一、linux應用程序如何接收參數?
1. argc、argv
Linux應用程序執行時,我們往往通過命令行帶入參數給程序,比如
ls /dev/ -l
其中參數 /dev/ 、-l都是作為參數傳遞給命令 ls
應用程序又是如何接收這些參數的?
通常應用程序都是從main函數開始執行,傳統的main函數風格如下:
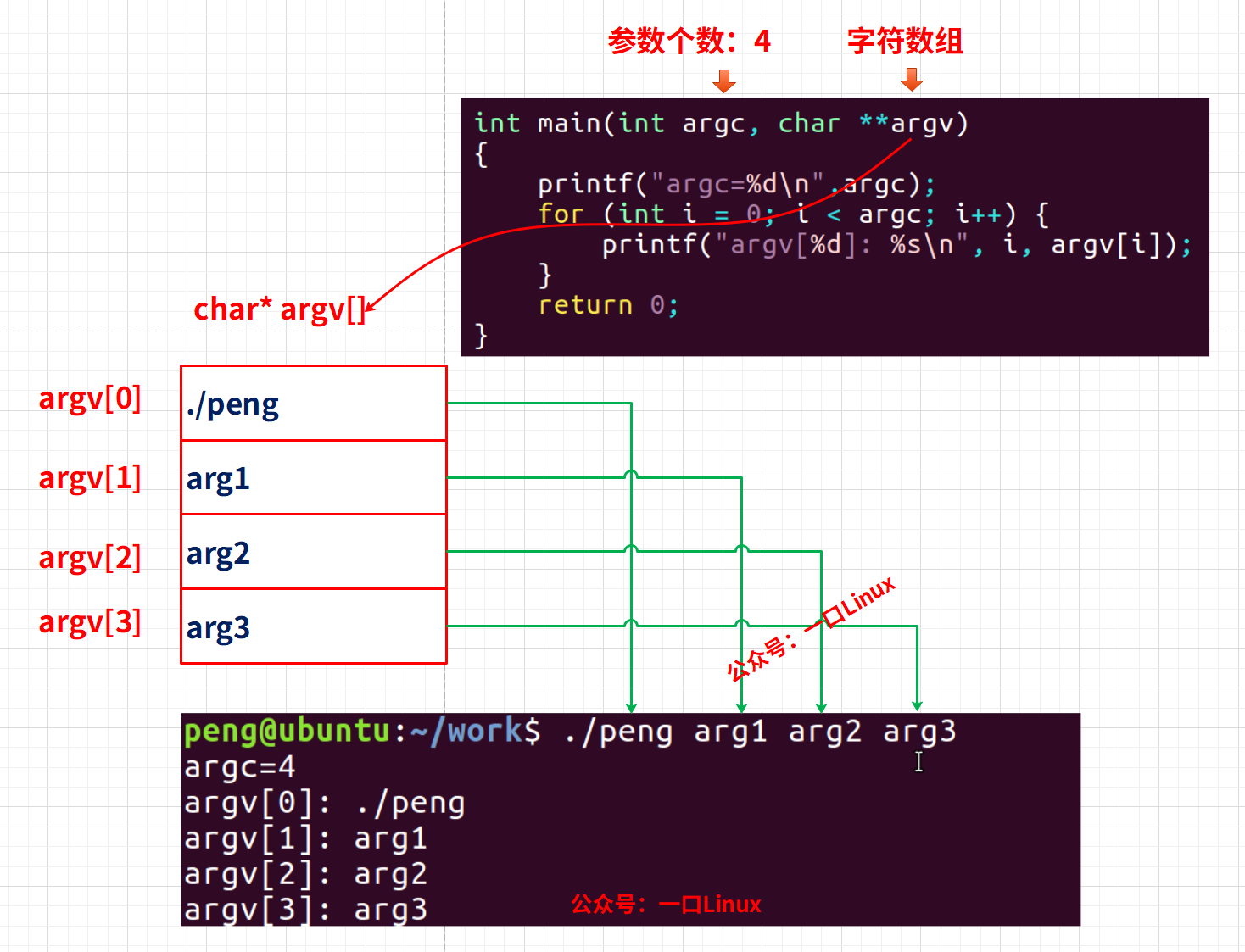
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
argc:
程序的命令行參數的數量,用于統計參數數量。
argv:
是一個指向一個字符串數組的指針,數組包含了參數,每個字符串就是一個參數,最后一個元素為0。
過一般習慣使用多級指針來操作字符串。
*char argv[]有時候我們也寫成char argv,
**argv[]**是一個存放字符類型元素地址的數組。
因為 C 中是有字符串的概念的:將每個字符存放在 char 數組,最后一個元素為**\0**表示字符串的結束。
**printf(%s)**就是輸出字符串。
并且一般使用argv指針來訪問、處理argv[]數組的內容。
C語言中,數組就是一個指針加偏移量。
所以argv則是指向一個指針數組argv[]的指針,不用定義,直接可以用。
在argv[]數組中存放的的指針指向輸入命令的各部分**(調用程序、選項、參數)**。
2. 舉例
下面我們用一個實例來理解argc和argv
/*
* argc: 命令行參數的個數
* argv: 字符指針數組(指向各個命令行參數的字符指針所構成的數組)
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) // 接收命令行參數
{printf("argc=%d\n",argc);for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++) {printf("argv[%d]: %s\n", i, argv[i]); // 遍歷字符指針數組argv}return 0;
}
執行結果
peng@ubuntu:~/work$ ./peng arg1 arg2 arg3
argc=4
argv[0]: ./peng
argv[1]: arg1
argv[2]: arg2
argv[3]: arg3參數與argc,argv關系如下:
二、選項
1. 選項含義
linux程序除了上述情況以外,我們還經常會遇到一個使用方法就是選項應用,
比如:ping命令
peng@ubuntu:~/work$ ping -h
Usage: ping [-aAbBdDfhLnOqrRUvV] [-c count] [-i interval] [-I interface][-m mark] [-M pmtudisc_option] [-l preload] [-p pattern] [-Q tos][-s packetsize] [-S sndbuf] [-t ttl] [-T timestamp_option][-w deadline] [-W timeout] [hop1 ...] destination
參數含義:
-a:嘗試將IP地址解析為主機名。
-A:使用響應數據包中的附加數據。
-b:允許ping廣播地址。
-B:不允許ping廣播地址。
-c count:設置要發送的數據包數量。
-d:使用SO_DEBUG選項。
-D:不將socket設為分離模式。
-f:向目標發送一個“強制”數據包。
-h:顯示幫助信息。
-i interval:設置發送數據包之間的時間間隔。
-I interface:設置要使用的網絡接口。
-l preload:設置發送的數據包數量。
-m mark:設置ping數據包的標記。
-M pmtudisc_option:設置MTU發現選項。
-n:不要將IP地址解析為主機名。
-O:啟用原始輸出。
-p pattern:設置數據包的模式。
-Q tos:設置服務類型。
-r:不使用路由表,直接發送數據包到目標主機。
-R:啟用記錄路由。
-s packetsize:設置數據包的大小。
-S sndbuf:設置套接字的發送緩沖區大小。
-t ttl:設置數據包的TTL值。
-T timestamp_option:設置時間戳選項。
-U:使用UDP數據包。
-v:顯示詳細的ping命令輸出。
-V:顯示ping命令的版本信息。
-w deadline:設置等待響應的時間。
-W timeout:設置等待響應的超時時間。destination:指定要ping的目標主機或IP地址。
這些 - 開頭的都是選項,
[]表示可選的意思
[-aAbBdDfhLnOqrRUvV] 是無參的選項
[-c count] [-i interval] [-I interface]
[-m mark] [-M pmtudisc_option] [-l preload] [-p pattern] [-Q tos]
[-s packetsize] [-S sndbuf] [-t ttl] [-T timestamp_option]
[-w deadline] [-W timeout] [hop1 ...] 這些都是有參數的選項
destination 必須填寫的參數
前輩們利用這點發明了“UNIX 風格”的命令,選項前面加一個橫杠-,用于區分選項和參數。
2. 程序如何區分參數和選項?
在程序的代碼實現中,按照 UNIX 的代碼慣例,上來直接跳過第一個,然后判斷指針指向的字符串第一個字符是不是-,如果是的,那么進入一個switch判斷,用case列出多種支持的情況下,應該執行什么代碼。
例如下面這樣就可以判斷選項和處理參數:
int c;
while (--argc > 0 && (*++argv)[0] == '-' {while (c = *++argv[0] {switch(c){case 'x':...break;case 'n':...break;default:printf("xxx: illegal opyion %c\n", c);...break;}}
}
3. getopt、getopt_long
事實這么處理選項參數是比較麻煩的,
linux提供了選項解析的函數:
// 頭文件
#include<unistd.h>
#include<getopt.h> /*所在頭文件 */
int getopt(intargc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring);
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring,const struct option *longopts, int*longindex);
int getopt_long_only(int argc, char * const argv[],const char *optstring,const struct option *longopts, int*longindex);
extern char *optarg; /*系統聲明的全局變量 */
extern int optind, opterr, optopt;
三、getopt
1. 定義:
int getopt(int argc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring);
功能:getopt是用來解析命令行選項參數的,但是只能解析短選項: **-d 100**,不能解析長選項:**--prefix**
參數argc:main()函數傳遞過來的參數的個數argv:main()函數傳遞過來的參數的字符串指針數組optstring:選項字符串,告知 getopt()可以處理哪個選項以及哪個選項需要參數
返回:如果選項成功找到,返回選項字母;如果所有命令行選項都解析完畢,返回 -1;如果遇到選項字符不在 optstring 中,返回字符 ‘?’;如果遇到丟失參數,那么返回值依賴于 optstring 中第一個字符,如果第一個字符是 ‘:’ 則返回’:‘,否則返回’?'并提示出錯誤信息。
2. optstring 含義 【重要】
下邊重點舉例說明optstring的格式意義:
char*optstring = “ab:c::”;
單個字符a 表示選項a沒有參數 格式:-a即可,不加參數
單字符加冒號b: 表示選項b有且必須加參數 格式:-b 100或-b100,但-b=100錯
單字符加2冒號c:: 表示選項c可以有,也可以無 格式:-c200,其它格式錯誤
上面這個 optstring 在傳入之后,getopt 函數將依次檢查命令行是否指定了 -a, -b, -c(這需要多次調用 getopt 函數,直到其返回-1),當檢查到上面某一個參數被指定時,函數會返回被指定的參數名稱(即該字母)
系統聲明的4個全局變量含義如下:
optarg —— 指向當前選項參數(如果有)的指針。
optind —— 再次調用 getopt() 時的下一個 argv指針的索引。
optopt —— 最后一個未知選項。
opterr -—— 如果不希望getopt()打印出錯信息,則只要將全域變量opterr設為0即可。
3. 實例
說千道萬,不如來一個實例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<getopt.h>
int main(intargc, char *argv[])
{int opt;char *string = "a::b:c:d";while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, string))!= -1){ printf("opt = %c\t\t", opt);printf("optarg = %s\t\t",optarg);printf("optind = %d\t\t",optind);printf("argv[optind] = %s\n",argv[optind]);}
}
- 正確輸入參數,執行結果如下:
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./peng -a100 -b 200 -c 300 -d
opt = a optarg = 100 optind = 2 argv[optind] = -b
opt = b optarg = 200 optind = 4 argv[optind] = -c
opt = c optarg = 300 optind = 6 argv[optind] = -d
opt = d optarg = (null) optind = 7 argv[optind] = (null)
或者
ork/test$ ./peng -a100 -b200 -c300 -d
opt = a optarg = 100 optind = 2 argv[optind] = -b200
opt = b optarg = 200 optind = 3 argv[optind] = -c300
opt = c optarg = 300 optind = 4 argv[optind] = -d
opt = d optarg = (null) optind = 5 argv[optind] = (null)
- 輸入選項參數錯誤的情況
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./peng -a 100 -b 200 -c 300 -d
opt = a optarg = (null) optind = 2 argv[optind] = 100
opt = b optarg = 200 optind = 5 argv[optind] = -c
opt = c optarg = 300 optind = 7 argv[optind] = -d
opt = d optarg = (null) optind = 8 argv[optind] = (null)
導致解析錯誤,第一個 optarg = null,實際輸入參數 100,由于格式不正確造成的(可選參數格式固定)
- 參數丟失,也會導致錯誤
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./peng -a -b 200 -c
opt = a optarg = (null) optind = 2 argv[optind] = -b
opt = b optarg = 200 optind = 4 argv[optind] = -c
./peng: option requires an argument -- 'c'
opt = ? optarg = (null) optind = 5 argv[optind] = (null)
c選項是必須有參數的
- 命令行選項未定義,-e選項未在optstring中定義,會報錯:
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./peng -t
./peng: invalid option -- 't'
opt = ? optarg = (null) optind = 2 argv[optind] = (null)
四、getopt_long
1. 定義:
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring,
const struct option *longopts,int *longindex);
功能:包含 getopt 功能,增加了解析長選項的功能如:--prefix --help
參數:longopts 指明了長參數的名稱和屬性longindex 如果longindex非空,它指向的變量將記錄當前找到參數符合longopts里的第幾個元素的描述,即是 longopts 的下標值
返回:對于短選項,返回值同 getopt 函數;對于長選項,如果 flag 是 NULL ,返回 val ,否則返回 0 ;對于錯誤情況返回值同 getopt 函數
2. struct option
struct option {const char *name; /* 參數名稱 */int has_arg; /* 指明是否帶有參數 */int *flag; /* flag=NULL時,返回value;不為空時,*flag=val,返回0 */int val; /* 用于指定函數找到選項的返回值或flag非空時指定*flag的值 */
};
參數has_arg 說明:
has_arg 指明是否帶參數值,其數值可選:
no_argument 表明長選項不帶參數,如:–name, --helprequired_argument 表明長選項必須帶參數,如:–prefix /root或 --prefix=/rootoptional_argument 表明長選項的參數是可選的,如:–help或 –prefix=/root,其它都是錯誤
3. 實例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<getopt.h>
int main(intargc, char *argv[])
{int opt;int digit_optind = 0;int option_index = 0;char *string = "a::b:c:d";static struct option long_options[] ={ {"reqarg", required_argument,NULL, 'r'},{"optarg", optional_argument,NULL, 'o'},{"noarg", no_argument, NULL,'n'},{NULL, 0, NULL, 0},}; while((opt =getopt_long_only(argc,argv,string,long_options,&option_index))!= -1){ printf("opt = %c\t\t", opt);printf("optarg = %s\t\t",optarg);printf("optind = %d\t\t",optind);printf("argv[optind] =%s\t\t", argv[optind]);printf("option_index = %d\n",option_index);}
}
- 正確執行命令
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./long --reqarg 100 --optarg=200 --noarg
opt = r optarg = 100 optind = 3 argv[optind] =--optarg=200 option_index = 0
opt = o optarg = 200 optind = 4 argv[optind] =--noarg option_index = 1
opt = n optarg = (null) optind = 5 argv[optind] =(null) option_index = 2
或者
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./long –reqarg=100 --optarg=200 --noarg
opt = o optarg = 200 optind = 3 argv[optind] =--noarg option_index = 1
opt = n optarg = (null) optind = 4 argv[optind] =(null) option_index = 2
- 可選選項可以不給參數
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./long --reqarg 100 --optarg --noarg
opt = r optarg = 100 optind = 3 argv[optind] =--optarg option_index = 0
opt = o optarg = (null) optind = 4 argv[optind] =--noarg option_index = 1
opt = n optarg = (null) optind = 5 argv[optind] =(null) option_index = 2
- 輸入長選項錯誤的情況
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./long --reqarg 100 --optarg 200 --noarg
opt = r optarg = 100 optind = 3 argv[optind] =--optarg option_index = 0
opt = o optarg = (null) optind = 4 argv[optind] =200 option_index = 1
opt = n optarg = (null) optind = 6 argv[optind] =(null) option_index = 2
五、getopt_long_only
getopt_long_only 函數與 getopt_long 函數使用相同的參數表,在功能上基本一致
只是 getopt_long 只將 --name 當作長參數,但 getopt_long_only 會將 --name 和 -name 兩種選項都當作長參數來匹配
getopt_long_only 如果選項 -name 不能在 longopts 中匹配,但能匹配一個短選項,它就會解析為短選項。
六、綜合實例
下面這個例子,是一口君從開源項目ifplug提取出來的命令提取小例子,
大家可以根據自己需要,基于這個框架,定制自己的程序。
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/param.h>#define ETHCHECKD_VERSION "1.1"int delay_up = 0;
char *interface = "eth0";void usage(char *p) {if (strrchr(p, '/'))p = strchr(p, '/')+1;printf("%s [options]\n"" -i --iface=IFACE Specify ethernet interface (%s)\n" " -d --delay-up=SECS Specify delay time (%i)\n"" -h --help Show this help\n",p,interface,delay_up);
}void parse_args(int argc, char *argv[]) {static struct option long_options[] = {{"iface", required_argument, 0, 'i'},{"delay-up", required_argument, 0, 'd'},{"help", no_argument, 0, 'h'},{"version", no_argument, 0, 'v'},{0, 0, 0, 0}};int option_index = 0;int help = 0, _kill = 0, _check = 0, _version = 0, _suspend = 0, _resume = 0, _info = 0;for (;;) {int c;if ((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "i:d:hv", long_options, &option_index)) < 0)break;switch (c) {case 'i' :interface = strdup(optarg);printf("interface %s\n",interface);break;case 'd':delay_up = atoi(optarg);printf("delay_up %d\n",delay_up);break;case 'h':usage(argv[0]);break;case 'v':printf("peng "ETHCHECKD_VERSION"\n");break;default:fprintf(stderr, "Unknown parameter.\n");exit(1);}}}static volatile int alarmed = 0;int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {parse_args(argc, argv);return 0;
}
下面是測試結果
- 短選項
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param -h
param [options]-i --iface=IFACE Specify ethernet interface (eth0)-d --delay-up=SECS Specify delay time (0)-h --help Show this help
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param -v
peng 1.1peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param -vh
peng 1.1
param [options]-i --iface=IFACE Specify ethernet interface (eth0)-d --delay-up=SECS Specify delay time (0)-h --help Show this help peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param -i eth3 -d 15
interface eth3
delay_up 15 peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param -i eth3 -d 15 -h
interface eth3
delay_up 15
param [options]-i --iface=IFACE Specify ethernet interface (eth3)-d --delay-up=SECS Specify delay time (15)-h --help Show this help
- 長選項
peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param --help
param [options]-i --iface=IFACE Specify ethernet interface (eth0)-d --delay-up=SECS Specify delay time (0)-h --help Show this helppeng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param --version
peng 1.1peng@ubuntu:~/work/test$ ./param --iface eth3 --delay-up 15
interface eth3
delay_up 15
talk is cheap!
test this code!
快操練起來吧!!!
更多嵌入式linux資料,后臺留言:資料
也可以加一口君好友
)



![【Mysql】[Err] 1293 - Incorrect table definition;](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/【Mysql】[Err] 1293 - Incorrect table definition;)














