Introduction??介紹
In the ever-evolving world of software development, finding the right architectural pattern is akin to selecting the foundation for a building. One such architectural paradigm that has gained recognition for its ability to promote maintainability, flexibility, and testability is the Onion Architecture. This article takes you on a journey through the layers of Onion Architecture, unveiling its principles, benefits, and real-world applications. Whether you're a seasoned developer looking to deepen your architectural knowledge or a curious novice eager to explore innovative software design, this article will serve as your guide to understanding and implementing Onion Architecture in your projects.
在不斷發展的軟件開發世界中,找到正確的建筑模式類似于選擇建筑物的地基。洋蔥架構就是這樣一種架構范式,因其提高可維護性、靈活性和可測試性的能力而獲得認可。本文將帶您了解洋蔥架構的各個層面,揭示其原理、優點和實際應用。無論您是希望加深架構知識的經驗豐富的開發人員,還是渴望探索創新軟件設計的好奇新手,本文都將作為您在項目中理解和實施洋蔥架構的指南。
What Is Onion Architecture?
什么是洋蔥架構?
Onion Architecture is a software architectural pattern that emphasizes the separation of concerns and the organization of an application into distinct, concentric layers or "onions."
洋蔥架構是一種軟件架構模式,強調關注點的分離以及將應用程序組織成不同的同心層或“洋蔥”。
At the core of Onion Architecture is the concept of dependency inversion.
洋蔥架構的核心是依賴倒置的概念。
This principle, which is one of the SOLID principles, encourages the inversion of the traditional dependencies between higher-level and lower-level modules. In the context of Onion Architecture, this means that inner layers depend on outer layers, while outer layers remain independent of the inner layers.
這一原則是 SOLID 原則之一,它鼓勵在更高級別和較低級別模塊之間顛倒傳統依賴關系。在洋蔥架構的背景下,這意味著內層依賴于外層,而外層則獨立于內層。
Run Code from Your Browser - No Installation Required
從瀏覽器運行代碼 - 無需安裝
Get started??開始使用

Key Layers of Onion Architecture
洋蔥架構的關鍵層
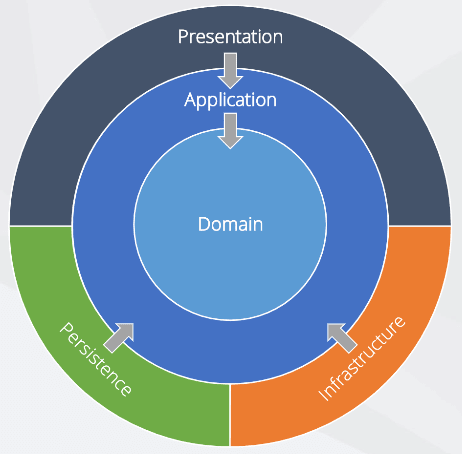
The Onion Architecture typically consists of several concentric layers, each with a specific responsibility:
洋蔥架構通常由幾個同心層組成,每個層都有特定的職責:
- Core Layer: This innermost layer, also known as the "Domain Layer" or "Model Layer," contains the core business logic, entities, and domain-specific rules. It is agnostic to any external frameworks or technologies;核心層 :這個最里層,也稱為“域層”或“模型層”,包含核心業務邏輯、實體和特定于域的規則。它與任何外部框架或技術無關;
- Application Layer: The layer surrounding the Core is the "Application Layer." It acts as an intermediary between the Core and the outer layers, handling application-specific use cases, orchestrating business logic, and often containing application services;應用層 :核心周圍的層是“應用層”。它充當核心層和外層之間的中介,處理特定于應用程序的用例,編排業務邏輯,并且通常包含應用程序服務;
- Infrastructure Layer: The Infrastructure Layer is responsible for interacting with external systems, services, and frameworks. It includes database access, third-party integrations, and any technology-specific implementations. This layer typically depends on the Core and Application layers but is not dependent on them;基礎設施層 :基礎設施層負責與外部系統、服務和框架進行交互。它包括數據庫訪問、第三方集成和任何特定于技術的實現。該層通常依賴于核心層和應用程序層,但不依賴于它們;
- Presentation Layer: The outermost layer is the "Presentation Layer," which deals with user interfaces and user interaction. This layer can be web-based, desktop-based, or any other form of user interface. It communicates with the Application Layer to request and display data, but it is independent of the inner layers.表示層 :最外層是“表示層”,它處理用戶界面和用戶交互。此層可以是基于 Web、基于桌面或任何其他形式的用戶界面。它與應用層通信以請求和顯示數據,但它獨立于內部層。
You can find more information about Onion Architecture in this Article.
您可以在本文中找到有關洋蔥架構的更多信息 。
Onion Architecture Implementation Example in Python
Python 中的洋蔥架構實現示例
Let's consider the following Python code:
讓我們考慮以下 Python 代碼:
# Application layer (entry point)
def main():
app = Application()
app.run()
# Domain layer (business logic)
class Application:
def __init__(self):
self.service = Service()
def run(self):
result = self.service.process_data()
print(result)
# Infrastructure layer (data processing, external dependencies)
class Service:
def __init__(self):
self.repository = Repository()
def process_data(self):
data = self.repository.get_data()
return data
# Data access layer (abstraction over data storage)
class Repository:
def get_data(self):
# Implementation for accessing data from a database, file, API, etc.
return "Data from external source"
- Application layer: This layer is the entry point to the application. It creates an instance of the Application class and calls its run method;應用層: 此層是應用程序的入口點。它創建 Application 類的實例并調用其 run 方法;
- Domain layer: This layer contains the core business logic of the application. The Application class encapsulates the use of the Service class, which represents a higher-level domain service;域層: 該層包含應用程序的核心業務邏輯。Application 類封裝了 Service 類的使用,該類表示更高級別的域服務;
- Infrastructure layer: This layer handles data access and external dependencies. The Service class uses the Repository class to access data;基礎設施層: 該層處理數據訪問和外部依賴關系。Service 類使用 Repository 類訪問數據;
- Data access layer: This layer abstracts the details of data storage. The Repository class provides a generic interface for retrieving data, without specifying the underlying implementation (e.g., database, file).數據接入層: 該層抽象了數據存儲的細節。Repository 類提供了一個用于檢索數據的通用接口,而無需指定底層實現(例如,數據庫、文件)。
Key points of onion architecture
洋蔥架構的要點
- Dependency direction: Inner layers depend only on outer layers, promoting loose coupling;依賴方向: 內層僅依賴于外層,促進松耦合;
- Abstraction: The Repository class acts as an abstraction layer, hiding the details of data storage;抽象化:Repository 類充當抽象層,隱藏數據存儲的細節;
- Layers: The application is divided into distinct layers, each with a specific responsibility;層: 應用程序分為不同的層,每個層都有特定的職責;
- Testability: The onion architecture makes it easier to write unit tests, as inner layers can be tested independently.測試: 洋蔥架構使編寫單元測試變得更加容易,因為內層可以獨立測試。
What is Dependency Inversion?
什么是依賴倒置?
Dependency Inversion is a crucial concept in software design and architecture that promotes the decoupling of high-level modules from low-level modules, reducing the dependency of one on the other. It is one of the SOLID principles, initially introduced by Robert C. Martin, which stands for the "D" in SOLID.
依賴倒置是軟件設計和架構中的一個關鍵概念,它促進了高級模塊與低級模塊的解耦,減少了一個模塊對另一個模塊的依賴。它是 SOLID 原則之一,最初由 Robert C. Martin 提出,代表 SOLID 中的“D”。
Understanding dependency inversion principle
了解依賴倒置原理
At its core, the Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP) suggests two essential guidelines:
從本質上講,依賴倒置原則 (DIP) 提出了兩個基本準則:
- High-level modules (or abstractions) should not depend on low-level modules (concrete implementations). Both should depend on abstractions;高級模塊 (或抽象)不應依賴于低級模塊(具體實現)。兩者都應該依賴于抽象;
- Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstractions.抽象不應依賴于細節。細節應取決于抽象。
In other words, rather than coding to specific implementations, developers should code to interfaces or abstract classes. This inversion of control allows for more flexible, extensible, and maintainable software systems.
換句話說,開發人員應該對接口或抽象類進行編碼,而不是對特定實現進行編碼。這種控制反轉允許更靈活、可擴展和可維護的軟件系統。
Dependency inversion with Python
使用 Python 進行依賴關系反轉
Dependency Inversion is closely related to the use of interfaces, abstract classes, and dependency injection techniques.
依賴倒置與接口、抽象類和依賴注入技術的使用密切相關。
In the context of onion architecture, this principle is applied to ensure that: ?
在洋蔥架構的上下文中 ,應用此原則來確保: ?
- Inner layers (core domain logic) remain independent of external dependencies (infrastructure);內部層(核心域邏輯) 保持獨立于外部依賴項(基礎設施);
- Outer layers (infrastructure) are built around abstractions defined by inner layers.外層(基礎設施) 是圍繞內層定義的抽象構建的。
For example, we can consider the following code in Python:
例如,我們可以考慮 Python 中的以下代碼:
# Application layer
class Application:
def __init__(self, data_service):
self.data_service = data_service
def run(self):
data = self.data_service.fetch_data()
# Process data
print(data)
# Domain layer
class DataService:
def __init__(self, data_repository):
self.data_repository = data_repository
def fetch_data(self):
data = self.data_repository.get_data()
# Process data
return data
# Infrastructure layer
class DataRepository:
def get_data(self):
# Retrieve data from a database
return "Data from database"
- Dependency Inversion:依賴關系倒置 :
- The Application class depends on the DataService interface, not a specific implementation;Application 類依賴于 DataService 接口,而不是特定的實現;
- The DataService class depends on the DataRepository interface, not a specific implementation.DataService 類依賴于 DataRepository 接口,而不是特定的實現。
-
- Onion Architecture:洋蔥架構 :
- The Application layer (inner layer) depends on the DataService (domain layer);應用層(內層)依賴于 DataService(域層);
- The DataService depends on the DataRepository (infrastructure layer). This ensures that the core domain logic (application and data service) is independent of the specific data source (file or database).DataService 依賴于 DataRepository(基礎設施層)。這可確保核心域邏輯(應用程序和數據服務)獨立于特定數據源(文件或數據庫)。
-
- Flexibility: ??靈活性 :
- To change the data source, you only need to replace the DataRepository implementation. The DataService and Application classes remain unchanged.要更改數據源,您只需替換 DataRepository 實現。DataService 和 Application 類保持不變。
-
You can find more information about Dependency Inversion via this Article.
您可以通過本文找到有關依賴關系反轉的更多信息 。
Start Learning Coding today and boost your Career Potential
立即開始學習編碼并提升您的職業潛力
Start today!??從今天開始!

Pros and Cons of Onion Architecture
洋蔥架構的優缺點
| Feature??特征 | Pros??優點 | Cons??缺點 |
| Modularity??模塊性 | Easier to understand, maintain, and extend codebase 更易于理解、維護和擴展代碼庫 | Increased complexity for smaller applications 小型應用的復雜性增加 |
| Testability??測試 | Facilitates unit testing and reduces debugging time 促進單元測試并減少調試時間 | Initial learning curve for developers 開發人員的初始學習曲線 |
| Flexibility??靈活性 | Allows for easy changes to business requirements 允許輕松更改業務需求 | Potential for performance overhead 潛在的性能開銷 |
| Isolation of Concerns??關注點的隔離 | Separates business logic from external concerns 將業務邏輯與外部關注點分開 | May require more boilerplate code 可能需要更多樣板代碼 |
| Maintainability??可維護性 | Improves code maintainability and reduces the impact of changes 提高代碼可維護性并減少更改的影響 | Dependency management can be challenging 依賴項管理可能具有挑戰性 |
| Scalability??可擴展性 | Enables easy scaling of specific layers or components 能夠輕松擴展特定層或組件 | Not suitable for every project 并非適合每個項目 |
| Dependency Inversion??依賴關系反轉 | Promotes loose coupling and flexibility 促進松散耦合和靈活性 | Increased development time for setup 增加設置的開發時間 |
| Reusability??可 重用 | Encourages code reuse and modularity 鼓勵代碼重用和模塊化 | Can introduce unnecessary complexity for smaller applications 對于較小的應用程序,可能會帶來不必要的復雜性 |
It's important to weigh the pros and cons of Onion Architecture carefully based on your project's specific requirements and constraints. While it offers several advantages in terms of maintainability and flexibility, it may not be the best choice for every software development endeavor.
根據項目的具體要求和限制仔細權衡洋蔥架構的優缺點非常重要。雖然它在可維護性和靈活性方面提供了多種優勢,但它可能不是每個軟件開發工作的最佳選擇。
FAQs??常見問題
Q: What is Onion Architecture?
問: 什么是洋蔥架構?
A: Onion Architecture is a software architectural pattern that emphasizes the separation of concerns by organizing a software application into concentric layers, with each layer serving a specific purpose and level of abstraction.
一個: 洋蔥架構是一種軟件架構模式,它強調通過將軟件應用程序組織成同心層來分離關注點,每一層都有特定的目的和抽象級別。
Q: What are the main components or layers in Onion Architecture?
問: 洋蔥架構中的主要組件或層是什么?
A: Onion Architecture typically consists of four main layers: Core, Application, Infrastructure, and Presentation. The Core layer contains the application's business logic, the Application layer handles use cases and application services, the Infrastructure layer deals with data access and external dependencies, and the Presentation layer is responsible for user interfaces.
一個: 洋蔥架構通常由四個主要層組成:核心層、應用程序層、基礎設施層和演示層。核心層包含應用程序的業務邏輯,應用層處理用例和應用程序服務,基礎設施層處理數據訪問和外部依賴關系,表示層負責用戶界面。
Q: What is the advantage of using Onion Architecture?
問: 使用洋蔥架構有什么優勢?
A: One of the main advantages of Onion Architecture is its modularity and testability. It promotes clean separation of concerns, making it easier to develop and maintain software. It also allows for extensive unit testing.
一個: 洋蔥架構的主要優勢之一是其模塊化和可測試性。它促進關注點的干凈分離,使軟件的開發和維護變得更加容易。它還允許進行廣泛的單元測試。
Q: How does Onion Architecture relate to the Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)?
問: 洋蔥架構與依賴反轉原則 (DIP) 有何關系?
A: Onion Architecture adheres closely to the Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP), which states that high-level modules should not depend on low-level modules but rather both should depend on abstractions. This principle helps achieve flexibility and loose coupling in the architecture.
一個: 洋蔥架構嚴格遵守依賴反轉原則 (DIP),該原則指出高級模塊不應依賴于低級模塊,而兩者都應依賴于抽象。這一原理有助于在架構中實現靈活性和松耦合。
Q: Is Onion Architecture suitable for all types of software projects?
問: 洋蔥架構是否適用于所有類型的軟件項目?
A: While Onion Architecture offers benefits like maintainability and testability, it may not be necessary for small or straightforward projects. It is best suited for complex applications with evolving requirements.
一個: 雖然 Onion Architecture 提供了可維護性和可測試性等優勢,但對于小型或簡單的項目來說可能沒有必要。它最適合要求不斷變化的復雜應用。
Q: Can existing projects be refactored to use Onion Architecture?
問: 現有項目可以重構以使用 Onion Architecture 嗎?
A: Yes, it is possible to refactor existing projects to follow Onion Architecture principles. However, it may require careful planning and migration strategies to avoid disrupting the existing functionality.
一個: 是的,可以重構現有項目以遵循 Onion 架構原則。但是,可能需要仔細規劃和遷移策略,以避免中斷現有功能。
Q: Are there any specific tools or frameworks for implementing Onion Architecture?
問: 是否有任何特定的工具或框架來實現洋蔥架構?
A: Onion Architecture is more of a design principle than a specific framework. Developers can implement it in various programming languages and platforms. However, some development frameworks, such as ASP.NET Core, offer features that align well with Onion Architecture.
一個: 洋蔥架構更像是一種設計原則,而不是一個特定的框架。開發人員可以用各種編程語言和平臺實現它。然而,一些開發框架(例如 ASP.NET Core)提供了與 Onion Architecture 非常一致的功能。
Q: What are some real-world examples of applications using Onion Architecture?
問: 使用 Onion Architecture 的應用程序有哪些實際示例?
A: Several software applications and systems, including content management systems, e-commerce platforms, and enterprise-level applications, have successfully adopted Onion Architecture to improve maintainability and scalability.
一個: 一些軟件應用程序和系統,包括內容管理系統、電子商務平臺和企業級應用程序,已經成功采用了洋蔥架構來提高可維護性和可擴展性。
Q: Does Onion Architecture impose performance overhead due to its layers?
問: 洋蔥架構是否會因其層而產生性能開銷?
A: While Onion Architecture introduces some level of abstraction, the performance overhead is generally minimal in most applications. The benefits of clean separation of concerns often outweigh any minor performance considerations.
一個: 雖然洋蔥架構引入了一定程度的抽象,但在大多數應用程序中,性能開銷通常很小。干凈地分離關注點的好處通常超過任何次要的性能考慮因素。
Q: Are there any recommended practices for implementing Onion Architecture?
問: 實施洋蔥架構有什么推薦的做法嗎?
A: Best practices for implementing Onion Architecture include clearly defining responsibilities for each layer, using dependency injection for managing dependencies, and focusing on adherence to the Dependency Inversion Principle.
一個: 實施洋蔥架構的最佳實踐包括明確定義每一層的職責、使用依賴注入來管理依賴關系以及專注于遵守依賴倒置原則。

 ARM 軟中斷, IMX6ULL 點燈)
)

:idea2025.1.3版本啟動springboot服務輸入jvm參數解決辦法)











)

)
