Linux 1.2.13 -- IP分片重組源碼分析
- 引言
- 為什么需要分片
- 傳輸層是否存在分段操作
- IP分片重組源碼分析
- ip_create
- ip_find
- ip_frag_create
- ip_done
- ip_glue
- ip_free
- ip_expire
- ip_defrag
- ip_rcv
- 總結
本文源碼解析參考: 深入理解TCP/IP協議的實現之ip分片重組 – 基于linux1.2.13
計網理論部分參考: << 自頂向下學習計算機網絡 >>
Linux 1.2.13 源碼倉庫鏈接: read-linux-1.2.13-net-code
引言
筆者在完成cs144 lab 后,發現自己對IP層分片這部分知識點模糊不清,閱讀了自頂向下學習計算機網絡書籍對應章節后,發現書上對IP層分片這部分內容講解較為簡單,所以特此翻閱Linux網絡子系統源碼進行學習。
在正式進入主題之前,我想先拋出我在沒有研究源碼前的一些疑惑:
- 既然書上說IP協議是不可靠的協議,那么IP層進行分片,又需要進行分片重組,只有重組完畢后才能將數據報交給上層,那么如果分片丟失或者超時遲遲未到該如何處理呢?
- 如果IP層需要被分片的數據再完全組裝后才能上交上層,那么是否需要使用到序列號,ACK,重傳等機制確保可靠性呢?
- 如果IP層需要實現可靠性傳輸,那么為什么又說IP協議是不可靠的呢?
- . . .
帶著以上種種疑惑,我開啟了對Linux 1.2.13 net模塊的探索之路。
本文所講內容未必完全正確,如有錯誤,歡迎在評論區指出。
為什么需要分片
不同的鏈路層協議所能承載的網絡層分組大小是不同的,有的協議能承載大數據報,而有的協議只能承載小分組。例如:
- 以太網幀能夠承載不超過1500字節的數據,而某些廣域網鏈路的幀可承載不超過576字節的數據
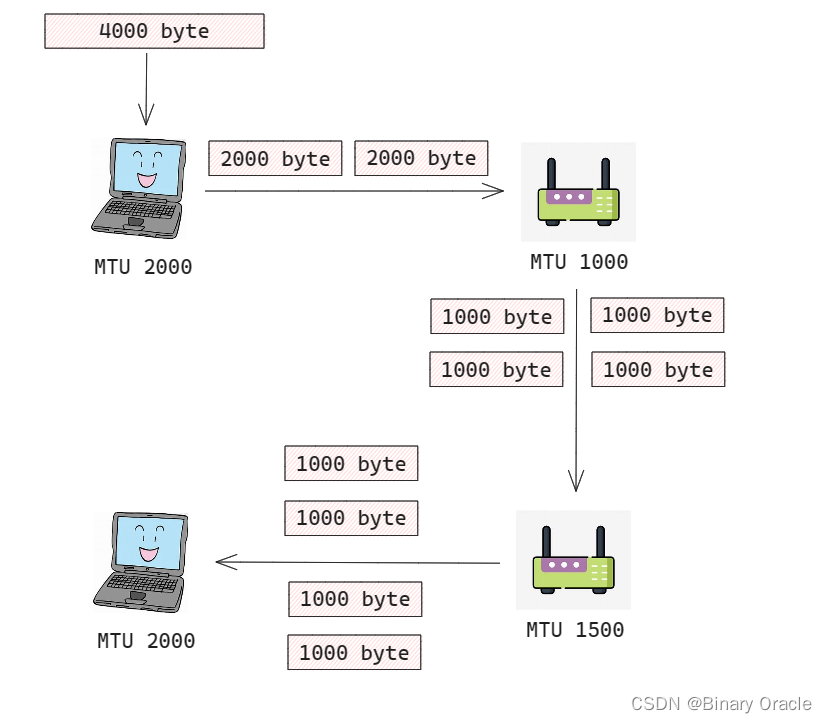
我們將一個鏈路層幀能承載的最大數據量叫做最大傳送單元(MTU),因為每個IP數據報封裝在鏈路層幀中從一臺路由器傳輸到下一臺路由器,因此鏈路層協議的MTU嚴格限制著IP數據報的長度。同時發送方與目的地路徑上每段鏈路可能使用不同的鏈路層協議,且每種協議可能具有不同的MTU,這意味著已經分片的IP數據報可能面臨再次分片,那么我們該如何處理這種情況呢?
- 如果遇到MTU更小的鏈路層協議,則將現有分片分成兩個或多個更小的IP數據報,用單獨的鏈路層幀封裝這些較小的IP數據報,然后通過輸出鏈路發送這些幀
使用IPV4協議的路由器才會執行再分片操作,使用IPV6協議的路由器不會進行再分片操作,而是回復一個ICMP錯誤報文,表示IP數據包過大
TCP與UDP都希望從網絡層接受到完整的,未分片的報文,那么如果我們在路由器中重新組裝數據報是否合理呢?
- 很顯然,這很不河里 ! 路由器中重新組裝數據報會給協議帶來相當大的復雜性并且影響路由器的性能,為堅持網路內核保持簡單的原則,IPV4設計者決定將數據報的重新組裝工作放到端系統中,而不是網絡路由器中。
當一臺目的主機從相同源收到一系列數據報時,它需要確定這些數據報中的某些是否是一些原來較大的數據報的片,這個該如何實現呢? 如果某些數據報是這些片的話,則它必須進一步確定何時收到了最后一片,并且將這些接收到的片拼接到一起以形成初始的數據報,這又該如何實現呢?
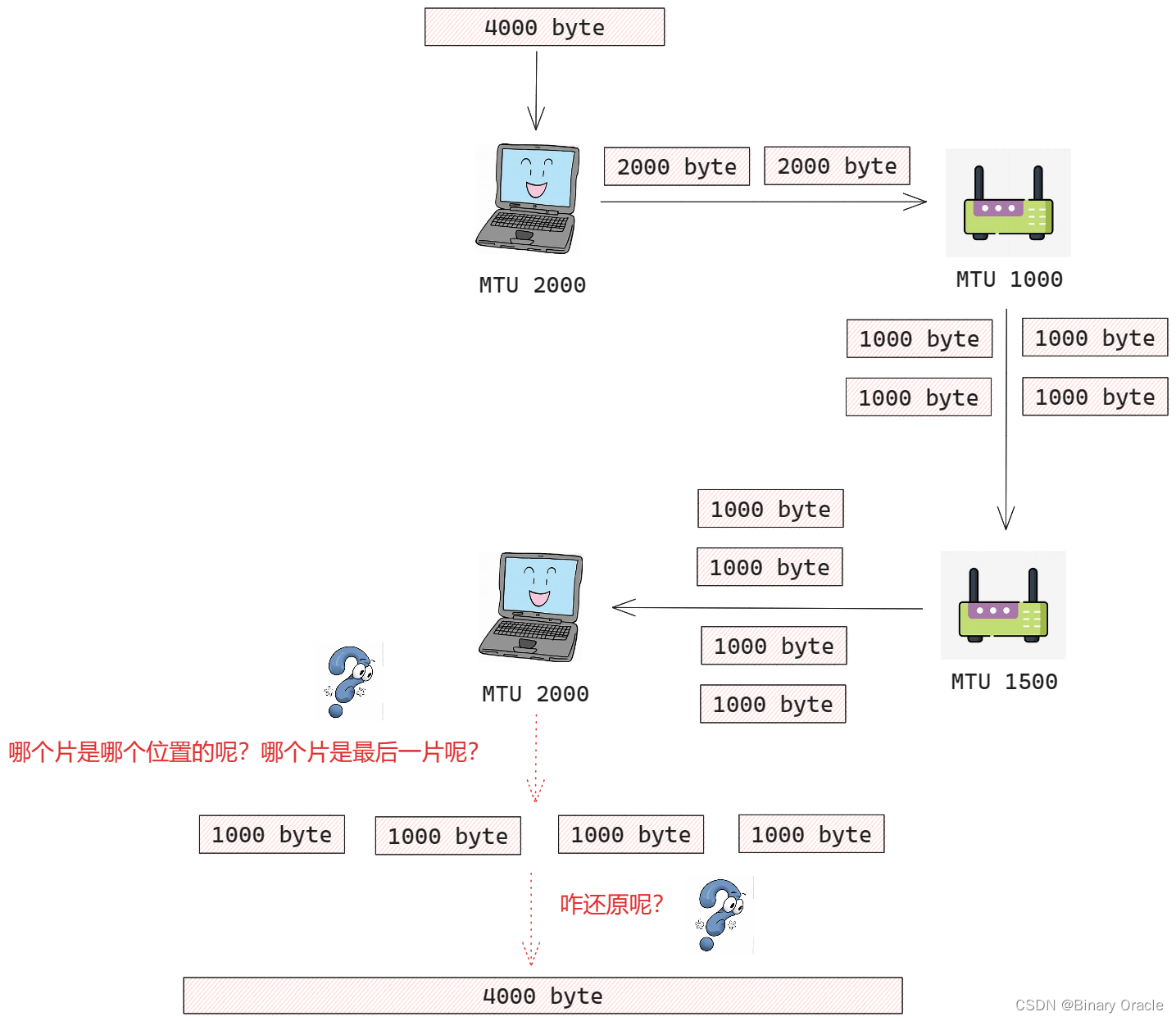
IPV4的設計者將標識,標志和片偏移字段放在IP數據報首部中:
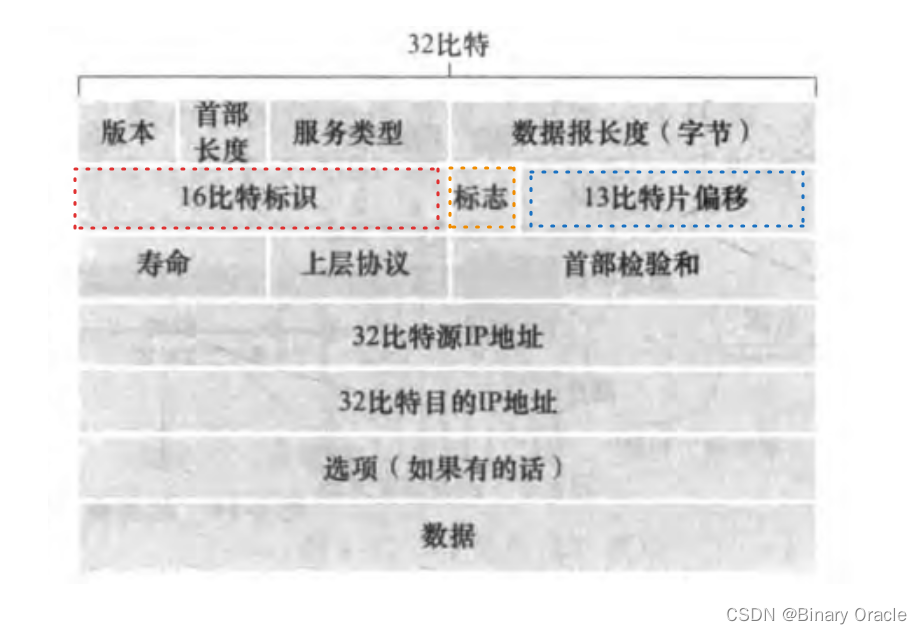
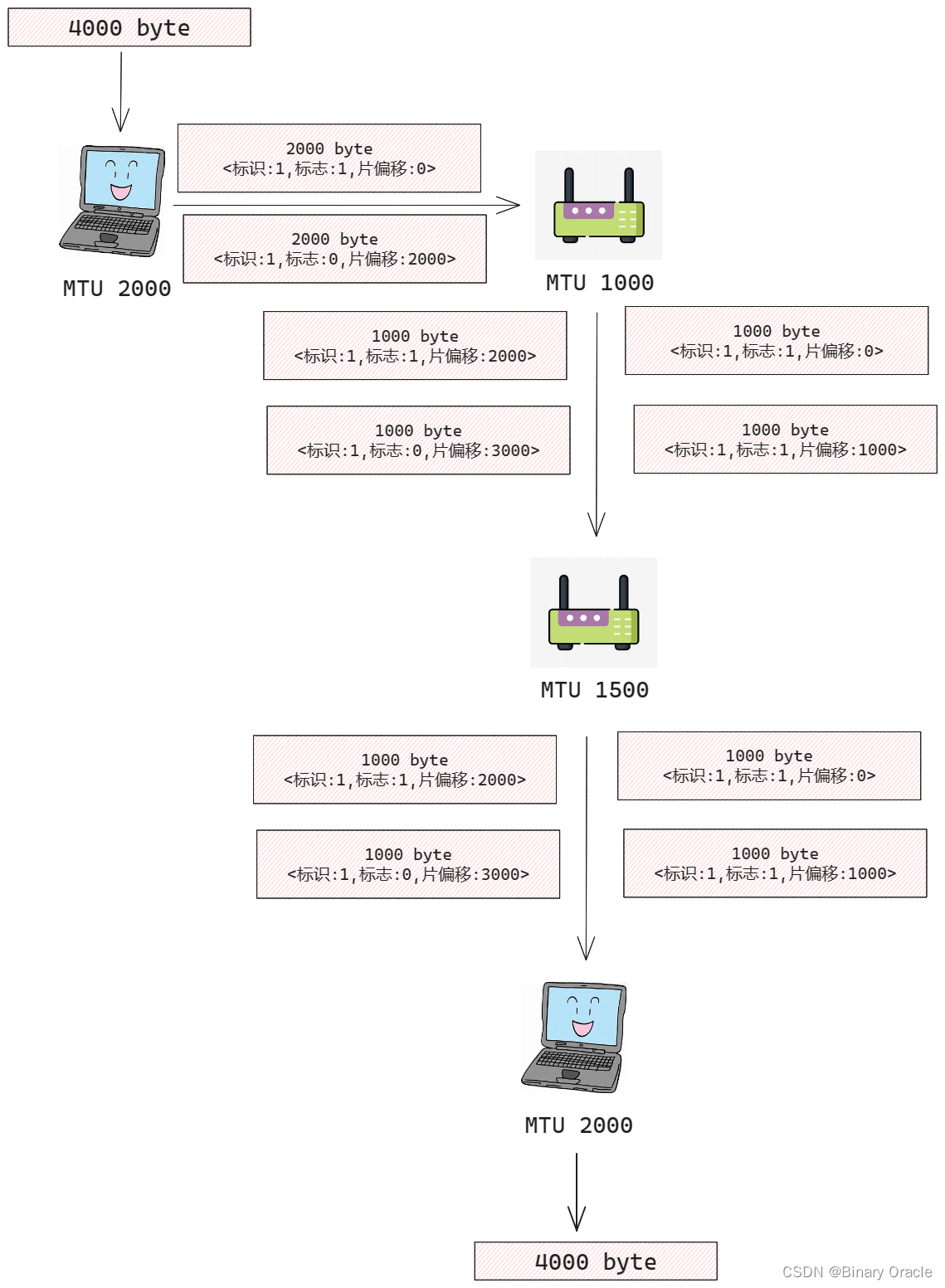
- 標識 : 檢查標識號以確定哪些數據報實際是同一較大數據報的分片
- 標志: 當前分片是否是最后一個分片
(最后一個片的比特設為0,其他片均設置為1),由于IP是一種不可靠服務,一個或多個片可能永遠也無法達到目的地,所以即使接收到了最后一個分片,也未必等同于接收到了所有分片,還需要重組后通過校驗和來檢驗是否接收到完整數據報數據 - 片偏移: 偏移字段指定當前片應放在IP數據報的哪個位置
傳輸層是否存在分段操作
傳輸層是否存在分段行為,這個問題需要分協議而論之,但就不可靠無連接的UDP協議而言,回答是NO!UDP協議除了端口復用/分解功能及少量的差錯檢測外,它幾乎沒有對IP增加別的東西。實際上,如果應用程序開發人員選擇UDP而不是TCP,則該應用程序差不多就是直接和IP打交道。
對于UDP協議棧而言,它會把應用程序傳下來的數據直接封裝為一個大的UDP數據報,然后傳遞給網絡層,如果數據報大于當前主機鏈路層協議的MTU協議限制,則會由IP層進行分片和重組處理,正如上一小節所講。而接收端會接收到IP層重組后得到的完整UDP數據報,然后進行校驗和檢驗后,將payload傳遞給應用程序,整個過程中UDP協議并不會對接收的應用程序進行分段:
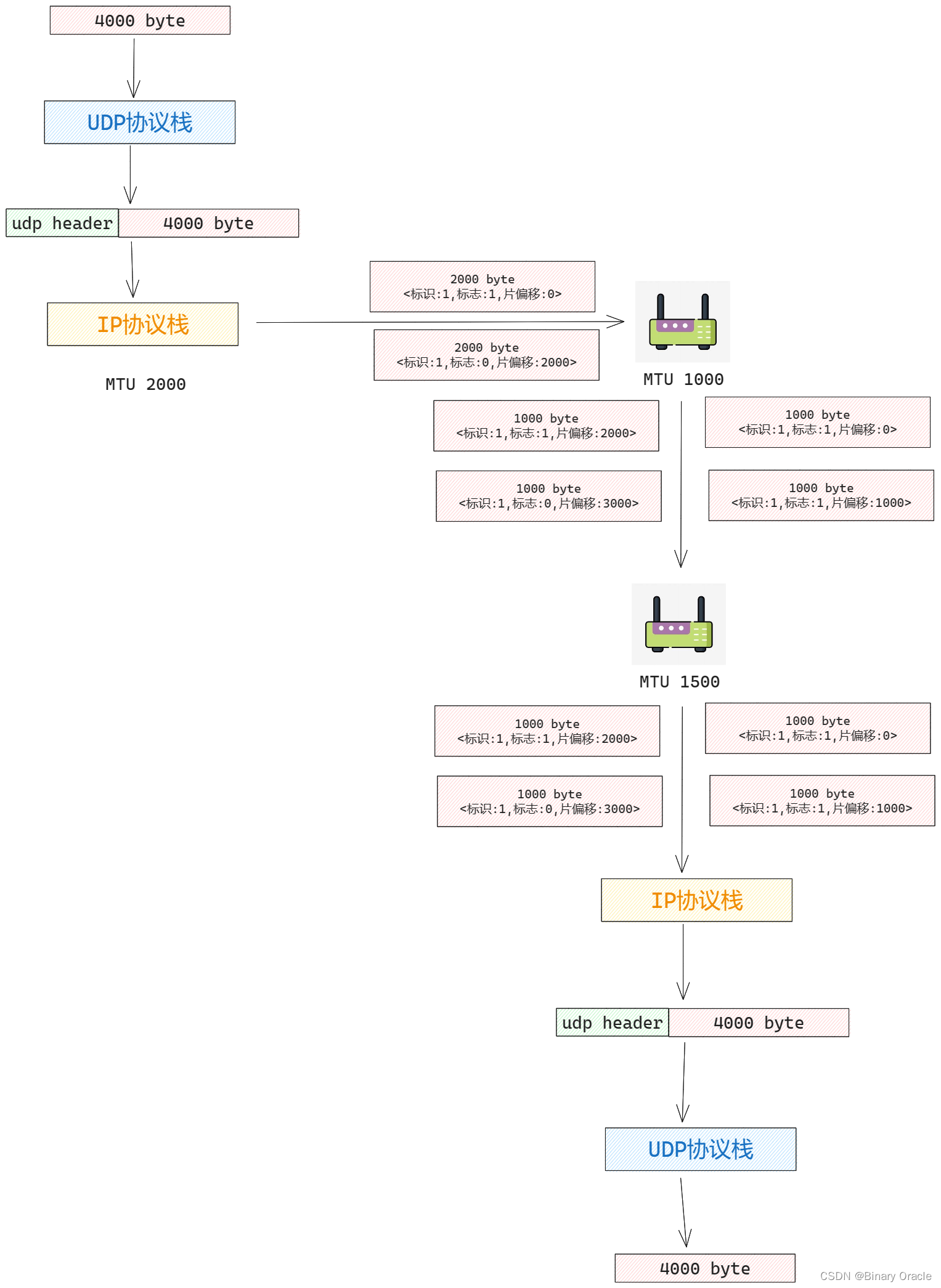
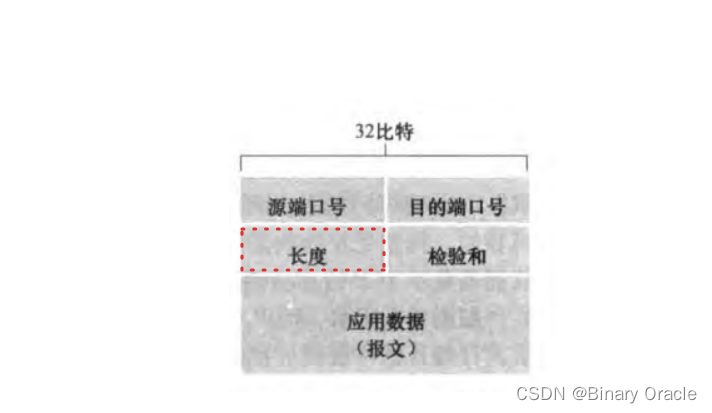
但是UDP協議的header頭部中存在長度字段,因此整個UDP數據報的大小會受到該字段的長度限制:
但是對于TCP協議而言,這個回答是YES,TCP協議本身是可靠的有連接的流傳輸協議,通過GBN(回退N步)加SR(選擇重傳)協議混合實現可靠傳輸,依靠滑動窗口實現流量控制,最后依靠擁塞窗口實現擁塞控制。
對于TCP協議而言,當應用程序傳遞下來數據需要發送時,是將數據全部封裝在單個TCP數據報中一次性發送出去,還是拆分成多次發送取決于以下五個因素:
-
當前TCP連接發送窗口的剩余空閑大小

-
當前TCP連接對端的接收窗口剩余空閑大小
-
最大報文段長度(MSS)
-
擁塞窗口大小
-
tcp數據報中len字段長度
本次發送數據大小 = Min(當前TCP連接發送窗口的剩余空閑大小,當前TCP連接對端的接收窗口剩余空閑大小,最大報文段長度(MSS),擁塞窗口大小,tcp數據報中len字段長度, 應用程序傳輸數據大小)
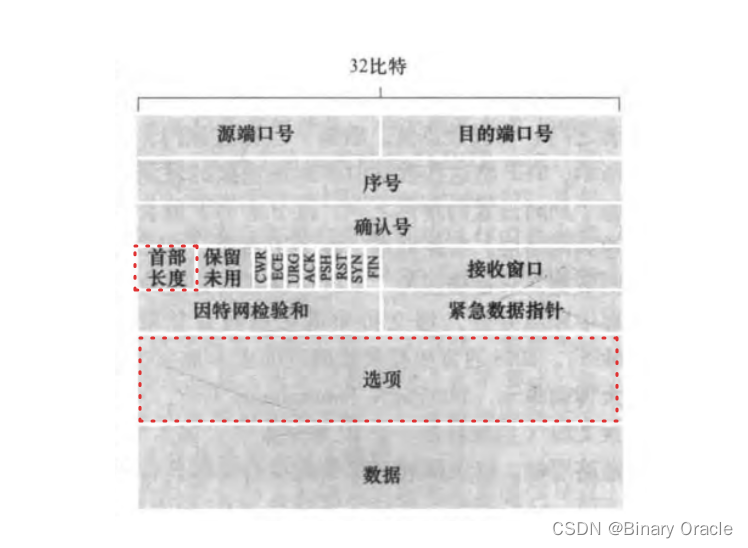
MSS通常根據最初確定的由本地發送主機發送的最大鏈路層幀長度(MTU)設置,MSS的值實際可以看做是MTU - TCP首部 - IP首部剩下的大小,也就是說MSS實際指代的是TCP報文段中應用層數據的最大長度,而不是指包括TCP首部的整個TCP報文段的最大長度。
TCP協議通常會通過首部中的選項字段完成發送方和接收方對最大報文段長度(MSS)的協商。
所以對于TCP協議而言,如果應用程序傳下來一個較大的數據包,協議棧可能會分為多批次進行傳輸,也就是進行分段,大的數據報切分成多個小數據報進行傳輸,并且由于tcp協議棧會保證單次傳輸的數據報大小小于MTU限制,所以一般不會在IP層發生分片操作,但是如果傳輸鏈路上出現了更小的MTU限制,還是會進行IP分片和重組:
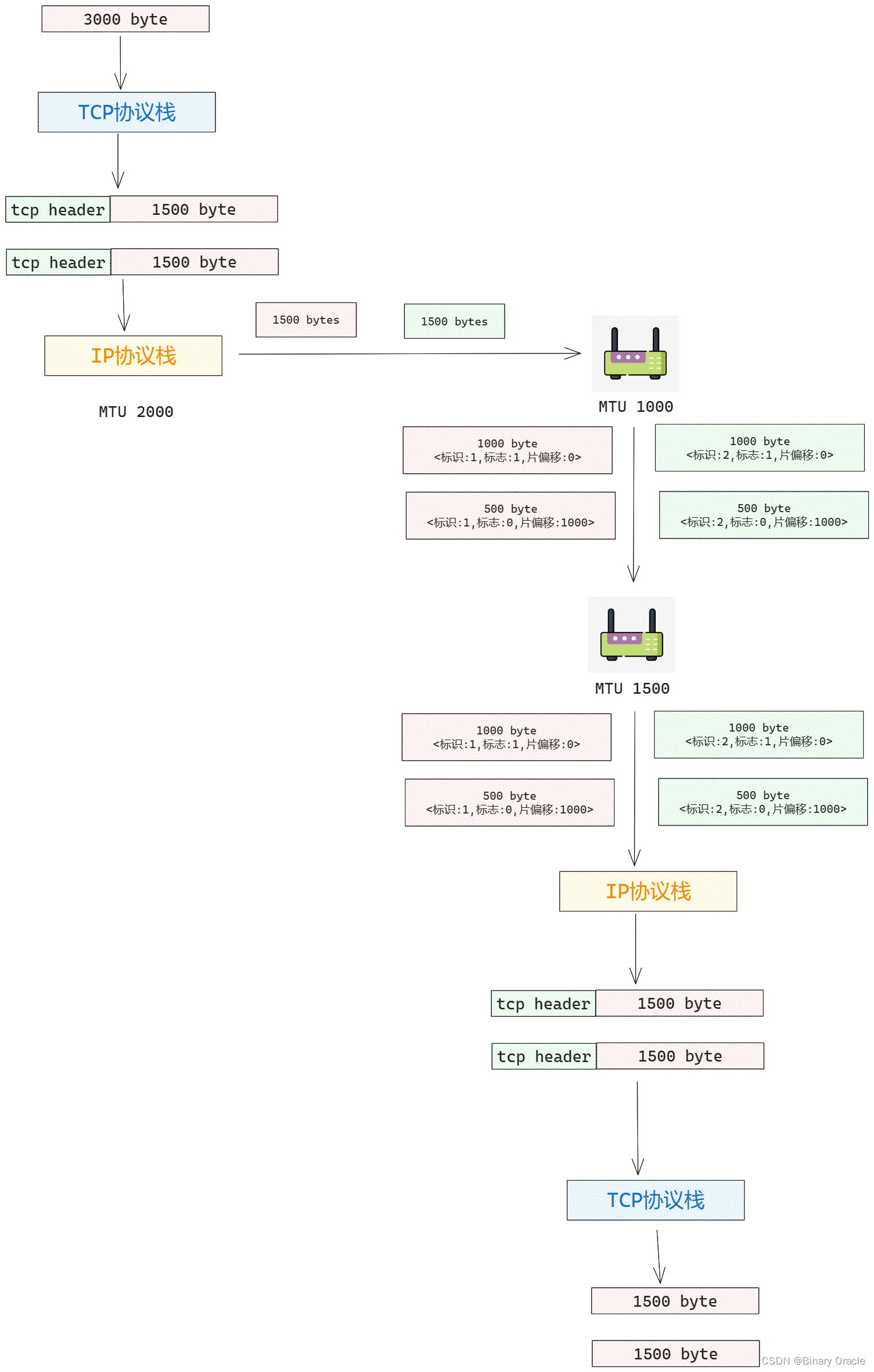
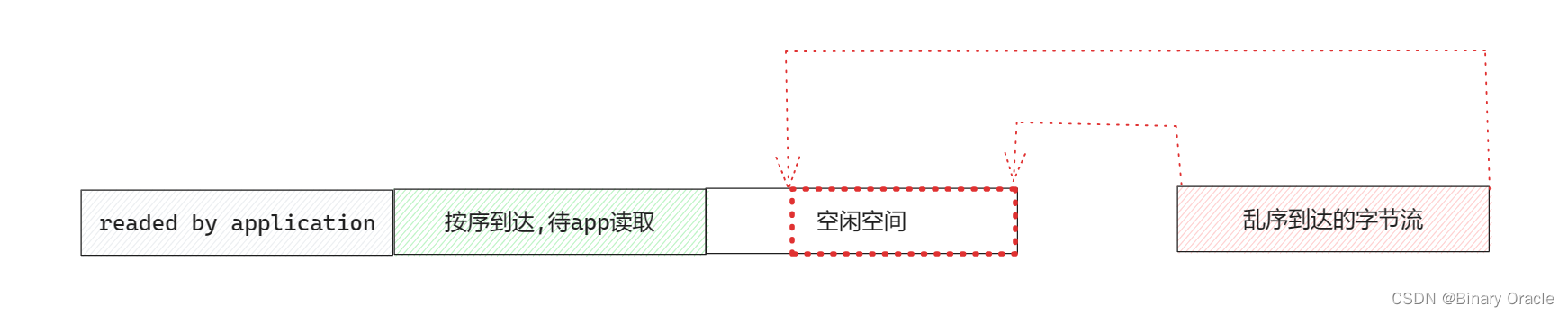
并且和UDP不同的一點時,TCP只要接收到按序到達的一段字節流,并且此時應用程序正在等待讀取數據,TCP協議棧就會把這段按序到達的數據丟給應用程序,然后把接收窗口的已讀指針向前推進部分,因此這也是為什么稱TCP為流式協議 – 就像水龍頭一樣,只要有水就會流出來。
如果UDP發送端發送的是一個大的數據報,那么UDP接收端會在接收完整個大的數據報后,才會把接收到的數據丟給應用程序,因此也稱UDP協議為數據報協議。
IP分片重組源碼分析
上面鋪墊了很多理論知識,從本節開始,我們進入實踐環節,看看IP分片重組過程是否如我們所言一般。
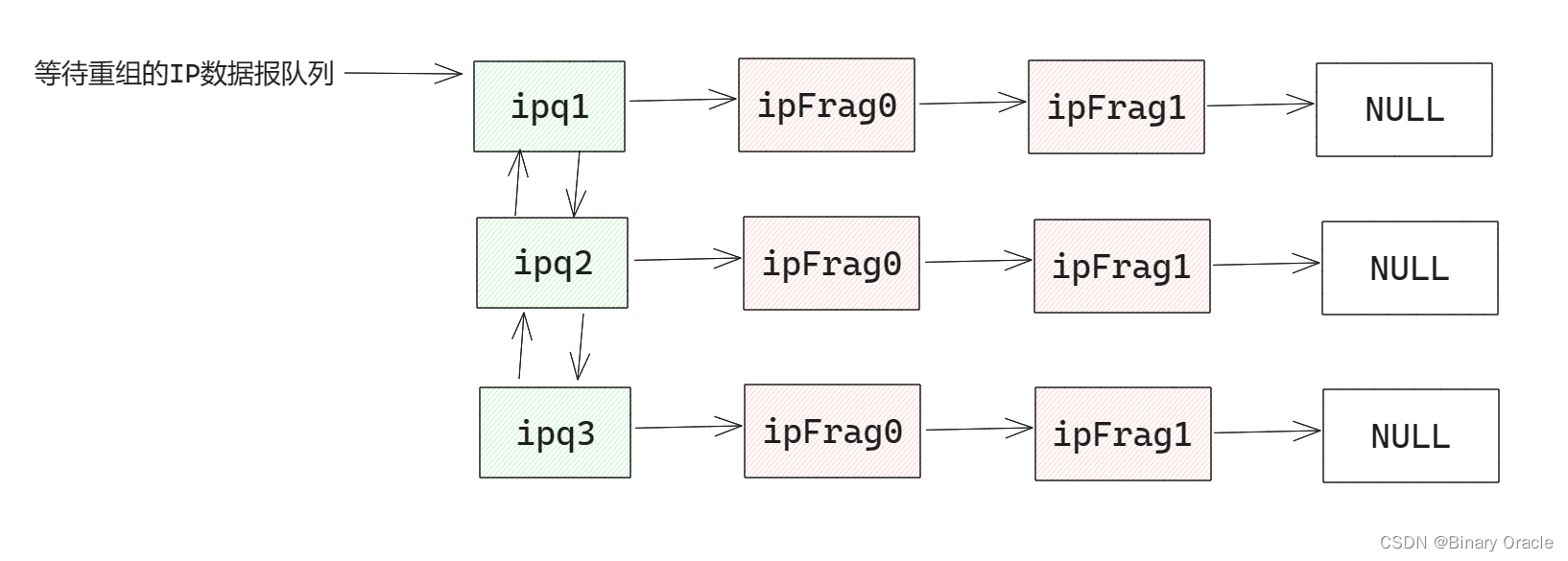
在Linux 1.2.13的net模塊中,使用ipfrag結構來描述一個ip分片信息,使用ipq結構來描述一個完整的傳輸層數據包信息:
ip.h:
/* Describe an IP fragment. */
// 描述一個IP分片
struct ipfrag {int offset; /* offset of fragment in IP datagram - IP分片的在IP數據報里面的偏移 */int end; /* last byte of data in datagram - 是否是最后一個分片 */int len; /* length of this fragment -- 當前分片大小 */struct sk_buff *skb; /* complete received fragment */unsigned char *ptr; /* pointer into real fragment data -- 指向分片數據 */struct ipfrag *next; /* linked list pointers -- 串聯起前后分片 */struct ipfrag *prev;
};/* Describe an entry in the "incomplete datagrams" queue. */
// 用于描述一個完整的傳輸層數據包,同時通過前后指針將未重組完成的IP數據報串聯起來
struct ipq {unsigned char *mac; /* pointer to MAC header -- MAC頭部地址 */struct iphdr *iph; /* pointer to IP header -- IP頭 */int len; /* total length of original datagram -- 原始數據報大小 */short ihlen; /* length of the IP header -- IP頭大小 */short maclen; /* length of the MAC header -- MAC頭大小 */struct timer_list timer; /* when will this queue expire? -- 定時器 --> 重組分片最大等待時長 */struct ipfrag *fragments; /* linked list of received fragments -- IP分片鏈表 */struct ipq *next; /* linked list pointers -- 串聯起未完成重組的IP數據報 */struct ipq *prev;struct device *dev; /* Device - for icmp replies -- 重組失敗后通過該接口發送ICMP包 */
};
ip.c:
ip_create
- ip_create函數用于添加一個新的ipq節點到已有的ipq隊列中,該隊列用于等待接收一個新的IP數據報的所有分片到達,其維護了屬于同一個分片組(同一個傳輸層數據包)的多個分片
/** Add an entry to the 'ipq' queue for a newly received IP datagram.* We will (hopefully :-) receive all other fragments of this datagram* in time, so we just create a queue for this datagram, in which we* will insert the received fragments at their respective positions.*/
// 創建一個隊列用于重組分片
// 參數: 承載當前分片數據信息,ip首部,從哪個鏈路層設備上接收到的以太網幀
static struct ipq *ip_create(struct sk_buff *skb, struct iphdr *iph, struct device *dev)
{struct ipq *qp;int maclen;int ihlen;// 分片一個新的表示分片隊列的節點qp = (struct ipq *) kmalloc(sizeof(struct ipq), GFP_ATOMIC);if (qp == NULL){printk("IP: create: no memory left !\n");return(NULL);skb->dev = qp->dev;}memset(qp, 0, sizeof(struct ipq));/** Allocate memory for the MAC header.** FIXME: We have a maximum MAC address size limit and define* elsewhere. We should use it here and avoid the 3 kmalloc() calls*/// mac頭長度等于ip頭減去mac頭首地址maclen = ((unsigned long) iph) - ((unsigned long) skb->data);qp->mac = (unsigned char *) kmalloc(maclen, GFP_ATOMIC);if (qp->mac == NULL){printk("IP: create: no memory left !\n");kfree_s(qp, sizeof(struct ipq));return(NULL);}/** Allocate memory for the IP header (plus 8 octets for ICMP).*/// ip頭長度由ip頭字段得出,多分配8個字節給icmpihlen = (iph->ihl * sizeof(unsigned long));qp->iph = (struct iphdr *) kmalloc(ihlen + 8, GFP_ATOMIC);if (qp->iph == NULL){printk("IP: create: no memory left !\n");kfree_s(qp->mac, maclen);kfree_s(qp, sizeof(struct ipq));return(NULL);}/* Fill in the structure. */// 把mac頭內容復制到mac字段// 第一個參數是dst,第二個是source,是將skb中相關信息copy到qp中memcpy(qp->mac, skb->data, maclen);// 把ip頭和傳輸層的8個字節復制到iph字段,8個字段的內容用于發送icmp報文時memcpy(qp->iph, iph, ihlen + 8);// 未分片的ip報文的總長度,未知,收到所有分片后重新賦值qp->len = 0;// 當前分片的ip頭和mac頭長度qp->ihlen = ihlen;qp->maclen = maclen;qp->fragments = NULL;qp->dev = dev;/* Start a timer for this entry. */// 開始計時,一定時間內還沒收到所有分片則重組失敗,發送icmp報文qp->timer.expires = IP_FRAG_TIME; /* about 30 seconds */qp->timer.data = (unsigned long) qp; /* pointer to queue */qp->timer.function = ip_expire; /* expire function */add_timer(&qp->timer);/* Add this entry to the queue. */qp->prev = NULL;cli();// 頭插法插入分片重組的隊列// ipqueue是全局頭指針,指向ipq隊列首元素qp->next = ipqueue;// 如果當前新增的節點不是第一個節點則把當前第一個節點的prev指針指向新增的節點if (qp->next != NULL)qp->next->prev = qp;//更新ipqueue指向新增的節點,新增節點是首節點 ipqueue = qp;sti();return(qp);
}
ip_find
- ip_find函數負責根據ip頭查找對應的ipq隊列
/** Find the correct entry in the "incomplete datagrams" queue for* this IP datagram, and return the queue entry address if found.*/
// 根據ip頭找到分片隊列的頭指針
static struct ipq *ip_find(struct iphdr *iph)
{struct ipq *qp;struct ipq *qplast;cli();qplast = NULL;for(qp = ipqueue; qp != NULL; qplast = qp, qp = qp->next){ // 對比ip頭里的幾個字段if (iph->id== qp->iph->id && iph->saddr == qp->iph->saddr &&iph->daddr == qp->iph->daddr && iph->protocol == qp->iph->protocol){ // 找到后重置計時器,在這刪除,在ip_find外面新增一個計時del_timer(&qp->timer); /* So it doesn't vanish on us. The timer will be reset anyway */sti();return(qp);}}sti();return(NULL);
}
ip_frag_create
- ip_frag_create函數負責創建一個表示單個ip分片的結構體ipfrag – 它表示其中一個分片
/** Create a new fragment entry.*/
// 創建一個表示ip分片的結構體
static struct ipfrag *ip_frag_create(int offset, int end, struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned char *ptr)
{struct ipfrag *fp;fp = (struct ipfrag *) kmalloc(sizeof(struct ipfrag), GFP_ATOMIC);if (fp == NULL){printk("IP: frag_create: no memory left !\n");return(NULL);}memset(fp, 0, sizeof(struct ipfrag));/* Fill in the structure. */fp->offset = offset; // ip分配的首字節在未分片數據中的偏移fp->end = end; // 最后一個字節的偏移 + 1,即下一個分片的首字節偏移fp->len = end - offset; // 分片長度fp->skb = skb;fp->ptr = ptr; // 指向分片的數據首地址return(fp);
}
ip_done
- ip_done函數負責判斷分片是否已經全部到達
/** See if a fragment queue is complete.*/
// 判斷分片是否全部到達
static int ip_done(struct ipq *qp)
{struct ipfrag *fp;int offset;/* Only possible if we received the final fragment. */// 收到最后分片的時候會更新len字段,如果沒有收到他就是初始化0,所以為0說明最后一個分片還沒到達,直接返回未完成if (qp->len == 0)return(0);// 接收到最后一個分片,但分片可能是無序到達的,因此需要檢查是否接收到了當前IP數據報的所有IP分片/* Check all fragment offsets to see if they connect. */fp = qp->fragments;offset = 0;// 檢查所有分片,每個分片是按照偏移量從小到大排序的鏈表,因為每次分片節點到達時會插入相應的位置while (fp != NULL){ /*如果當前節點的偏移大于期待的偏移(即上一個節點的最后一個字節的偏移+1,由end字段表示),說明有中間節點沒到達,直接返回未完成*/if (fp->offset > offset)return(0); /* fragment(s) missing */offset = fp->end;fp = fp->next;}/* All fragments are present. */// 分片全部到達并且每個分片的字節連續則重組完成return(1);
}
ip_glue
- ip_glue函數負責重組同一隊列里的所有ip分片
/** Build a new IP datagram from all its fragments.** FIXME: We copy here because we lack an effective way of handling lists* of bits on input. Until the new skb data handling is in I'm not going* to touch this with a bargepole. This also causes a 4Kish limit on* packet sizes.*/
// 重組成功后構造完整的ip報文
static struct sk_buff *ip_glue(struct ipq *qp)
{struct sk_buff *skb;struct iphdr *iph;struct ipfrag *fp;unsigned char *ptr;int count, len;/** Allocate a new buffer for the datagram.*/// 整個包的長度等于mac頭長度+ip頭長度+數據長度len = qp->maclen + qp->ihlen + qp->len;// 分配新的skb if ((skb = alloc_skb(len,GFP_ATOMIC)) == NULL){ip_statistics.IpReasmFails++;printk("IP: queue_glue: no memory for gluing queue 0x%X\n", (int) qp);ip_free(qp);return(NULL);}/* Fill in the basic details. */// 這里應該是等于qp->len?skb->len = (len - qp->maclen);skb->h.raw = skb->data; // data字段指向新分配的內存首地址skb->free = 1;/* Copy the original MAC and IP headers into the new buffer. */ptr = (unsigned char *) skb->h.raw;memcpy(ptr, ((unsigned char *) qp->mac), qp->maclen); // 把mac頭復制到新的內存ptr += qp->maclen;memcpy(ptr, ((unsigned char *) qp->iph), qp->ihlen); // 把ip頭復制到新的內存ptr += qp->ihlen; // 指向數據部分的首地址skb->h.raw += qp->maclen;// 指向ip頭首地址count = 0;/* Copy the data portions of all fragments into the new buffer. */fp = qp->fragments;// 開始復制數據部分while(fp != NULL){ // 如果當前節點的數據長度+已經復制的內容長度大于skb->len則說明內容溢出了,丟棄該數據包if(count+fp->len > skb->len){printk("Invalid fragment list: Fragment over size.\n");ip_free(qp);kfree_skb(skb,FREE_WRITE);ip_statistics.IpReasmFails++;return NULL;}// 把分片中的數據復制到對應偏移的位置 memcpy((ptr + fp->offset), fp->ptr, fp->len);// 已復制的數據長度count += fp->len;fp = fp->next;}/* We glued together all fragments, so remove the queue entry. */ip_free(qp);// 數據復制完后可以釋放分片隊列了/* Done with all fragments. Fixup the new IP header. */iph = skb->h.iph; // 上面的raw字段指向了ip頭首地址,skb->h.iph等價于raw字段的值iph->frag_off = 0; // 清除分片字段// 更新總長度為ip頭+數據的長度iph->tot_len = htons((iph->ihl * sizeof(unsigned long)) + count);skb->ip_hdr = iph;ip_statistics.IpReasmOKs++;return(skb);
}
重組的大致流程就是申請一塊新內存,然后把mac頭、ip頭復制過去。再遍歷分片隊列,把每個分片的數據拼起來。最后更新一些字段。
ip_free
- ip_free函數負責釋放ip分片隊列
/** Remove an entry from the "incomplete datagrams" queue, either* because we completed, reassembled and processed it, or because* it timed out.*/
// 釋放ip分片隊列
static void ip_free(struct ipq *qp)
{struct ipfrag *fp;struct ipfrag *xp;/** Stop the timer for this entry.*/// 刪除定時器del_timer(&qp->timer);/* Remove this entry from the "incomplete datagrams" queue. */cli();/* 被刪除的節點前面沒有節點說明他是第一個節點,因為不是循環鏈表,修改首指針ipqueue指向被刪除節點的下一個,如果下一個不為空,下一個節點的prev節點指向空,因為這時候他為第一個節點。*/if (qp->prev == NULL){ipqueue = qp->next;if (ipqueue != NULL)ipqueue->prev = NULL;}else{ /*被刪除節點不是第一個節點,但可能是最后一個,被刪除節點的前一個節點的next指針指向被刪除節點的下一個節點,如果如果被刪除節點的下一個節點不為空則他的prev指針執行被刪除節點前面的節點*/qp->prev->next = qp->next;if (qp->next != NULL)qp->next->prev = qp->prev;}/* Release all fragment data. */fp = qp->fragments;// 刪除所有分片節點while (fp != NULL){xp = fp->next;IS_SKB(fp->skb);kfree_skb(fp->skb,FREE_READ);kfree_s(fp, sizeof(struct ipfrag));fp = xp;}// 刪除mac頭和ip頭,8字節是icmp用的,存放傳輸層的前8個字節/* Release the MAC header. */kfree_s(qp->mac, qp->maclen);/* Release the IP header. */kfree_s(qp->iph, qp->ihlen + 8);/* Finally, release the queue descriptor itself. */kfree_s(qp, sizeof(struct ipq));sti();
}
ip_expire
- ip_expire函數負責處理分片重組超時的情況
/** Oops- a fragment queue timed out. Kill it and send an ICMP reply.*/
// 分片重組超時處理函數
static void ip_expire(unsigned long arg)
{struct ipq *qp;qp = (struct ipq *)arg;/** Send an ICMP "Fragment Reassembly Timeout" message.*/ip_statistics.IpReasmTimeout++;ip_statistics.IpReasmFails++; /* This if is always true... shrug */// 發送icmp超時報文if(qp->fragments!=NULL)icmp_send(qp->fragments->skb,ICMP_TIME_EXCEEDED,ICMP_EXC_FRAGTIME, 0, qp->dev);/** Nuke the fragment queue.*/// 釋放分片隊列ip_free(qp);
}
ip_defrag
- ip_defrag函數接收到一個IP數據報后判斷是否為某個IP數據報分片的一部分,如果是,則處理好分片重疊問題,然后將當前分片插入ipq隊列對應位置處,最后檢查當前IP數據報全部分片是否都已到達,如果是,則進入重組階段,最終返回重組后的IP數據報
/** Process an incoming IP datagram fragment.*/
// 處理分片報文
static struct sk_buff *ip_defrag(struct iphdr *iph, struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev)
{struct ipfrag *prev, *next;struct ipfrag *tfp;struct ipq *qp;struct sk_buff *skb2;unsigned char *ptr;int flags, offset;int i, ihl, end;ip_statistics.IpReasmReqds++;/* Find the entry of this IP datagram in the "incomplete datagrams" queue. */qp = ip_find(iph); // 根據ip頭找是否已經存在分片隊列/* Is this a non-fragmented datagram? */offset = ntohs(iph->frag_off);flags = offset & ~IP_OFFSET; // 取得三個分片標記位offset &= IP_OFFSET; // 取得分片偏移// 如果沒有更多分片了,并且offset=0(第一個分片),則屬于出錯,第一個分片后面肯定還有分片,否則干嘛要分片if (((flags & IP_MF) == 0) && (offset == 0)){if (qp != NULL)ip_free(qp); /* Huh? How could this exist?? */return(skb);}// 偏移乘以8得到數據的真實偏移offset <<= 3; /* offset is in 8-byte chunks *//** If the queue already existed, keep restarting its timer as long* as we still are receiving fragments. Otherwise, create a fresh* queue entry.*//*如果已經存在分片隊列,說明之前已經有分片到達,重置計時器,所以超時的邏輯是,如果IP_FRAG_TIME時間內沒有分片到達,則認為重組超時,這里沒有以總時間來判斷。*/if (qp != NULL){del_timer(&qp->timer);qp->timer.expires = IP_FRAG_TIME; /* about 30 seconds */qp->timer.data = (unsigned long) qp; /* pointer to queue */qp->timer.function = ip_expire; /* expire function */add_timer(&qp->timer);}else{/** If we failed to create it, then discard the frame*/// 新建一個管理分片隊列的節點if ((qp = ip_create(skb, iph, dev)) == NULL){skb->sk = NULL;kfree_skb(skb, FREE_READ);ip_statistics.IpReasmFails++;return NULL;}}/** Determine the position of this fragment.*/// ip頭長度ihl = (iph->ihl * sizeof(unsigned long));// 偏移+數據部分長度等于end,end的值是最后一個字節+1end = offset + ntohs(iph->tot_len) - ihl;/** Point into the IP datagram 'data' part.*/// data指向整個報文首地址,即mac頭首地址,ptr指向ip報文的數據部分ptr = skb->data + dev->hard_header_len + ihl;/** Is this the final fragment?*/// 是否是最后一個分片,是的話,未分片的ip報文長度為end,即最后一個報文的最后一個字節的偏移+1,因為偏移從0算起if ((flags & IP_MF) == 0)qp->len = end;/** Find out which fragments are in front and at the back of us* in the chain of fragments so far. We must know where to put* this fragment, right?*/prev = NULL;// 插入分片隊列相應的位置,保證分片的有序for(next = qp->fragments; next != NULL; next = next->next){ // 找出第一個比當前分片偏移大的節點if (next->offset > offset)break; /* bingo! */prev = next;}/** We found where to put this one.* Check for overlap with preceding fragment, and, if needed,* align things so that any overlaps are eliminated.*/// 處理分片重疊問題/*處理當前節點和前面節點的重疊問題,因為上面保證了offset >= prev->offset,所以只需要比較當前節點的偏移和prev節點的end字段*/if (prev != NULL && offset < prev->end){ // 說明存在重疊,算出重疊的大小,把當前節點的重疊部分丟棄,更新offset和ptr指針往前走,沒處理完全重疊的情況i = prev->end - offset;offset += i; /* ptr into datagram */ptr += i; /* ptr into fragment data */}/** Look for overlap with succeeding segments.* If we can merge fragments, do it.*/// 處理當前節點和后面節點的重疊問題for(; next != NULL; next = tfp){tfp = next->next;// 當前節點及其后面的節點都不會發生重疊了if (next->offset >= end)break; /* no overlaps at all */// 反之發生了重疊,算出重疊大小i = end - next->offset; /* overlap is 'i' bytes */// 更新和當前節點重疊的節點的字段,往后挪next->len -= i; /* so reduce size of */next->offset += i; /* next fragment */next->ptr += i;/** If we get a frag size of <= 0, remove it and the packet* that it goes with.*/// 發生了完全重疊,則刪除舊的節點if (next->len <= 0){if (next->prev != NULL)next->prev->next = next->next;// 說明舊節點不是第一個節點elseqp->fragments = next->next;// 說明舊節點是第一個節點// 這里應該是tfp !=NULL ?if (tfp->next != NULL)next->next->prev = next->prev;kfree_skb(next->skb,FREE_READ);kfree_s(next, sizeof(struct ipfrag));}}/** Insert this fragment in the chain of fragments.*/tfp = NULL;// 創建一個分片節點tfp = ip_frag_create(offset, end, skb, ptr);/** No memory to save the fragment - so throw the lot*/if (!tfp){skb->sk = NULL;kfree_skb(skb, FREE_READ);return NULL;}// 插入分片隊列tfp->prev = prev;tfp->next = next;if (prev != NULL)prev->next = tfp;elseqp->fragments = tfp;if (next != NULL)next->prev = tfp;/** OK, so we inserted this new fragment into the chain.* Check if we now have a full IP datagram which we can* bump up to the IP layer...*/// 判斷全部分片是否到達,是的話重組if (ip_done(qp)){skb2 = ip_glue(qp); /* glue together the fragments */return(skb2);}return(NULL);
}
ip_rcv
- ip_rcv函數負責完成一個IP數據報的接收過程
/** This function receives all incoming IP datagrams.*/int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev, struct packet_type *pt)
{struct iphdr *iph = skb->h.iph;struct sock *raw_sk=NULL;unsigned char hash;unsigned char flag = 0;unsigned char opts_p = 0; /* Set iff the packet has options. */struct inet_protocol *ipprot;static struct options opt; /* since we don't use these yet, and theytake up stack space. */int brd=IS_MYADDR;int is_frag=0;
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_FIREWALLint err;
#endif ip_statistics.IpInReceives++;/** Tag the ip header of this packet so we can find it*/skb->ip_hdr = iph;/** Is the datagram acceptable?** 1. Length at least the size of an ip header* 2. Version of 4* 3. Checksums correctly. [Speed optimisation for later, skip loopback checksums]* (4. We ought to check for IP multicast addresses and undefined types.. does this matter ?)*/// 參數檢查if (skb->len<sizeof(struct iphdr) || iph->ihl<5 || iph->version != 4 ||skb->len<ntohs(iph->tot_len) || ip_fast_csum((unsigned char *)iph, iph->ihl) !=0){ip_statistics.IpInHdrErrors++;kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);return(0);}/** See if the firewall wants to dispose of the packet. */
// 配置了防火墻,則先檢查是否符合防火墻的過濾規則,否則則丟掉
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_FIREWALLif ((err=ip_fw_chk(iph,dev,ip_fw_blk_chain,ip_fw_blk_policy, 0))!=1){if(err==-1)icmp_send(skb, ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_PORT_UNREACH, 0, dev);kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);return 0; }#endif/** Our transport medium may have padded the buffer out. Now we know it* is IP we can trim to the true length of the frame.*/skb->len=ntohs(iph->tot_len);/** Next analyse the packet for options. Studies show under one packet in* a thousand have options....*/// ip頭超過20字節,說明有選項if (iph->ihl != 5){ /* Fast path for the typical optionless IP packet. */memset((char *) &opt, 0, sizeof(opt));if (do_options(iph, &opt) != 0)return 0;opts_p = 1;}/** Remember if the frame is fragmented.*/// 非0則說明是分片 if(iph->frag_off){ // 是否設置了MF,即還有更多分片,是的話is_frag等于1if (iph->frag_off & 0x0020)is_frag|=1;/** Last fragment ?*/// 非0說明有偏移,即不是第一個塊分片if (ntohs(iph->frag_off) & 0x1fff)is_frag|=2;}/** Do any IP forwarding required. chk_addr() is expensive -- avoid it someday.** This is inefficient. While finding out if it is for us we could also compute* the routing table entry. This is where the great unified cache theory comes* in as and when someone implements it** For most hosts over 99% of packets match the first conditional* and don't go via ip_chk_addr. Note: brd is set to IS_MYADDR at* function entry.*/if ( iph->daddr != skb->dev->pa_addr && (brd = ip_chk_addr(iph->daddr)) == 0){/** Don't forward multicast or broadcast frames.*/if(skb->pkt_type!=PACKET_HOST || brd==IS_BROADCAST){kfree_skb(skb,FREE_WRITE);return 0;}/** The packet is for another target. Forward the frame*/#ifdef CONFIG_IP_FORWARDip_forward(skb, dev, is_frag);
#else
/* printk("Machine %lx tried to use us as a forwarder to %lx but we have forwarding disabled!\n",iph->saddr,iph->daddr);*/ip_statistics.IpInAddrErrors++;
#endif/** The forwarder is inefficient and copies the packet. We* free the original now.*/kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);return(0);}#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST if(brd==IS_MULTICAST && iph->daddr!=IGMP_ALL_HOSTS && !(dev->flags&IFF_LOOPBACK)){/** Check it is for one of our groups*/struct ip_mc_list *ip_mc=dev->ip_mc_list;do{if(ip_mc==NULL){ kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);return 0;}if(ip_mc->multiaddr==iph->daddr)break;ip_mc=ip_mc->next;}while(1);}
#endif/** Account for the packet*/#ifdef CONFIG_IP_ACCTip_acct_cnt(iph,dev, ip_acct_chain);
#endif /** Reassemble IP fragments.*/// 還有更多分片(等于1),不是第一個分片(等于2)或者兩者(等于3)則分片重組 if(is_frag){/* Defragment. Obtain the complete packet if there is one */skb=ip_defrag(iph,skb,dev);if(skb==NULL)return 0;skb->dev = dev;iph=skb->h.iph;}/** Point into the IP datagram, just past the header.*/skb->ip_hdr = iph;// 往上層傳之前先指向上層的頭skb->h.raw += iph->ihl*4;/** Deliver to raw sockets. This is fun as to avoid copies we want to make no surplus copies.*/hash = iph->protocol & (SOCK_ARRAY_SIZE-1);/* If there maybe a raw socket we must check - if not we don't care less */if((raw_sk=raw_prot.sock_array[hash])!=NULL){struct sock *sknext=NULL;struct sk_buff *skb1;// 找對應的socketraw_sk=get_sock_raw(raw_sk, hash, iph->saddr, iph->daddr);if(raw_sk) /* Any raw sockets */{do{/* Find the next */// 從隊列中raw_sk的下一個節點開始找滿足條件的socket,因為之前的的肯定不滿足條件了sknext=get_sock_raw(raw_sk->next, hash, iph->saddr, iph->daddr);// 復制一份skb給符合條件的socketif(sknext)skb1=skb_clone(skb, GFP_ATOMIC);elsebreak; /* One pending raw socket left */if(skb1)raw_rcv(raw_sk, skb1, dev, iph->saddr,iph->daddr);// 記錄最近符合條件的socketraw_sk=sknext;}while(raw_sk!=NULL);/* Here either raw_sk is the last raw socket, or NULL if none *//* We deliver to the last raw socket AFTER the protocol checks as it avoids a surplus copy */}}/** skb->h.raw now points at the protocol beyond the IP header.*/// 傳給ip層的上傳協議hash = iph->protocol & (MAX_INET_PROTOS -1);// 獲取哈希鏈表中的一個隊列,遍歷for (ipprot = (struct inet_protocol *)inet_protos[hash];ipprot != NULL;ipprot=(struct inet_protocol *)ipprot->next){struct sk_buff *skb2;if (ipprot->protocol != iph->protocol)continue;/** See if we need to make a copy of it. This will* only be set if more than one protocol wants it.* and then not for the last one. If there is a pending* raw delivery wait for that*/ /*是否需要復制一份skb,copy字段這個版本中都是0,有多個一樣的協議才需要復制一份,否則一份就夠,因為只有一個協議需要使用,raw_sk的值是上面代碼決定的*/if (ipprot->copy || raw_sk){skb2 = skb_clone(skb, GFP_ATOMIC);if(skb2==NULL)continue;}else{skb2 = skb;}// 找到了處理該數據包的上層協議flag = 1;/** Pass on the datagram to each protocol that wants it,* based on the datagram protocol. We should really* check the protocol handler's return values here...*/ipprot->handler(skb2, dev, opts_p ? &opt : 0, iph->daddr,(ntohs(iph->tot_len) - (iph->ihl * 4)),iph->saddr, 0, ipprot);}/** All protocols checked.* If this packet was a broadcast, we may *not* reply to it, since that* causes (proven, grin) ARP storms and a leakage of memory (i.e. all* ICMP reply messages get queued up for transmission...)*/if(raw_sk!=NULL) /* Shift to last raw user */raw_rcv(raw_sk, skb, dev, iph->saddr, iph->daddr);// 沒找到處理該數據包的上層協議,報告錯誤else if (!flag) /* Free and report errors */{ // 不是廣播不是多播,發送目的地不可達的icmp包if (brd != IS_BROADCAST && brd!=IS_MULTICAST)icmp_send(skb, ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_PROT_UNREACH, 0, dev);kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);}return(0);
}
總結
經過理論和實踐,相信各位已經知道了最開始拋出的答案了:
- IP協議是不可靠協議,雖然IP層需要進行分片和重組,但是不會使用ACK,重傳等機制確保該過程的可靠性,而僅僅使用超時定時器來判斷分組重組過程是否超時,如果超時,則回應一個ICMP重組超時錯誤報文

















庫)

