1.概念
????????策略(Strategy)模式定義了一系列算法,并將每個算法封裝起來,使它們可以相互替換,且算法的變化不會影響使用算法的客戶。策略模式屬于行為型設計模式,它通過對算法進行封裝,把使用算法的責任和算法的實現分割開來,并委派給不同的對象對這些算法進行管理。
?策略模式可以簡單理解為:“一件事有多種做法,你可以隨時換著來,不用改其他地方”。
打個生活比方:
比如你要去上班(這是 “目標”),可以有多種方式(這些方式就是 “策略”):
- 晴天騎共享單車
- 下雨打出租車
- 趕時間就坐地鐵
????????這些方式都是去上班的辦法,互不影響。你可以根據天氣、時間隨時換,而 “上班” 這個目標本身不用變,換方式時也不用改其他安排。
????????核心就是:把做一件事的不同方法單獨拎出來,想用哪個就用哪個,切換起來很方便,還不影響其他部分。
2.策略模式結構
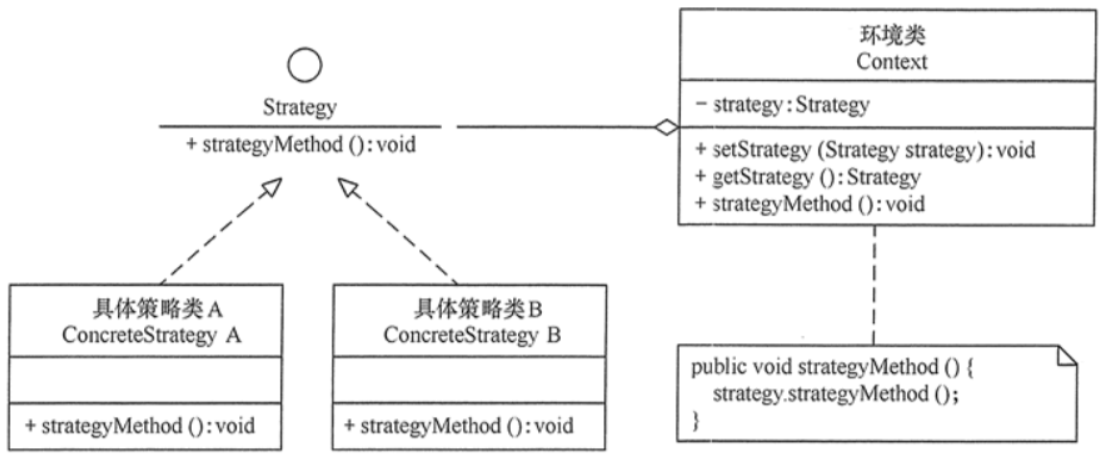
策略模式包含 3 個核心角色:
- 策略接口(Strategy):定義所有支持的算法的公共接口(或抽象類),聲明算法的核心方法。
- 具體策略(ConcreteStrategy):實現策略接口,包含具體的算法邏輯(如不同的排序算法、支付方式等)。
- 上下文(Context):持有一個策略接口的引用,負責調用策略的算法。客戶端通過上下文間接使用策略,且上下文可動態切換策略(通過 setter 方法)。
3.優點
- 靈活性高:算法可動態切換,客戶端無需修改代碼即可更換策略。
- 符合開閉原則:新增算法只需新增具體策略類,無需修改上下文或其他策略。
- 避免多重條件判斷:用多態代替
if-else或switch語句,代碼更清晰。 - 算法復用:策略類可在不同場景中復用。
4.適用場景
- 當一個問題有多種解決方案(算法),且需要動態選擇其中一種時(如支付系統的多種支付方式、排序算法的選擇)。
- 當代碼中存在大量與算法相關的
if-else判斷,且這些算法可能頻繁變化時。 - 當需要隱藏算法的具體實現細節,只暴露其接口時。
5.策略模式示例
說明:設計一個?“折扣計算” 模塊,支持 3 種折扣策略:
- 新用戶折扣(滿 100 減 20)
- 會員折扣(9 折)
- 促銷折扣(滿 200 減 50)
// 1. 策略接口:定義折扣計算方法
public interface DiscountStrategy {// 計算折扣后金額:參數為原價,返回折后價double calculate(double originalPrice);
}// 2. 具體策略:新用戶折扣
public class NewUserDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {// 滿100減20return originalPrice >= 100 ? originalPrice - 20 : originalPrice;}
}// 具體策略:會員折扣(9折)
public class MemberDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {return originalPrice * 0.9;}
}// 具體策略:促銷折扣(滿200減50)
public class PromotionDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {return originalPrice >= 200 ? originalPrice - 50 : originalPrice;}
}// 3. 上下文:折扣計算器(使用策略的類)
public class DiscountContext {// 持有策略接口的引用private DiscountStrategy strategy;// 構造方法:初始化時指定策略public DiscountContext(DiscountStrategy strategy) {this.strategy = strategy;}// 動態切換策略public void setStrategy(DiscountStrategy strategy) {this.strategy = strategy;}// 調用策略計算折扣public double getFinalPrice(double originalPrice) {return strategy.calculate(originalPrice);}
}// 1. 策略接口:定義折扣計算方法
public interface DiscountStrategy {// 計算折扣后金額:參數為原價,返回折后價double calculate(double originalPrice);
}// 2. 具體策略:新用戶折扣
public class NewUserDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {// 滿100減20return originalPrice >= 100 ? originalPrice - 20 : originalPrice;}
}// 具體策略:會員折扣(9折)
public class MemberDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {return originalPrice * 0.9;}
}// 具體策略:促銷折扣(滿200減50)
public class PromotionDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {@Overridepublic double calculate(double originalPrice) {return originalPrice >= 200 ? originalPrice - 50 : originalPrice;}
}// 3. 上下文:折扣計算器(使用策略的類)
public class DiscountContext {// 持有策略接口的引用private DiscountStrategy strategy;// 構造方法:初始化時指定策略public DiscountContext(DiscountStrategy strategy) {this.strategy = strategy;}// 動態切換策略public void setStrategy(DiscountStrategy strategy) {this.strategy = strategy;}// 調用策略計算折扣public double getFinalPrice(double originalPrice) {return strategy.calculate(originalPrice);}
}客戶端:
public DiscountStrategy strategy(String role) {switch (role) {case "new":return new NewUserDiscount();case "member":return new MemberDiscount();case "promotion":return new PromotionDiscount();default:throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知用戶類型");}}
? ? ? ? 可見雖然我們采用策略模式進行算法封裝,但是在邏輯分配時還是使用到了if-else式硬編碼格式,到后續我們想要新增新的策略也需要修改客戶端的代碼!
6.策略模式優化
????????策略模式的核心是封裝算法變化,讓客戶端可以靈活切換不同實現,避免冗余的條件判斷。它與工廠方法模式都通過抽象接口實現解耦,但策略模式聚焦 “行為 / 算法的使用”,工廠方法聚焦 “對象的創建”。實際開發中,兩者常結合使用:用工廠方法創建策略對象,用策略模式使用這些對象,既簡化了對象創建,又實現了算法的靈活切換。
說明:使用工廠方法+Map集合+策略模式優化
????????使用工廠方法可將對象的創建解耦,使用Map集合可消除if-else,使用策略模式可將算法的使用解耦。
/*** 角色處理器接口* 策略模式的核心接口,定義不同角色的處理行為*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface RoleHandler {/*** 處理用戶角色相關業務邏輯* @param userDTO 用戶數據傳輸對象*/void handle(UserDTO userDTO);
}/*** 管理員角色處理器* 處理管理員角色相關的業務邏輯*/
@Component
public class ManagerRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {@Resourceprivate ManagerMapper managerMapper;@Overridepublic void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {managerMapper.insertManager(userDTO);}
}/*** 學生角色處理器* 處理學生角色相關的業務邏輯*/
@Component
public class StudentRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {@Resourceprivate StudentMapper studentMapper;@Overridepublic void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {studentMapper.insertStudent(userDTO);}
}/*** 教師角色處理器* 處理教師角色相關的業務邏輯*/
@Component
public class TeacherRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {@Resourceprivate TeacherMapper teacherMapper;@Overridepublic void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {teacherMapper.insertTeacher(userDTO);}
}/*** 角色處理器工廠* 用于獲取不同角色的處理器實例*/
@Component
public class RoleHandlerFactory {private final Map<String, RoleHandler> roleHandlerMap = new HashMap<>();public RoleHandlerFactory(StudentRoleHandler studentRoleHandler, TeacherRoleHandler teacherRoleHandler, ManagerRoleHandler managerRoleHandler) {roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.STUDENT, studentRoleHandler);roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.TEACHER, teacherRoleHandler);roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.MANAGER, managerRoleHandler);}/*** 根據角色名稱獲取對應的處理器* @param roleName 角色名稱* @return 角色處理器* @throws TypeException 當角色不支持時拋出異常*/public RoleHandler getRoleHandler(String roleName) {RoleHandler handler = roleHandlerMap.get(roleName);if (handler == null) {throw new TypeException("不支持的用戶角色: " + roleName);}return handler;}
}客戶端使用:
RoleHandler handler = roleHandlerFactory.getRoleHandler(role);
handler.handle(userDTO);



并支持擴縮容的操作)





和cbind()使用)



)


)

