文章目錄
- 1. 前言——問題引出
- 2. 線索二叉樹的基本介紹
- 3. 線索二叉樹的應用案例
- 3.1. 思路分析
- 3.2. 代碼實現
- 4. 遍歷線索化二叉樹
- 4.1. 代碼實現
1. 前言——問題引出
????
問題:
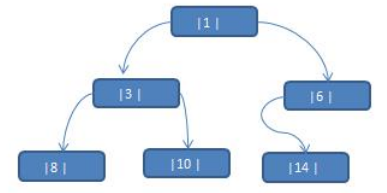
????將數列 {1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 14 } 構建成一顆二叉樹. (n+1=7個空指針域)

????
問題分析:
1.當對上面的二叉樹進行中序遍歷時,數列為 {8, 3, 10, 1, 6, 14 }
2.但是 6 的 右指針,8、10、14 這幾個節點的 左右指針,并沒有完全的利用上(共7個空指針域)
3.如果希望充分的利用 各個節點的左右指針,讓各個節點可以指向自己的前后節點,怎么辦?
????
解決方案:線索二叉樹
2. 線索二叉樹的基本介紹

- n n n 個結點的二叉鏈表中含有 n + 1 n+1 n+1 【公式 2 n ? ( n ? 1 ) = n + 1 2n-(n-1)=n+1 2n?(n?1)=n+1】 個空指針域。利用二叉鏈表中的空指針域,存放指向該結點在某種遍歷次序下的前驅和后繼結點的指針(這種附加的指針稱為"線索")。
- 這種加上了線索的二叉鏈表稱為線索鏈表,相應的二叉樹稱為線索二叉樹(Threaded BinaryTree)。根據線索性質的不同,線索二叉樹可分為前序線索二叉樹、中序線索二叉樹和后序線索二叉樹三種。
- 一個結點的前一個結點,稱為前驅結點。
- 一個結點的后一個結點,稱為后繼結點。
3. 線索二叉樹的應用案例
應用案例說明:
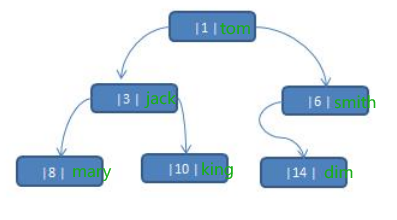
????將下面的二叉樹,進行中序線索二叉樹。中序遍歷的數列為 {8, 3, 10, 1, 14, 6}
3.1. 思路分析
中序遍歷的結果:{8, 3, 10, 1, 14, 6}

說明:
當線索化二叉樹后,Node節點的 屬性left和right,有如下情況:
(1)left指向的是左子樹,也可能是指向的前驅節點,比如 “1節點” 的left 指向的左子樹, 而 “10節點” 的 left 指向的就是前驅節點.
(2)right指向的是右子樹,也可能是指向后繼節點,比如 “1節點” 的right 指向的是右子樹,而 “10節點” 的right 指向的是后繼節點.
3.2. 代碼實現
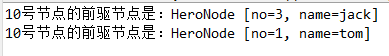
package tree.threadedbinarytree;//import tree.HeroNode;public class ThreadedBinaryTreeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "tom");HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(3, "jack");HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(6, "smith");HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(8, "mary");HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(10, "king");HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(14, "dim");// 二叉樹,這里手動創建方法比較低級,后面要學習遞歸創建root.setLeft(node2);root.setRight(node3);node2.setLeft(node4);node2.setRight(node5);node3.setLeft(node6);// 測試線索化ThreadedBinaryTree threadedBinaryTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree();threadedBinaryTree.setRoot(root);threadedBinaryTree.threadedNodes();// 測試,以10節點測試HeroNode leftNode = node5.getLeft();System.out.println("10號節點的前驅節點是:" + leftNode);HeroNode rightNode = node5.getRight();System.out.println("10號節點的前驅節點是:" + rightNode);}}//
//編寫一個ArrayBinaryTree,實現順序存儲二叉樹遍歷
//定義一個ThreadedBinaryTree,實現了線索化功能的二叉樹
class ThreadedBinaryTree {private HeroNode root;// 為了實現線索化,需要創建要指向當前節點的前驅節點的指針// 在遞歸進行線索化時,pre 總是保留前一個節點private HeroNode pre = null;public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {this.root = root;}// 重載public void threadedNodes() {this.threadedNodes(root);}// 編寫對二叉樹進行中序線索化的方法/*** * @param node 就是當前需要線索化的節點*/public void threadedNodes(HeroNode node) {// 如果node==null,不能線索化if (node == null) {return;}// 1. 先線索化左子樹threadedNodes(node.getLeft());// 2. 然后線索化當前節點[有難度]// 先處理當前節點的前驅節點// 以8節點來理解// 8節點的.left=null, 8節點的.leftType=1if (node.getLeft() == null) {// 讓當前節點的左指針指向前驅節點node.setLeft(pre);// 修改當前節點的左指針的類型node.setLeftType(1);}// 處理后繼結點if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {// 讓前驅節點的有指針指向當前節點pre.setRight(node);// 修改前驅節點的有指針類型pre.setRightType(1);}// !!!每處理一個節點后,讓當前節點是下一個節點的前驅節點pre = node;// 3. 再線索化右子樹threadedNodes(node.getRight());}// 刪除節點public void delNode(int no) {if (root != null) {// 如果只有一個root節點,這里立即判斷root是不是就是要刪除的節點if (root.getNo() == no) {root = null;} else {// 遞歸刪除root.delNode(no);}} else {System.out.println("空數,不能刪除~");}}// 前序遍歷public void preOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.preOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 中序遍歷public void infixOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.infixOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 后序遍歷public void postOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.postOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 前序遍歷查找public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return root.preOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}// 中序遍歷public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return root.infixOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}// 后序遍歷public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return this.root.postOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}
}//創建HeroNode
//先創建HeroNode節點
class HeroNode {private int no;private String name;private HeroNode left;// 默認nullprivate HeroNode right;// 默認null// 說明// 1. 如果leftType == 0 表示指向的是左子樹,如果1 則表示指向前驅節點// 2. 如果rightType == 0 表示指向的是右子樹,如果1 則表示指向后繼結點private int leftType;private int rightType;public int getLeftType() {return leftType;}public void setLeftType(int leftType) {this.leftType = leftType;}public int getRightType() {return rightType;}public void setRightType(int rightType) {this.rightType = rightType;}public HeroNode(int no, String name) {super();this.no = no;this.name = name;}public int getNo() {return this.no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public String getName() {return this.name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public HeroNode getLeft() {return this.left;}public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {this.left = left;}public HeroNode getRight() {return this.right;}public void setRight(HeroNode right) {this.right = right;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + "]";}// 遞歸刪除節點// 1. 如果刪除的節點是葉子節點,則刪除該節點// 2. 如果刪除的節點是非葉子節點,則刪除該子樹public void delNode(int no) {// 思路/** 1.因為我們的二叉樹是單向的,所以我們是判斷當前節點的子節點是否需要刪除結點,而不能去判斷當前這個節點是不是需要刪除節點。* 2.如果當前節點的左子節點不為空,并且左子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.left=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)* 3.如果當前節點的右子節點不為空,并且右子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.right=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)* 4.如果第2和第3步沒有刪除節點,那么就需要向左子樹進行遞歸刪除 5.如果第4步也沒有刪除節點,則應當向右子樹進行遞歸刪除*/// 2.如果當前節點的左子節點不為空,并且左子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.left=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {this.left = null;return;}// 3.如果當前節點的右子節點不為空,并且右子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.right=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {this.right = null;return;}// 4.如果第2和第3步沒有刪除節點,那么就需要向左子樹進行遞歸刪除if (this.left != null) {this.left.delNode(no);}// 5.如果第4步也沒有刪除節點,則應當向右子樹進行遞歸刪除if (this.right != null) {this.right.delNode(no);}}// 編寫前序遍歷的方法public void preOrder() {System.out.println(this);// 先輸出父節點// 遞歸向左子樹前序遍歷if (this.left != null) {this.left.preOrder();}// 遞歸向右子樹前序遍歷if (this.right != null) {this.right.preOrder();}}// 編寫中序遍歷的方法public void infixOrder() {// 遞歸向左子樹中序遍歷if (this.left != null) {this.left.infixOrder();}// 輸出父節點System.out.println(this);// 遞歸向右子樹中序遍歷if (this.right != null) {this.right.infixOrder();}}// 編寫后序遍歷的方法public void postOrder() {if (this.left != null) {this.left.postOrder();}if (this.right != null) {this.right.postOrder();}System.out.println(this);}// 前序遍歷查找/*** * @param no 查找的編號* @return 如果找到就返回該Node,如果沒有找到就返回null*/public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {System.out.println("進入了前序查找一次~~");// 比較當前節點是不是if (this.no == no) {return this;}// 1. 判斷當前節點的左子節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸前序查找// 2. 如果左遞歸前序查找,找到節點,則返回HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {// 說明我們左子樹找到return resNode;}// 1. 左遞歸前序查找,找到節點,則返回,否繼續判斷,// 2.當前的節點的右子節點是否為空,如果不空,則繼續向右遞歸前序查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);}return resNode;}// 中序遍歷查找public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {// 判斷當前節點的左子節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸中序查找HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {return resNode;}System.out.println("進入了中序查找一次~~");// 如果找到,則返回,如果沒有找到,就和當前結點比較,如果是則返回當前節點if (this.no == no) {return this;}// 否則繼續進行右遞歸的中序查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);}return resNode;}// 后序遍歷查找public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {// 判斷當前節點的左節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸后序查找HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {// 說明在左子樹找到return resNode;}// 如果左子樹沒有找到,則向右子樹遞歸進行后序遍歷查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {return resNode;}System.out.println("進入了后序查找一次~~");// 如果左右子樹都沒有找到,就比較當前節點是不是if (this.no == no) {return this;}return resNode;}}
運行結果:
4. 遍歷線索化二叉樹
????
問題:
????對前面的中序線索化的二叉樹, 進行遍歷
分析:
????因為線索化后,各個結點指向有變化,因此原來的遍歷方式不能使用,這時需要使用新的方式遍歷線索化二叉樹,各個節點可以通過線型方式遍歷,因此無需使用遞歸方式,這樣也提高了遍歷的效率。 遍歷的次序應當和中序遍歷保持一致。
4.1. 代碼實現
package tree.threadedbinarytree;//import tree.HeroNode;public class ThreadedBinaryTreeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "tom");HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(3, "jack");HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(6, "smith");HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(8, "mary");HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(10, "king");HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(14, "dim");// 二叉樹,這里手動創建方法比較低級,后面要學習遞歸創建root.setLeft(node2);root.setRight(node3);node2.setLeft(node4);node2.setRight(node5);node3.setLeft(node6);// 測試線索化ThreadedBinaryTree threadedBinaryTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree();threadedBinaryTree.setRoot(root);threadedBinaryTree.threadedNodes();// 測試,以10節點測試HeroNode leftNode = node5.getLeft();System.out.println("10號節點的前驅節點是:" + leftNode);HeroNode rightNode = node5.getRight();System.out.println("10號節點的前驅節點是:" + rightNode);// 當線索化二叉樹后,不能再使用原來的遍歷方法(threadedBinaryTree.infixOrder();)System.out.println("使用線索化的方式遍歷 線索化二叉樹");threadedBinaryTree.threadedList();}}//編寫一個ArrayBinaryTree,實現順序存儲二叉樹遍歷
//定義一個ThreadedBinaryTree,實現了線索化功能的二叉樹
class ThreadedBinaryTree {private HeroNode root;// 為了實現線索化,需要創建要指向當前節點的前驅節點的指針// 在遞歸進行線索化時,pre 總是保留前一個節點private HeroNode pre = null;public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {this.root = root;}// 重載public void threadedNodes() {this.threadedNodes(root);}// 遍歷線索化二叉樹的方法public void threadedList() {// 定義一個變量,存儲當前遍歷的節點,從root開始HeroNode node = root;while (node != null) {// 循環的找到leftType==1的節點,第一個找到的就是8節點// 后面隨著遍歷而變化,因為當leftType==1時,說明該節點是按照線索化處理后的有效節點while (node.getLeftType() == 0) {node = node.getLeft();}// 打印當前這個節點System.out.println(node);// 如果當前節點的右指針指向的是后繼節點,就一直輸出while (node.getRightType() == 1) {// 獲取到當前節點的后繼節點node = node.getRight();System.out.println(node);}// 替換遍歷的節點node = node.getRight();}}// 編寫對二叉樹進行中序線索化的方法/*** * @param node 就是當前需要線索化的節點*/public void threadedNodes(HeroNode node) {// 如果node==null,不能線索化if (node == null) {return;}// 1. 先線索化左子樹threadedNodes(node.getLeft());// 2. 然后線索化當前節點[有難度]// 先處理當前節點的前驅節點// 以8節點來理解// 8節點的.left=null, 8節點的.leftType=1if (node.getLeft() == null) {// 讓當前節點的左指針指向前驅節點node.setLeft(pre);// 修改當前節點的左指針的類型node.setLeftType(1);}// 處理后繼結點if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {// 讓前驅節點的有指針指向當前節點pre.setRight(node);// 修改前驅節點的有指針類型pre.setRightType(1);}// !!!每處理一個節點后,讓當前節點是下一個節點的前驅節點pre = node;// 3. 再線索化右子樹threadedNodes(node.getRight());}// 刪除節點public void delNode(int no) {if (root != null) {// 如果只有一個root節點,這里立即判斷root是不是就是要刪除的節點if (root.getNo() == no) {root = null;} else {// 遞歸刪除root.delNode(no);}} else {System.out.println("空數,不能刪除~");}}// 前序遍歷public void preOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.preOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 中序遍歷public void infixOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.infixOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 后序遍歷public void postOrder() {if (this.root != null) {this.root.postOrder();} else {System.out.println("二叉樹為空,無法遍歷");}}// 前序遍歷查找public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return root.preOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}// 中序遍歷public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return root.infixOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}// 后序遍歷public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {if (root != null) {return this.root.postOrderSearch(no);} else {return null;}}
}//創建HeroNode
//先創建HeroNode節點
class HeroNode {private int no;private String name;private HeroNode left;// 默認nullprivate HeroNode right;// 默認null// 說明// 1. 如果leftType == 0 表示指向的是左子樹,如果1 則表示指向前驅節點// 2. 如果rightType == 0 表示指向的是右子樹,如果1 則表示指向后繼結點private int leftType;private int rightType;public int getLeftType() {return leftType;}public void setLeftType(int leftType) {this.leftType = leftType;}public int getRightType() {return rightType;}public void setRightType(int rightType) {this.rightType = rightType;}public HeroNode(int no, String name) {super();this.no = no;this.name = name;}public int getNo() {return this.no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public String getName() {return this.name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public HeroNode getLeft() {return this.left;}public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {this.left = left;}public HeroNode getRight() {return this.right;}public void setRight(HeroNode right) {this.right = right;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + "]";}// 遞歸刪除節點// 1. 如果刪除的節點是葉子節點,則刪除該節點// 2. 如果刪除的節點是非葉子節點,則刪除該子樹public void delNode(int no) {// 思路/** 1.因為我們的二叉樹是單向的,所以我們是判斷當前節點的子節點是否需要刪除結點,而不能去判斷當前這個節點是不是需要刪除節點。* 2.如果當前節點的左子節點不為空,并且左子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.left=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)* 3.如果當前節點的右子節點不為空,并且右子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.right=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)* 4.如果第2和第3步沒有刪除節點,那么就需要向左子樹進行遞歸刪除 5.如果第4步也沒有刪除節點,則應當向右子樹進行遞歸刪除*/// 2.如果當前節點的左子節點不為空,并且左子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.left=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {this.left = null;return;}// 3.如果當前節點的右子節點不為空,并且右子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.right=null,并且就返回(結束遞歸刪除)if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {this.right = null;return;}// 4.如果第2和第3步沒有刪除節點,那么就需要向左子樹進行遞歸刪除if (this.left != null) {this.left.delNode(no);}// 5.如果第4步也沒有刪除節點,則應當向右子樹進行遞歸刪除if (this.right != null) {this.right.delNode(no);}}// 編寫前序遍歷的方法public void preOrder() {System.out.println(this);// 先輸出父節點// 遞歸向左子樹前序遍歷if (this.left != null) {this.left.preOrder();}// 遞歸向右子樹前序遍歷if (this.right != null) {this.right.preOrder();}}// 編寫中序遍歷的方法public void infixOrder() {// 遞歸向左子樹中序遍歷if (this.left != null) {this.left.infixOrder();}// 輸出父節點System.out.println(this);// 遞歸向右子樹中序遍歷if (this.right != null) {this.right.infixOrder();}}// 編寫后序遍歷的方法public void postOrder() {if (this.left != null) {this.left.postOrder();}if (this.right != null) {this.right.postOrder();}System.out.println(this);}// 前序遍歷查找/*** * @param no 查找的編號* @return 如果找到就返回該Node,如果沒有找到就返回null*/public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {System.out.println("進入了前序查找一次~~");// 比較當前節點是不是if (this.no == no) {return this;}// 1. 判斷當前節點的左子節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸前序查找// 2. 如果左遞歸前序查找,找到節點,則返回HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {// 說明我們左子樹找到return resNode;}// 1. 左遞歸前序查找,找到節點,則返回,否繼續判斷,// 2.當前的節點的右子節點是否為空,如果不空,則繼續向右遞歸前序查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);}return resNode;}// 中序遍歷查找public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {// 判斷當前節點的左子節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸中序查找HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {return resNode;}System.out.println("進入了中序查找一次~~");// 如果找到,則返回,如果沒有找到,就和當前結點比較,如果是則返回當前節點if (this.no == no) {return this;}// 否則繼續進行右遞歸的中序查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);}return resNode;}// 后序遍歷查找public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {// 判斷當前節點的左節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸后序查找HeroNode resNode = null;if (this.left != null) {resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {// 說明在左子樹找到return resNode;}// 如果左子樹沒有找到,則向右子樹遞歸進行后序遍歷查找if (this.right != null) {resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);}if (resNode != null) {return resNode;}System.out.println("進入了后序查找一次~~");// 如果左右子樹都沒有找到,就比較當前節點是不是if (this.no == no) {return this;}return resNode;}}
運行結果:



![[動態規劃]最長公共子序列](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[動態規劃]最長公共子序列)




)
)





| 建模秘籍文章代碼思路大全)


)

