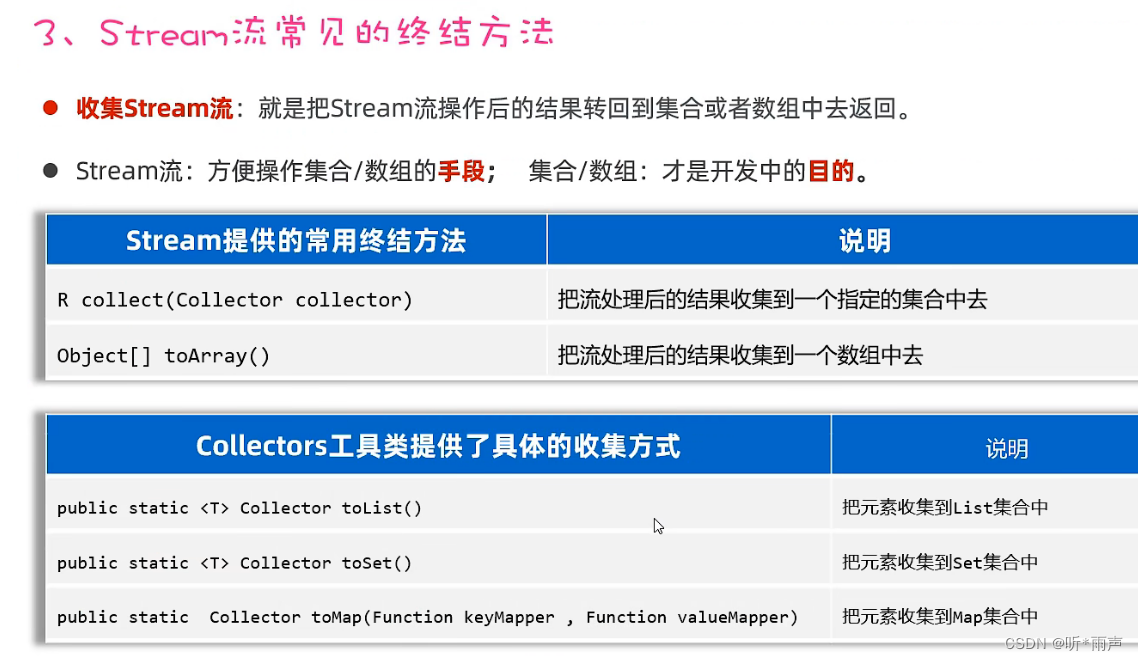
話不多說,直接上代碼
/*** 目標:Stream流的終結方法*/
public class StreamTest4 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);// 需求1:請計算出身高超過168的學生有幾人。long size = students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).count();System.out.println(size);// 需求2:請找出身高最高的學生對象,并輸出。Student s = students.stream().max((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();System.out.println(s);// 需求3:請找出身高最矮的學生對象,并輸出。Student ss = students.stream().min((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();System.out.println(ss);// 需求4:請找出身高超過170的學生對象,并放到一個新集合中去返回。// 流只能收集一次。List<Student> students1 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(students1);Set<Student> students2 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(students2);// 需求5:請找出身高超過170的學生對象,并把學生對象的名字和身高,存入到一個Map集合返回。Map<String, Double> map =students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).distinct().collect(Collectors.toMap(a -> a.getName(), a -> a.getHeight()));//把什么作為鍵,把什么作為值System.out.println(map);// Object[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray();Student[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray(len -> new Student[len]);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}




-模塊化)





FPGA代碼篇)

)





不停機遷移方案)
