1.終端下連接mysql服務
mysql -uroot -p回車后輸入設定的密碼即可。
進去后每條命令結尾要帶分號;退出命令exit
單行注釋有兩種:# 或 --空格。多行注釋/* */
2.基本命令集合
針對數據庫:use sys; show databases;
查看當前操作的數據庫:select databse();
針對表:1.創建表eg1示例:create table? eg1( #此時回車
stuid int,
stuname varchar(20),
gender? char, #代表單個字符
borndate datetime); #命令結尾時才帶分號
2. desc eg1; #查看表的描述 describe
select * from eg1; #查看表中所有字段數據,新創建的表應返回為Empty set
insert into eg1 values(1,'張三','男','1999-6-6'); #向表中插入數據,注意使用英文逗號
insert into eg1 values(2,'李四','男','1999-6-6');
#若提示格式不對,set names utf8;修改my.ini里的utf8為gbk
update eg1 set borndate='2020-02-02' where stuid=2; #更新/修改表中的數據,如果沒有后面的where,會更新整列數據delete from eg1 where stuid=1; #刪除數據alter table eg1 add column email varchar(20); #修改表的結構,添加列drop table eg1; #刪除整個表
3.基礎查詢
查詢結果是個虛擬表,不能直接操作數據。
select? ?#? 常量? 表達式(這兩個不用寫來自哪個表)? 函數?字段。對于來自哪個表可以雙擊表頭,將自動用著重符·填寫。不是關鍵字的可以不加著重符號
F12鍵 可對齊命令。
select version() #查詢版本
select? user() #查詢用戶
起別名
select user() as 用戶名; #as 也可以省略為空格
select user() as '用? 戶名'; #包含了空格,避免使用查詢時出現語法錯誤
select user() as "用戶? ?名";
例如:select last_name? as? "姓? ?名" from table; #若不使用引號,會出現語法錯誤。
+ 在mysql中作為運算符時,字符型強制轉換為整形失敗,則默認為0。其中一個操作數為null時,null+null=null=null+12=null。
字段拼接查詢
select concat(字段1,字段2) as "新? 字? 段" from? table;
去重查詢: select distict字段? from table;
顯示全部列,各個列用逗號連接,列頭顯示為out_put:
select concat(字段1,','字段2,','字段3) as 新字段 from table;
ifnull(表達式1,表達式2) #如果表達式1為null,顯示結果為表達式2.
避免查詢出null: select concat(字段1,','字段2,','ifnull(字段3,'')) as 新字段 from table;
4.條件查詢
select查詢列表from table
where 篩選條件;
執行順序為:from->where->select
select * from table where id<>100; #查詢id不等于100的信息。
select * from table where not(id>=20 and id<= 60); #查詢id小于20大于60的信息。雖然可以用!代替not, &&代替and? 但是不建議,這樣不專業。
模糊查詢:like 一般和通配符_(單個字符) %(多個字符)
select * from table where like '%條件%' #查詢包含? 條件? 的信息。
查詢下劃線_: '$_%' escape '$'; #escape 使$符號 變為使轉義字符,相當于\ 不過不建議,不炫。
in (常量表達式1,常量表達式2,常量表達式3) not? in 非數值的常量值,比如字符,要用單引號引起來。
select 字段 from table where id in(55,66,77); #查詢id 為 55? 66 ? 77
between? and #判斷某個字符的值是否介于xx之間。
select 字段 from table where id between 30 and 90; #
= #用于普通內容
is null is not? null? #用于null
<=> #安全等于,既能判斷普通內容,又能判斷null值
舉例:id<=> null; id<=>22;
5.排序查詢
select查詢列表from table
where 篩選條件
order by 排序列表
select? * from table where id>100 order by salary asc; #asc是升序,不寫默認為升序。降序為desc。
select *,num*12 總額 from table where id is not null order by 總額 desc; #插入新算術表達式,并降序排列。
按函數的結果排序:
select 字段 from table order bylenth(字段); #按字段字節長度升序排列
select 字段 from table order by char_lenth(字段); #按字符長度排列
select字段1 字段2 字段3from table
order by 字段1,字段2 desc; #先按字段1升序排列,再滿足按字段2降序排列。
select * from table order by 字段; #字段為第2列時,就寫個 order by 2 也行。
6.函數
字符函數:拼接字符:concat
select lenth('ab天'); #結果為5,一個漢字三個字節
select char_lenth('ab天') #結果為3。
截取字符:SELECT SUBSTR('因為自己不夠沙雕而感到自卑',7,2); #7為起始索引(從1開始),2為長度,輸出結果為 沙雕,不寫長度截取到最后。
獲取字符出現索引:select instr('因為自己不夠沙雕而感到自卑','自己'); #結果為3
去空格:默認是去空格
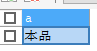
select trim('x' from 'xxxxxx本品xxxx' ) as? a ;
SELECT TRIM( '? ?本品 ' ) AS? a ; #結果都是下圖
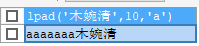
填充:左填充 lpad 右填充rpad
select lpad('木婉清',10,'a');
select rpad('木婉清',4,'a');
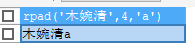 #列寬為1時,就一個木 字。
#列寬為1時,就一個木 字。
)

)

)

)

; 很牛逼)
)

)




)


—— 選主)