這篇文章介紹一下linux中斷的底半部分的tasklet和workquene兩種處理機制,其中tasklet中不能有延時函數,workquene的處理函數可以加入延時操作
目錄
- (一)tasklet小任務處理機制
- (1)tasklet相關函數接口
- (2)tasklet使用流程
- (3)tasklet實例代碼
- (二)workquene工作隊列處理機制
- (1)workqueue相關函數接口
- (2)共享工作隊列使用流程
- (3)自定義工作隊列使用流程
- (4)共享workqueue實例代碼
在Linux中為了提高系統的響應速度及并發能力,將Linux的中斷劃分為頂半部和底半部兩部分。
頂半部(top half):做中斷的登記操作,當然也可以做不耗時的中斷處理(內核中會創建一個中斷登記表)。
頂半部完成的一般是緊急的硬件操作,一般包括讀取寄存的中斷狀態,清除中斷標志,將底半部處理程序掛到底半部的執行隊列中去,此過程不可被打斷
底半部(bottom half):處理耗時操作,把耗時的操作放入底半部執行,這個過程可以被打斷,耗時操作推后執行
(一)tasklet小任務處理機制
內核中關于tasklet的介紹:
/* Tasklets --- multithreaded analogue of BHs.Main feature differing them of generic softirqs: taskletis running only on one CPU simultaneously.Main feature differing them of BHs: different taskletsmay be run simultaneously on different CPUs.Properties:* If tasklet_schedule() is called, then tasklet is guaranteedto be executed on some cpu at least once after this.* If the tasklet is already scheduled, but its execution is still notstarted, it will be executed only once.* If this tasklet is already running on another CPU (or schedule is calledfrom tasklet itself), it is rescheduled for later.* Tasklet is strictly serialized wrt itself, but notwrt another tasklets. If client needs some intertask synchronization,he makes it with spinlocks.
(1)tasklet相關函數接口
小任務機制相關的數據結構:
struct tasklet_struct
{struct tasklet_struct *next; //用來實現多個tasklet_struct結構鏈表unsigned long state; //當前這個tasklet是否已經被調度atomic_t count; //值為0的時候用戶才可以調度/*原子變量操作:指的是操作過程中不允許被打斷機制typedef struct {int counter;} atomic_t; */void (*func)(unsigned long); //指向tasklet綁定的函數指針unsigned long data; //傳向tasklet綁定的函數的參數
};
小任務數據結構創建:
#define DECLARE_TASKLET(name, func, data) \ //靜態初始化,默認為使能
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, 0, ATOMIC_INIT(0), func, data }#define DECLARE_TASKLET_DISABLED(name, func, data) \ //靜態初始化,默認為失能
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, 0, ATOMIC_INIT(1), func, data }
初始化小任務:
extern void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data);
小任務加鎖解鎖:
//嘗試加鎖
static inline int tasklet_trylock(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{return !test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_RUN, &(t)->state);
}//解鎖
static inline void tasklet_unlock(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{smp_mb__before_clear_bit(); clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_RUN, &(t)->state);
}
/*** test_and_set_bit - Set a bit and return its old value* @nr: Bit to set* @addr: Address to count from** This operation is atomic and cannot be reordered.* It may be reordered on other architectures than x86.* It also implies a memory barrier.*/
static inline int test_and_set_bit(int nr, volatile unsigned long *addr)
{unsigned long mask = BIT_MASK(nr);unsigned long *p = ((unsigned long *)addr) + BIT_WORD(nr);unsigned long old;unsigned long flags;_atomic_spin_lock_irqsave(p, flags);old = *p;*p = old | mask;_atomic_spin_unlock_irqrestore(p, flags);return (old & mask) != 0;
}小任務登記:
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
小任務失能:
static inline void tasklet_disable_nosync(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{atomic_inc(&t->count);smp_mb__after_atomic_inc();
}static inline void tasklet_disable(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{tasklet_disable_nosync(t);tasklet_unlock_wait(t);smp_mb();
}
小任務使能:
static inline void tasklet_enable(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{smp_mb__before_atomic_dec();atomic_dec(&t->count); //單純的將count減一操作
}
結束小任務:
extern void tasklet_kill(struct tasklet_struct *t);
extern void tasklet_kill_immediate(struct tasklet_struct *t, unsigned int cpu);
(2)tasklet使用流程
- 定義結構體并初始化
struct tasklet_struct task;
tasklet_init(&task,自定義函數功能名,函數形參);
- 在合適的地方(一般在中斷里)對tasklet登記
tasklet_schedule(&task);
(3)tasklet實例代碼
chrdev.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>struct tasklet_struct task;void tasklet_fun(unsigned long data)
{printk("this is tasklet test\n");
}static int __init tasklet_module_init(void)
{tasklet_init(&task,tasklet_fun,(unsigned long)10);//tasklet_disable(&task);//失能后不能卸載該tasklettasklet_schedule(&task);return 0;
}static void __exit tasklet_module_cleanup(void)
{tasklet_kill(&task);
}
module_init(tasklet_module_init);
module_exit(tasklet_module_cleanup);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");(二)workquene工作隊列處理機制
工作隊列提供了將功能推遲到下半部分的通用方法。核心是工作隊列(struct workqueue_struct),這是工作所在的結構。內核中通過work_struct結構標識要延遲的工作和要使用的延遲功能。events / X內核線程(每個CPU一個)從工作隊列中提取工作,并激活下半部處理程序之一。
工作隊列是更新的延遲機制,已在2.5 Linux內核版本中添加。工作隊列不是通用的延遲機制,不像Tasklet那樣提供一站式的延遲方案,在該機制中,工作隊列的處理函數可以休眠(在Tasklet模型中是不可能的),工作隊列的延遲可能比任務小,但包含更豐富的API以進行工作延遲,延遲之前是通過keventd任務隊列管理,現在由名為events / X的內核工作線程管理。
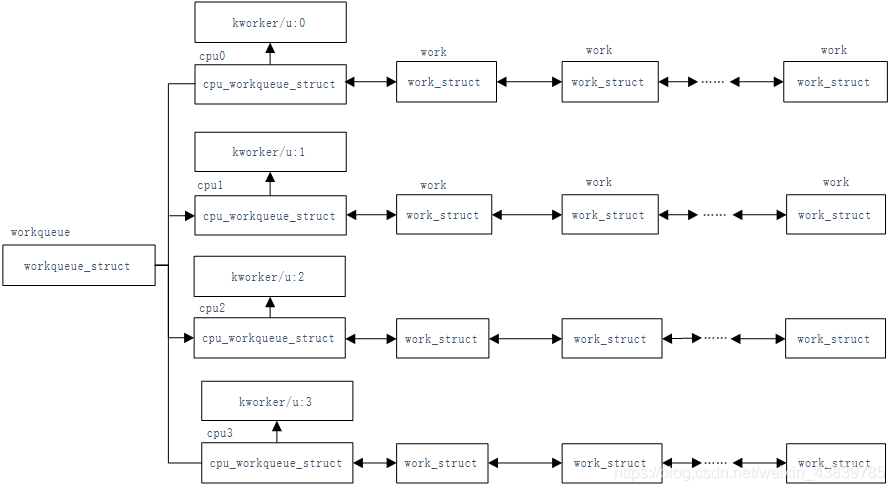
內核中有兩種工作隊列,一種是共享工作隊列,另一種是自定義工作隊列
共享工作隊列 :內核提供,用戶可直接使用,秩序調用對應的接口即可,更多的時候選擇共享消息隊列
自定義工作隊列:需要用戶手動創建,并手動銷毀
| 共享工作隊列 | 自定義工作隊列 |
|---|---|
| 內核啟動期間會創建一個工作全局的工作隊列,所有的驅動都可以把自己延后執行的工作函數掛到這個共享工作隊列中。 | 當你要執行工作不希望受到其他工作的影響時,可以自己創建一個工作隊列,然后把自己的工作放在自定義的工作隊列調度。 |
| 優點:不需要自己創建工作隊列,簡單,快捷,方便。 | 優點:不會受到其他工作的影響,工作函數執行有保障。 |
| 缺點:可能會受到其他工作的影響,前面的工作阻塞,影響到后面的工作的執 | 缺點:造成系統巨大開銷大,如果過多創建自定義工作隊列,會嚴重影響系統實時 |
(1)workqueue相關函數接口
工作隊列數據結構:
struct work_struct {atomic_long_t data;struct list_head entry;work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEPstruct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};typedef void (*work_func_t)(struct work_struct *work);
聲明并初始化工作隊列:
1.靜態方式:
#define DECLARE_WORK(n, f) \struct work_struct n = __WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f)#define DECLARE_DELAYED_WORK(n, f) \struct delayed_work n = __DELAYED_WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f)2. 動態形式初始化:
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \do { \__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0); \} while (0)
創建自定義工作隊列的時候使用:
extern int queue_work(struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work);
工作隊列登記:
extern int schedule_work(struct work_struct *work);
/*** schedule_work - put work task in global workqueue* @work: job to be done** Returns zero if @work was already on the kernel-global workqueue and* non-zero otherwise.** This puts a job in the kernel-global workqueue if it was not already* queued and leaves it in the same position on the kernel-global* workqueue otherwise.*/
int schedule_work(struct work_struct *work)
{return queue_work(system_wq, work);
}
根據結構體成員找到結構體首地址:
/*** container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure* @ptr: the pointer to the member.* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the member within the struct.**/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})container_of使用示例:
struct mywork{int m;int n;struct work_struct works;
}test;container_of根據結構體內部的某一成員獲取結構的首地址container_of(ptr, type, member) @ptr: 指向結構體成員的指針. 如 struct work_struct *works;* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in. 結構體類型 struct mywork* @member: the name of the member within the struct. works
(2)共享工作隊列使用流程
1.定義共享工作隊列結構體并初始化
struct work_struct works;
INIT_WORK(&works,workqueue_fun);
2.在合適位置(一般為中斷)對工作隊列登記
schedule_work(&works);
(3)自定義工作隊列使用流程
1、創建工作隊列
struct workqueue_struct my_workqueue;
struct workqueue_struct *create_workqueue(&my_workqueue);
//struct workqueue_struct *create_singlethread_workqueue(const char *name);
//create_workqueue函數會在系統中的每個處理器上創建一個線程(多線程),而create_singlethread_workqueue只是創建一個單一的線程,如果單個線程足夠使用,那么應該使用create_singlethread_workqueue函數。
2、創建任務
struct work_struct works;
INIT_WORK(&works,workqueue_fun);
3、提交任務,要將任務提交到工作隊列中,內核提供了下面兩個API:
int queue_work(struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work);
int queue_delayed_work(struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct delayed_work *work, unsigned long delay);
這兩個函數都會將任務提交到工作隊列中,使用queue_delayed_work函數,則提交的任務至少延時由參數delay指定的時間才被執行。
如果要取消工作隊列中的某個任務,使用cancel_delayed_work,原型如下:
int cancel_delayed_work(struct work_struct *work);
如果任務在被執行之前取消,那么cancel_delayed_work函數返回非零值,調用該函數之后內核會確保被取消的任務不被執行。但是返回0,則表示任務已經被執行,因此調用cancel_delayed_work函數后,任務有可能仍在運行,所以為了確保任務測地被取消,需要調用flush_workqueue函數,與方法1中的不同。
void flush_workqueue(struct workqueue_struct *wq);
4、銷毀工作隊列, 使用完工作隊列之后,可以使用destroy_workqueue銷毀工作隊列:
void destroy_workqueue(struct workqueue_struct *wq);
(4)共享workqueue實例代碼
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>struct work_struct works;
void workqueue_fun(struct work_struct * work)
{printk("this is workqueue test\n");
}
static int __init workqueue_module_init(void)
{INIT_WORK(&works,workqueue_fun);//初始化共享工作隊列結構體schedule_work(&works);//將工作隊列進行登記return 0;
}
static void __exit workqueue_module_cleanup(void)
{printk("module is exit\n");
}
module_init(workqueue_module_init);
module_exit(workqueue_module_cleanup);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
本文章僅供學習交流用禁止用作商業用途,文中內容來水枂編輯,如需轉載請告知,謝謝合作
微信公眾號:zhjj0729
微博:文藝to青年
 B. Pasha and Phone C. Duff and Weight Lifting)

與 $()區別)




)
)





)

)


