注:機翻,未校對。
What is the Five Layers Model? The Framework of the Internet Explained 五層模型互聯網框架解釋
Computer Networks are a beautiful, amazing topic. Networks involve so much knowledge from different fields, from physics to algorithms.
計算機網絡是一個美麗而神奇的話題。網絡涉及來自不同領域的大量知識,從物理學到算法。
When dealing with Computer Networks, there is one framework that puts everything into place – and that is the layers model.
在處理計算機網絡時,有一個框架可以將所有內容都放在適當的位置,這就是層模型。
In this post you’ll learn why we need layers, as well as what the five layers model is. You will also understand the role of each layer in this model.
在這篇文章中,您將了解為什么我們需要層,以及什么是五層模型。您還將了解此模型中每個圖層的作用。
Layers? 為什么選擇層?
Imagine you are given the task to design and implement the Internet! Where do you start? What do we actually want from a network, and an important one such as the Internet?
想象一下,你的任務是設計和實現互聯網!你從哪里開始?我們實際上想從網絡中得到什么,以及像互聯網這樣的重要網絡?
Well, we actually want quite a lot of things. To name a few:
好吧,我們實際上想要很多東西。僅舉幾例:
-
We want it to be fast – that is, allow fast communication. We don’t want to wait long for a message to get from one host to another.
我們希望它快速 - 也就是說,允許快速通信。我們不想等待很長時間才能將消息從一臺主機發送到另一臺主機。 -
It should also be reliable – when sending a message, we want the receiver to actually receive it.
它也應該是可靠的——在發送消息時,我們希望接收者能夠實際接收它。 -
The network should be extendable – that is, allow more devices to join. We wouldn’t want to start with two computers, and then not bee able to add a third one.
網絡應該是可擴展的,也就是說,允許更多的設備加入。我們不想從兩臺計算機開始,然后無法添加第三臺計算機。 -
The network should support different devices and connections – it should be able to connect a wired PC, wireless laptop, and a cellphone, for example.-
網絡應該支持不同的設備和連接——例如,它應該能夠連接有線 PC、無線筆記本電腦和手機。
And this is just a partial list.
這只是一個部分列表。
So, how do we go about implementing the internet when we want to achieve so many different things?
那么,當我們想要實現這么多不同的事情時,我們如何去實施互聯網呢?

Computer Networks are complex
計算機網絡是復雜的
In order to simplify things and make networks flexible, the communication is divided into layers.
為了簡化事情并使網絡靈活,通信被劃分為幾層。
Each layer has its own responsibility. It provides services to an upper layer, and uses services provided by a lower layer.
每一層都有自己的責任。它向上層提供服務,并使用下層提供的服務。
Consider an example network consisting of three devices:
考慮一個由三個設備組成的示例網絡:
An example network with three devices
一個包含三臺設備的示例網絡
We have two layers:
我們有兩個層次:
Layer Alpha is responsible for transmitting data between hosts that are directly connected to each other. In the diagram above, it’s between hosts A and B, or between hosts B and C.
Layer Alpha 負責在彼此直接連接的主機之間傳輸數據。在上圖中,它位于主機 A 和 B 之間,或主機 B 和 C 之間。
Layer Beta is responsible for transmitting data between distant hosts. In the diagram, it’s between hosts A and C.
Layer Beta 負責在遠程主機之間傳輸數據。在圖中,它位于主機 A 和 C 之間。
What did we gain from this division? We gained a lot of flexibility.
我們從這次分層中得到了什么?我們獲得了很大的靈活性。
Each layer can be developed and implemented by different people. The upper layer doesn’t care about the implementation of the lower layer, and vice versa.
每一層都可以由不同的人開發和實現。上層不關心下層的實現,反之亦然。
For instance, the connection between hosts A and B could be a WiFi connection, while the connection between B and C could consist of a carrier pigeon. These are (completely) different implementations of Layer Alpha.
例如,主機 A 和 B 之間的連接可以是 WiFi 連接,而 B 和 C 之間的連接可以由信鴿組成。這些是 Layer Alpha 的(完全)不同實現。
Notice that this way also enables us to have different specializations and expertise – an expert in training carrier pigeons does not necessarily have to be qualified at building solid WiFi network cards, or vice versa.
請注意,這種方式還使我們能夠擁有不同的專業化和專業知識 —— 一個擅長訓練信鴿的專家不一定需要在構建穩固的 WiFi 網卡上具備資質,反之亦然。
“Carrier pigeon” ,信鴿。在這里是一種比喻,用來表示一種不常見或老的通信方式。(
斐夷所非 注釋)

The Alpha Layer may have different implementations on the same network
Alpha 層在同一網絡中可能有不同的實現
Developers of Layer Beta don’t need to bother themselves with this difference. At this layer, host A needs to know that in order to reach host C, it first needs to send his message to host B, rather than, say, host D. Then, host B will forward it to host C.
Layer Beta 的開發人員無需為這種差異而煩惱。在此層,主機 A 需要知道,為了到達主機 C,它首先需要向主機 B 發送消息,而不是向主機 D 發送消息。然后,主機 B 會將其轉發給主機 C。
This way, Layer Beta is only responsible for finding the route to send the message. It uses the service provided by Layer Alpha – transmitting data between directly connected hosts.
這樣,Layer Beta 只負責查找發送消息的路由。它使用 Layer Alpha 提供的服務——在直接連接的主機之間傳輸數據。
In general, networks are very complicated, and have various requirements. Dividing the communication into layers will allow us to simplify things and make communication more flexible.
一般來說,網絡非常復雜,并且有各種要求。將溝通分成幾層將使我們能夠簡化事情并使溝通更加靈活。
Now that you understand why we need layers, we can go on to learn about the layers that are actually used in networks.
現在您已經了解了我們為什么需要層,我們可以繼續了解網絡中實際使用的層。
What is the Five Layers Model? 什么是五層模型?
There have been a few layer models proposed along the years – most notably, the five layers model, the 7 layers model (aka OSI model), or the 4 layers model (aka the TCP/IP model).
多年來,已經提出了一些層模型,其中最著名的是五層模型、七層模型(又名 OSI 模型)或四層模型(又名 TCP/IP 模型)。

They are way more similar than different, and I choose to focus on the five layers model as it is the most practical of all – and best describes the way the Internet actually works.
它們的相似之處多于不同之處,我選擇關注五層模型,因為它是最實用的,并且最能描述互聯網的實際工作方式。
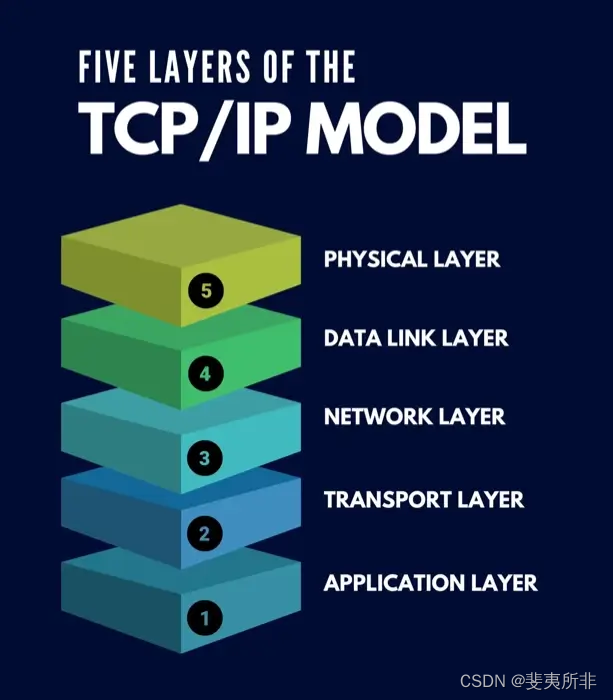
The First Layer – The Physical Layer 第一層 – 物理層
The first layer is responsible for transmitting a single bit – 0 or 1 – over the network.
第一層負責通過網絡傳輸單個比特(0 或 1)。
To get some intuition as to what this layer is responsible for, consider the time of transmission. Assume that we have some kind of cable to transmit our data, and we use +5 Voltage to transmit 1, and -5 Voltage to transmit 0. What bits does the following diagram represent?
要獲得有關該層負責什么的直覺,請考慮傳輸時間。假設我們有某種電纜來傳輸數據,我們使用 +5 電壓傳輸 1,使用 -5 電壓傳輸 0。下圖表示哪些位?
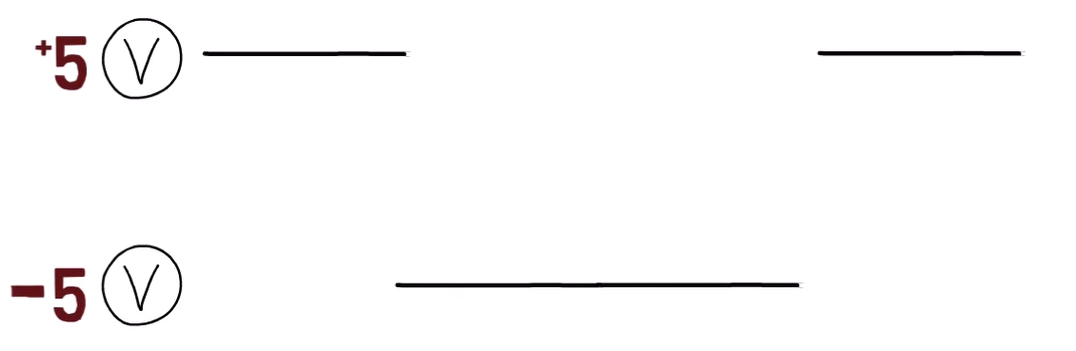
A physical layer implementation encoding 1 as +5 Voltage and 0 as -5 Voltage
Well, it might be 1001. That is the case if it takes this long to transmit a single bit (demonstrated by the dashed orange line in the diagram below):
好吧,它可能是 1001。如果傳輸一個比特需要這么長時間(如下圖中的橙色虛線所示),就是這種情況:
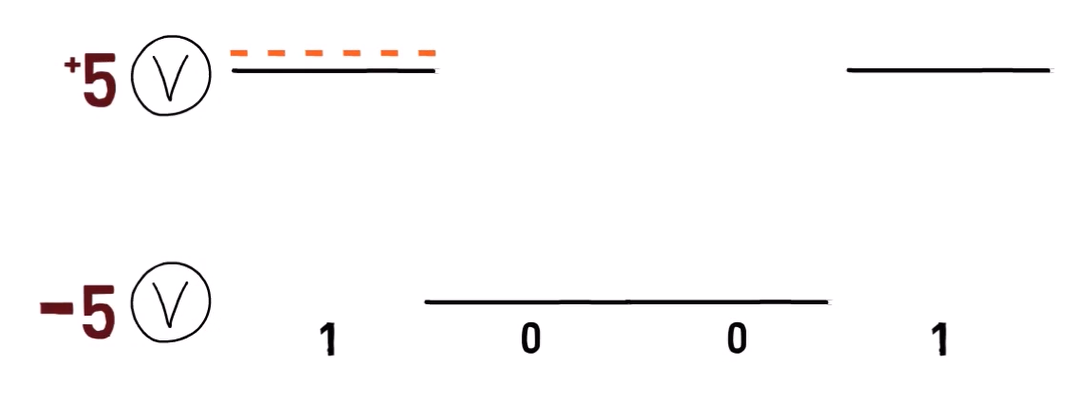
An example bitstream encoded by this signal
However, it might also represent other bit streams. For instance, if it only takes half the time to transmit a single bit (demonstrated by the dashed green line below), then the bit stream might be 11000011:
但是,它也可能表示其他位流。例如,如果傳輸一個比特只需要一半的時間(由下圖的綠色虛線表示),則比特流可能是 11000011:
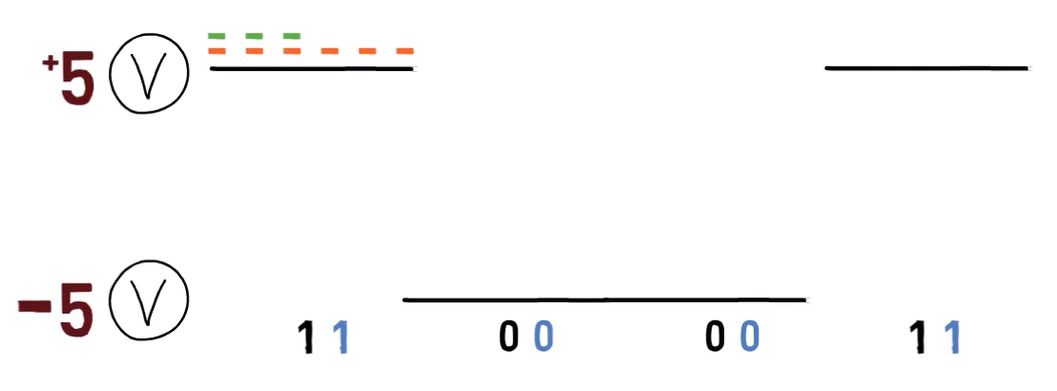
Another possible bitstream encoded by the same signal
The difference lies in the time dedicated for transmitting a single bit. This is called the bitrate – that is, the number of bits that are conveyed per unit of time.
區別在于用于傳輸單個比特的時間。這稱為比特率,即每單位時間傳輸的位數。
Of course, achieving a high bitrate is preferable, as it means we can send many bits in a short timeframe. But it is hard to achieve high bitrates without getting many errors.
當然,實現高比特率是可取的,因為這意味著我們可以在短時間內發送許多比特。但是很難在不出現很多錯誤的情況下實現高比特率。
This is only one of the things that the first layer needs to take into consideration. The important thing for now is the goal of this layer: to transmit and receive a single bit.
這只是第一層需要考慮的事情之一。現在重要的是這一層的目標:發送和接收單個比特。
The Second Layer – The Data Link Layer 第二層 – 數據鏈路層
The second layer is responsible for transmitting data between two hosts that are directly linked, despite possible errors.
第二層負責在直接鏈接的兩臺主機之間傳輸數據,盡管可能存在錯誤。
What do we mean by “directly linked”? For now, imagine that there is no device in between the two devices. So, if we have two computers here – computer A and computer B, and they are connected via computer M – then computer A and computer B are NOT directly linked. But computer A and computer M are directly linked, and so are computer M and computer B.
我們所說的“直接鏈接”是什么意思?現在,假設兩個設備之間沒有設備。因此,如果我們這里有兩臺計算機——計算機 A 和計算機 B,并且它們通過計算機 M 連接——那么計算機 A 和計算機 B 不是直接鏈接的。但是計算機 A 和計算機 M 是直接鏈接的,計算機 M 和計算機 B 也是直接鏈接的。
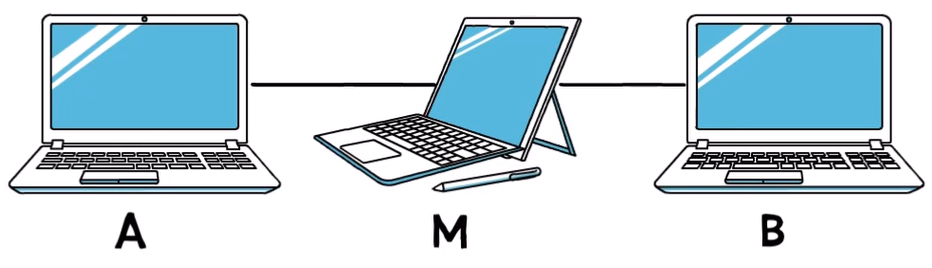
Two remote hosts connected via another device
Another way to put it is that computer A and computer M are one hop away from one another, whereas computer A and computer B are two hops away.
另一種說法是,計算機 A 和計算機 M 彼此相距一跳,而計算機 A 和計算機 B 相距兩跳。
That is, in order to get from computer A to computer B we need two “hops” – one hop from A to M, and another hop from M to B.
也就是說,為了從計算機 A 到計算機 B,我們需要兩個“躍點”——一個從 A 跳到 M,另一個從 M 跳到 B。

Every direct connection is called a Hop
Going back to the second layer’s responsibility – we mentioned it is responsible for transmitting data between two hosts that are directly linked, despite possible errors.
回到第二層的職責——我們提到它負責在兩個直接鏈接的主機之間傳輸數據,盡管可能存在錯誤。
What do we mean by errors? The physical layer might provide erroneous data. For example, 1 instead of 0. So a stream of bits such as 000110, might be received as 001110.
我們所說的錯誤是什么意思?物理層可能會提供錯誤的數據。例如,1 而不是 0。因此,像 000110 這樣的位流可能被接收為 001110。
Many reasons might cause these kind of errors. For instance, we can think of a truck literally running over the wire where the bits are transmitted, causing some problem. Regardless of the reason, the second layer must handle the communication despite these errors.
許多原因可能會導致此類錯誤。例如,我們可以想象一輛卡車從字面上碾過傳輸比特的電線,從而導致一些問題。無論出于何種原因,盡管存在這些錯誤,第二層仍必須處理通信。
The second layer sends data in datagrams, that is, in chunks. Datagrams in this layer are called Frames. Frames will usually contain MAC addresses, which are physical addresses, one identifying the sender, and another identifying the receiver.
第二層以數據報的形式發送數據,即以塊的形式發送數據。此層中的數據報稱為幀。幀通常包含MAC地址,這些地址是物理地址,一個標識發送方,另一個標識接收方。
Why would we need a MAC address?
為什么我們需要MAC地址?
First, the receiving devices would like to know whether the frame is intended for them. The receiver wouldn’t like to waste precious time reading data intended for someone else. If the frame contains a MAC address that doesn’t belong to a receiver’s device, that device can simply ignore this frame.
首先,接收設備想知道幀是否適合它們。接收者不想浪費寶貴的時間來讀取用于其他人的數據。如果幀包含不屬于接收器設備的 MAC 地址,則該設備可以簡單地忽略此幀。
Second, for privacy reasons - we would like messages to arrive only at intended receivers, so only they can read the data.
其次,出于隱私原因 - 我們希望消息只到達預期的接收者,因此只有他們才能讀取數據。
Third, the sender would like the receiver to know who sent the frame. That way, the receiver will be able to send their response back to the sender, and not to someone else.
第三,發送方希望接收方知道是誰發送了幀。這樣,接收者將能夠將他們的響應發送回發送者,而不是其他人。
Note that we would like these addresses to be unique. That is, we want one address to identify a single device. That way, we know that if we send a message to a specific address it will be sent to the intended device only.
請注意,我們希望這些地址是唯一的。也就是說,我們需要一個地址來標識單個設備。這樣,我們知道,如果我們向特定地址發送消息,它只會發送到預期的設備。
The Third Layer – The Network Layer 第三層 – 網絡層
The third layer is responsible for routing – that is, determining the path where the data will “travel”.
第三層負責路由,即確定數據將“傳輸”的路徑。
You can think of this layer as the successful routing app, Google Maps. When you get in the car and use Google Maps, you tell the app your destination, and Google Maps finds out the best route for you to drive in.
您可以將此圖層視為成功的路徑應用程序 Google Maps。當你上車并使用谷歌地圖時,你告訴應用程序你的目的地,谷歌地圖就會為你找到最好的開車路線。
Notice that Google Maps is dynamic – it won’t necessarily pick the same route each time. Sometimes, one path will have a traffic jam, so Google Maps will prefer another route.
請注意,谷歌地圖是動態的——它不一定每次都選擇相同的路線。有時,一條路徑會出現交通擁堵,因此谷歌地圖會更喜歡另一條路線。
We said that the second layer has physical addresses, called MAC addresses. The third layer is responsible for logical addresses, such as IP addresses.
我們說第二層有物理地址,稱為MAC地址。第三層負責邏輯地址,例如 IP 地址。
In this layer, datagrams are called packets.
在此層中,數據報稱為數據包。
Consider the following network diagram:
請參考以下網絡圖:

A network diagram with Computer A in France, Computer B in the US, and 10 routers in between
We have two computers here – one in France, and one in the United States. Of course, they are not directly linked. Rather, they are linked via third layer devices called routers.
我們這里有兩臺電腦,一臺在法國,一臺在美國。當然,它們沒有直接聯系。相反,它們通過稱為路由器的第三層設備進行鏈接。
Which layer is responsible for each connection?
哪個層負責每個連接?
Consider the connection between Computer A and Router 1. The second layer is responsible for this connection. Right, again, this is the second layer. The same applies for each connection between two directly linked devices.
考慮計算機 A 和路由器 1 之間的連接。第二層負責此連接。對,再說一遍,這是第二層。這同樣適用于兩個直接鏈接設備之間的每個連接。
What about the connection between Router 2 and Router 5?
路由器 2 和路由器 5 之間的連接情況如何?
The third layer is responsible for defining the route – that the message sent from Computer A to Computer B will go through Routers 1, 2, 5, 8 and 10, and not in another way.
第三層負責定義路由——從計算機 A 發送到計算機 B 的消息將通過路由器 1、2、5、8 和 10,而不是以其他方式。
Note that there may be different implementations for each layer. For instance, we may have different implementations of the second layer. So while the connection between computer A and Router 1 might be over an Ethernet cable, the connection between Router 1 and 2 might be wireless and use WiFi. The connection between Router 2 and Router 5 might use a carrier pigeon, while the connection between router 5 and 9 will also use WiFi.
請注意,每一層可能有不同的實現。例如,我們可能有不同的第二層實現。因此,雖然計算機 A 和路由器 1 之間的連接可能通過以太網電纜連接,但路由器 1 和路由器 2 之間的連接可能是使用無線 WiFi 的 。路由器 2 和路由器 5 之間的連接可能使用信鴿,而路由器 5 和 9 之間的連接也將使用 WiFi。
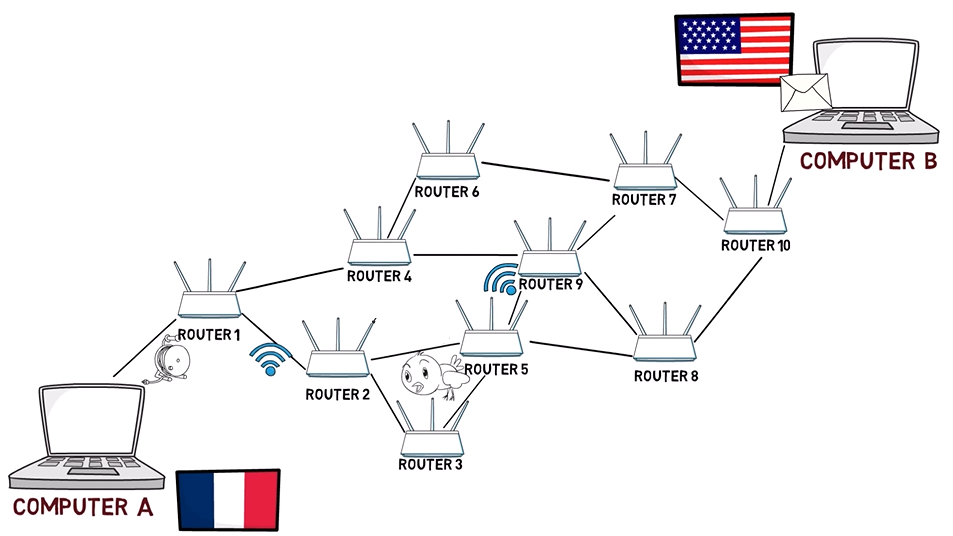
The second layer may be implemented differently on every link
The third layer does not care about these changes, but the second layer definitely does. If the carrier pigeon that transmits data from Router 2 to Router 5 is sick, the second layer will have to handle it. The data link layer will also have to make sure the data transmitted over the air between routers 1 and 5 is valid and without errors.
第三層不關心這些變化,但第二層肯定關心。如果將數據從路由器 2 傳輸到路由器 5 的信鴿生病了,則第二層將不得不處理它。數據鏈路層還必須確保路由器 1 和 5 之間通過無線傳輸的數據有效且沒有錯誤。
Interim Summary 中期摘要
So far we have covered three of the five layers. To recap:
到目前為止,我們已經涵蓋了五層中的三層。 回顧一下:
-
The physical layer is responsible for transmitting a single bit,
1or0, over the network.
物理層負責通過網絡傳輸單個位1或0。 -
The data link layer is responsible for transmitting data between directly linked devices, that is – devices connected via a single hop.
數據鏈路層負責在直接鏈接的設備之間傳輸數據,即通過單跳連接的設備。 -
The third layer is responsible for transferring data between hosts that are connected via multiple hops. It determines the route, the path that the packets will travel.
第三層負責在通過多個躍點連接的主機之間傳輸數據。它決定了路由,即數據包將經過的路徑。
The Fourth Layer – The Transportation Layer 第四層 – 運輸層
The fourth layer is an end-to-end layer. That is, it is responsible for communication from the source, all the way to the ultimate destination.
第四層是端到端層。也就是說,它負責從源頭一直到最終目的地的通信。
It allows multiplexing of multiple services. For example, one server may serve as a Web server, as well as a Mail server. When a client turns to that server, the client should be able to specify which service it would like to access. While the third layer specifies the address of the server, the transport layer identifies which service is relevant for the current communication.
它允許多個服務的多路復用。例如,一臺服務器既可以用作 Web 服務器,也可以用作郵件服務器。當客戶端轉向該服務器時,客戶端應該能夠指定它要訪問的服務。第三層指定服務器的地址,而傳輸層則標識與當前通信相關的服務。
In addition, the transport layer may ensure reliability. So when this layer receives data from the upper layer, it splits it into chunks, sends them, and makes sure that all those chunks arrive correctly at the other end.
此外,傳輸層可以確保可靠性。因此,當這一層從上層接收數據時,它會將其拆分為塊,發送它們,并確保所有這些塊都正確到達另一端。
Notice that the network layer is usually not reliable. Packets may arrive in incorrect order, they can arrive with incorrect data, or even not arrive at all. A reliable transportation layer makes sure that the data is correctly received.
請注意,網絡層通常不可靠。數據包可能以不正確的順序到達,它們可能以不正確的數據到達,甚至根本沒有到達。可靠的傳輸層可確保正確接收數據。
In this layer, datagrams are called segments.
在此層中,數據報稱為段。
Consider the following network diagram once more:
再次參考以下網絡圖:

Which layer is responsible for what?
各層負責什么?
We have already said that the network layer is responsible for the route, that is, the path in which the packets travel. We also mentioned that the second layer is responsible for the transmission of the data between two, directly connected devices. For example, the link between Router 1 and Router 2.
我們已經說過,網絡層負責路由,即數據包傳輸的路徑。我們還提到,第二層負責在兩個直接連接的設備之間傳輸數據。例如,路由器 1 和路由器 2 之間的鏈路。
The fourth layer views all of this network diagram as an abstract cloud. It doesn’t know the routers, and it doesn’t care about the structure of the network, or the routing. It assumes that the network can send a packet from one end to another:
第四層將所有這些網絡圖視為一個抽象的云。它不知道路由器,也不關心網絡的結構或路由。它假設網絡可以從一端向另一端發送數據包:
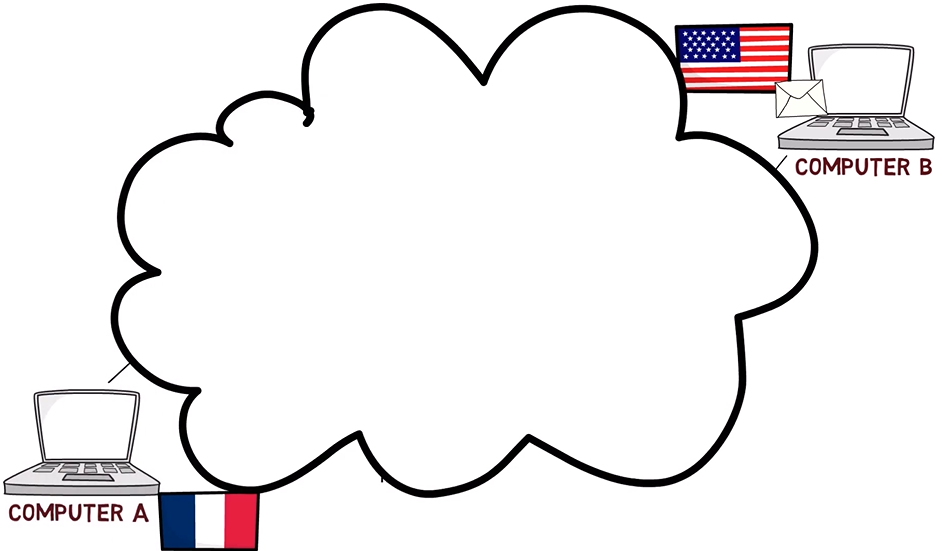
The fourth layer sees the network as an abstract cloud
The transportation layer makes sure that the endpoints can communicate over different services – for example, web and email. In addition, it might make sure that the connection is reliable.
傳輸層確保端點可以通過不同的服務(例如 Web 和電子郵件)進行通信。此外,它可以確保連接可靠。
One example would be to acknowledge every received segment. For instance, when computer A sends a segment to computer B, computer B will send a special Acknowledgement segment, announcing that it has received the packet.
一個示例是確認每個收到的段。例如,當計算機 A 向計算機 B 發送分段時,計算機 B 將發送一個特殊的確認分段,宣布它已收到數據包。
The Fifth Layer – The Application Layer 第五層 – 應用層
Last but definitely not least, we have the fifth layer, or Application Layer. This layer provides the service to the user’s application – web service, Voice over IP (VoIP), network games, streaming, and so on.
最后但并非最不重要的一點是,我們有第五層,或應用層。此層為用戶的應用程序提供服務 - Web 服務、IP 語音 (VoIP)、網絡游戲、流媒體等。
According to the layers model, the fifth layer doesn’t care at all about the network. It relies on the fourth layer, as well as the lower layers, to transmit the data from one endpoint to another. The fifth layer will use this service for the various needs of the application.
根據層模型,第五層根本不關心網絡。它依賴于第四層以及更低的層,將數據從一個端點傳輸到另一個端點。第五層將使用此服務來滿足應用程序的各種需求。
Different protocols will be used for different applications. For instance, HTTP protocol is commonly used for serving web pages on the World Wide Web. SMTP is a protocol used for emails, FTP for exchanging files, and there are many, many more.
不同的協議將用于不同的應用。例如,HTTP協議通常用于在萬維網上提供網頁。SMTP是一種用于電子郵件的協議,用于交換文件的FTP,還有很多很多。
Summary 總結
In this post you learned what the five layers model is and why we need layers. You should now understand what each layer is responsible for, and you can fit every topic you encounter in Computer Networks into this model.
在這篇文章中,您了解了什么是五層模型以及為什么我們需要層。現在,您應該了解每一層負責什么,并且可以將計算機網絡中遇到的每個主題都放入此模型中。
via: Omer Rosenbaum OCTOBER, 2022

![[數據集][目標檢測]城市街道井蓋破損未蓋丟失檢測數據集VOC+YOLO格式4404張5類別](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[數據集][目標檢測]城市街道井蓋破損未蓋丟失檢測數據集VOC+YOLO格式4404張5類別)

















