文章目錄
- Windows編程概述
- 獲取Windows
- 理解Windows消息機制
- 多任務
- 多線程
- 事件處理
- DirectX快速概覽
- Direct3D是什么
- Window程序基礎
- 創建第一個Win32項目
- 理解WinMain
- WinMain函數調用
- 完整的WinMain
- GetMessage函數調用
- 尋求幫助
Windows編程概述
DirectX,流行的游戲編程庫。它上手易,精通難。
Windows is a multi-tasking, multi-threaded operating system. What this means is that Windows can run many programs at the same time, and each of those programs can have several threads running as well. As you might imagine, this operating system architecture works well with multi-core processors.
獲取Windows
舊版本Windows的軟件(游戲除外,因PC規格日新月異)無需過多修改便可在新版本Windows運行。
Windows編程可簡可繁。
Windows是優秀多任務操作系統,因為它是消息驅動的。
理解Windows消息機制
外部事件,如鼠標單擊,會導致小的電信號從鼠標轉移到USB口再進入系統總線。Windows操作系統從系統總線拾取這一信號并且生成一個消息傳遞給正在運行的應用程序(比如我們的游戲),程序對這消息做出反應。
計算機的潛意識(處理所有時間處理邏輯的操作系統)將這一事件“呈現”給程序,讓其知曉。
DirectX 9舊版依然很好只在現在流行Windows7。
多任務
Windows使用搶占式任務preemptive multi-tasking。
This means that your PC can run many programs at the same time. Windows accomplishes this by running each program for a very short amount of time, counted in microseconds, or millionths of a second.
This jumping from one program to another very quickly is called time slicing時間分片, and Windows handles time slicing by creating a virtual address space (a small “simulated” computer) for each program in memory.
Each time Windows jumps to the next program, the state of the current program is stored so that it can be brought back again when it is that program’s turn to receive some processor time. This includes processor register values and any data that might be overwritten by the next process.
Then, when the program comes around again in the time-slicing scheme, these values are restored into the processor registers, and program execution continues where it left off. This happens at a very low level, at the processor register level, and is handled by the Windows core.
切換程序在人角度開看,是非常迅速的,不必擔心。
If this sounds like a wasteful use of processor cycles, you should be aware that during those few microseconds, the processor is able to run thousands of instructions. Modern processors already run at the gigaflop level, able to easily crunch a billion math calculations in a short “time slice.”
What this means is that the operating system has a very low-level core that manages the computer system. Preemptive搶占式 means that the operating system can preempt the functioning of a program, causing it to pause, and the operating system can then allow the program to start running again later.
When you have many programs and processes (each with one or more threads) begging for processor time, this is called a time-slicing system時間分片系統, which is how Windows works. As you might imagine, having a multi-processor system is a real advantage when you are using an operating system such as this.
多線程
Multi-threading is the process of breaking up a program into multiple threads, each of
which is like a separate program running. This is not the same as multi-tasking on the
system level 多任務不同于多線程. Multi-threading is sort of like multi-multi-tasking, where each program has running parts of its own, and those small program fragments are oblivious of the timeslicing system performed by the operating system.
As far as your main Windows program and all of its threads are concerned, they all have complete control over the system and have no “sense” that the operating system is slicing up the time allotted to each thread or process. Therefore, multi-threading means that each program is capable of delegating processes to its own mini-programs.
For instance, a chess program might create a thread to think ahead while the player is working on his next move. The “thought” thread would continue to update moves and counter-moves while waiting for the player. While this might just as easily be accomplished with a program loop that thinks while waiting for user input, the ability to delegate the process out to a thread might have significant benefits for a program.
Just as an example, you can create two threads in a Windows program and give each thread its own loop.
As far as each thread is concerned, its loop runs endlessly and it runs extremely fast, without interruption.
But at the system level, each thread is given a slice of processor time.
Depending on the speed of the processor and operating system, a thread may be interrupted 1,000 times per second, but the source code running in that thread will not be interrupted in any way.
Multi-threading is very useful for game programming.
多線程在游戲中的應用
The many tasks involved in a game loop might be delegated into separate threads that will execute independently, each one communicating with the main program.
A thread might be set up to handle screen updates automatically.
All the program would have to do then is update the double buffer with all of the objects on the screen, and the thread will do the work on a regular basis— perhaps even with timing built in so that the game will run at a uniform speed regardless of the processor.
All of the popular game engines today are multi-threaded (such as Unreal and Unity).
事件處理
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “How does Windows keep track of so many programs running at the same time?” Windows handles the problem,
- first of all, by requiring that programs be event-driven.
- Secondly, Windows uses system-wide messages to communicate.
Windows messages are small packets of data sent by the operating system to each running program with three primary features telling that program that some event has occurred:
- window handle,
- instance identifier,
- message type
The events will normally involve user input, such as a mouse click or key press, but might be from a communications port or a TCP/IP socket used by a networking library (which is used in multiplayer games).
Each Windows program must check every message that comes in through the message handler to determine whether the message is important. Messages that are not identified are sent along to the default message handler. (類比)Think of messages as fish—when you catch a fish that is too small or that you don’t like, you throw it back. But you keep the fish that you want.
It is similar in the Windows event-driven architecture; if your program recognizes a message that it wants to keep, that message is taken out of the message stream. Most of the messages will be key presses and mouse movement events (and they are still passed along even if you don’t need to use them).
(MyNote:個人認為它有點像壽司店回轉壽司臺)
Once you have experimented with Windows programming and have learned to handle some Windows messages, you will see how it was designed for applications, not games. The trick is learning to “tap into” the Windows messaging system and inject your own code, such as a DirectX initialization routine or a function call to refresh the screen.
All of the actions in a game are handled through the Windows messaging system; it is your job to intercept and deal with messages that are relevant to your game.
DirectX快速概覽
We’re not going to begin writing any DirectX code just yet, but I do want you to see how it works with Windows.
DirectX provides an interface to the low-level hardware of your PC, providing a consistent一致的 and reliable set of functions for games that tap into the hardware (such as a video card).
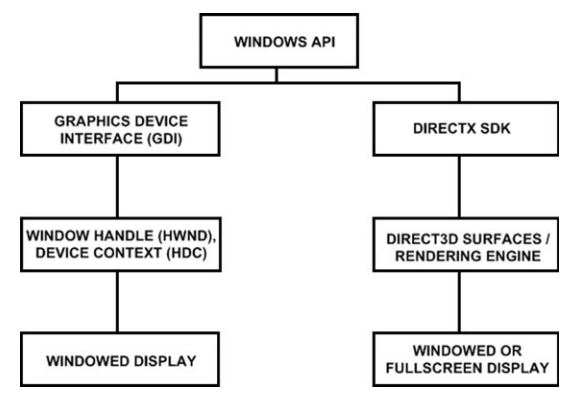
DirectX is closely integrated into Windows and will not work with any other OS, as it relies on the basic libraries in the Windows API to function. Here is a rundown梗概 of the DirectX components:
-
Direct3D is the rendering library that provides access to the video card to render 2D and 3D graphics. This is the most important component.
-
DirectSound is the audio library used to play digital samples loaded from wave files with a multi-channel audio mixer.
-
XACT is a newer audio library that supplements DirectSound.
-
DirectInput is the device input library used to access keyboard, mouse, and joystick游戲桿 devices.
-
XInput is an input library that provides support for an Xbox 360 controller connected via wireless adapter or USB port.
-
DirectPlay is the old networking library that is no longer supported.
Direct3D是什么
Since Direct3D is the most important component of DirectX. Direct3D handles all of the 2D and 3D rendering in a game.
In later chapters, you will learn Direct3D beginning and how to load an image into memory as a texture and then draw the texture (in 2D mode), as well as apply the texture when rendering a 3D model.
You can still program a 2D game using Direct3D or use 2D sprites to enhance a 3D game. You will need to display information on the screen with a 2D font, so learning how to draw 2D graphics is a necessity必要的. For the short term, a brief overview of 2D textures and sprites will help you to understand Direct3D when we explore 3D programming later on.
**Our primary goal is to learn about 2D and 3D rendering necessary to program a game.**My intent is not to try to make you into an expert game programmer, just to give you
enough information (and enthusiasm!) to take yourself to the next level and learn more
about this subject.
We will eventually get into rendering 3D models with texturing and lighting, but that’s pretty advanced, so we’ll spend most of our time learning about 2D sprite-based games. Have fun with the material!
**Try not to get bogged down in the details!**不要過分陷于細節中 Because the details of 3D game programming are complex, the average一般 beginner’s eyes tend to glaze over when hearing about vertex buffers頂點緩沖 and texture coordinates紋理坐標.
I can relate, because it takes time to build up to details like that when you’re just getting started. Honestly, it’s better to program a great 2D sprite精靈 game than a dull 3D game that just isn’t fun.
Window程序基礎
Every Windows program includes a function called WinMain at minimum. Most Windows programs also include a message handler function called WinProc that receives messages (such as key presses and mouse movement).
If you were writing a full-blown Windows application (for instance, a commercial software product like 3ds Max or Microsoft Word), then you would have a very large and complicated
WinProc function in the program to handle the many program states and events.
But in a DirectX program, you don’t really have to mess with events because your main
interest lies with the DirectX interfaces that provide their own functions for dealing with
events.
DirectX is mostly a polled輪詢 SDK, in that you must ask for data rather than having it
thrown at you (which is the case with WinProc). For instance, when you start learning
about DirectInput, you’ll find that keyboard and mouse input is mainly gathered by calling functions to see what values have changed.
(MyNote:DirectX 消息接收者主動輪詢才能得到信息。)
創建第一個Win32項目
項目實際上是一個管理程序中所有文件的文件。
Visual Studio Express 2013 for Windows Desktop 下載地址
安裝過程按照其安裝向導步驟安裝即可。
1.菜單欄FILE->New Project
2.選擇項目模板Installed,Visual C++,Win32->Win32 Project,并命名項目名,選后點擊OK

3.接下來是設置向導Overview,點擊Next
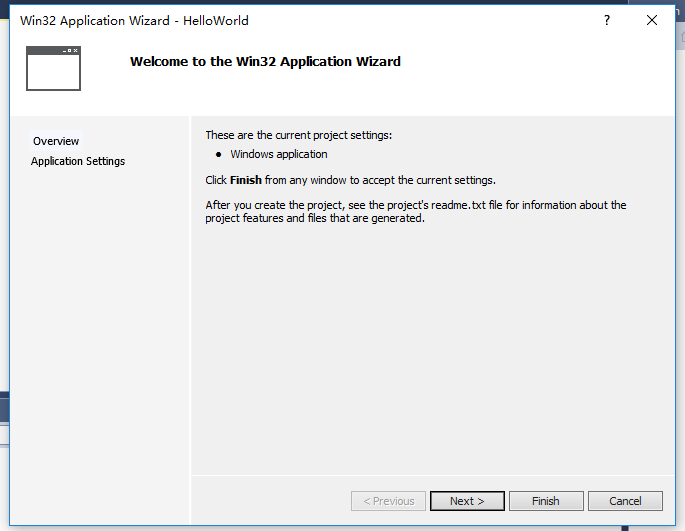
4.Application Settings中,勾選Empty project,不勾選Security Development Lifecycle(SDL)checks,點擊Finish。

5.添加一cpp源文件,菜單欄PROJECT->Add New Item,創建命名為main.cpp源文件。

6.輸入以下代碼:
#include <windows.h>int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nShowCmd)
{MessageBox(NULL, "Welcome to Windows Programming!","HELLO WORLD", MB_OK | MB_ICONEXCLAMATION);
}
這個程序僅僅在屏幕上顯示一個對話框。
一開始BUILD編譯時拋出error C2664: 'int MessageBoxW(HWND,LPCWSTR,LPCWSTR,UINT)' : cannot convert argument 2 from 'const char [32]' to 'LPCWSTR'
Now let’s resolve this error.
It has to do with the character set, which can be either ANSI (8-bit) or Unicode (16-bit). Unicode is important for localization—a software engineering term that refers to converting the text in a program to other languages. Not all languages need Unicode characters, but some do—such as Mandarin and Japanese.
We could write all of our code to support Unicode character strings, with funky code雞肋代碼 that is not part of the C++ standard (like the infamous “L” character and TCHAR). But we want to write standards-compliant software without special codes.
解決方法:
菜單欄PROJECT-> XXXProperties->Configuration Properties->General->Project Defaults->Character Set 選擇 Use Multi-Byte Character Set
編譯運行后結果:
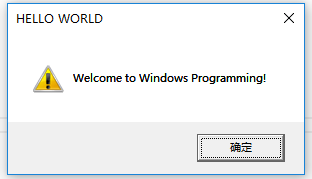
When you compile a C++ program with Visual Studio, the executable file(可執行文件exe) is usually written to a folder called Debug (inside your project’s folder).
理解WinMain
Every Windows program has a function called WinMain. WinMain is the Windows equivalent of the main function in console C++ programs, and is the initial entry point for a Windows program.
The most important function in your program will be WinMain, but after you have set up the messaging calls, you probably won’t come back to WinMain while working on other parts of the program.
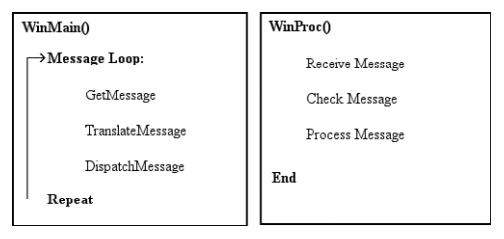
The WinMain function hasn’t changed much since 16-bit Windows 3.0 back in 1991. WinMain is like the foreman工頭 that tells the program what to work on. The job of WinMain is to set up the program, and then to set up the main message loop for the program. This loop processes all of the messages received by the program. Windows sends these messages to every running program.
Most of the messages will not be used by your program, and so the operating system doesn’t even send some messages to your program. Usually, WinMain will send messages over to another function called WinProc, which works closely with WinMain to process user input and other messages.
WinMain函數調用
int WINAPI WinMain( HINSTANCE hInstance,HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,LPTSTR lpCmdLine,int nCmdShow )
HINSTANCE hInstance. The first parameter identifies the instance of the program
being called, as a program may be run several times. hInstance tells the program
which instance is trying to run. If the program is run more than once, the
general practice is to just close the new instance rather than running the
program again.(MyNote:這句看得不太懂。)HINSTANCE hPrevInstance. The second parameter identifies the previous instance of
the program and is related to the first parameter. If hPrevInstance is NULL, then this
is the first instance of the program.LPTSTR lpCmdLine. The third parameter is a string that contains the command-line
parameters passed to the program. This could be used to tell the program to use
certain options.int nCmdShow. The last parameter specifies the options used when creating the
program window. 該參數可以是下列值之一:- SW_HIDE:隱藏窗口并且激活另外一個窗口。
- SW_MINIMIZE:最小化指定的窗口,并且激活在系統表中的頂層窗口。
- SW_RESTORE:激活并顯示窗口。如果窗口已經最小化或最大化,系統將以恢復到原來的尺寸和位置顯示窗口(與SW_SHOWNORMAL相同)。
- SW_SHOW:激活一個窗口并以原來的尺寸和位置顯示窗口。
- SW_SHOWMAXIMIZED:激活窗口并且將其最大化。
- SW_SHOWMINIMIZED:激活窗口并將其目標化。
- SW_SHOWMINNOACTIVE:將一個窗口顯示為圖標。激活窗口維持活動狀態。
- SW_SHOWNA:以窗口的當前狀態顯示窗口。激活窗口保持活動狀態。
- SW_SHOWNOACTIVATE:以窗口的最近一次的尺寸和位置顯示窗口。激活窗口維持激活狀態。
- SW_SHOWNORMAL:激活并顯示窗口。如果窗口最大化或最小化,系統將其恢復到原來的尺寸和位置(與SW_RESTORE相同)
You might have noticed that WinMain returns a value with the words int WINAPI in front of the function call. This is also standard practice and goes back to Windows 3.0.
A return value of zero indicates that the program never made it to the main loop and was terminated prematurely. Any non-zero value indicates success.
hInstance是程序的當前實例的句柄。在Windows這樣的多任務操作系統中,一個程序可以同時運行多個實例。不同的實例間需要彼此區別,句柄就是干這個的。
Link
HINSTANCE 實際是本模塊在內存中的首地址。
程序的資源如菜單 對話框 字符 串 光標等等 還有函數 導入導出表等,都存儲在本模塊里。
所以要使用這些資源必須知道首地址,然后根據預定義的 找到各個資源 。Link
完整的WinMain
Listed below is more of a standard version of WinMain that you will often see in app code.
This is just an example, not a complete project.
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,LPSTR lpCmdLine,int nCmdShow)
{//1. declare variables//The MSG variable is used by the GetMessage function to retrieve the details of each Windows message. MSG msg;// register the class// 還未介紹MyRegisterClass(hInstance);// initialize application// **This code uses the hInstance variable passed to WinMain by Windows**. The variable is then passed on to the InitInstance function. //InitInstance is located farther down in the program, and basically checks to see whether the program is already running and then creates the main program window.if (!InitInstance (hInstance, nCmdShow)) return FALSE;// main message loop// The while loop in this part of WinMain will continue to run forever unless a message to kill the program comes along.while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)){TranslateMessage(&msg);DispatchMessage(&msg);}return msg.wParam;
}
Even the simplest of graphics programs will need to process messages. Believe it or not, doing something as simple as printing “Hello World” on the screen requires that you wait for a message to come along for painting the screen.
Message handling does take some getting used to if you’re used to just calling a function when you need something (such as displaying text on the screen) done. (MyNote:不是”呼之即來揮之即去“易用性???)
GetMessage函數調用
-
LPMSG lpMsg. This parameter is a pointer to a MSG structure that handles the message
information. -
HWND hWnd. The second parameter is a handle to a specific window’s messages. If
NULL is passed, then GetMessage will return all of the messages for the current
instance of the program. -
UINT wMsgFilterMinandUINT wMsgFilterMax. These parameters tell GetMessage to
return messages in a certain range. The GetMessage call is the most crucial決定性的 line of code
in the entire Windows program! Without this single line in WinMain, your program
will be sensory-deprived感覺剝奪, unable to respond to the world.
The two core lines of code within the GetMessage loop work to process the message returned by GetMessage.
The Windows API Reference states that the TranslateMessage function is used to translate virtual-key messages into character messages, and then sent back through the Windows messaging system with DispatchMessage. These two functions will jointly set up the messages that you will expect to receive in WinProc (the window callback function) for your game window, such as WM_CREATE to create a window and WM_PAINT to draw the window.
I will cover WinProc in the next chapter. If you feel confused about Windows messaging, don’t worry about it, because this is just a precursor前導 to working with DirectX; once you have written a Windows message loop, you will not need to deal with it again, and you can focus on your DirectX code.
尋求幫助
If you need help with a Windows or DirectX function (such as Direct3DCreate9), highlight it in Visual Studio and press F1. This will bring up context-sensitive help in the default web browser by opening a Microsoft Developer Network web page with details about that function.
1-5)
:監聽Windows消息)
6-10)


:個人總結)
11-15)




:個人總結)

:單例模式)
)

》筆記(1 / 12):緒論)


》筆記(2 / 12):線性表)