商戶查詢緩存
為什么用緩存?
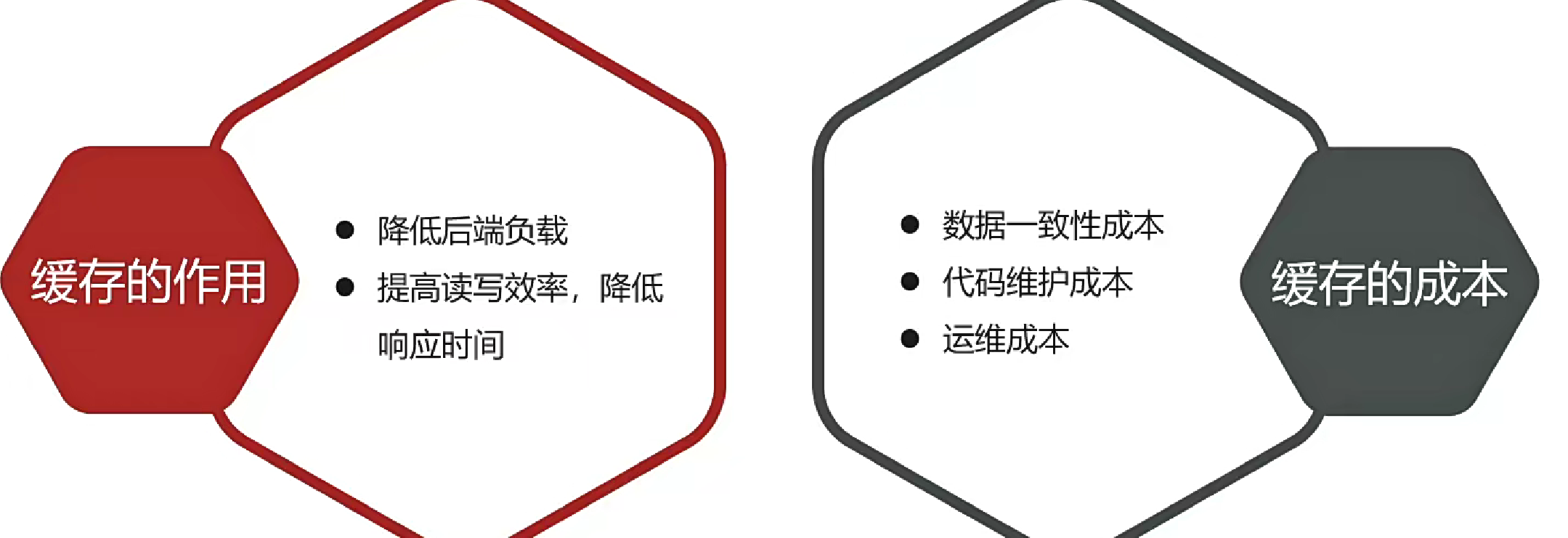
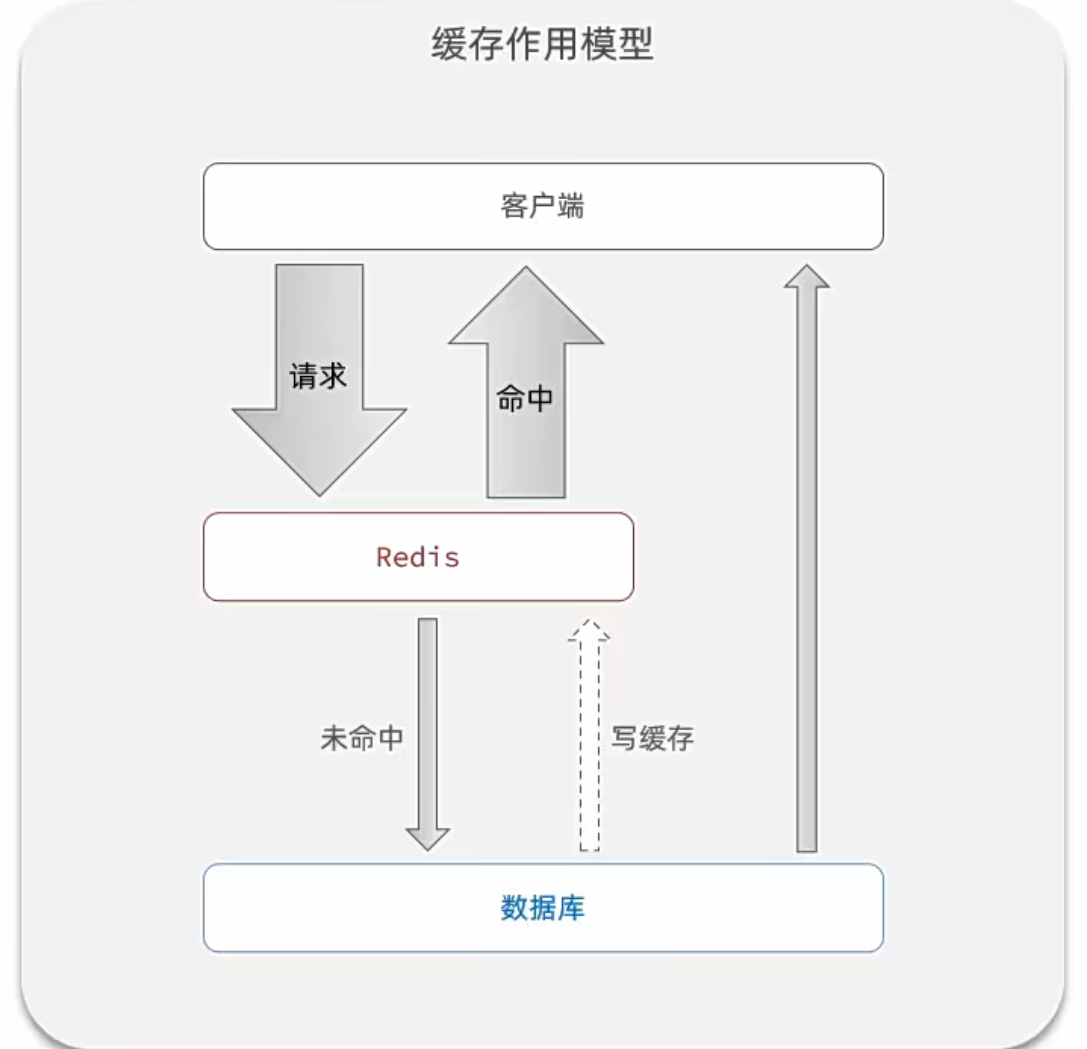
作用模型
緩存流程
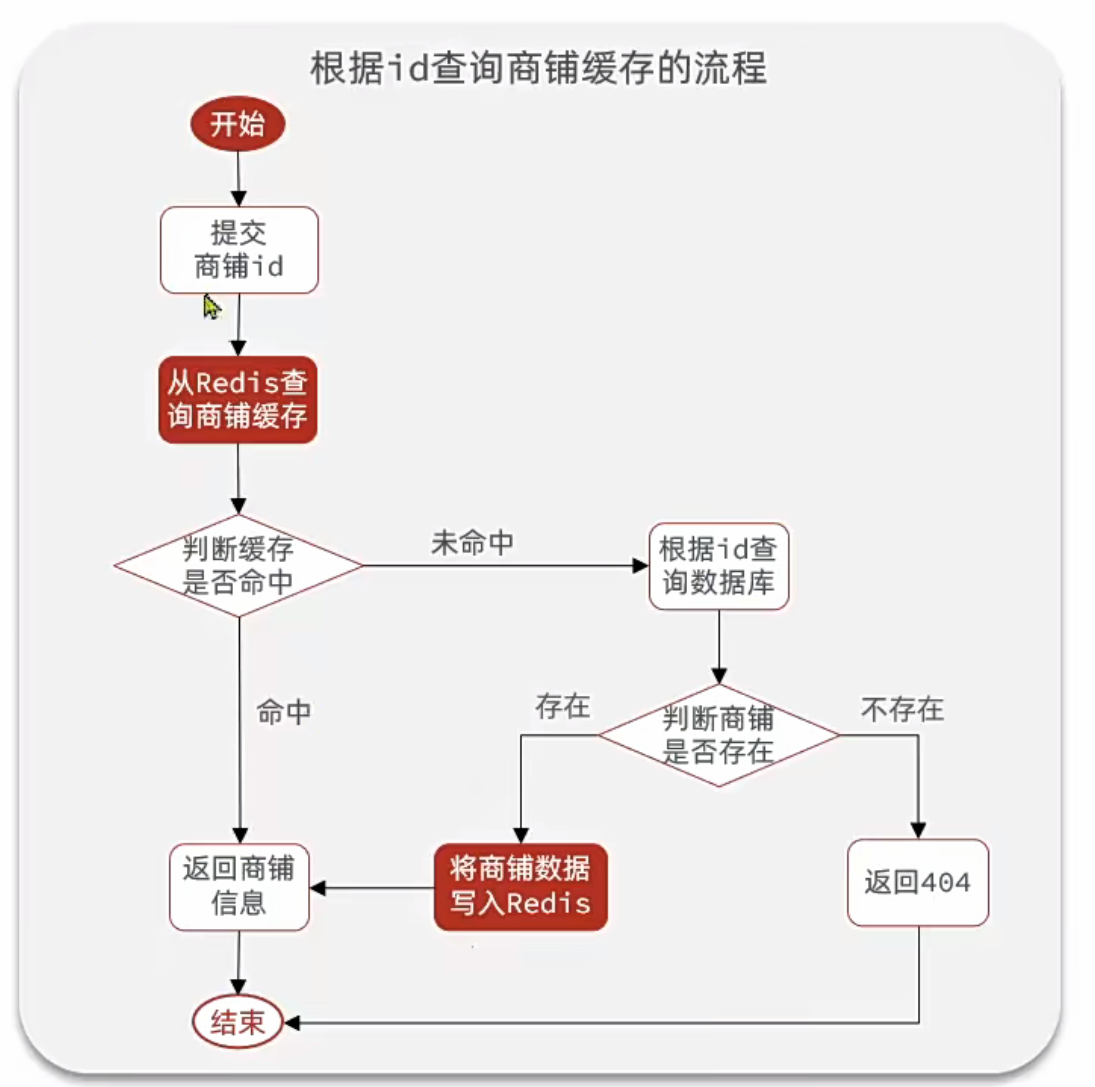
按照流程編寫代碼如下
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {@Resourceprivate StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Overridepublic Result queryById(Long id) {String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;//從redis查詢商鋪緩存String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);if(StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)){//存在,返回Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);return Result.ok(shop);}//不存在,查詢數據庫Shop shop = getById(id);//數據庫中不存在,報錯if(shop == null){return Result.fail("店鋪不存在!");}//存在,寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop));//返回return Result.ok(shop);}
}
給shop-type添加Redis緩存
這部分需要自己實現,課程沒有答案。
請求URL:[http://localhost:8080/api/shop-type/list](http://localhost:8080/api/shop-type/list)
根據之前給店鋪做緩存的思路,這次我們同樣使用String類型,用來保存list類型的店鋪類型數據。
代碼實現思路仿照給查詢店鋪緩存的過程。只不過這次是要轉為list類型。
@Service
public class ShopTypeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopTypeMapper, ShopType> implements IShopTypeService {@Resourceprivate StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Overridepublic Result queryByType() {String key = "cache:type";// 首先查詢redisString shopTypeJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);if(StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopTypeJson)){// 如果存在List<ShopType> shopTypes = JSONUtil.toList(shopTypeJson, ShopType.class);return Result.ok(shopTypes);}// 如果不存在,那么查詢數據庫List<ShopType> shopTypes = query().orderByAsc("sort").list();// 如果數據庫中不存在,報錯if(shopTypes == null){return Result.fail("無法查詢到相關店鋪");}// 存在,寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shopTypes));return Result.ok(shopTypes);}
}
緩存更新策略
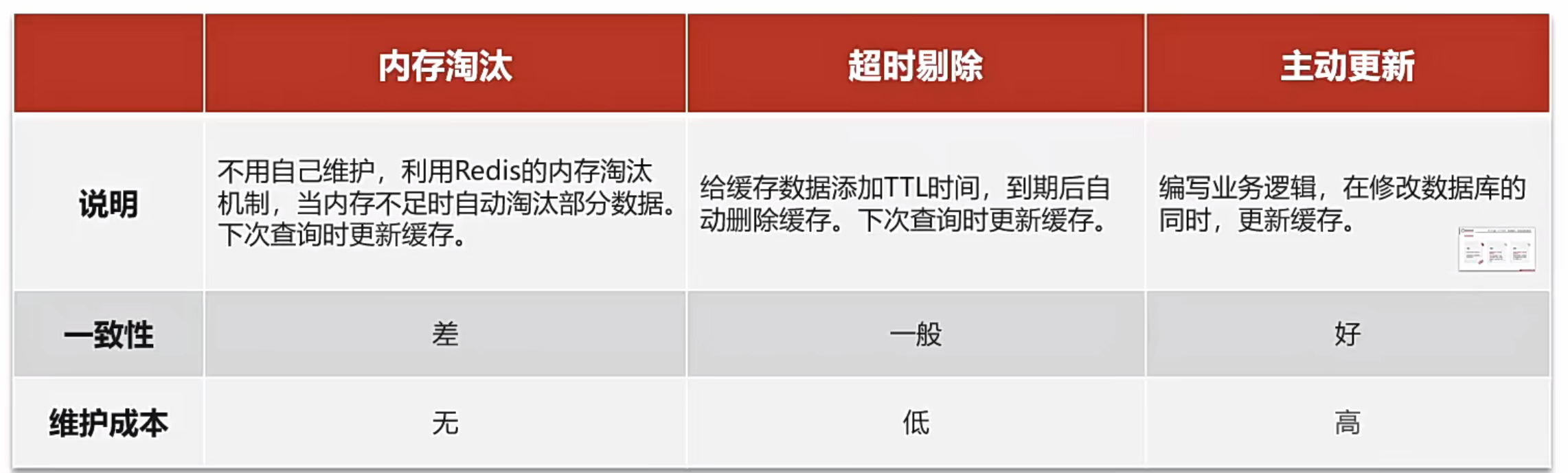
策略選擇:

主動更新策略
Cache Aside Pattern
由緩存的調用者,在更新數據庫的同時更新緩存
操作緩存和數據庫時有三個問題需要考慮:
- 刪除緩存還是更新緩存?
- 更新緩存:每次更新數據庫都更新緩存,無效寫操作較多(F)
- 刪除緩存:更新數據庫時讓緩存失效,查詢時再更新緩存(T)
- 如何保證緩存與數據庫的操作的同時成功或失敗?
- 單體系統,將緩存與數據庫操作放在一個事務
- 分布式系統,利用TCC等分布式事務方案
- 先操作緩存還是先操作數據庫?
- 先刪除緩存,再操作數據庫
- 先操作數據庫,再刪除緩存
對比一下緩存數據庫操作順序的影響(代表異常情況下)
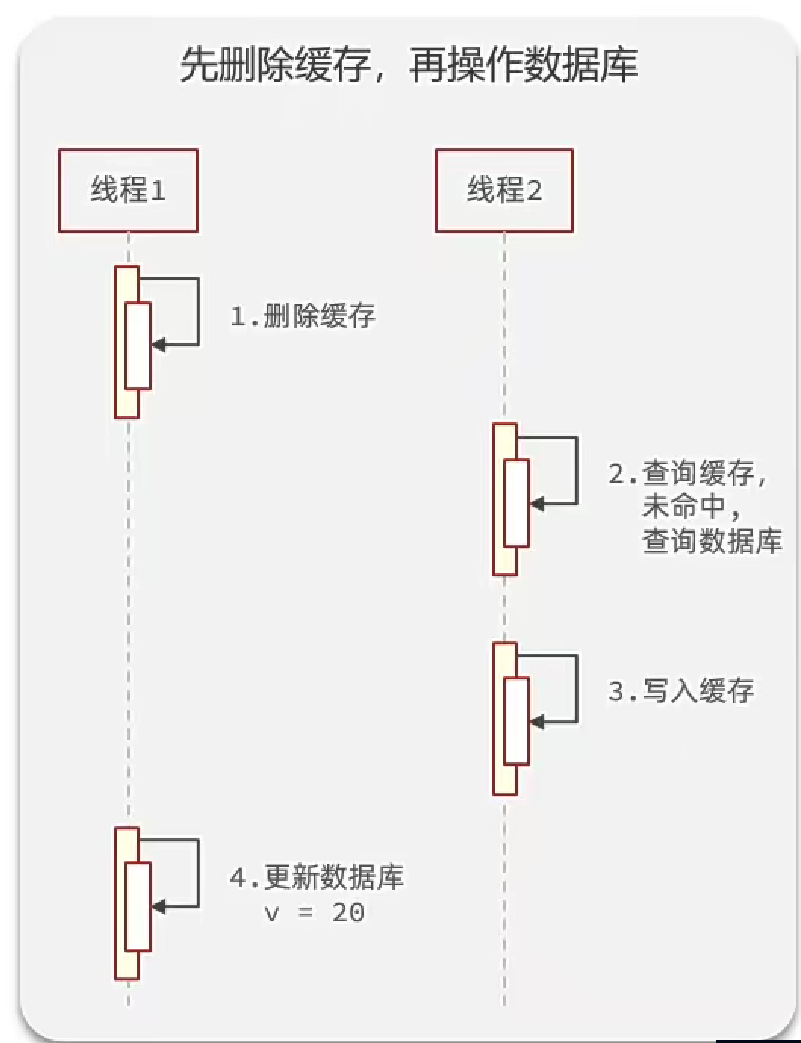
線程一執行刪除緩存,這個是快操作,但是更新數據庫是慢操作,在二者之間很可能會有線程二,緩存已被刪除,查詢緩存時未命中,去查數據庫寫入緩存,這兩個都是快操作,數據庫和緩存數據不一致,從而導致數據不一致情況。這種情況出現概率較大。
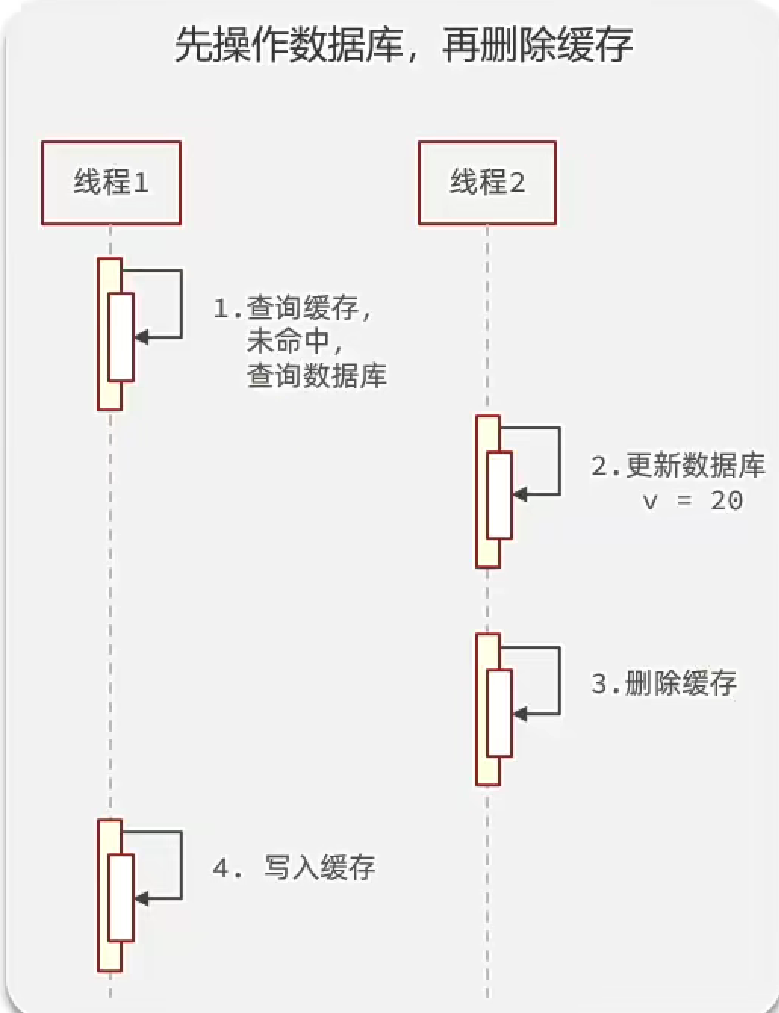
假設剛好線程一進來時緩存失效,那么查詢數據庫,獲得了某個值a。不巧的是,在線程一寫緩存之前,線程二更新了數據庫,數據庫中變為新的值b,執行刪除緩存(緩存本來就什么也沒有),線程一接著寫入緩存,可是線程一寫入的緩存內容是a,那么現在數據庫的值是b,緩存中的是a,導致數據不一致。但是這種情況出現概率較小,因為查詢緩存寫緩存的速度是很快的,很難有另一個線程穿插在這之間并完成了更新數據庫刪除緩存。
所以我們一般選擇先操作數據庫,再操作緩存。
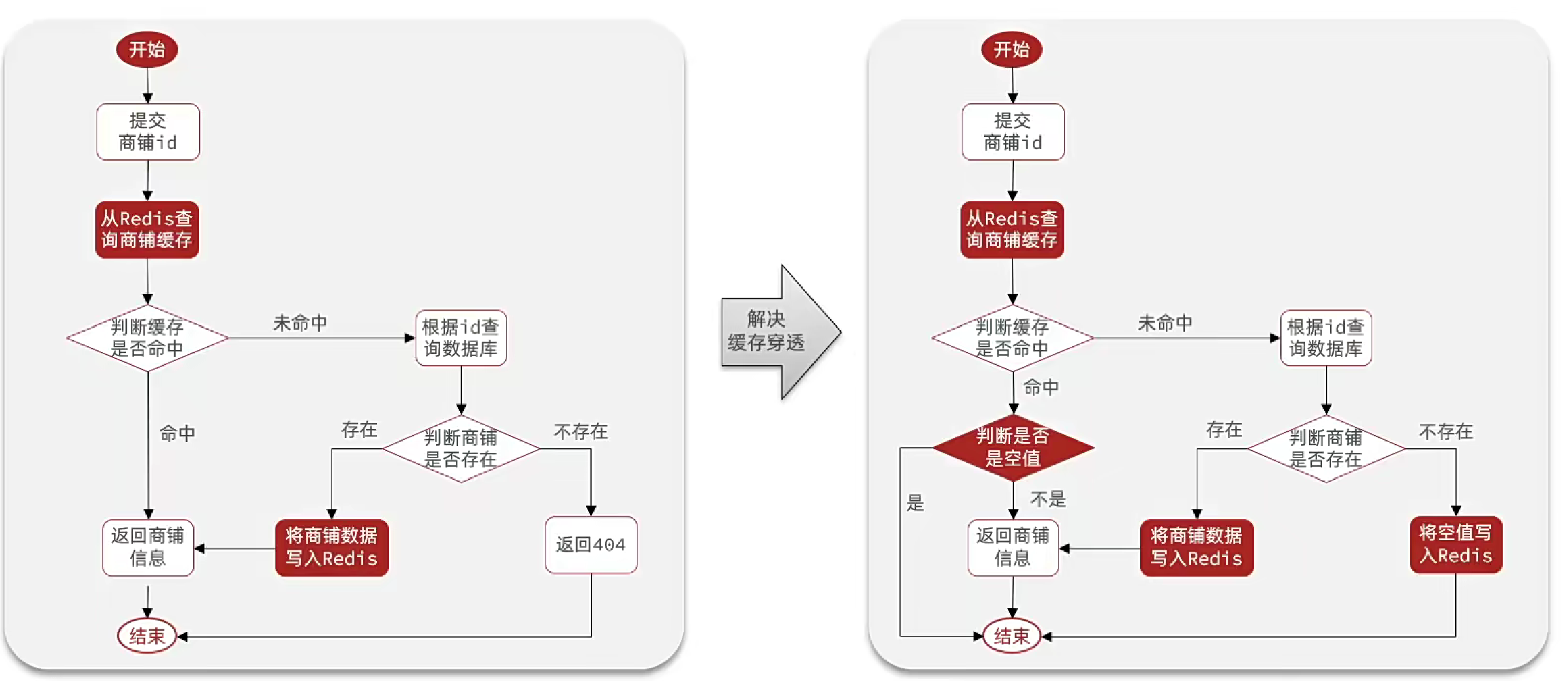
緩存穿透
緩存穿透是指用戶請求的數據在緩存和數據庫中都不存在,這樣緩存永遠不會生效,這些請求都會打到數據庫。如果發生大量這樣的請求,會造成數據庫癱瘓。
常見的解決方案有兩種:
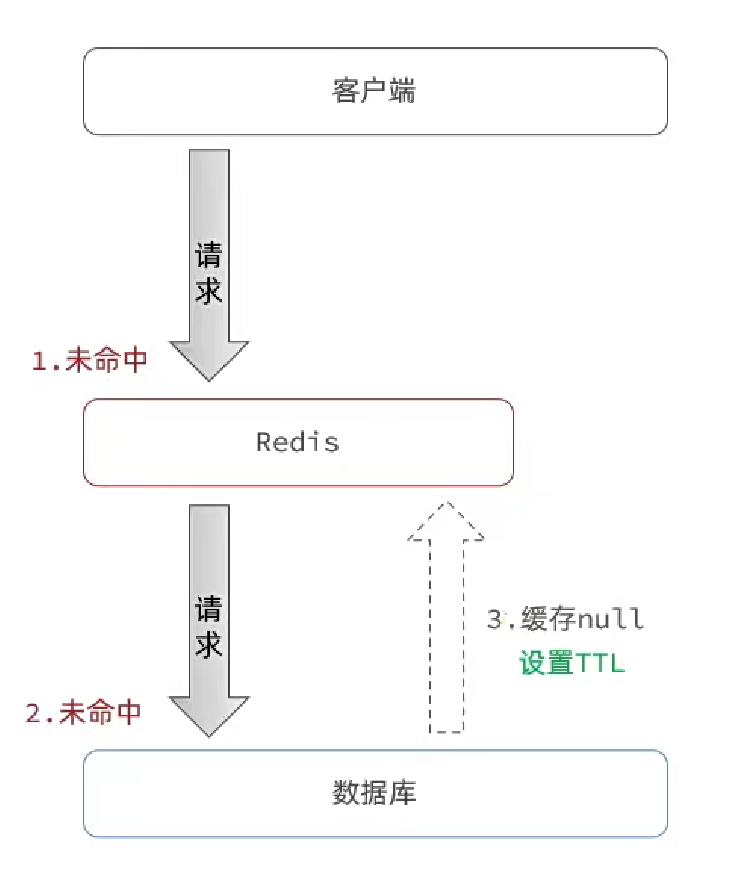
- 緩存空對象
當用戶請求的數據在緩存和數據庫都不存在時,我們可以設置當前緩存值為null。
但是如果無休止的請求不存在的數據,就會導致緩存值越來越多,內存消耗越來越大。所以需要設置過期時間TTL。
同時緩存設置為null了,如果下次更新數據在數據庫中更新了,此時就會導致數據不一致。可以把過期時間設置的短一些,緩解此問題。
- 優點:實現簡單,維護方便
- 缺點:
- 額外的內存消耗
- 可能造成短期的不一致
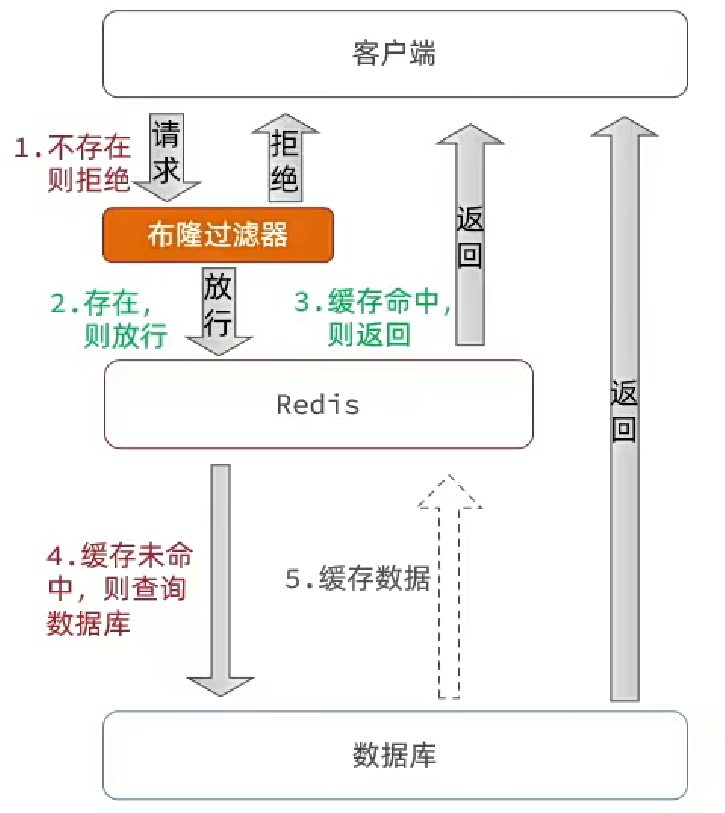
- 布隆過濾器
- 優點:內存占用較少, 沒有多余key
- 缺點:
- 實現復雜
- 存在誤判可能
- 增強id的復雜度,避免被猜測id規律
- 做好數據的基礎格式校驗
- 加強用戶權限校驗
- 做好熱點參數的限流
為解決穿透問題我們需要修改業務代碼,這里采用緩存null值方法
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {@Resourceprivate StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Overridepublic Result queryById(Long id) {String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;//從redis查詢商鋪緩存String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);if(StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)){//存在,返回Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);return Result.ok(shop);}//判斷命中的是否是空值if(shopJson != null){// 返回一個錯誤信息return Result.fail("店鋪信息不存在!");}//不存在,查詢數據庫Shop shop = getById(id);//數據庫中不存在,報錯if(shop == null){//將空值寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);return Result.fail("店鋪不存在!");}//存在,寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);//返回return Result.ok(shop);}@Override@Transactionalpublic Result update(Shop shop) {Long id = shop.getId();if(id == null){return Result.fail("商鋪id不能為空");}//先更新數據庫updateById(shop);//再刪緩存stringRedisTemplate.delete(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + shop.getId());return Result.ok(shop);}
}
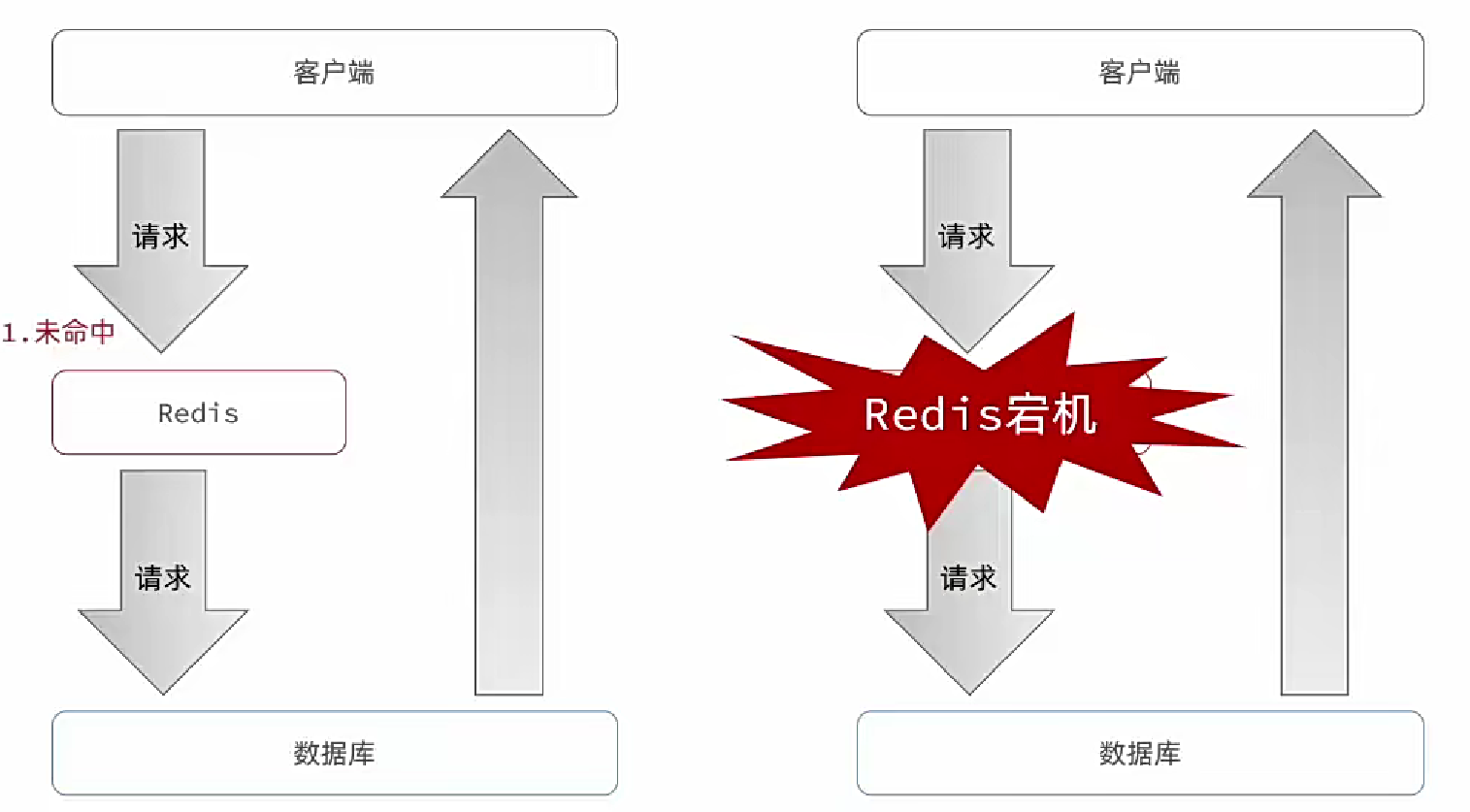
緩存雪崩
緩存雪崩是指在同一時段大量的緩存key同時失效或者Redis服務宕機,導致大量請求到達數據庫,帶來巨大壓力。
解決方案:
- 給不同的Key的TTL添加隨機值
- 利用Redis集群提高服務的可用性
- 給緩存業務添加降級限流策略
- 給業務添加多級緩存
緩存擊穿
緩存擊穿問題也叫熱點Key問題,就是一個被高并發訪問并且緩存重建業務較復雜的key突然失效了,無數的請求訪問會在瞬間給數據庫帶來巨大的沖擊。
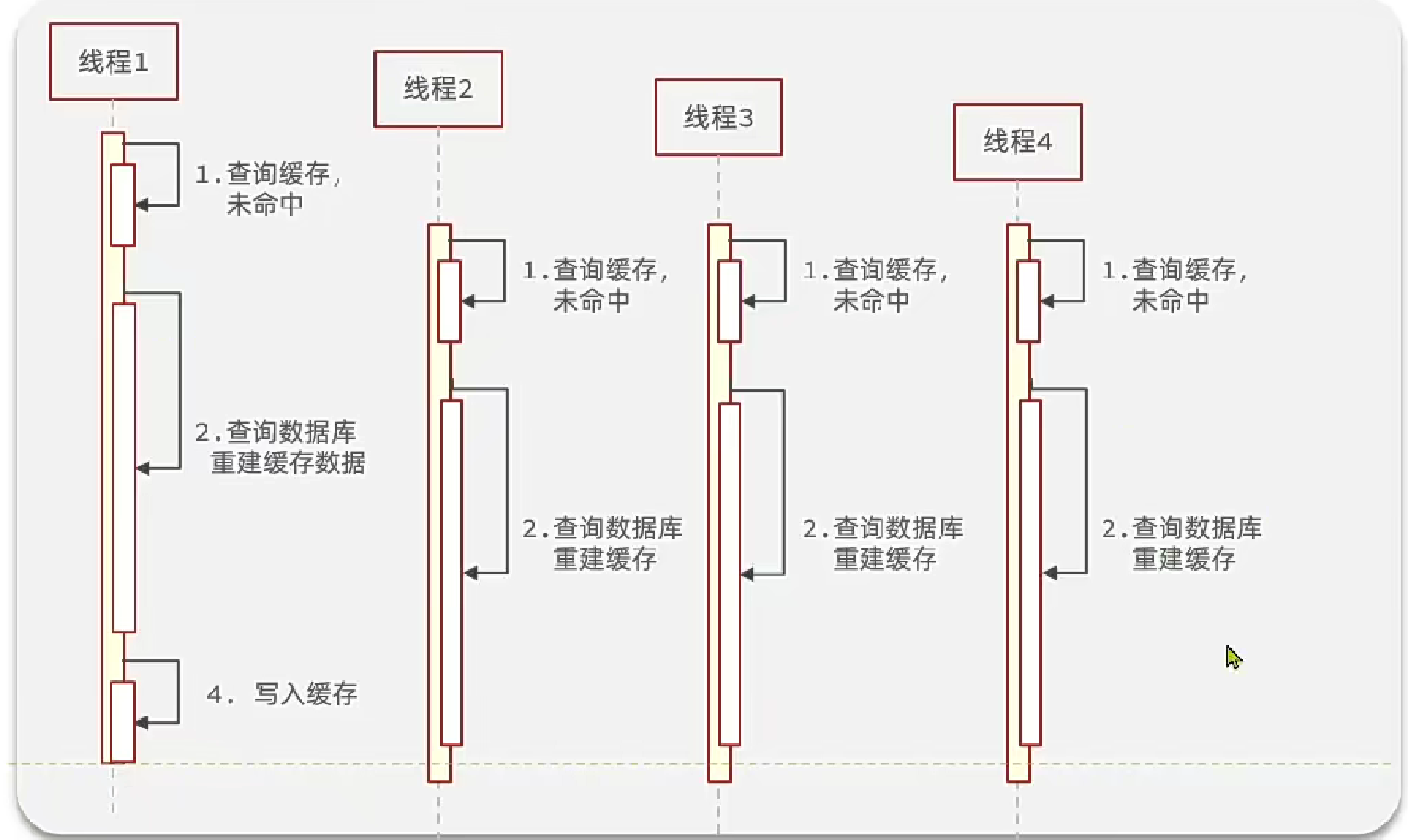
常見的解決方案有兩種:
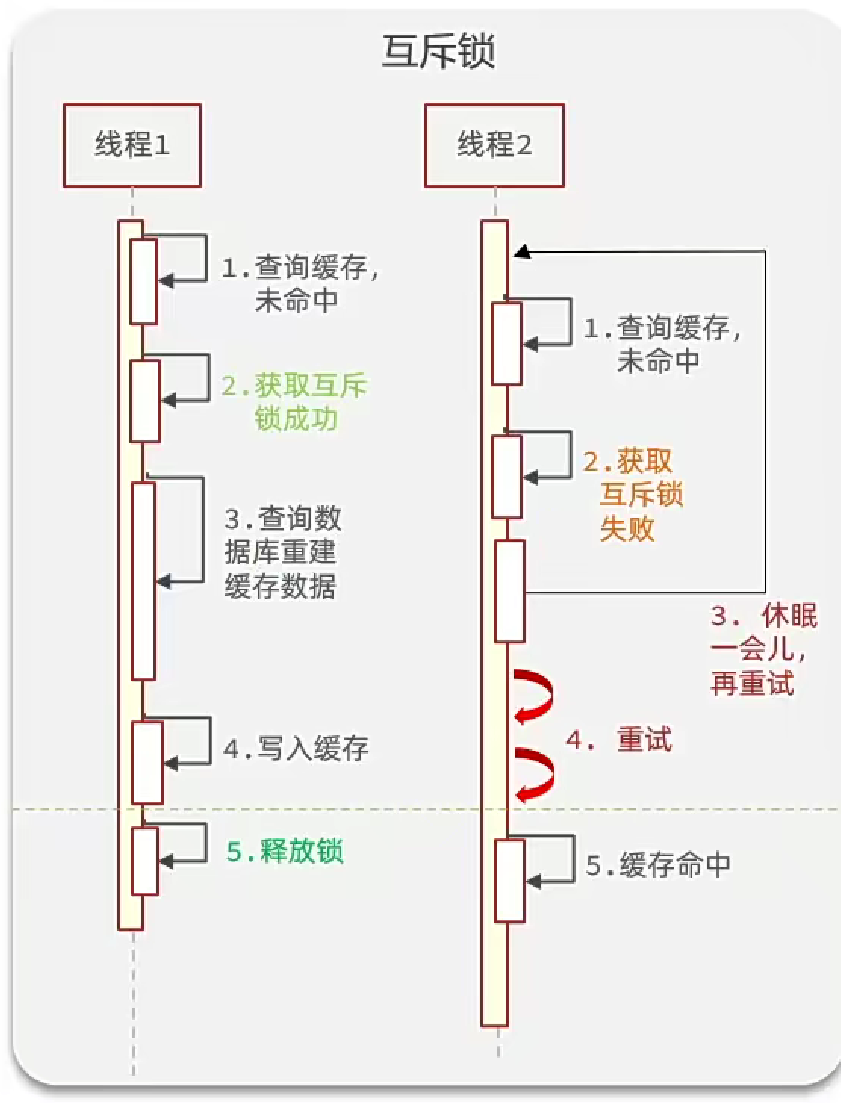
- 互斥鎖
- 邏輯過期
| 解決方案 | 優點 | 缺點 |
|---|---|---|
| 互斥鎖 | 沒有額外的內存消耗 保證一致性 實現簡單 | 線程需要等待, 性能受影響 可能有死鎖風險 |
| 邏輯過期 | 線程無需等待, 性能較好 | 不保證一致性 有額外內存消耗 實現復雜 |
利用互斥鎖解決緩存擊穿問題
修改根據id查詢商鋪的業務
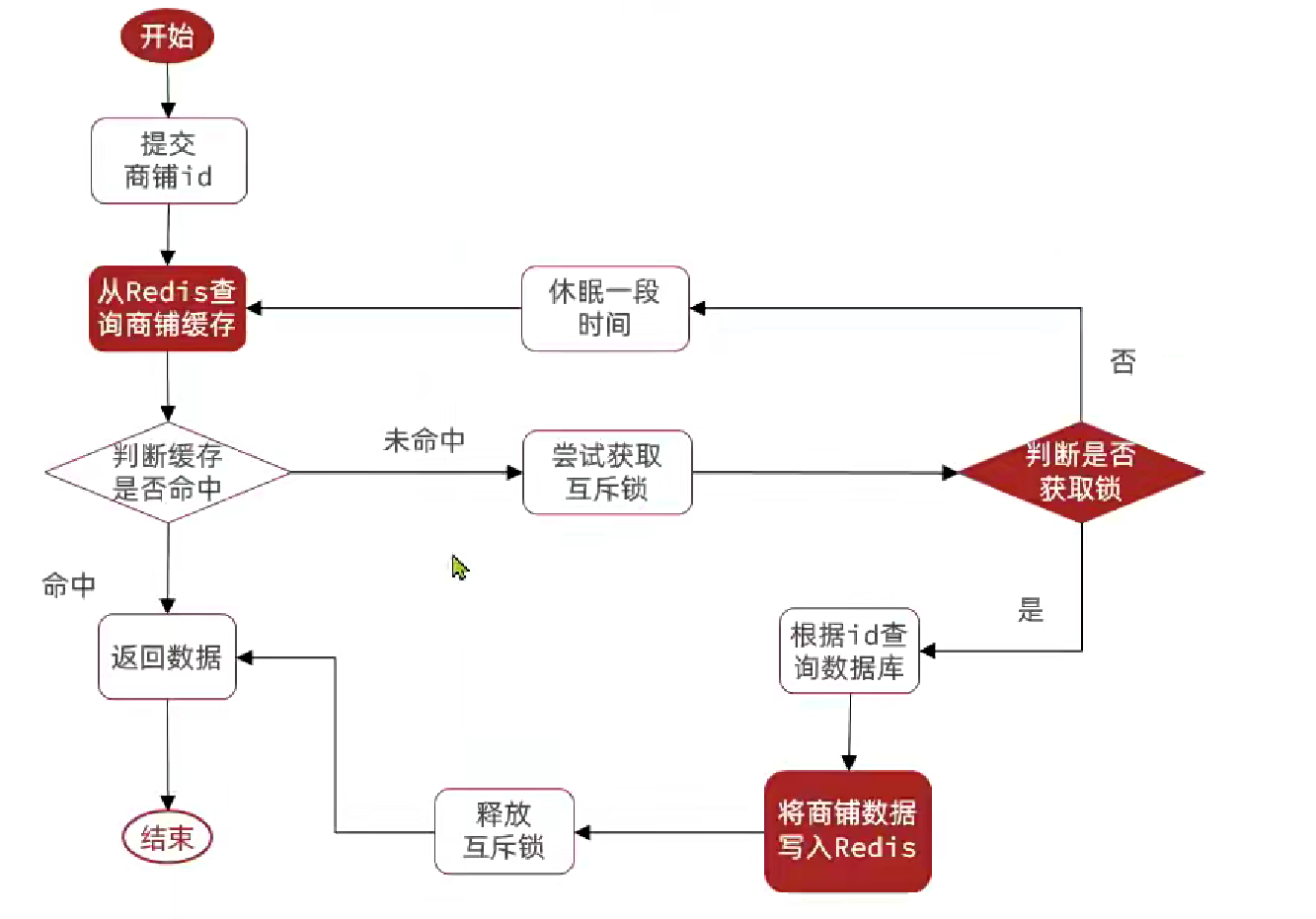
這里我們使用Redis中String的setnx模擬上鎖,setnx僅當值為空時才可以修改值,這可以模擬互斥鎖,當大量請求到當前緩存時,只有一個請求能進一步的進行查數據庫、寫入Redis、釋放鎖等功能。這樣其他線程就會休眠直到當前線程釋放鎖。
public Shop queryWithMutex(Long id){
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
//從redis查詢商鋪緩存
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)){//存在,返回return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);
}
//判斷命中的是否是空值
if(shopJson != null){// 返回一個錯誤信息return null;
}
// 實現緩存重建
// 獲取互斥鎖
String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
Shop shop = null;
try {boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);// 判斷是否獲取成功if(!isLock){// 失敗則休眠重試Thread.sleep(50);return queryWithMutex(id);}// 成功,根據id查詢數據庫shop = getById(id);// 模擬重建延時Thread.sleep(200);//數據庫中不存在,報錯if(shop == null){//將空值寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);return null;}//存在,寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {// 釋放互斥鎖unlock(lockKey);}
//返回
return shop;
}private boolean tryLock(String key){Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag); //不直接return flag,因為在拆箱過程中可能產生空指針
}private void unlock(String key){
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
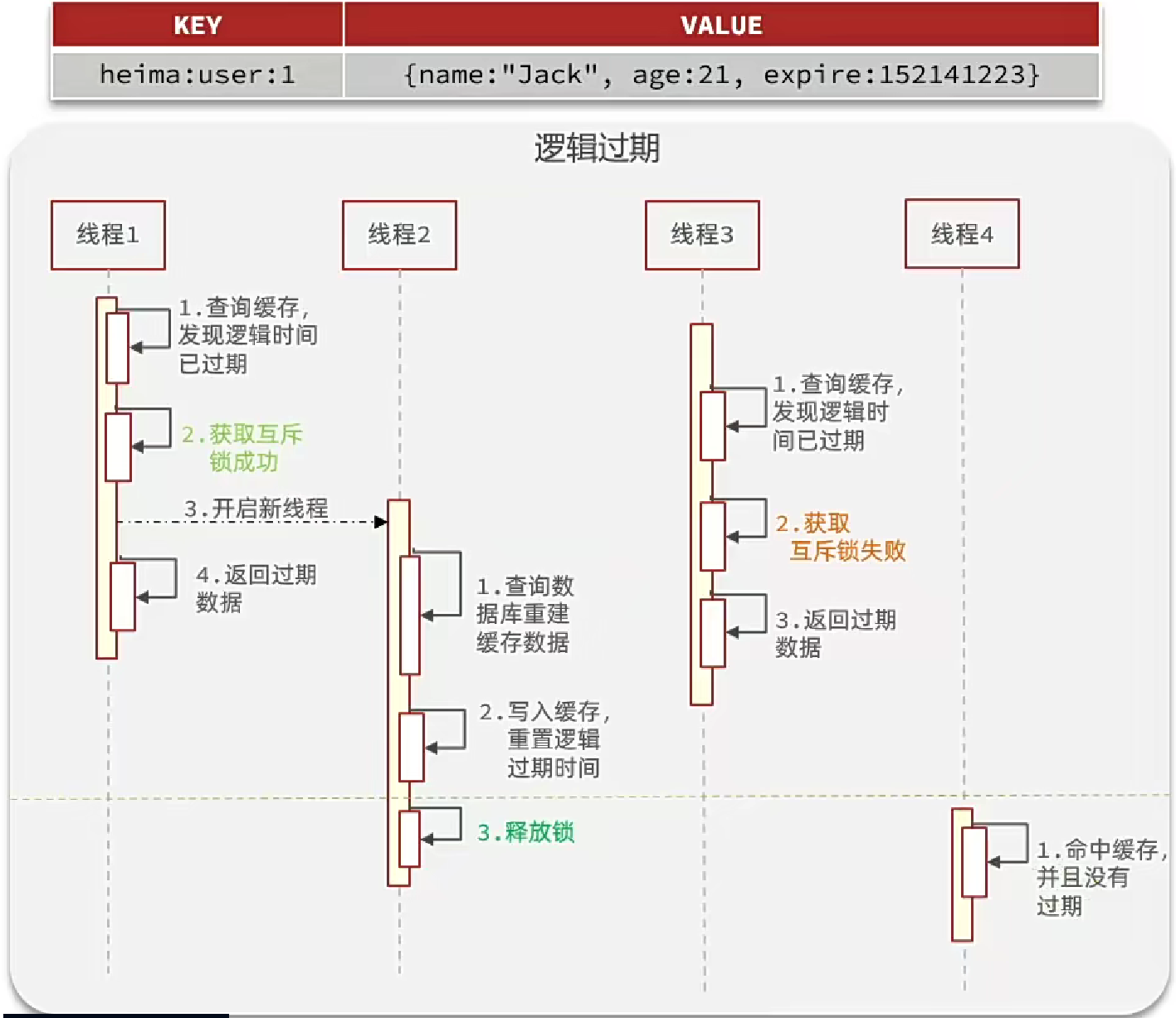
利用邏輯過期解決緩存擊穿問題
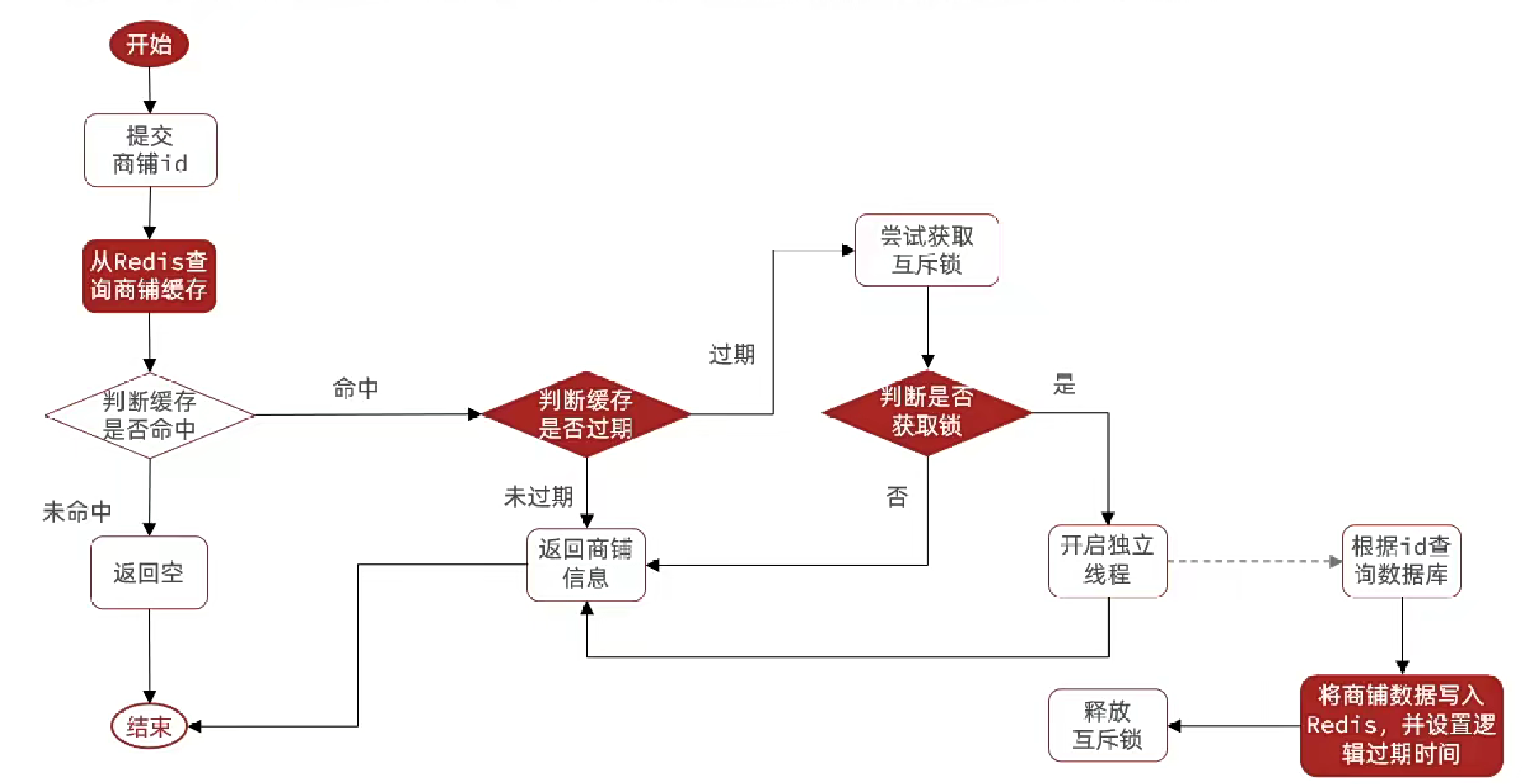
重建緩存的方法
private void saveShop2Redis(Long id, Long expireSeconds) {// 1.查詢店鋪數據Shop shop = getById(id);// 2.封裝邏輯過期時間RedisData redisData = new RedisData();redisData.setData(shop);redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireSeconds));// 3.寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}
業務邏輯實現
這里使用了線程池,避免了線程頻繁的創建銷毀帶來的性能開銷。
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public Shop queryWithLogicalExpire(Long id) {
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
//從redis查詢商鋪緩存
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {//不存在,返回return null;
}
// 命中,把Json反序列化為對象
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), Shop.class);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
// 判斷是否過期
if(expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){// 未過期,返回商鋪信息return shop;
}
// 已過期,需要緩存重建
// 緩存重建
// 獲取互斥鎖
String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
// 判斷是否獲取成功
if(isLock){//成功則開啟獨立線程,緩存重建CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(()->{try {//重建緩存this.saveShop2Redis(id, 20L);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {//釋放鎖unlock(lockKey);}});
}//失敗則返回過期的商戶信息
return shop;
}
封裝緩存工具類
封裝Redis工具類
基于StringRedisTemplate封裝一個緩存工具類,滿足下列需求:
- 方法1:將任意Java對象序列化為json并存儲在string類型的key中,并且可以設置TTL過期時間
- 方法2:將任意Java對象序列化為json并存儲在string類型的key中,并且可以設置邏輯過期時間,用于處理緩
存擊穿問題
- 方法3:根據指定的key查詢緩存,并反序列化為指定類型,利用緩存空值的方式解決緩存穿透問題
- 方法4:根據指定的key查詢緩存,并反序列化為指定類型,需要利用邏輯過期解決緩存擊穿問題
將邏輯進行封裝
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CacheClient {private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public CacheClient(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;}public void set(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(value), time, unit);}public void setWithLogicalExpire(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {// 設置邏輯過期RedisData redisData = new RedisData();redisData.setData(value);redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(unit.toSeconds(time)));// 寫入RedisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));}public <R,ID> R queryWithPassThrough(String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit){String key = keyPrefix + id;// 1.從redis查詢商鋪緩存String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);// 2.判斷是否存在if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)) {// 3.存在,直接返回return JSONUtil.toBean(json, type);}// 判斷命中的是否是空值if (json != null) {// 返回一個錯誤信息return null;}// 4.不存在,根據id查詢數據庫R r = dbFallback.apply(id);// 5.不存在,返回錯誤if (r == null) {// 將空值寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 返回錯誤信息return null;}// 6.存在,寫入redisthis.set(key, r, time, unit);return r;}public <R, ID> R queryWithLogicalExpire(String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {String key = keyPrefix + id;// 1.從redis查詢商鋪緩存String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);// 2.判斷是否存在if (StrUtil.isBlank(json)) {// 3.存在,直接返回return null;}// 4.命中,需要先把json反序列化為對象RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(json, RedisData.class);R r = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), type);LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();// 5.判斷是否過期if(expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())) {// 5.1.未過期,直接返回店鋪信息return r;}// 5.2.已過期,需要緩存重建// 6.緩存重建// 6.1.獲取互斥鎖String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);// 6.2.判斷是否獲取鎖成功if (isLock){// 6.3.成功,開啟獨立線程,實現緩存重建CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {try {// 查詢數據庫R newR = dbFallback.apply(id);// 重建緩存this.setWithLogicalExpire(key, newR, time, unit);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}finally {// 釋放鎖unlock(lockKey);}});}// 6.4.返回過期的商鋪信息return r;}public <R, ID> R queryWithMutex(String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {String key = keyPrefix + id;// 1.從redis查詢商鋪緩存String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);// 2.判斷是否存在if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) {// 3.存在,直接返回return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, type);}// 判斷命中的是否是空值if (shopJson != null) {// 返回一個錯誤信息return null;}// 4.實現緩存重建// 4.1.獲取互斥鎖String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;R r = null;try {boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);// 4.2.判斷是否獲取成功if (!isLock) {// 4.3.獲取鎖失敗,休眠并重試Thread.sleep(50);return queryWithMutex(keyPrefix, id, type, dbFallback, time, unit);}// 4.4.獲取鎖成功,根據id查詢數據庫r = dbFallback.apply(id);// 5.不存在,返回錯誤if (r == null) {// 將空值寫入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 返回錯誤信息return null;}// 6.存在,寫入redisthis.set(key, r, time, unit);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}finally {// 7.釋放鎖unlock(lockKey);}// 8.返回return r;}private boolean tryLock(String key) {Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);}private void unlock(String key) {stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);}
}
在shopServiceImpl中
@Resource
private CacheClient cacheClient;@Overridepublic Result queryById(Long id) {// 解決緩存穿透Shop shop = cacheClient.queryWithPassThrough(CACHE_SHOP_KEY, id, Shop.class, this::getById, CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 互斥鎖解決緩存擊穿// Shop shop = cacheClient// .queryWithMutex(CACHE_SHOP_KEY, id, Shop.class, this::getById, CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 邏輯過期解決緩存擊穿// Shop shop = cacheClient// .queryWithLogicalExpire(CACHE_SHOP_KEY, id, Shop.class, this::getById, 20L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (shop == null) {return Result.fail("店鋪不存在!");}// 7.返回return Result.ok(shop);}
如果內容對你有所幫助,請點贊、評論、收藏,創作不易,你的支持是我創作的動力。



Matlab程序)





)

)







