1.理論知識
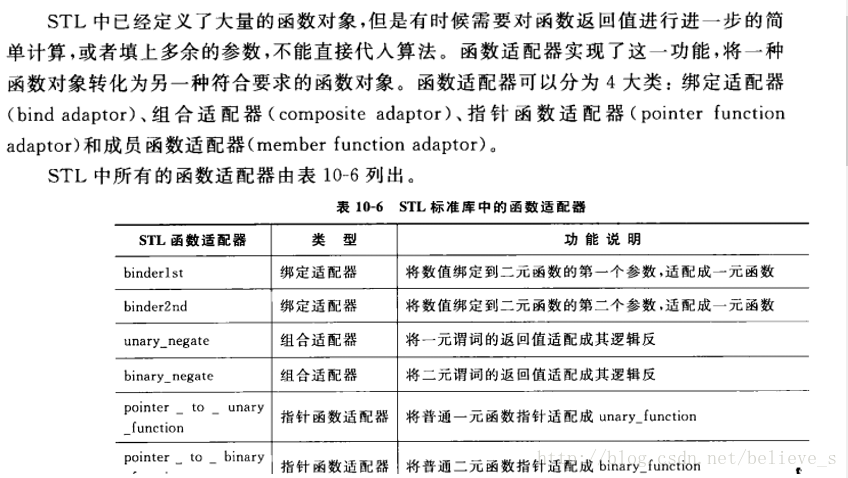

2.常用函數適配器
標準庫提供一組函數適配器,用來特殊化或者擴展一元和二元函數對象。常用適配器是:
1綁定器(binder):
binder通過把二元函數對象的一個實參綁定到一個特殊的值上,將其轉換成一元函數對象。C++標準庫提供兩種預定義的binder適配器:bind1st和bind2nd,前者把值綁定到二元函數對象的第一個實參上,后者綁定在第二個實參上。
2取反器(negator) :
negator是一個將函數對象的值翻轉的函數適配器。標準庫提供兩個預定義的ngeator適配器:not1翻轉預定義一元函數對象的真值,而not2翻轉二元謂詞函數的真值。
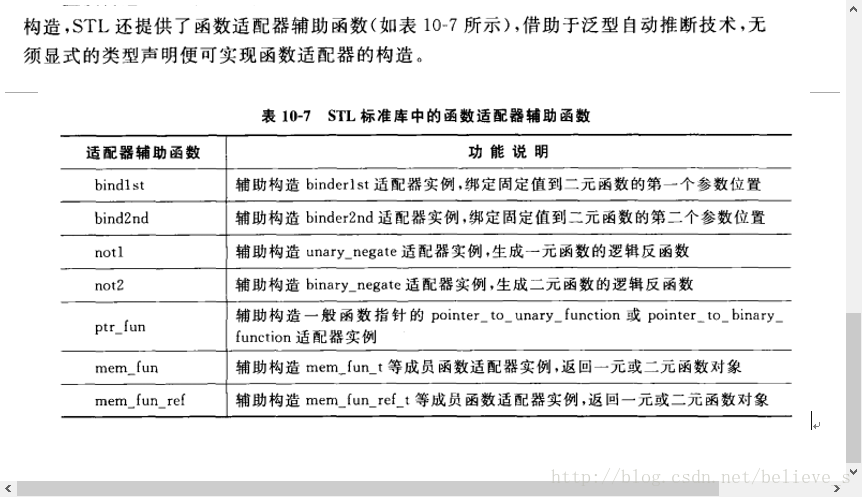
常用函數適配器列表如下:
bind1st(op, value)
bind2nd(op, value)
not1(op)
not2(op)
mem_fun_ref(op)
mem_fun(op)
ptr_fun(op)3.典型案例
class IsGreat
{
public:IsGreat(int i){m_num = i;}bool operator()(int &num){if (num > m_num){return true;}return false;}
protected:
private:int m_num;
};void main43()
{vector<int> v1;for (int i=0; i<5; i++){v1.push_back(i+1);}for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it!=v1.end(); it ++){cout << *it << " " ;}int num1 = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);cout << "num1:" << num1 << endl;//通過謂詞求大于2的個數int num2 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), IsGreat(2)); cout << "num2:" << num2 << endl;//通過預定義函數對象求大于2的個數 greater<int>() 有2個參數 // param > 2int num3 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(greater<int>(), 2 ) );cout << "num3:" << num3 << endl;//取模 能被2整除的數 求奇數int num4 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(modulus <int>(), 2 ) ); cout << "奇數num4:" << num4 << endl;int num5 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), not1( bind2nd(modulus <int>(), 2 ) ) ); cout << "偶數num5:" << num5 << endl;return ;
}4.預定義函數對象和適配器案例代碼
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;#include "string"
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include "set"
#include <algorithm>
#include "functional"//plus<int> 預定義好的函數對象 能實現不同類型的數據的 + 運算
//實現了 數據類型 和算法的分離 ===》通過函數對象技術實現的。。。。//思考:怎么樣知道 plus<type> 是兩個參數
void main21()
{/*template<class _Ty>struct plus: public binary_function<_Ty, _Ty, _Ty>{ // functor for operator+_Ty operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const{ // apply operator+ to operandsreturn (_Left + _Right);}};*/plus<int> intAdd;int x = 10; int y = 20;int z = intAdd(x, y); // x + y cout << "z:" << z << endl;plus<string> stringAdd;string s1 = "aaa";string s2 = "bbb";string s3 = stringAdd(s1, s2);cout << "s3:" << s3 << endl;vector<string> v1;v1.push_back("bbb");v1.push_back("aaa");v1.push_back("ccc");v1.push_back("zzz");v1.push_back("ccc");v1.push_back("ccc");/*template<class _Ty>struct greater: public binary_function<_Ty, _Ty, bool>{ // functor for operator>bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const{ // apply operator> to operandsreturn (_Left > _Right);}};*/sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<string>() );for (vector<string>::iterator it=v1.begin(); it!=v1.end(); it++){cout << *it << endl;}//求 ccc 出現的個數string sc = "ccc";//equal_to<string>() 有兩個參數 left參數來自容器,right參數來自sc//bind2nd函數適配器 :把預定義函數對象 和 第二個參數進行綁定int num = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(equal_to<string>(), sc) );cout << "num: " << num << endl;
}class IsGreat
{
public:IsGreat(int i){m_num = i;}bool operator()(int &num){if (num > m_num){return true;}return false;}
private:int m_num;
};void main22()
{vector<int> v1;for (int i=0; i<10; i++){v1.push_back(i+1);}for (vector<int>::iterator it=v1.begin(); it!=v1.end(); it++ ){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;int num1 = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);cout << "num1:" << num1 <<endl;//通過 謂詞 求大于2 的個數int num2 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), IsGreat(2));cout << "num2:" << num2 <<endl;/*template<class _Ty>struct greater: public binary_function<_Ty, _Ty, bool>{ // functor for operator>bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const{ // apply operator> to operandsreturn (_Left > _Right);}};*///通過 預定義的函數對象 求大于2 的個數//greater<int>() 有兩個參數 左參數來自容器的元素 ,右參數固定成2 (通過bind2nd做的)int num3 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd (greater<int>(), 2) );cout << "num3:" << num3 <<endl;//求 奇數的個數int num4 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd (modulus<int>(), 2) );cout << "奇數的個數num4:" << num4 <<endl;//求 偶數的個數 取反器(negator) int num5 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), not1( bind2nd (modulus<int>(), 2) ) );cout << "偶數的個數 num5:" << num5 <<endl;}
void main2222()
{//main21();main22(); //函數適配器綜合案例cout<<"hello..."<<endl;system("pause");return ;
}




)



![[Git高級教程 (一)] 通過 Tag 標簽回退版本修復 bug](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Git高級教程 (一)] 通過 Tag 標簽回退版本修復 bug)



![[Git高級教程(二)] 遠程倉庫版本回退方法](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Git高級教程(二)] 遠程倉庫版本回退方法)






