2 Process Scheduling
>Type of scheduling
>Scheduling Criteria (準則)
>Scheduling Algorithm
>Real-Time Scheduling (嵌入式系統)
?
2.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture you should be able to
·Explain what is Response Time 響應時間--分時系統
???Turnaround Time 周轉時間--批處理系統
???Deadlines 截止時間--實時系統
???Throughput 吞吐量--批處理系統
·理解進程調度的目標、類型、原則
·理解Decision Mode:Non-preemptive 非剝奪 ?Preemptive 剝奪
·理解經典的調度算法
FCFS
Round Robin
Shortest Process Next ?需估計
Shortest Remaining Time Next ?需估計
Highest Response Ratio Next ?工程上難實現
Feed Back
·理解Real--Time System 及 類型
·理解掌握 Real--Time Scheduling
???Deadline Scheduling
???Rate Monotonic Scheduling (速度調節)
?
Type of Scheduling
Aim of Scheduling
·Response Time 響應時間 分時系統
·Throughout 系統吞吐量 批處理系統
·效率
·公平
?
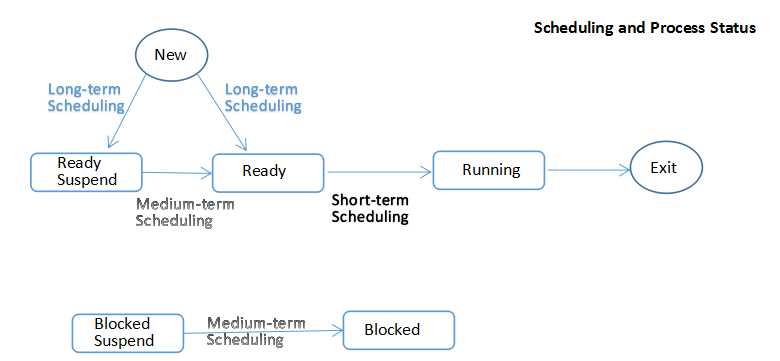
2.2 Types of Scheduling
·按OS的類型劃分:
批處理調度、分時調度、實時調度、多處理機調度
·按OS的層次劃分
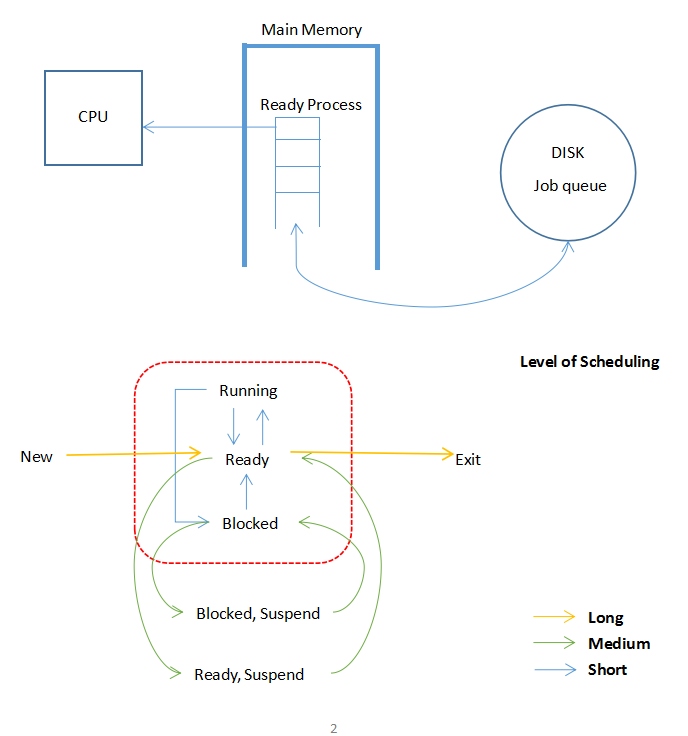
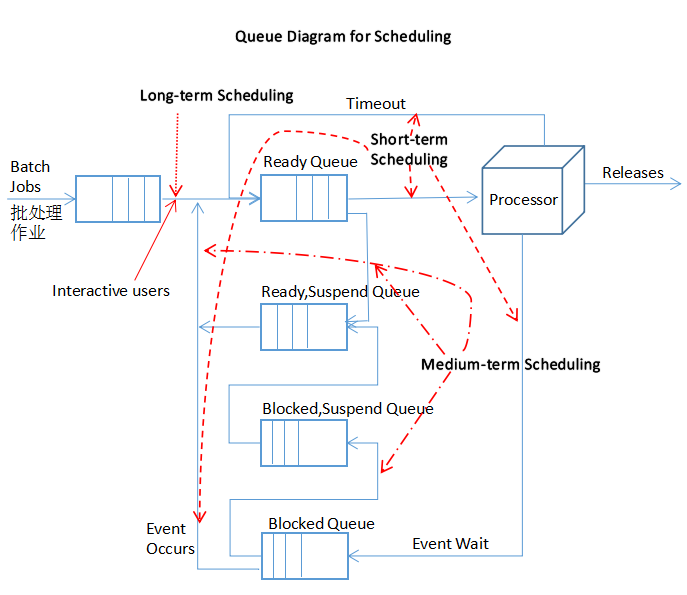
Long-term Scheduling 長程調度 ? ?作業-->進程
Medium-term Scheduling 中程調度 ?進程在內存中的調度
Short-term Scheduling 短程調度 ? ?Swap調度
?
??
Long-term Scheduling
頻率較低,通常幾分鐘一次,甚至更久
又稱高級調度,作業調度,它為被調度作業或用戶程序創建進程,分配必要的系統資源,并將新創建的進程插入就緒隊列,等待Short-term Scheduling.
·Determines which?programs are admitted to the system for processing.
這取決于調度算法,如FCFS、短作業優先、基于優先權、響應比高者優先等調度算法。
·How many?programs are admitted to the system?
---controls the degree of multi-programming.
·When does the scheduler be invoked?
---Each time a job terminates.
---Processor is idle exceeds a certain threshold.
?
Medium-term Scheduling
又稱中級調度,它調度換出到磁盤的進程進入內存,準備執行
·中程調度配合對換技術使用;
·其目的是為了提高內存的利用率和系統吞吐量;
·在多道程序度允許的情況下,從外存選擇一個掛起狀態的進程調度到內存(換入)
?Short-term Scheduling
·又稱為進程調度,低級調度,調度內存中的就緒狀態執行。
·know as the dispatcher ?決定就緒隊列which進程將獲得處理機
·Executes most frequently
· Invoked when an event occurs
---Clock interrupts
---IO interrupts
---Operating System calls
---Signals(信號)
?
進程調度程序主要功能
1、選擇占有處理機進程;
2、進程上下文切換。
?
進程調度依據的算法與系統的設計目標相一致。
對不同的系統,通常采用不同的調度算法。
批處理:短作業進程優先 ?目標:增加系統吞吐量,提高系統資源利用率
分時:時間片輪轉 ?目標:保證每個用戶能容忍的響應時間
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————?
2.3 Scheduling Criteria
面向用戶
面向系統
?
User-oriented
·Response Time 響應時間
---Elapsed time between the submission of a request until there is output. 常用于評價分時系統性能。
·Turnaround Time 周轉時間
---是指從作業提交給系統開始,到作業完成為止的這段時間間隔,也稱為作業周轉時間,常用語評價批處理系統的性能。
·Deadlines 截止時間
---是指某任務必須開始執行的最遲時間(starting deadline)或必須完成的最遲時間(completion deadline),常用于評價實時系統的性能。
?
BEST EFFORT 原則
?
System-oriented
·Throughput 吞吐量
---單位時間內系統所完成的作業數,用于評價批處理系統的性能。
·處理機利用率
---This is the percentage of time that the processor is busy.
---Effective and efficient utilization of the processor.
·Balance Resource 資源平衡
---keep the resources of the system busy. 適用于長程調度和中程調度。
·Fairness 公平性
---Process should be treated the same, and no process should suffer starvation.
?
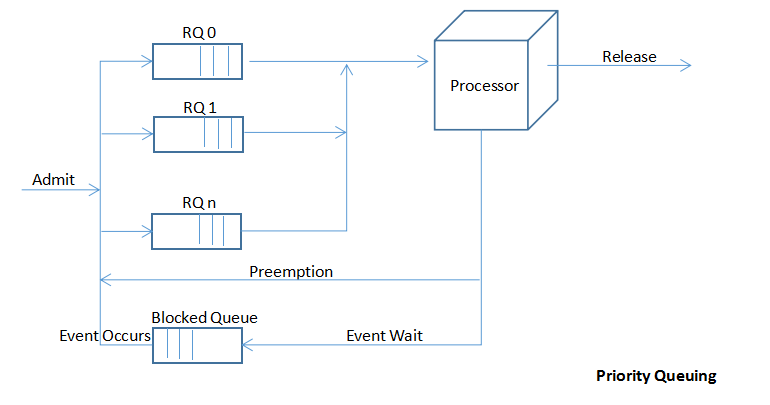
Priorities
·Scheduler will always choose a process of higher priority over one of lower priorities.
·Have multiple Ready Queues to represent each level of priority.
·Lower-priority may suffer starvation.
---allow a process to change its priority based on its age(生存期) or execution history.
?
??
2.4 Scheduling Algorithm
?
Decision Mode
·Non-preemptive (非剝奪方式)
---Once a process is in the running state, it will continue until it terminates or blocks itself for IO.
---主要用于批處理系統。
·Preemptive (剝奪方式) ?優先原則;短進程優先原則;時間片原則
---Currently running process may be interrupted and moved to the Ready State by the operating system.
---Allows for better service since any one process cannot monopolize the processor for very long.
---主要用于實時性要求較高的實時系統 及 性能要求較高的批處理系統 和 分時系統。
?
Process Scheduling?
1、First-Come-First-Served (FCFS)?
進程一旦獲得處理機,便一直進行下去,直到完成或阻塞
·Each process joins the Ready queue.
·When the current process ceases to execute, the oldest process in the Ready queue is selected.
·A short process may have to wait a very long time before it can execute.
·Favors CPU-bound processes
---IO processes have to wait until CPU-bound process completes.
FCFS is unfair to short process.
FCFS算法的實際應用
·一般,FCFS與其他調度算法混合使用
·系統可以按照不同的優先級維護多個就緒隊列,每個隊列內部按照FCFS算法調度。
??
2、短進程優先
3、最高響應比優先?
非剝奪調度算法 ?響應比 = (等待時間+要求服務的時間)/ 要求服務的時間
4、優先級
——靜態優先級:進程創建時確定其優先級 ? ?進程類型:系統進程優先; ? ?對資源的需求:需求少優先; ? ?用戶申請的優先級:付費高者優先
——動態優先級:優先級在進行期間動態調整 ? ?UNIX根據 ?占用處理機時間/等待處理機時間 ?動態調整
5、時間片輪轉
6、前后臺調度?用于批處理和分時相結合的系統中
分時--前臺--時間片輪轉 ?
批處理--后臺--先來先服務?
僅當前臺無作業時,才將處理機分配給后臺作業。
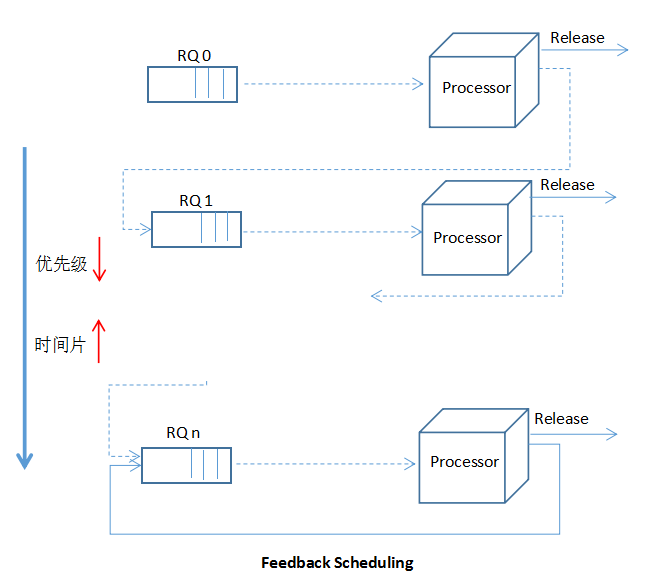
7、多級反饋隊列輪轉算法
時間片S0<S1<...<Sn
每個進程運行2~3個時間片,若未完成,則降級。
先調度優先級高的隊列,當高優先級隊列為空時,調度下一隊列。
只要有高優先級進程進入,則立即調度。
調度算法決定進程,分派程序完成分配處理機給該進程。
工程經驗很重要 ???小作業 --> 大設計
?
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
?
2.5 Real-Time Scheduling
?
Real-Time Systems
·Correctness of the system depends not only on the logical result of the computation but also the time at which the result are produced.
·Tasks or processes attempt to control or react to events that take place in the outside world.
·These events occur in “real time”?and process must be able to keep up with them.
?
?
Apply to
·Control of laboratory experiments
·Process control plants
·Robotics
·Aircraft control
·Telecommunications
·Military command and control system
?
指能及時響應外部事件的請求,在規定的時間內完成對該事件的處理,并控制所有實時任務協調一致的運行的計算機系統。
·實時控制系統:指要求進行實時控制的系統,用于生產過程的控制,實時采集現場數據,并對采集的數據進行及時處理。如飛機的自動駕駛系統,以及導彈的制導系統。
·實時信息處理系統:指能對信息進行實時處理的系統。典型的信息處理系統有:飛機訂票系統,情報 檢索系統。
?
Real-Time Task
·按任務執行時是否呈現周期性來劃分
>periodic (周期性)實時任務
>aperiodic (非周期性)實時任務,必須聯系著一個deadline
·根據對截止時間的要求來劃分
>hard real-time task 硬實時任務
---系統必須滿足任務對截止時間的要求,否則可能出現難以預測的結果。
>soft real-time task 軟實時任務
?
Characteristics of Real-Time Operating System
·Deterministic (確定性)
---Operations are performed at fixed, predetermined times or within predetermined time intervals.
---Concerned with how long the operating system delays before acknowledging an interrupt.
·Responsiveness (響應性)
---How long, after acknowledgment, it takes the operating system to service the interrupt.
---Includes amount of time to begin execution of the interrupt.
---Includes amount of time to perform the interrupt.
?
Features of Real-Time Operating Systems
·Fast context switch
·Small size
·Ability to respond to external interrupts quickly
·Multi-tasking with inter-process communication tools such as semaphores, signals and events
·Files that accumulate data at a fast rate
·Use of special sequential files that can accumulate data at a fast rate
·Preemptive scheduling based on priority
·Minimization of intervals during which interrupts are disabled
·Delay tasks for fixed amount of time
·Special alarms and timeouts 報警和超時處理
?
?
>Scheduling of a Real-Time process
>Real-Time Scheduling
>Deadline Scheduling
>Rate Monotonic Scheduling
?
Scheduling of a Real-Time Process
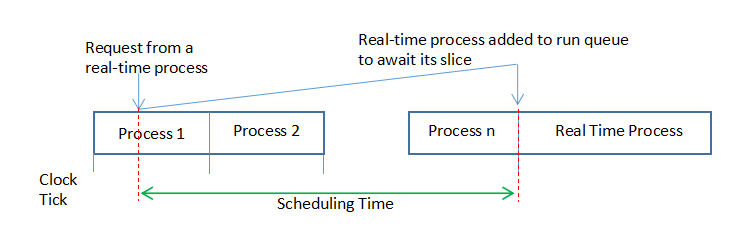
·Round Robin Preemptive Scheduler 基于時間片的輪轉調度算法
·Priority-driven Preemptive Scheduler 基于優先級的剝奪調度算法
·Priority-driven Non-preemptive Scheduler 基于優先級的非剝奪調度算法
·Immediate Preemptive Scheduler 立即剝奪調度算法
?
Round Robin Preemptive Scheduler
·響應時間在秒級
·廣泛應用于分時系統,也可用于一般的實時信息處理系統
·不適合于要求嚴格的實時控制系統
?
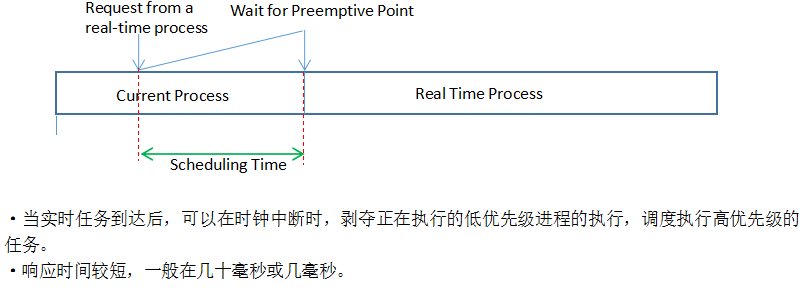
Priority-driven Preemptive Scheduler
·當實時任務到達后,可以在時鐘中斷時,剝奪正在執行的低優先級進程的執行,調度執行高優先級的任務。
·響應時間較短,一般在幾十毫秒或幾毫秒。
?
?
?
?
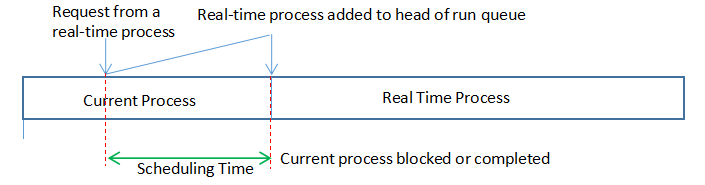
Priority-driven Non-preemptive Scheduler
·為實時任務賦予較高的優先級,將它插入就緒隊列隊首,只要正在執行的進程釋放processor,則立即調度實時任務執行。
·響應時間一般在數百毫秒到數秒之間。
·多用于多道批處理系統,也可以用于要求不太嚴格的實時系統。
?
Immediate Preemptive Scheduler
·要求操作系統具有快速響應外部事件的能力,一旦出現外部中斷,只要當前任務未處于臨界區,便立即剝奪其執行,把處理機分配給中斷請求。
·調度時延可以降至100微妙,甚至更低。
?
Aim of Real-Time Scheduling
·hard real-time task 在其規定的截止時間內完成
·盡可能使soft real-time task 也能在規定的截止時間內完成
公平性和最短平均響應時間等要求已不再重要。
但是,大多數現代實時操作系統無法直接處理任務的截止時間,它們只能盡量提高響應速度,以盡快地調度任務。
?
Real-Time Scheduling
·Static table-driven 靜態表驅動調度法
---Determines at run time when a table begins execution
·Static priority-driven preemptive 靜態優先級剝奪調度法
---Traditional priority-driven scheduler is used
·Dynamic planning-based 動態計劃調度法
·Dynamic best effort 動態最大努力調度法
Static table-driven approaches
·用于調度周期性實時任務
·按照任務周期到達的時間、執行時間、完成截止時間(ending deadline)以及任務的優先級,制定調度表,調度實時任務。
·最早截止時間優先(EDF)調度算法即屬于此類。
·此類算法不靈活,任何任務的調度申請改動都會引起調度表的修改。
·此類算法多用于非實時多道程序系統。
·優先級的確定方法很多,例如在分時系統中,可以對IO bound 和 processor bound的進程賦予不同的優先級,例如速度單調(RM)算法,即是為實時任務賦予靜態優先級。
?
Dynamic planning-based approaches
·當實時任務到達后,系統為新到達的任務和正在執行的任務動態創建一張調度表。
·在當前執行進程不會錯過其截止時間的條件下,如果也能使新到達任務在截止時間內完成,則立即調度執行新任務。
?
Dynamic best effort approaches
·實現簡單,廣泛用于非周期性實時任務調度
---當任務到達時,系統根據其屬性賦予優先級,優先級高的先調度。例如最早截止時間有限EDF調度算法就采用了這種方法。這種算法總是盡最大努力今早調度緊迫任務,因此成為最大努力調度算法。
·缺點在于,當任務完成,或截止時間到達,很難知道該任務是否滿足其約束時間。
?
Deadline Scheduling
·Information used
---Ready time
---Starting deadline
---Completion deadline 不會同時出現
---Processing time
---Resources requirement
---Priority
---Sub-task scheduler
一個任務可分解出強制子任務(mandatory sub-task)和非強制子任務(optional sub-task)。
只有強制子任務擁有硬截止時間 hard deadline
·Which task to schedule next?
---Scheduling tasks with the earliest deadlines minimized the fraction of tasks that miss their deadlines.
·What sort of preemptive is allowed?
---When starting deadlines are specified, then a non-preemptive scheduler make sense.
在執行完強制子任務或臨界區后,阻塞自己。
---For a system with completion deadlines, a preemptive strategy is most appropriate.
?
Earliest Deadline 最早截止時間優先,簡稱ED
·常用調度算法
·若指定任務的starting deadline,則采用Non-preemption,當某任務的開始截止時間到達時,正在執行的任務必須執行完其強制部分或臨界區,釋放CPU,調度開始截止時間的任務執行。
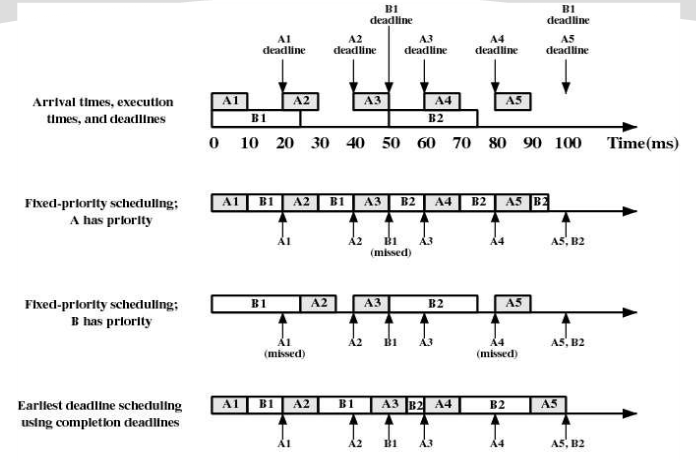
Periodic tasks with completion deadlines
·由于此類任務是周期性的,可預測的,可采用靜態表驅動之最早截止時間優先調度算法,使系統中的任務都能按要求完成。
·舉例:周期性任務A和B,指定了它們的完成截止時間,任務A每隔20毫秒完成一次,任務B每隔50毫秒完成一次。任務A每次需要執行10毫秒,任務B每次需要執行25毫秒。
Execution Profile of Two Periodic Tasks
| Process | Arrival Time | Execution Time | Ending Deadline |
| A(1) | 0 | 10 | 20 |
| A(2) | 20 | 10 | 40 |
| A(3) | 40 | 10 | 60 |
| A(4) | 60 | 10 | 80 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| B(1) | 0 | 25 | 50 |
| B(2) | 50 | 25 | 100 |
?
?
?
Aperiod tasks with starting deadlines
·可采用最早截止時間優先調度算法或允許CPU空閑的EDF調度算法。
·Earliest Deadline with Unforced Idle Times (允許CPU空閑的EDF調度算法)
指優先調度最早截止時間的任務,并將它執行完畢才調度下一個任務。即使選定的任務未就緒,允許CPU空閑等待,也不能調度其他任務。盡管CPU利用率不高,但這種調度算法可以保證系統中的任務都能按要求完成。
?
Rate Monotonic Scheduling
速度單調調度算法
·Assigns priorities to tasks on the basis of their periods.
·Highest-priority task is the one with the shortest period.
·Period(任務周期),指一個任務到達至下一個任務到達之間的時間范圍。
·Rate(任務速度),即周期(秒)的倒數,以赫茲為單位。
·任務周期的結束,表示任務的硬截止時間、任務的執行時間不能超過任務周期。
?
?——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Linux PCB 為task_struct,定義在文件include/linux/seched.h中
系統有一個task[]數組,用于存放每一個進程控制塊的指針。
fork() ?一個進程創建其子進程,除PID外,代碼段和數據的內容相同
exec() 進程執行
wait() 等待子進程結束
exit() 結束本進程
進程調度:
普通進程 ?SCHED_OTHER ?優先級 0~99 ?task_struct中的counter
實時進程 ?SCHED_RR/SCHED_FIFO ?1~99 ?rt_priority
實時進程優先級高于其他進程
系統的3個TASK_QUEUE:tq_timer ?tq_imediate ?tq_scheduler
在文件sched.c中定義,DECLARE_TASK_QUEUE
Linux具體調度流程sched.c
調用run_task_queue處理任務隊列tq_scheduler,普通進程counter值,實時進程counter+1000
SPINLOCK自旋鎖 ?spinlock.h
普通自旋鎖
讀/寫自旋鎖 ?允許多個讀者,一個寫者
希望進入此區域的進程試圖將此鎖(是一個整數)的初始值從0置為1。如果是1,則再次嘗試,此時進程好像在一段循環代碼中自旋。
對包含此鎖的內存區域的存取必須是原子性的。
控制進程離開臨界區時,遞減自旋鎖。
任何自旋進程都可讀取它,最快讀取的將遞增此值并進入臨界區。
?
?










數組的擴展)








