python 面試問題
Interview questions are quite tricky to predict. In most cases, even peoples with great programming ability fail to answer some simple questions. Solving the problem with your code is not enough. Often, the interviewer will expect you to have depth knowledge in a particular domain. One must have knowledge of internal mechanisms of the programming concepts. This article will help you to understand the most important concepts in Python.
面試問題很難預測。 在大多數情況下,即使編程能力強的人也無法回答一些簡單的問題。 解決您的代碼問題還不夠。 面試官通常會希望您對特定領域有深入的了解。 必須了解編程概念的內部機制。 本文將幫助您了解Python中最重要的概念。
Let’s get started with the questions.
讓我們開始思考這些問題。
1.為什么Python被稱為解釋語言? (1. Why Python is called as Interpreted language?)
Many books state that Python is an interpreted language. A programming language follows any one of the two approaches to implement the code. The approaches are compilation and interpretation. Some languages follow both concepts.
許多書指出Python是一種解釋語言。 編程語言遵循兩種方法中的任何一種來實現代碼。 這些方法是編譯和解釋。 某些語言遵循這兩個概念。

During compilation, the entire source code is converted into machine code. Machine code is understandable by the CPU. The program will be executed only if the entire code is compiled successfully.
在編譯期間,整個源代碼都將轉換為機器代碼。 CPU可以理解機器代碼。 僅在成功編譯整個代碼后,程序才會執行。
In interpretation, the code is executed line by line. Each line of source code in Python is translated into machine code during the execution. There is a Virtual Machine available to interpret the python code. The compilation and interpretation runtime structure is given in the above diagram.
在解釋中,代碼是逐行執行的。 在執行過程中,Python中的每一行源代碼都會轉換為機器代碼。 有一個虛擬機可用于解釋python代碼。 上圖中給出了編譯和解釋運行時結構。
2.什么是動態類型語言? (2. What is dynamically typed language?)
It is one of the behaviors of high level programming language to check the type of data stored in a variable during the execution. In programming languages such as C, we must declare the type of data before using it.
在執行過程中檢查存儲在變量中的數據類型是高級編程語言的行為之一。 在諸如C的編程語言中,我們必須在使用數據之前聲明數據的類型。

Python do not requires and declaration of data type. The python interpreter will know the data type when we assign a value to a variable. This is why python is known as dynamically typed language.
Python不需要數據類型的聲明。 當我們給變量賦值時,python解釋器會知道數據類型。 這就是為什么python被稱為動態類型語言的原因。
3. Python中的PEP8是什么? (3. What is PEP8 in Python?)
Python known for its readability. In most cases, we can understand the python code better than any other programming languages. Writing beautiful and readable code is an art. PEP8 is an official style guide given by the community to improve the readability to the top.
Python以可讀性著稱。 在大多數情況下,我們可以比其他任何編程語言更好地理解python代碼。 編寫漂亮且可讀的代碼是一門藝術。 PEP8是社區提供的官方樣式指南,旨在提高頂部的可讀性。
“The code is read much more often than it is written”
“代碼被讀取的次數要多于其編寫的次數”
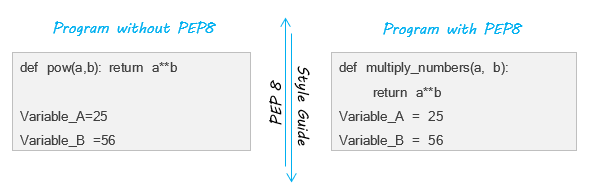
PEP8 enables you to write the python code more effective. Some naming conventions and comments will be helpful to share your code with other people to understand the code better.
PEP8使您可以更有效地編寫python代碼。 一些命名約定和注釋將有助于與其他人共享您的代碼以更好地理解代碼。
4. Python的內存管理系統如何工作? (4. How Python’s memory management system works?)
A python program will contain many objects and data types in it. Allocating memory for each object is must. In python heap spaces are used to store data chunks. CPython contains a memory manager that manages the heap space in memory.
python程序中將包含許多對象和數據類型。 必須為每個對象分配內存。 在python中,堆空間用于存儲數據塊。 CPython包含一個內存管理器,用于管理內存中的堆空間。
Managing memory is an important thing in a program. The memory allocation determines the performance of the program. Python’s memory manager handles sharing of information, data caching and garbage collection, etc. This memory manager contains automatic garbage collection.
管理內存在程序中很重要。 內存分配決定了程序的性能。 Python的內存管理器處理信息共享,數據緩存和垃圾回收等。此內存管理器包含自動垃圾回收。
5.什么是可變性? 每種數據類型有何不同? (5. What is mutability? How it differs in each data types?)
The ability of a python object to change itself is called mutability. All objects in python are either mutable or immutable. Once created the immutable objects cannot be changed. But, the mutable objects can be changed.
python對象改變自身的能力稱為可變性。 python中的所有對象都是可變的或不可變的。 一旦創建了不變的對象就無法更改。 但是,可變對象可以更改。
Let us try to check the mutability of two different type of objects in Python.
讓我們嘗試檢查Python中兩種不同類型的對象的可變性。
List - Mutable object
列表-可變對象
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
my_list[2] = 7
print(my_list)Output
輸出量
[1, 2, 7, 4, 5]Tuple - Immutable object
元組-不可變對象
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
my_tuple[2] = 7
print(my_tuple)Output
輸出量
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 2, in <module>
my_tuple[2] = 7
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment6. Python中的命名空間是什么? (6. What is Namespace in Python?)
Name is an identifier given to an object in Python. Every object in python is associated with a particular name. For example, when we assign the value 9 to a variable name number , the object that holds the number is associated with the name number.
名稱是在Python中賦予對象的標識符。 python中的每個對象都與一個特定的名稱相關聯。 例如,當我們將值9分配給變量名稱number ,保存該數字的對象與name number相關聯。
Namespace is a collection of names associated with every object in Python. The namespace contains all the isolated names and created when we executing the program. As the namespace contains the useful keywords and methods, we can access the , methods easily. The namespace stack controls the scope of variables in python.
命名空間是與Python中每個對象關聯的名稱的集合。 命名空間包含所有隔離的名稱,并在我們執行程序時創建。 由于名稱空間包含有用的關鍵字和方法,因此我們可以輕松地訪問方法。 命名空間堆棧控制python中變量的范圍。
7. System中的空執行是什么? (7. What is null execution in System?)
In python, the keyword pass is used to create a statement that do nothing. If someone need to create a function with null operation then we can use the pass statement.
在python中,關鍵字pass用于創建不執行任何操作的語句。 如果有人需要使用null操作創建函數,則可以使用pass語句。
We can create null function to check whether it works or not. If you are going to develop the implementation steps in a function in future, we can use pass statement in it.
我們可以創建null函數來檢查它是否有效。 如果將來要在某個函數中開發實現步驟,則可以在其中使用pass語句。
Don’t get confused with comments. Comments and pass statements are different things. The interpreter ignores the comments in a program whereas pass statement do null operation.
不要與評論混淆。 注釋和通過語句是不同的東西。 解釋器忽略程序中的注釋,而pass語句則執行空操作。
The following program is using pass statement in it.
以下程序在其中使用pass語句。
def function():
pass
function()8.什么是字符串切片? (8. What is string slicing?)
String slicing is the process of making subsets from strings. We can pass a range in the following syntax to slice the string.
字符串切片是從字符串中產生子集的過程。 我們可以使用以下語法傳遞范圍以對字符串進行切片。
Syntax: string[start:end:step]
語法: 字符串[開始:結束:步驟]
Consider the string “Hello World”. We can slice the string using the range values. To print ‘Hello’ from the string. Our range should be 0 to 5. The slicing creates sub string from start index to end-1 th index.
考慮字符串“ Hello World”。 我們可以使用范圍值對字符串進行切片。 從字符串中打印“ Hello”。 我們的范圍應為0到5。切片將創建從start索引到第end-1個end-1索引的子字符串。
string = "Hello World"
print(string[0:5:1])
print(string[6:11:1])Output
輸出量
Hello
World9.用Python連接兩個字符串的方法是什么? 哪個更好? (9. What are the ways to concatenate two strings in Python? Which is better?)
We can use join() or + for concatenating two or more strings. The following codes will explain how to use those methods in Python.
我們可以使用join()或+連接兩個或多個字符串。 以下代碼將說明如何在Python中使用這些方法。
string_1 = "Hello"
string_2 = "World"
print(string_1 + string_2)
print(''.join([string_1, string_2]))Output
輸出量
HelloWorld
Hello WorldComparing the both methods using join method is good choice. When we need to create a sentence from more than two strings we should use + each time. Join method is helpful to join an iterable with more strings in it.
比較使用join方法的兩種方法是不錯的選擇。 當我們需要用兩個以上的字符串創建一個句子時,我們應該每次使用+ 。 Join方法有助于連接其中包含更多字符串的迭代器。
10. Python中的裝飾器是什么? (10. What is decorator in Python?)
Decorator is tool that allows us to modify the behavior of a function or a class. The decorator objects are called just before the function that you want modify.
裝飾器是允許我們修改函數或類的行為的工具。 裝飾器對象在要修改的函數之前調用。
11. Python中的生成器是什么? (11. What is generator in Python?)
Generator is a method to create iterable objects in python. Creating generators are same as creating functions. Instead of return statement we have to use yield in generator function. It returns iterating object each time it is called.
Generator是在python中創建可迭代對象的方法。 創建生成器與創建函數相同。 代替return語句,我們必須在生成器函數中使用yield。 每次調用它都會返回迭代對象。
12. Python中的lambda表達式是什么? (12. What is lambda expression in Python?)
Lambda is an anonymous function that helps us to create functions in single line of code. This is an important thing in functional programming. The lambda function should contains only one expressions in it.
Lambda是一個匿名函數,可以幫助我們在單行代碼中創建函數。 這在函數式編程中很重要。 lambda函數中應僅包含一個表達式。
Syntax: lambda arguments : expression
語法: lambda參數:表達式
Y = lambda X : X*5
print(Y(7))Output
輸出量
3513.如何用逗號分隔的輸入列出清單? (13. How to make a list from comma separated inputs?)
To make a list from a comma separated values or string we can use split method. Split method splits the comma separated values by taking comma as dilimeter.
要使用逗號分隔的值或字符串列出列表,我們可以使用split方法。 拆分方法將逗號分隔為逗號分隔值。
a = "A,B,C,D,E"
print(a.split(','))Output
輸出量
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']14.普通分隔和地板分隔有什么區別? (14. What is the difference between normal division and floor division?)
The arithmetic operators contains two different types of division operators. One is normal division \ another one is \\ . The normal division returns the float value as result. The floor division returns the whole number as result.
算術運算符包含兩種不同類型的除法運算符。 一個是普通除法\另一個是\\ 。 普通除法返回浮點值作為結果。 樓層劃分返回整數結果。
a = 5
b = 2
print(a/b)
print(a//b)Output
輸出量
2.5
215. Python中'is'和'=='有什么區別? (15. What is the difference between ‘is’ and ‘==’ in Python?)
We use is and == to comparing to objects. But both works in different manner. The == compares the values of two objects whereas the is keyword checks whether two objects are same or not.
我們使用is和==與對象進行比較。 但是兩者的工作方式不同。 ==比較兩個對象的值,而is關鍵字檢查兩個對象是否相同。
Using == in Python
在Python中使用==
a = [1, 3, 5]
b = [1, 3, 5]c = a #Copy of a in cprint(a==b) #Same Values but different objects
print(a==c) #Same Values Same objectsOutput
輸出量
True
TrueUsing is in Python
使用is在Python
a = [1, 3, 5]
b = [1, 3, 5]c = a #Copy of a in cprint(a is b) #Same Values but different objects
print(a is c) #Same Values Same ObjectsOutput
輸出量
False
True16. Python中的List和Tuple有什么區別? (16. What are the difference between List and Tuple in Python?)
- List is enclosed by brackets whereas the tuples are created using parenthesis. 列表用方括號括起來,而元組使用括號創建。
- The effectiveness of tuple is higher than the list. So it works faster. 元組的有效性高于列表。 因此它工作更快。
- The list is mutable object whereas the tuples are immutable objects. 該列表是可變對象,而元組是不可變對象。
17.什么是Python中的負取整? (17. What is negative rounding in Python?)
We know that the round keyword in python is used to to rounding of decimal places. It can be used to round off whole numbers sing negative rounding. Let the value of the variable X be 1345. To make is 1300 we have use negative rounding.
我們知道python中的round關鍵字用于舍入小數位。 可以使用負數舍入來舍入整數。 假設變量X的值為1345。為了使值為1300,我們使用了負取整。
X = 1345
print(round(X,-2))Output
輸出量
130018.如何防止以下代碼異常? (18. How do you prevent the following code from exception?)
def function():
a = 5
function()
print(a)The scope of the variable a is inside the function. To access the variable across the program we have declare it as global variable.
變量a的范圍在函數內部。 要在程序中訪問變量,我們已將其聲明為全局變量。
def function():
global a
a = 5
function()
print(a)Output
輸出量
519.在Python中交換兩個變量的獨特方法是什么? (19. What is the unique way to swap two variables in Python?)
Python has unique way to swap two variables. The swapping can be done in one line of code. Let the values of the variables a and b be 5 and 6 respectively. The swapping program will be the following.
Python具有交換兩個變量的獨特方法。 交換可以在一行代碼中完成。 令變量a和b的值分別為5和6。 交換程序如下。
a = 5
b = 6
a,b = b,a
print(a)
print(b)Output
輸出量
6
520. Python中的迭代器是什么? (20. What are Iterators in Python?)
The objects in python that implements the iterator protocols are called iterators. iter is the keyword used to create the iterable objects. It iterates throough various iterable objects such as List, dictionary.
python中實現迭代器協議的對象稱為迭代器。 iter是用于創建可迭代對象的關鍵字。 它遍歷各種可迭代對象,例如List,Dictionary。
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
my_iterator = iter(my_list)print(next(my_iterator))
print(next(my_iterator))
print(next(my_iterator))Output
輸出量
1
2
321. Python中的淺表復制和深表復制有什么區別? (21. What is the difference between shallow copy and deep copy in Python?)
In python, when we assign a value of a variable to another variable using assignment operator we are just creating a new variable associated with the old object. The copy module in python contains two different type of copying method called copy and deepcopy.
在python中,當我們使用賦值運算符將一個變量的值分配給另一個變量時,我們只是在創建一個與舊對象關聯的新變量。 python中的copy模塊包含兩種不同類型的復制方法,分別稱為copy和deepcopy 。
Shallow Copy
淺拷貝
The shallow copy works same as the assignment operator. It just create a new variable that is associated with the old object.
淺表副本的工作方式與賦值運算符相同。 它只是創建一個與舊對象關聯的新變量。
import copy
my_list = [[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3]]
new_list = copy.copy(my_list)
new_list[2][2] = 50print(my_list)
print(new_list)Output
輸出量
[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 50]]
[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 50]]Deep Copy
深拷貝
The deep copy method creates independent copy of an object. If we edit the element in a copied object, that does not affect the other object.
深層復制方法創建對象的獨立副本。 如果我們在復制的對象中編輯元素,則不會影響其他對象。
import copy
my_list = [[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3]]
new_list = copy.deepcopy(my_list)
new_list[2][2] = 50print(my_list)
print(new_list)Output
輸出量
[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3]]
[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 50]]22.如何在Python中生成隨機數? (22. How to generate random numbers in Python?)
There is no in-bulit function in python to generate random numbers We can use random module for this purpose. We can create random number from a range or list. randint is the simple method used to create a random number between two numbers.
python中沒有inbulit函數來生成隨機數。為此,我們可以使用random模塊。 我們可以從范圍或列表中創建隨機數。 randint是用于在兩個數字之間創建隨機數的簡單方法。
import random
print( random.randint(0,9))Output
輸出量
123.如何禁用字符串中的轉義序列? (23. How to disable the escape sequences in a string?)
The escape sequences in a string can be disabled using regular expression in Python. The raw output of string can be printed using formatting. The following code will show you the process of printing raw string.
可以使用Python中的正則表達式禁用字符串中的轉義序列。 字符串的原始輸出可以使用格式打印。 以下代碼將向您展示打印原始字符串的過程。
import re
print(r'Hi.\nThis is \t a String') Output
輸出量
Hi.\nThis is \t a String24.什么是負索引? (24. What is negative indexing?)
Python allows us to access the string and list objects using negative indexes. The negative index of 0th index is -len(iterable). If a string contains five characters then the first character can be accessed with the help of 0 and -5. The last character of the string points to -1.
Python允許我們使用負索引訪問字符串和列表對象。 第0個索引的負索引是-len(iterable)。 如果字符串包含五個字符,則可以使用0和-5訪問第一個字符。 字符串的最后一個字符指向-1。
my_string = "Hello"
print(my_string[-1])
print(my_string[-5])Output
輸出量
o
H26.如何在Python中創建多行字符串? (26. How to create multi line string in Python?)
We can use the escape character \n to split the strings in the output console. But, to write a string in multiple lines inside the code we need to use triple quotes.
我們可以使用轉義符\ n在輸出控制臺中分割字符串。 但是,要在代碼內的多行中編寫字符串,我們需要使用三引號。
my_string = """Hello.
This is a multi line string"""print(my_string)Output
輸出量
Hello.
This is a multi line string27.如何在Python中創建私有數據? (27. How to create private data in Python?)
Not like other object oriented programming languages such as java an C++ , Python does not have any keywords to define public and protected data. Normally, the objects created in python can be accessed by public members.
與其他面向對象的編程語言(例如Java C ++)不同,Python沒有任何關鍵字來定義公共數據和受保護數據。 通常,公共成員可以訪問在python中創建的對象。
Protected members can be accessed only by the class and its sub classes. The following code examples shows that how the private and public members works in python.
受保護的成員只能由該類及其子類訪問。 以下代碼示例顯示了私有成員和公共成員如何在python中工作。
Program with public member
與公眾成員一起計劃
class emp:
def __init__(self, s):
self.salary = s
t = emp(25000)
t.salary = 30000
print(t.salary)Output
輸出量
30000Program with private member
私人會員計劃
class emp:
def __init__(self, s):
self.__salary = s
t = emp(25000)
print(t.__salary)Output
輸出量
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 5, in <module>
print(t.__salary)
AttributeError: 'emp' object has no attribute '__salary'28.什么是酸洗和酸洗? (28. What is pickling and unpickling?)
Pickle is a module in Python that converts a python object and converts the object into string representation and the string is further converted into a file using dump method.
Pickle是Python中的一個模塊,可轉換python對象并將對象轉換為字符串表示形式,然后使用dump方法將字符串進一步轉換為文件。
Unpickling is the exact opposite to the process of pickling. The file created is converted into the old version of python object. The following code contains both pickling and unpickling methods.
與酸洗過程完全相反。 創建的文件將轉換為舊版本的python對象。 以下代碼包含酸洗和解酸方法。
import pickle
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
with open("my_file.out", "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(my_list,f)
with open("my_file.out", "rb") as f:
my_new_list = pickle.load(f)
if(my_list == my_new_list):
print("The objects are same")Output
輸出量
The objects are same29. Python中的Frozenset是什么? (29. What is frozenset in Python?)
The immutable and hashable version of a normal set is called frozenset. It possess all the properties of normal sets in python. The updating the set is not possible in frozenset.
普通集的不可變和可哈希化版本稱為Frozenset。 它具有python中常規集的所有屬性。 在Frozenset中無法更新集。
30. Python提供了哪些函數式編程概念? (30. What are the functional programming concepts available in Python?)
Splitting a program into multiple parts is called functional programming. It is one of the widely used programming paradigm. The functional programming concepts that are available as in built features in Python are zip , map , filter and reduce .
將程序分為多個部分稱為功能編程。 它是廣泛使用的編程范例之一。 Python的內置功能中可用的功能編程概念是zip , map , filter和reduce 。
Thank you all for reading this article. I hope it will help you to learn something.
謝謝大家閱讀本文。 我希望它將幫助您學習一些東西。
翻譯自: https://towardsdatascience.com/30-python-interview-questions-that-worth-reading-63b868e682e5
python 面試問題
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。 如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/390983.shtml 繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/390983.shtml 英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/390983.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!













和==)




