本系列堅持格式:1個抖機靈算法+2個較簡單但是天秀的算法+1個較難天秀算法。
?
bogo排序
Bogo排序(Bogo-sort),又被稱為猴子排序,是一種惡搞排序算法。
將元素隨機打亂,然后檢查其是否符合排列順序,若否,則繼續進行隨機打亂,繼續檢查結果,直到符合排列順序。
Bogo排序的最壞時間復雜度為O(∞),一輩子也不能輸出排序結果,平均時間復雜度為O(n·n!)。
這讓我想到了另一個理論:猴子理論,只要讓一只猴子一直敲打計算機,理論上會有一天,它能敲出一本圣經出來,但是這個概率小到宇宙毀滅也很難敲出來。。
真的不知道這個排序應該叫做天才還是垃圾哈哈哈,但是閑的沒事的我就把他實現出來了。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};System.out.println("排序次數" + bogo(arr));for (int i : arr) {System.out.print(i + " ");}}public static int bogo(int[] arr) {int count = 0;while (!isOrdered(arr)) {shuffle(arr);count++;}return count;}// 判斷是否有序方法public static boolean isOrdered(int[] arr) {for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {if (arr[i - 1] > arr[i]) {return false;}}return true;}// 隨機排序方法public static void shuffle(int[] arr) {int temp;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {int j = (int) (Math.random() * arr.length);temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}}}
9是中國最大的數字嘛,我就把數組長度設為9,結果平均排序次數要60萬次,不知道我的運氣怎么樣哈哈,你們也試試吧?
?
然而,有個看似笑話的方法聲稱可以用O(n)實現Bogo排序,依照量子理論的平行宇宙解釋,使用量子隨機性隨機地重新排列元素,不同的可能性將在不同的宇宙中展開,總有一種可能猴子得到了正確的順序,量子計算機找到了這個宇宙后,就開始毀滅其他排序不成功的宇宙,剩下一個觀察者可以看到的正確順序的宇宙。
如果想要邁出這個看似荒誕,但令人無比興奮的"高效算法"的第一步,請先證明"平行宇宙解釋"的正確性。
位運算
關于位運算有很多天秀的技巧,這里舉一個例子。
給定一個非空整數數組,除了某個元素只出現一次以外,其余每個元素均出現兩次。找出那個只出現了一次的元素。
說明:你的算法應該具有線性時間復雜度。 你可以不使用額外空間來實現嗎?
示例 1:
輸入: [2,2,1]輸出: 1
示例?2:
輸入: [4,1,2,1,2]輸出: 4
思路:拿map,set,都不符合要求,那怎么辦呢?
我們知道什么數字和自己異或,都等于0.
什么數字和0異或,都等于它本身,
異或又符合交換律
所以全部異或一遍,答案就是那個出現一次的數字。
class Solution {public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {int ans = 0;for(int i :nums)ans ^= i;return ans;}
}有沒有被秒了?
?
打擂臺
給定一個大小為 n 的數組,找到其中的多數元素。多數元素是指在數組中出現次數大于?? n/2 ??的元素。
你可以假設數組是非空的,并且給定的數組總是存在多數元素。
把狂野般的思緒收一收,咱們來看看最優解。
class Solution {public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {int count = 0;//當前答案出現的次數Integer candidate = null;//答案for (int num : nums) {if (count == 0) candidate = num;count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1;}return candidate;}
}我來解釋一下策略:記錄當前的答案candidate ,記錄count。這時,我們遍歷了一個新的數字,如果和candidate 一樣,我們就讓count+1,否則讓count-1.如果count變成了0,那candidate 就下擂臺,換新的擂主(數字)上,也就是說把candidate 更新成新的數字,count也更新成1.
最后在擂臺上的一定是答案。
肯定有人懷疑這個做法的正確性吧?我就來說一下它為啥對?
首先,我們想像一下對最終隱藏答案ans最不利的情況:每個其他數字全部都打擂這個答案ans,那ans的count最后也會剩1,不會被打下來。
正常情況呢?其他數字還會互相打擂,這些數字如此“內耗”,又怎么能斗得過最終答案ans呢?對不對?
?
morris遍歷
通常,實現二叉樹的前序(preorder)、中序(inorder)、后序(postorder)遍歷有兩個常用的方法:一是遞歸(recursive),二是使用棧實現的迭代版本(stack+iterative)。這兩種方法都是O(n)的空間復雜度(遞歸本身占用stack空間或者用戶自定義的stack),我分別給出一個例子
遞歸:
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{if(BT==NULL)return ;printf(" %c", BT->Data);PreorderTraversal(BT->Left);PreorderTraversal(BT->Right);
}非遞歸:
*p=root;
while(p || !st.empty())
{if(p)//非空{//visit(p);進行操作st.push(p);//入棧p = p->lchild;左} else//空{p = st.top();//取出st.pop();p = p->rchild;//右}
}為啥這個O(n)的空間就是省不掉呢?因為我們需要空間來記錄之前的位置,好在遍歷完了可以回到父節點。所以這個空間是必須的!如下圖:

比如我們遍歷2,想遍歷4,這時候我們要保證遍歷完4以后,還能回到2,我們好去繼續遍歷5等等結點,所以必須花空間記錄。
?
但是,還就有這么一種算法,能實現空間O(1)的遍歷,服不服。
你們可能會問,你剛說的,必須有空間來記錄路徑,怎么又可以不用空間了呢?
這就是morris遍歷,它其實是利用了葉子節點大量的空余空間來實現的,只要把他們利用起來,我們就可以省掉額外空間啦。
我們不說先序中序后序,先說morris遍歷的原則:
1、如果沒有左孩子,繼續遍歷右子樹,比如:

這個2就沒有左孩子,這時直接遍歷右孩子即可。
2、如果有左孩子,找到左子樹最右節點。
比如上圖,6就是2的最右節點。
? ? 1)如果最右節點的右指針為空(說明第一次遇到),把它指向當前節點,當前節點向左繼續處理。
修改后:
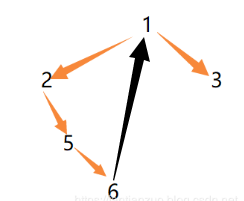
? ? 2)如果最右節點的右指針不為空(說明它指向之前結點),把右指針設為空,當前節點向右繼續處理。
?
這就是morris遍歷。
請手動模擬深度至少為4的樹的morris遍歷來熟悉流程。
下面給出實現:
定義結點:
public static class Node {public int value;Node left;Node right;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}先序:(完全按規則寫就好。)
//打印時機(第一次遇到):發現左子樹最右的孩子右指針指向空,或無左子樹。public static void morrisPre(Node head) {if (head == null) {return;}Node cur1 = head;Node cur2 = null;while (cur1 != null) {cur2 = cur1.left;if (cur2 != null) {while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {cur2 = cur2.right;}if (cur2.right == null) {cur2.right = cur1;System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");cur1 = cur1.left;continue;} else {cur2.right = null;}} else {System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");}cur1 = cur1.right;}System.out.println();}morris在發表文章時只寫出了中序遍歷。而先序遍歷只是打印時機不同而已,所以后人改進出了先序遍歷。至于后序,是通過打印所有的右邊界來實現的:對每個有邊界逆序,打印,再逆序回去。注意要原地逆序,否則我們morris遍歷的意義也就沒有了。
完整代碼:?
public class MorrisTraversal {public static void process(Node head) {if(head == null) {return;}// 1//System.out.println(head.value);process(head.left);// 2//System.out.println(head.value);process(head.right);// 3//System.out.println(head.value);}public static class Node {public int value;Node left;Node right;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}//打印時機:向右走之前public static void morrisIn(Node head) {if (head == null) {return;}Node cur1 = head;//當前節點Node cur2 = null;//最右while (cur1 != null) {cur2 = cur1.left;//左孩子不為空if (cur2 != null) {while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {cur2 = cur2.right;}//找到最右//右指針為空,指向cur1,cur1向左繼續if (cur2.right == null) {cur2.right = cur1;cur1 = cur1.left;continue;} else {cur2.right = null;}//右指針不為空,設為空}System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");cur1 = cur1.right;}System.out.println();}//打印時機(第一次遇到):發現左子樹最右的孩子右指針指向空,或無左子樹。public static void morrisPre(Node head) {if (head == null) {return;}Node cur1 = head;Node cur2 = null;while (cur1 != null) {cur2 = cur1.left;if (cur2 != null) {while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {cur2 = cur2.right;}if (cur2.right == null) {cur2.right = cur1;System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");cur1 = cur1.left;continue;} else {cur2.right = null;}} else {System.out.print(cur1.value + " ");}cur1 = cur1.right;}System.out.println();}//逆序打印所有右邊界public static void morrisPos(Node head) {if (head == null) {return;}Node cur1 = head;Node cur2 = null;while (cur1 != null) {cur2 = cur1.left;if (cur2 != null) {while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {cur2 = cur2.right;}if (cur2.right == null) {cur2.right = cur1;cur1 = cur1.left;continue;} else {cur2.right = null;printEdge(cur1.left);}}cur1 = cur1.right;}printEdge(head);System.out.println();}
//逆序打印public static void printEdge(Node head) {Node tail = reverseEdge(head);Node cur = tail;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.value + " ");cur = cur.right;}reverseEdge(tail);}
//逆序(類似鏈表逆序)public static Node reverseEdge(Node from) {Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (from != null) {next = from.right;from.right = pre;pre = from;from = next;}return pre;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(4);head.left = new Node(2);head.right = new Node(6);head.left.left = new Node(1);head.left.right = new Node(3);head.right.left = new Node(5);head.right.right = new Node(7);morrisIn(head);morrisPre(head);morrisPos(head);}})
通過docker安裝)
)
-)
)
-)

 ubuntu16.04 安裝方法)

-深度推薦模型-AutoRec、DeepCrossing、NeuralCF、PNN、WideDeep、FNN、DeepFM、NFM)
)

)
-)

-注意力機制+深度推薦模型、強化學習推薦系統)


)
