一、字符串函數介紹:
字符串作為程序中常用的數據類型,學會對字符串進行處理是作為一名C/C++程序員的基本功,我們要學會使用相關函數,并且對重點函數要會自己手動實現(下文對重點函數有實現代碼以及相關示例)
二、字符串函數詳解
1.strlen:
作用:求字符串的大小
使用:

實現:
size_t MyStrlen1(const char* str)
{assert(str!=nullptr);int len = 0;while (str[len] != '\0')len++;return len;
}示例:
int main()
{const char* str = "123456";printf("%d\n", strlen(str));printf("%d\n", MyStrlen1(str));return 0;
}注意:strlen記錄字符串函數大小,不包括'\0';
2.strcpy:
作用:將source字符串拷貝到destnation
使用:

實現:
char* MyStrcpy(char* destination, const char* source)
{assert(destination != nullptr);assert(source != nullptr);int pos = 0;while (source[pos] != '\0'){destination[pos] = source[pos];pos++;}destination[pos] = '\0';return destination;
}示例:
int main()
{const char* str = "123456";char* str1 = (char*)malloc(strlen(str) + 1);printf("%s", strcpy(str1, str));printf("%s", MyStrcpy(str1, str));return 0;
}3.strncpy:
作用:從source字符串拷貝指定長度到destnation字符串中
使用:

4.strcmp:
作用:字符串的比較
使用:

實現:
int MyStrcmp(const char* dst, const char* src)
{int pos1 = 0,pos2=0;while (dst[pos1]==src[pos2]&&dst[pos1]!='\0'){pos1++;pos2++;}return dst[pos1] - src[pos2];
}示例:
int main()
{const char* str = "123456";const char* str1 = "123456";printf("%d\n", strcmp(str1, str));printf("%d", MyStrcmp(str1, str));return 0;
}5.strncmp:
作用:指定長度的字符串比較
使用:

6.strcat:
作用:字符串的拼接
使用:

實現:
char* MyStrcat(char* destination, const char* source)
{assert(destination != nullptr);assert(source != nullptr);size_t pos1 = MyStrlen1(destination);size_t pos2 = 0;while (source[pos2] != '\0')destination[pos1++] = source[pos2++];destination[pos1] = '\0';return destination;
}示例:
int main()
{char str[80];char str1[80];strcpy(str, "these ");MyStrcpy(str1, "these ");strcat(str, "strings ");MyStrcat(str1, "strings ");strcat(str, "are ");MyStrcat(str1, "are ");strcat(str, "concatenated.");MyStrcat(str1, "concatenated.");printf("%s\n", str);printf("%s\n", str1);return 0;
}7.strncat:
作用:將source的指定長度字符串拼接到目標字符串末尾
使用:

8.strstr:
作用:查找子字符串在一個字符串的首次出現位置
使用:

實現:
char* MyStrstr(char* dst, const char* src)
{assert(dst);assert(src);int pos1 = 0;while (dst[pos1]!='\0'){int pos2 = 0;if (dst[pos1] == src[pos2]){int pos = pos1;while (dst[pos] == src[pos2]){pos++;pos2++;}if (src[pos2] == '\0')return dst + pos1;}pos1++;}return dst;
}示例:
int main()
{char str[] = "This is a simple string";char str1[] = "This is a simple string";char* pch;char* pch1;pch = strstr(str, "simple");pch1 = MyStrstr(str1, "simple");if (pch != NULL)strncpy(pch, "sample", 6);if(pch1!=nullptr)strncpy(pch1, "sample", 6);printf("%s\n", pch);printf("%s", pch1);return 0;
}9.strtok:
作用:將字符串按照指定的分割符切割成多個子串
使用:

示例:
int main()
{char str[] = "- This, a sample string.";char* pch;printf("Splitting string \"%s\" into tokens:\n", str);pch = strtok(str, " ,.-");while (pch != NULL){printf("%s\n", pch);pch = strtok(NULL, " ,.-");}return 0;
}三、總結:
學會使用常見字符串的函數,處理好字符串等各種問題,對我們在項目工程等方面有非常重要的基礎作用,例如解決算法問題、網絡協議的制定、C++string類實現等等,當然本篇文章只講述了常用的字符串函數,對于其他函數,有興趣的朋友們可以看一下如下網址:<cstring> (string.h) - C++ Reference
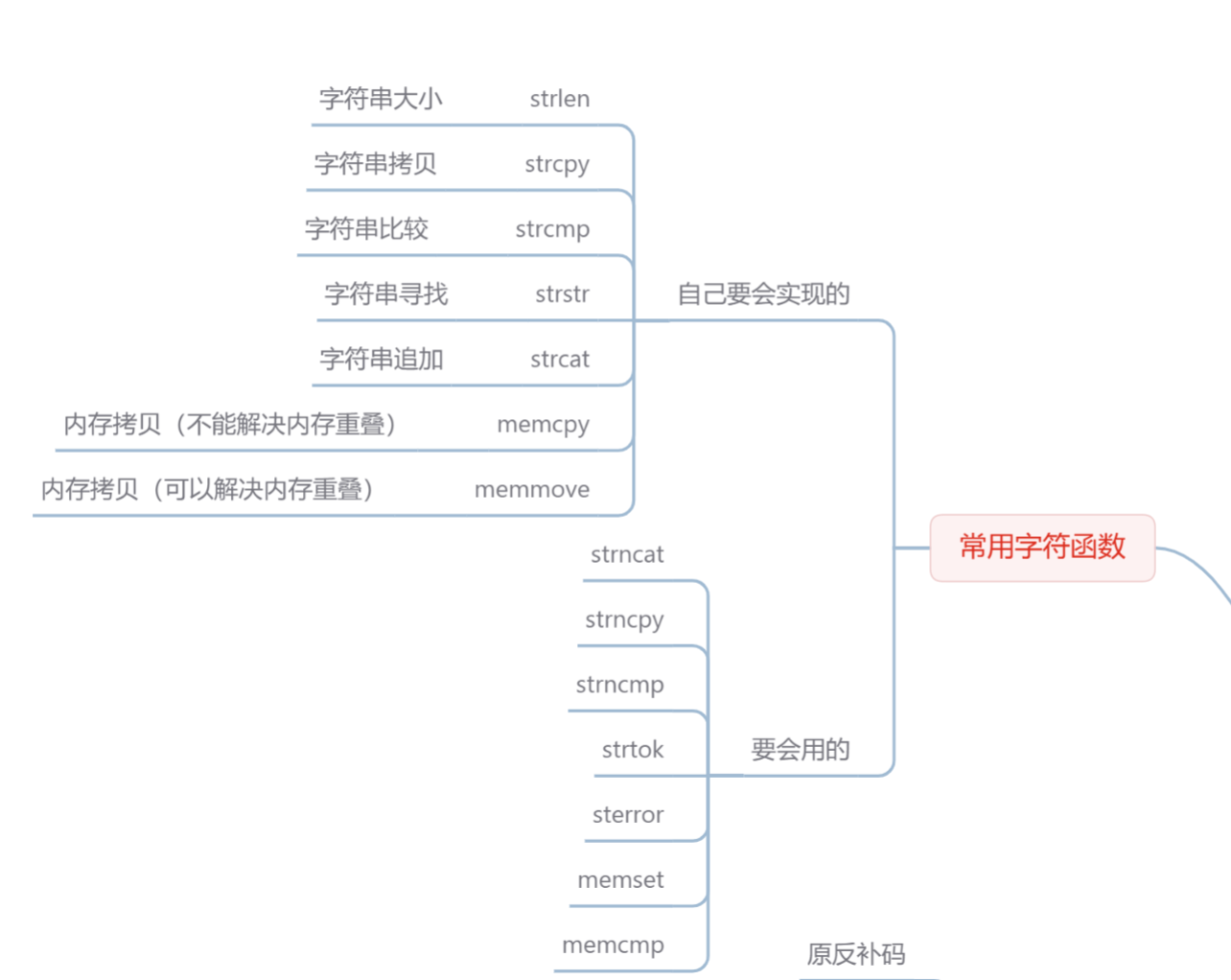
還有一個簡單的思維導圖,方便大家復習鞏固
結語:
以上就是我分享的字符串函數的全部內容了,希望對大家有些幫助,也希望與一樣喜歡編程的朋友們共進步
謝謝觀看
如果覺得還闊以的話,三連一下,以后會持續更新的,我會加油的
祝大家早安午安晚安




第7講:VS實用調試技巧)














-組件)