1.父傳后代 ( 后代拿到了父的數據 )
1. 父組件引入子組件,綁定數據
<List :str1=‘str1’></List>
子組件通過props來接收
props:{str1:{type:String,default:''}}
***這種方式父傳子很方便,但是父傳給孫子輩分的組件就很麻煩(父=》子=》孫)
這種方式:子不能直接修改父組件的數據
2. 子組件直接使用父組件的數據
子組件通過:this.$parent.xxx使用父組件的數據
這種方式:子可以直接修改父組件的數據
3. 依賴注入(使用 provide/inject API)
優勢:父組件可以直接向某個后代組件傳值(不讓一級一級的傳遞)
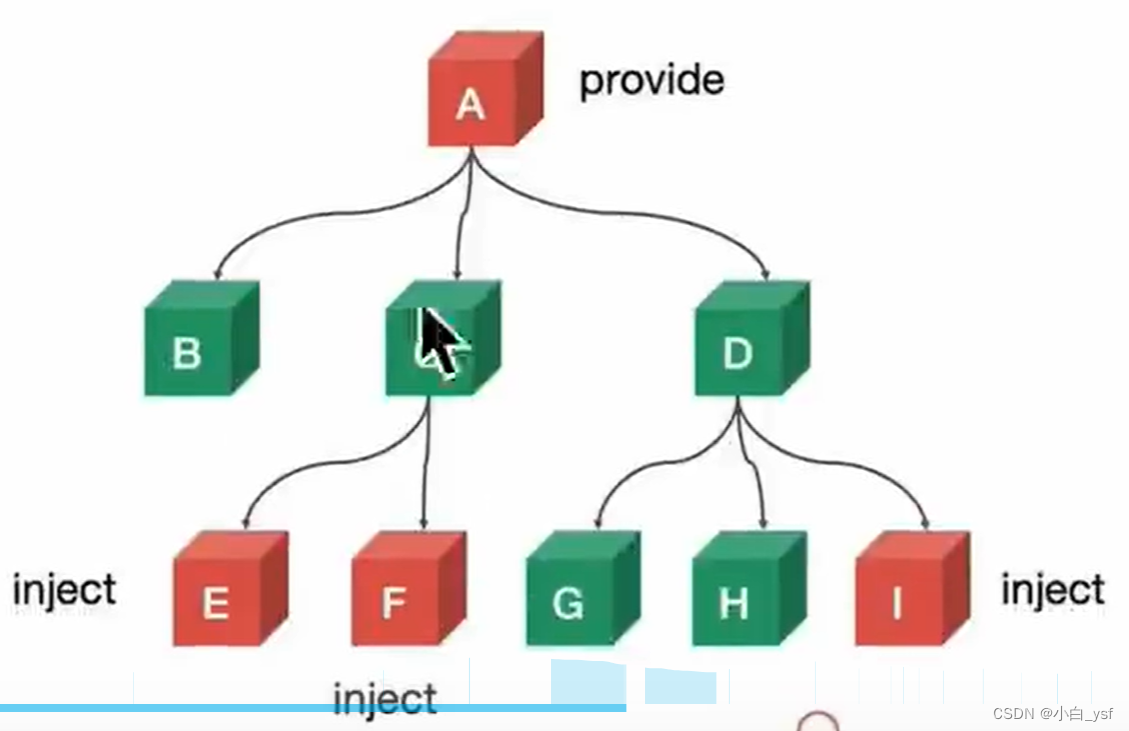
1.在祖先組件中使用 provide
在祖先組件中,你可以使用 provide 選項來提供數據或方法。這些數據或方法可以被任何后代組件通過 inject 選項來接收。
<!-- AncestorComponent.vue -->
<template> <div> <DescendantComponent /> </div>
</template> <script>
import DescendantComponent from './DescendantComponent.vue'; export default { components: { DescendantComponent }, provide() { return { foo: 'foo', myMethod: this.myMethod }; }, methods: { myMethod() { console.log('This is a method from AncestorComponent.'); } }
};
</script>
2.在后代組件中使用 inject
在后代組件中,你可以使用 inject 選項來接收在祖先組件中 provide 的數據或方法。
<!-- DescendantComponent.vue -->
<template> <div> <p>{{ foo }}</p> <button @click="callAncestorMethod">Call Ancestor Method</button> </div>
</template> <script>
export default { inject: ['foo', 'myMethod'], methods: { callAncestorMethod() { this.myMethod(); } }
};
</script>
在這個例子中,DescendantComponent 接收了 foo 字符串和 myMethod 方法,它們都是在 AncestorComponent 中通過 provide 提供的。
2.后代傳父 (父拿到了后代的數據)
1. 子組件傳值給父組件
子組件定義自定義事件 this.$emit
子組件中:
// ChildComponent.vue
export default { methods: { sendToParent() { this.$emit('child-event', 'Data from child'); } }
};
父組件中:
<!-- ParentComponent.vue -->
<template> <div> <ChildComponent @child-event="handleChildEvent" /> </div>
</template> <script>
// ...
export default { // ... methods: { handleChildEvent(data) { console.log('Received data from child:', data); } }
};
</script>
2. 父組件直接拿到子組件的數據
<List ref=‘child’></List>
this.$refs.child
下面是一個簡單的例子,展示了如何在父組件中通過 $refs 訪問子組件的方法:
<!-- ChildComponent.vue -->
<template> <div> <button @click="sayHello">Say Hello</button> </div>
</template> <script>
export default { methods: { sayHello() { console.log('Hello from ChildComponent!'); } }
};
</script> <!-- ParentComponent.vue -->
<template> <div> <ChildComponent ref="child" /> <button @click="callChildMethod">Call Child's Method</button> </div>
</template> <script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue'; export default { components: { ChildComponent }, methods: { callChildMethod() { this.$refs.child.sayHello(); // 調用子組件的 sayHello 方法 } }
};
</script>
在這個例子中,點擊父組件的按鈕會觸發 callChildMethod 方法,該方法通過 this.$refs.child.sayHello() 調用了子組件的 sayHello 方法。
3.平輩之間的傳值 ( 兄弟可以拿到數據 )
通過新建bus.js文件來做
在 Vue.js 中,如果你想要在不直接依賴父子組件關系的情況下進行組件間的通信,一個常見的方法是創建一個全局的事件總線(Event Bus)。你可以通過創建一個新的 Vue 實例來作為這個事件總線,并在你的組件中通過它來進行事件的觸發
($emit)和監聽($on)。
以下是如何通過新建一個 bus.js 文件來創建全局事件總線的步驟:
創建 bus.js 文件
在你的項目根目錄或合適的地方,創建一個 bus.js 文件,并導出一個新的 Vue 實例:
// bus.js
import Vue from 'vue'; export const EventBus = new Vue();
在組件中觸發事件 ,在你的組件中,你可以導入 EventBus 并使用 $emit 方法來觸發事件:
// ChildComponent.vue
<template> <button @click="notify">Notify Parent</button>
</template> <script>
import { EventBus } from './bus.js'; // 假設 bus.js 和當前文件在同一目錄下 export default { methods: { notify() { EventBus.$emit('child-event', 'Data from child'); } }
};
</script>
在組件中監聽事件, 在另一個組件中,你可以導入 EventBus 并使用 $on 方法來監聽事件:
// ParentComponent.vue 或其他任何組件
<script>
import { EventBus } from './bus.js'; // 假設 bus.js 和當前文件在同一目錄下 export default { created() { EventBus.$on('child-event', (data) => { console.log('Received data from child:', data); }); }, beforeDestroy() { // 清除事件監聽,避免內存泄漏 EventBus.$off('child-event'); }
};
</script>
注意,在組件銷毀(beforeDestroy 或 destroyed 鉤子)時,你應該使用 $off 方法來移除事件監聽器,以避免內存泄漏。
使用事件總線的一個缺點是它可能導致你的應用狀態變得難以追蹤,特別是當你的應用變得復雜并且有很多組件在相互通信時。因此,盡管事件總線在某些場景下很有用,但在設計你的應用架構時,也要考慮其他狀態管理解決方案,如 Vuex。



時需要使用哪些工具?)
)





 -- 斷線重連)
)



: Plugin ‘msql_native_password‘ is not loaded.)

)

