概述
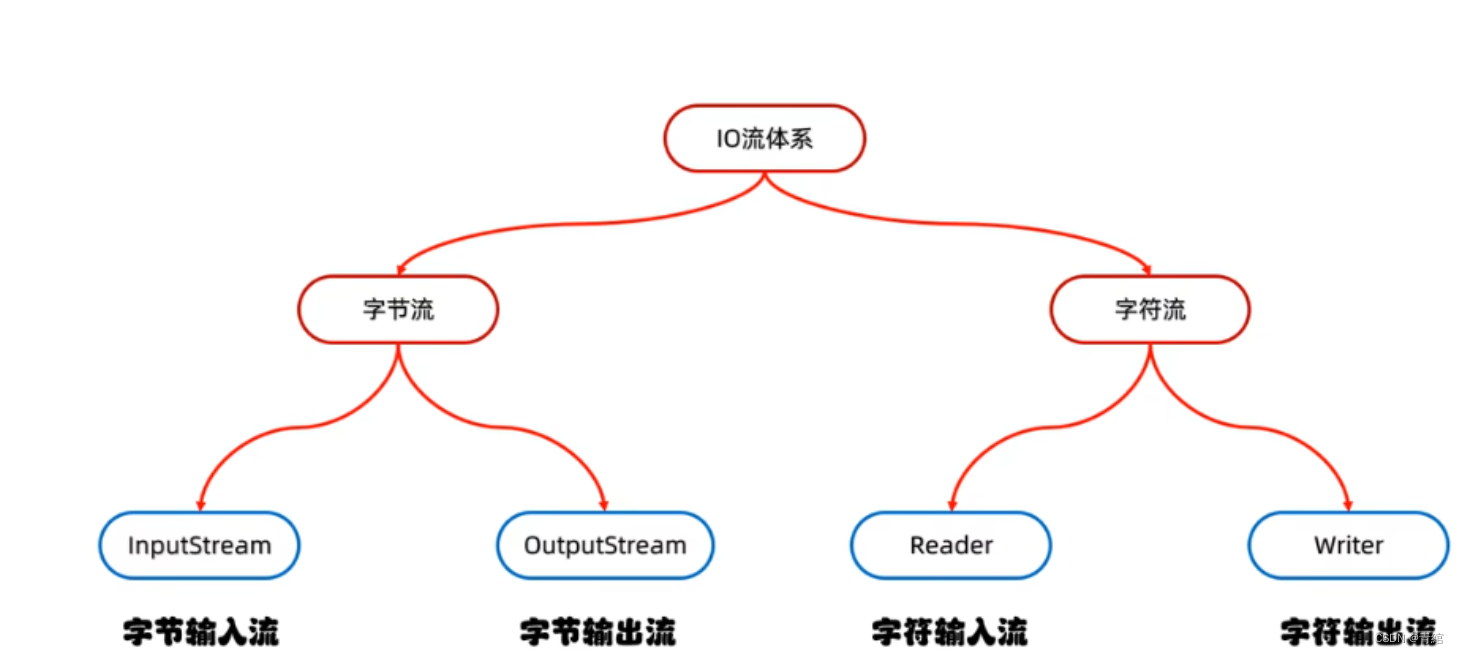
IO流的分類
IO流的體系
這四個類都是抽象類,所以需要實現類對象才能使用--->
字節流
FileInputStream-->
書寫細節
代碼示范
此時文件a.txt內容為abcde
使用char強轉和read方法調用五次read方法-->
使用char強轉和read方法調用六次read方法-->最后一個值為-1public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*演示:字節輸入流FileInputStream實現需求:讀取文件中的數據(暫時不寫中文)實現步驟:創建對象讀取數據釋放資源*///1.創建對象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.讀取數據int b1 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b1);//aint b2 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b2);//bint b3 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b3);//cint b4 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b4);//dint b5 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b5);//e//3.釋放資源fis.close();}循環讀取-->public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*演示:字節輸入流FileInputStream實現需求:讀取文件中的數據(暫時不寫中文)實現步驟:創建對象讀取數據釋放資源*///1.創建對象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.讀取數據int b1 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b1);//aint b2 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b2);//bint b3 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b3);//cint b4 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b4);//dint b5 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b5);//eint b6 = fis.read();System.out.println((char)b6);////3.釋放資源fis.close();}
?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*字節輸入流的循環讀取*///1.創建對象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.循環讀取int b;while ((b = fis.read()) != -1){System.out.println((char)b);}/*結果:abcde*///3.釋放資源fis.close();}
FileOutputStream-->
?書寫細節
代碼示范
先創建一個空的txt文件:a.txt
一次寫一個字節數據-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*演示:字節輸出流FileOutputStream實現需求:寫出一段文字到本地文件中(暫時不寫中文)實現步驟:創建對象寫出數據釋放資源*///1.創建對象//寫出 輸出流 OutputStreamFileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.寫出數據fos.write(97);//3.釋放資源fos.close();}結果-->>文件中添加了a
一次寫一個字節數組數據-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.創建對象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.寫出數據byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};fos.write(bytes);//3.釋放數據fos.close();}結果-->>文件中添加了abcde
一次寫一個字節數組的部分數據-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.創建對象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.寫出數據byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};fos.write(bytes,1,2);//3.釋放數據fos.close();}結果-->>文件中添加了bc
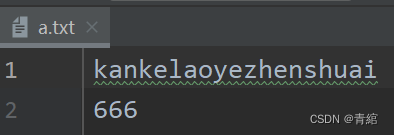
換行-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*換行寫:再次寫出一個換行符Windows:\r\nLinux:\nMac:\r細節:在Windows操作系統中,java對回車換行進行了優化雖然完整是\r\n,但是我們寫其中一個\r或者\njava也可以實現換行,因為java在底層會自動補全建議:不要省略*///1.創建對象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");//2.寫出數據String str1 = "kankelaoyezhenshuai";byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes();fos.write(bytes1);//再次寫出一個換行符String warp = "\r\n";byte[] bytes2 = warp.getBytes();fos.write(bytes2);String str2 = "666";byte[] bytes3 = str2.getBytes();fos.write(bytes3);//釋放資源fos.close();}結果-->>
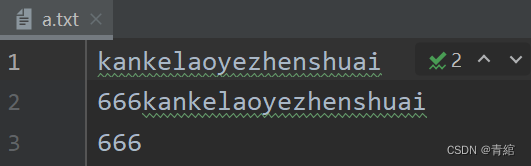
續寫-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*續寫:如果需要續寫,打開續寫開關即可開關位置:創建對象的第二個參數默認false:表示關閉續寫,此時創建對象會清空文件手動傳遞true:表示打開續寫,此時創建對象不會清空文件*///1.創建對象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt",true);//2.寫出數據String str1 = "kankelaoyezhenshuai";byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes();fos.write(bytes1);//再次寫出一個換行符String warp = "\r\n";byte[] bytes2 = warp.getBytes();fos.write(bytes2);String str2 = "666";byte[] bytes3 = str2.getBytes();fos.write(bytes3);//釋放資源fos.close();}結果-->>
小結
練習-->文件拷貝
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//文件拷貝//核心思想:邊讀邊寫//創建對象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\b.txt");//拷貝int b;while ((b = fis.read()) != -1){fos.write(b);}//規則:先開的最后關閉fos.close();fis.close();}FileInputStream讀取的問題
一次只讀取一個字節導致效率慢
解決方案
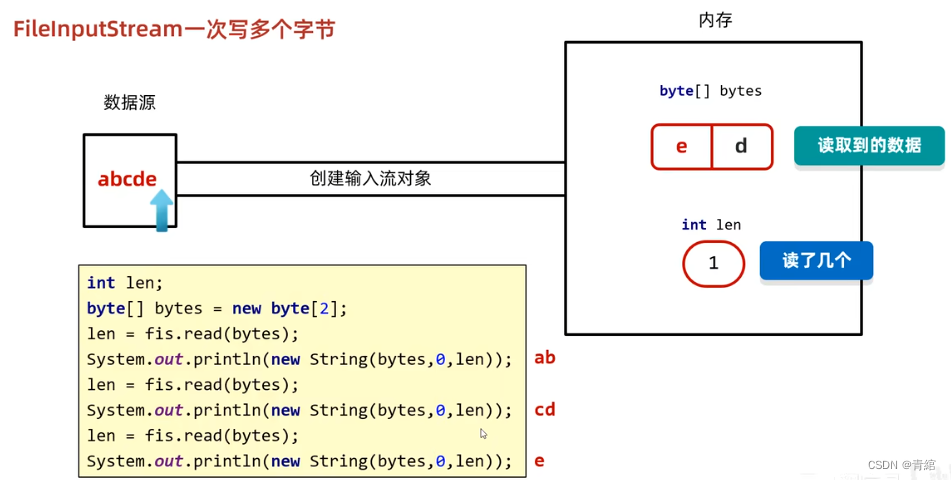
字節數組返回值:獲取了幾個字符
讀取abcde時,第三次會出現只讀取e的情況,只獲取了一個元素,而數組中存放了兩個,只會覆蓋一半,所以使用時應該加上起始索引和結束索引
代碼示范
try...catch異常處理
未來在springboot框架中一般使用拋出異常,try...catch掌握即可
由于代碼太過繁瑣,Java做出了簡化方案,提出了接口
接口:AutoCloseable
特點:特定情況下,可以自動釋放資源
代碼演示
基本做法-->
public static void main(String[] args) {//創建對象FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");//拷貝int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[2];while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}} catch (IOException e){//e.printStackTrace();} finally {//釋放資源if(fos != null){try {fos.close();} catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}if(fis != null){try {fis.close();} catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}JDK7方案-->
public static void main(String[] args) {/*JDK7:IO流中捕獲異常的寫法try后面的小括號寫創建對象的代碼注意:只有實現AutoCloseable接口的類,才能在小括號中創建對象*/try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt")){//拷貝int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[2];while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}JDK9方案-->
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {/*JDK9:IO流中捕獲異常的寫法*/FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");try(fis;fos){//拷貝int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[2];while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}



















——目錄與傳送門)
)











應用開發——從網絡獲取數據(題目答案))



的策略)