- 論文:《Improving Object DetectionWith One Line of Code》
- soft-NMS 英文論文鏈接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.04503.pdf
- soft-NMS github 鏈接:https://github.com/bharatsingh430/soft-nms
絕大部分目標檢測方法,最后都要用到 NMS 非極大值抑制進行后處理。 通常的做法是將檢測框按得分排序,然后保留得分最高的框,同時刪除與該框重疊面積大于一定比例的其它框。
這種貪心式方法存在如下圖所示的問題: 紅色框和綠色框是當前的檢測結果,二者的得分分別是0.95和0.80。如果按照傳統的NMS進行處理,首先選中得分最高的紅色框,然后綠色框就會因為與之重疊面積過大而被刪掉。
另一方面,NMS的閾值也不太容易確定,設小了會出現下圖的情況(綠色框因為和紅色框重疊面積較大而被刪掉),設置過高又容易增大誤檢。

思路:不要粗魯地刪除所有IOU大于閾值的框,而是降低其置信度。
soft NMS算法的大致思路為:M為當前得分最高框,bi 為待處理框,bi 和M的IOU越大,bi 的得分si 就下降的越厲害。

soft-NMS算法中的修剪步驟可以寫成如下的評分函數:
(1)線性加權:

(2)高斯加權:
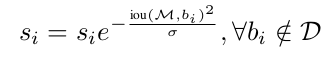

假如還檢測出了3號框(最細的紅色框),而我們的最終目標是檢測出1號和2號框,并且剔除3號框,原始的nms只會檢測出一個1號框并剔除2號框和3號框,而softnms算法可以對1、2、3號檢測狂進行置信度排序,可以知道這三個框的置信度從大到小的順序依次為:1-》2-》3(由于是使用了懲罰,所有可以獲得這種大小關系),如果我們再選擇了合適的置信度閾值,就可以保留1號和2號,同時剔除3號,實現我們的功能。
但是,這里也有一個問題就是置信度的閾值如何選擇,作者在這里依然使用手工設置的值,依然存在很大的局限性,所以該算法依然存在改進的空間
sotf-NMS算法實現代碼如下:
# coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
def soft_nms(boxes, sigma=0.5, Nt=0.1, threshold=0.001, method=1):N = boxes.shape[0]pos = 0maxscore = 0maxpos = 0for i in range(N):maxscore = boxes[i, 4]maxpos = itx1 = boxes[i,0]ty1 = boxes[i,1]tx2 = boxes[i,2]ty2 = boxes[i,3]ts = boxes[i,4]pos = i + 1# get max boxwhile pos < N:if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]:maxscore = boxes[pos, 4]maxpos = pospos = pos + 1# add max box as a detectionboxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0]boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1]boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2]boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3]boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4]# swap ith box with position of max boxboxes[maxpos,0] = tx1boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2boxes[maxpos,4] = tstx1 = boxes[i,0]ty1 = boxes[i,1]tx2 = boxes[i,2]ty2 = boxes[i,3]ts = boxes[i,4]pos = i + 1# NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below thresholdwhile pos < N:x1 = boxes[pos, 0]y1 = boxes[pos, 1]x2 = boxes[pos, 2]y2 = boxes[pos, 3]s = boxes[pos, 4]area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1)if iw > 0:ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1)if ih > 0:ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih)ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection boxif method == 1: # linearif ov > Nt:weight = 1 - ovelse:weight = 1elif method == 2: # gaussianweight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma)else: # original NMSif ov > Nt:weight = 0else:weight = 1boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4]print(boxes[:, 4])# if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box# update Nif boxes[pos, 4] < threshold:boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0]boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1]boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2]boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3]boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4]N = N - 1pos = pos - 1pos = pos + 1keep = [i for i in range(N)]return keep
boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 150, 168, 0.63],[166, 70, 312, 190, 0.55],[221, 250, 389, 500, 0.79],[12, 190, 300, 399, 0.9],[28, 130, 134, 302, 0.3]])
keep = soft_nms(boxes)
print(keep)
效果
下圖可以看出,基本可以獲得平均1%的提升,且不增加額外的訓練和計算負擔。






-可變形卷積)



)


)



)


