本章概要
- 隨機生成
- 泛型和基本數組
隨機生成
我們可以按照 Count.java 的結構創建一個生成隨機值的工具:
Rand.java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.*;import static com.example.test.ConvertTo.primitive;public interface Rand {int MOD = 10_000;class Boolean implements Supplier<java.lang.Boolean> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Boolean get() {return r.nextBoolean();}public java.lang.Boolean get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Boolean[] array(int sz) {java.lang.Boolean[] result =new java.lang.Boolean[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}class Pboolean {public boolean[] array(int sz) {return primitive(new Boolean().array(sz));}}class Byteimplements Supplier<java.lang.Byte> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Byte get() {return (byte) r.nextInt(MOD);}public java.lang.Byte get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Byte[] array(int sz) {java.lang.Byte[] result =new java.lang.Byte[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}class Pbyte {public byte[] array(int sz) {return primitive(new Byte().array(sz));}}class Characterimplements Supplier<java.lang.Character> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Character get() {return (char) r.nextInt('a', 'z' + 1);}public java.lang.Character get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Character[] array(int sz) {java.lang.Character[] result =new java.lang.Character[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}class Pchar {public char[] array(int sz) {return primitive(new Character().array(sz));}}class Shortimplements Supplier<java.lang.Short> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Short get() {return (short) r.nextInt(MOD);}public java.lang.Short get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Short[] array(int sz) {java.lang.Short[] result =new java.lang.Short[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}class Pshort {public short[] array(int sz) {return primitive(new Short().array(sz));}}class Integerimplements Supplier<java.lang.Integer> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Integer get() {return r.nextInt(MOD);}public java.lang.Integer get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Integer[] array(int sz) {int[] primitive = new Pint().array(sz);java.lang.Integer[] result =new java.lang.Integer[sz];for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {result[i] = primitive[i];}return result;}}class Pint implements IntSupplier {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic int getAsInt() {return r.nextInt(MOD);}public int get(int n) {return getAsInt();}public int[] array(int sz) {return r.ints(sz, 0, MOD).toArray();}}class Long implements Supplier<java.lang.Long> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Long get() {return r.nextLong(MOD);}public java.lang.Long get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Long[] array(int sz) {long[] primitive = new Plong().array(sz);java.lang.Long[] result =new java.lang.Long[sz];for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {result[i] = primitive[i];}return result;}}class Plong implements LongSupplier {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic long getAsLong() {return r.nextLong(MOD);}public long get(int n) {return getAsLong();}public long[] array(int sz) {return r.longs(sz, 0, MOD).toArray();}}class Floatimplements Supplier<java.lang.Float> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Float get() {return (float) trim(r.nextDouble());}public java.lang.Float get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Float[] array(int sz) {java.lang.Float[] result =new java.lang.Float[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}class Pfloat {public float[] array(int sz) {return primitive(new Float().array(sz));}}static double trim(double d) {return((double) Math.round(d * 1000.0)) / 100.0;}class Double implements Supplier<java.lang.Double> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic java.lang.Double get() {return trim(r.nextDouble());}public java.lang.Double get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.Double[] array(int sz) {double[] primitive =new Rand.Pdouble().array(sz);java.lang.Double[] result =new java.lang.Double[sz];for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {result[i] = primitive[i];}return result;}}class Pdouble implements DoubleSupplier {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);@Overridepublic double getAsDouble() {return trim(r.nextDouble());}public double get(int n) {return getAsDouble();}public double[] array(int sz) {double[] result = r.doubles(sz).toArray();Arrays.setAll(result,n -> result[n] = trim(result[n]));return result;}}class Stringimplements Supplier<java.lang.String> {SplittableRandom r = new SplittableRandom(47);private int strlen = 7; // Default lengthpublic String() {}public String(int strLength) {strlen = strLength;}@Overridepublic java.lang.String get() {return r.ints(strlen, 'a', 'z' + 1).collect(StringBuilder::new,StringBuilder::appendCodePoint,StringBuilder::append).toString();}public java.lang.String get(int n) {return get();}public java.lang.String[] array(int sz) {java.lang.String[] result =new java.lang.String[sz];Arrays.setAll(result, n -> get());return result;}}
}
ConvertTo.java
public interface ConvertTo {static boolean[] primitive(Boolean[] in) {boolean[] result = new boolean[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i]; // Autounboxing}return result;}static char[] primitive(Character[] in) {char[] result = new char[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static byte[] primitive(Byte[] in) {byte[] result = new byte[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static short[] primitive(Short[] in) {short[] result = new short[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static int[] primitive(Integer[] in) {int[] result = new int[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static long[] primitive(Long[] in) {long[] result = new long[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static float[] primitive(Float[] in) {float[] result = new float[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static double[] primitive(Double[] in) {double[] result = new double[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}// Convert from primitive array to wrapped array:static Boolean[] boxed(boolean[] in) {Boolean[] result = new Boolean[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i]; // Autoboxing}return result;}static Character[] boxed(char[] in) {Character[] result = new Character[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Byte[] boxed(byte[] in) {Byte[] result = new Byte[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Short[] boxed(short[] in) {Short[] result = new Short[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Integer[] boxed(int[] in) {Integer[] result = new Integer[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Long[] boxed(long[] in) {Long[] result = new Long[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Float[] boxed(float[] in) {Float[] result = new Float[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}static Double[] boxed(double[] in) {Double[] result = new Double[in.length];for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {result[i] = in[i];}return result;}
}
對于除了 int 、 long 和 double 之外的所有基本類型元素生成器,只生成數組,而不是 Count 中看到的完整操作集。這只是一個設計選擇,因為本書不需要額外的功能。
下面是對所有 Rand 工具的測試:
TestRand.java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;import static com.example.test.ArrayShow.show;public class TestRand {static final int SZ = 5;public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("Boolean");Boolean[] a1 = new Boolean[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a1, new Rand.Boolean()::get);show(a1);a1 = Stream.generate(new Rand.Boolean()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Boolean[]::new);show(a1);a1 = new Rand.Boolean().array(SZ + 2);show(a1);boolean[] a1b =new Rand.Pboolean().array(SZ + 3);show(a1b);System.out.println("Byte");Byte[] a2 = new Byte[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a2, new Rand.Byte()::get);show(a2);a2 = Stream.generate(new Rand.Byte()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Byte[]::new);show(a2);a2 = new Rand.Byte().array(SZ + 2);show(a2);byte[] a2b = new Rand.Pbyte().array(SZ + 3);show(a2b);System.out.println("Character");Character[] a3 = new Character[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a3, new Rand.Character()::get);show(a3);a3 = Stream.generate(new Rand.Character()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Character[]::new);show(a3);a3 = new Rand.Character().array(SZ + 2);show(a3);char[] a3b = new Rand.Pchar().array(SZ + 3);show(a3b);System.out.println("Short");Short[] a4 = new Short[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a4, new Rand.Short()::get);show(a4);a4 = Stream.generate(new Rand.Short()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Short[]::new);show(a4);a4 = new Rand.Short().array(SZ + 2);show(a4);short[] a4b = new Rand.Pshort().array(SZ + 3);show(a4b);System.out.println("Integer");int[] a5 = new int[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a5, new Rand.Integer()::get);show(a5);Integer[] a5b =Stream.generate(new Rand.Integer()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Integer[]::new);show(a5b);a5b = new Rand.Integer().array(SZ + 2);show(a5b);a5 = IntStream.generate(new Rand.Pint()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray();show(a5);a5 = new Rand.Pint().array(SZ + 3);show(a5);System.out.println("Long");long[] a6 = new long[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a6, new Rand.Long()::get);show(a6);Long[] a6b = Stream.generate(new Rand.Long()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Long[]::new);show(a6b);a6b = new Rand.Long().array(SZ + 2);show(a6b);a6 = LongStream.generate(new Rand.Plong()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray();show(a6);a6 = new Rand.Plong().array(SZ + 3);show(a6);System.out.println("Float");Float[] a7 = new Float[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a7, new Rand.Float()::get);show(a7);a7 = Stream.generate(new Rand.Float()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Float[]::new);show(a7);a7 = new Rand.Float().array(SZ + 2);show(a7);float[] a7b = new Rand.Pfloat().array(SZ + 3);show(a7b);System.out.println("Double");double[] a8 = new double[SZ];Arrays.setAll(a8, new Rand.Double()::get);show(a8);Double[] a8b =Stream.generate(new Rand.Double()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray(Double[]::new);show(a8b);a8b = new Rand.Double().array(SZ + 2);show(a8b);a8 = DoubleStream.generate(new Rand.Pdouble()).limit(SZ + 1).toArray();show(a8);a8 = new Rand.Pdouble().array(SZ + 3);show(a8);System.out.println("String");String[] s = new String[SZ - 1];Arrays.setAll(s, new Rand.String()::get);show(s);s = Stream.generate(new Rand.String()).limit(SZ).toArray(String[]::new);show(s);s = new Rand.String().array(SZ + 1);show(s);Arrays.setAll(s, new Rand.String(4)::get);show(s);s = Stream.generate(new Rand.String(4)).limit(SZ).toArray(String[]::new);show(s);s = new Rand.String(4).array(SZ + 1);show(s);}
}
ArrayShow.java
import java.util.*;public interface ArrayShow {static void show(Object[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(boolean[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(byte[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(char[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(short[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(int[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(long[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(float[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}static void show(double[] a) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));}// Start with a description:static void show(String info, Object[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, boolean[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, byte[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, char[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, short[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, int[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, long[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, float[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}static void show(String info, double[] a) {System.out.print(info + ": ");show(a);}
}
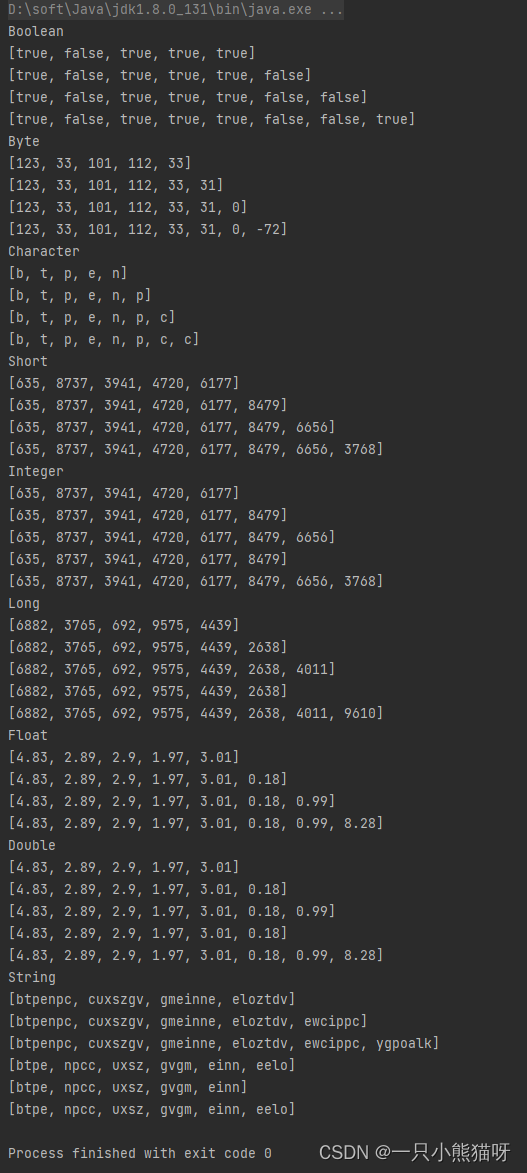
注意(除了 String 部分之外),這段代碼與 TestCount.java 中的代碼相同,Count 被 Rand 替換。
泛型和基本數組
在本章的前面,我們被提醒,泛型不能和基元一起工作。在這種情況下,我們必須從基元數組轉換為包裝類型的數組,并且還必須從另一個方向轉換。ConvertTo.java是一個轉換器可以同時對所有類型的數據執行操作。
primitive() 的每個版本都創建一個準確長度的適當基元數組,然后從包裝類的 in 數組中復制元素。如果任何包裝的數組元素是 null ,你將得到一個異常(這是合理的—否則無法選擇有意義的值進行替換)。注意在這個任務中自動裝箱如何發生。
下面是對 ConvertTo 中所有方法的測試:
import java.util.*;import static com.example.test.ArrayShow.show;
import static com.example.test.ConvertTo.boxed;
import static com.example.test.ConvertTo.primitive;public class TestConvertTo {static final int SIZE = 6;public static void main(String[] args) {Boolean[] a1 = new Boolean[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a1, new Rand.Boolean()::get);boolean[] a1p = primitive(a1);show("a1p", a1p);Boolean[] a1b = boxed(a1p);show("a1b", a1b);Byte[] a2 = new Byte[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a2, new Rand.Byte()::get);byte[] a2p = primitive(a2);show("a2p", a2p);Byte[] a2b = boxed(a2p);show("a2b", a2b);Character[] a3 = new Character[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a3, new Rand.Character()::get);char[] a3p = primitive(a3);show("a3p", a3p);Character[] a3b = boxed(a3p);show("a3b", a3b);Short[] a4 = new Short[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a4, new Rand.Short()::get);short[] a4p = primitive(a4);show("a4p", a4p);Short[] a4b = boxed(a4p);show("a4b", a4b);Integer[] a5 = new Integer[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a5, new Rand.Integer()::get);int[] a5p = primitive(a5);show("a5p", a5p);Integer[] a5b = boxed(a5p);show("a5b", a5b);Long[] a6 = new Long[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a6, new Rand.Long()::get);long[] a6p = primitive(a6);show("a6p", a6p);Long[] a6b = boxed(a6p);show("a6b", a6b);Float[] a7 = new Float[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a7, new Rand.Float()::get);float[] a7p = primitive(a7);show("a7p", a7p);Float[] a7b = boxed(a7p);show("a7b", a7b);Double[] a8 = new Double[SIZE];Arrays.setAll(a8, new Rand.Double()::get);double[] a8p = primitive(a8);show("a8p", a8p);Double[] a8b = boxed(a8p);show("a8b", a8b);}
}
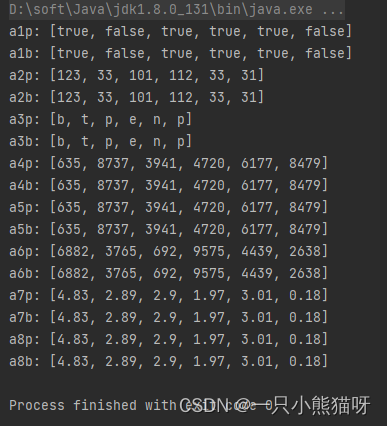
在每種情況下,原始數組都是為包裝類型創建的,并使用 Arrays.setAll() 填充,正如我們在 TestCouner.java 中所做的那樣(這也驗證了 Arrays.setAll() 是否能同 Integer ,Long ,和 Double )。然后 ConvertTo.primitive() 將包裝器數組轉換為對應的基元數組,ConverTo.boxed() 將其轉換回來。








)


)

)




)
