文章目錄
- 一、雙列集合Map
- 1.1 雙列集合介紹
- 1.2 雙列集合Map常見API
- 1.3 Map集合遍歷方式
- 1.3.1 通過集合的全部鍵來遍歷集合
- 1.3.2 Map集合遍歷方式2
- 1.3.3 Map集合遍歷方式3
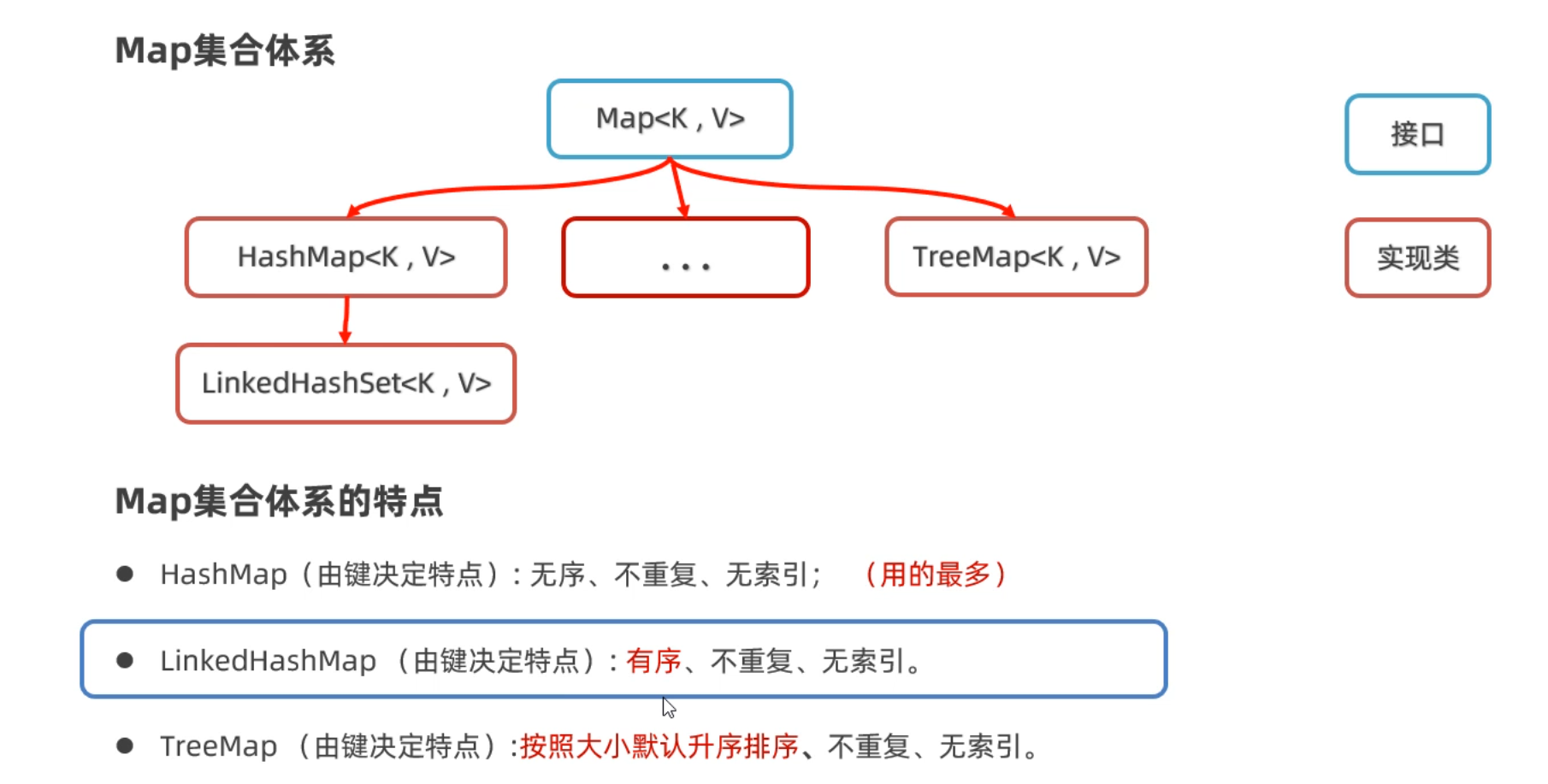
- 二、Map集合的實現類
- 2.1 HashMap類
- 2.2 LinkedHashMap
- 2.3 TreeMap
- 三、可變參數
- 四、Collections類
- 五、集合的嵌套
一、雙列集合Map
1.1 雙列集合介紹
所謂雙列集合,就是說集合中的元素是一對一對的。Map集合中的每一個元素是以
key=value的形式存在的,一個key=value就稱之為一個鍵值對,而且在Java中有一個類叫Entry類,Entry的對象用來表示鍵值對對象。
- 鍵不能重復,值可以重復,每一個鍵只能找到自己對應的值。
1.2 雙列集合Map常見API
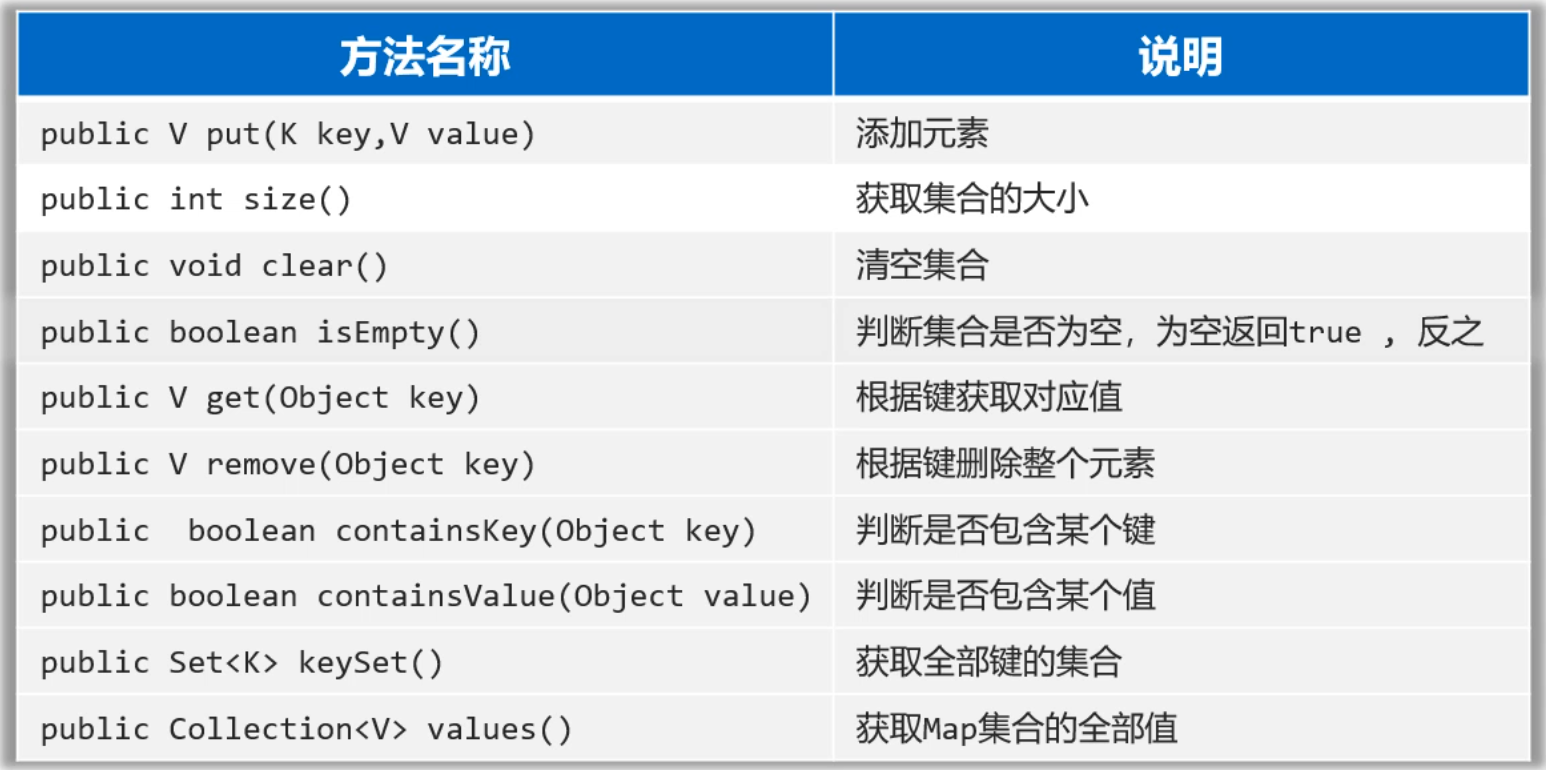
public class MapTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1.添加元素: 無序,不重復,無索引。//Map是一個接口,無法創建對象,只能創建其實現類的對象HashMapMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("手表", 100);map.put("手表", 220);map.put("手機", 2);map.put("Java", 2);map.put(null, null);System.out.println(map);// map = {null=null, 手表=220, Java=2, 手機=2}// 2.public int size():獲取集合的大小System.out.println(map.size());// 3、public void clear():清空集合//map.clear();//System.out.println(map);// 4.public boolean isEmpty(): 判斷集合是否為空,為空返回true ,反之!System.out.println(map.isEmpty());// 5.public V get(Object key):根據鍵獲取對應值int v1 = map.get("手表");System.out.println(v1);System.out.println(map.get("手機")); // 2System.out.println(map.get("張三")); // null// 6. public V remove(Object key):根據鍵刪除整個元素(刪除鍵會返回鍵的值)System.out.println(map.remove("手表"));System.out.println(map);// 7.public boolean containsKey(Object key): 判斷是否包含某個鍵 ,包含返回true ,反之System.out.println(map.containsKey("手表")); // falseSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("手機")); // trueSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("java")); // falseSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("Java")); // true// 8.public boolean containsValue(Object value): 判斷是否包含某個值。System.out.println(map.containsValue(2)); // trueSystem.out.println(map.containsValue("2")); // false// 9.public Set<K> keySet(): 獲取Map集合的全部鍵。Set<String> keys = map.keySet();System.out.println(keys);// 10.public Collection<V> values(); 獲取Map集合的全部值。Collection<Integer> values = map.values();System.out.println(values);// 11.把其他Map集合的數據倒入到自己集合中來。(拓展)Map<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();map1.put("java1", 10);map1.put("java2", 20);Map<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();map2.put("java3", 10);map2.put("java2", 222);map1.putAll(map2); // putAll:把map2集合中的元素全部倒入一份到map1集合中去。System.out.println(map1);System.out.println(map2);}
}
1.3 Map集合遍歷方式
1.3.1 通過集合的全部鍵來遍歷集合
通過鍵找值的方法遍歷集合,由于鍵值的唯一性
public class MapTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 準備一個Map集合。Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 162.5);map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊寶", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊寶=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}// 1、獲取Map集合的全部鍵Set<String> keys = map.keySet();// System.out.println(keys);// [蜘蛛精, 牛魔王, 至尊寶, 紫霞]// key// 2、增強for遍歷全部的鍵,根據鍵獲取其對應的值for (String key : keys) {// 根據鍵獲取對應的值double value = map.get(key);System.out.println(key + "=====>" + value);}}
}
1.3.2 Map集合遍歷方式2
通過鍵值對的方法遍歷集合
直接獲取每一個Entry對象,把Entry存儲到 Set集合中去,再通過Entry對象獲取鍵和值。
public class MapTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊寶", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊寶=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}// entries = [(蜘蛛精=169.8), (牛魔王=183.6), (至尊寶=169.5), (紫霞=165.8)]// entry = (蜘蛛精=169.8)// entry = (牛魔王=183.6)// ...// 1、調用Map集合提供entrySet方法,把Map集合轉換成鍵值對類型的Set集合//entry是Map類中的內部接口Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : entries) {String key = entry.getKey();double value = entry.getValue();System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);}}
}
1.3.3 Map集合遍歷方式3
用forEach方法
/*** 目標:掌握Map集合的第二種遍歷方式:鍵值對。*/
public class MapTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊寶", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊寶=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}//遍歷map集合,傳遞匿名內部類map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Double>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String k, Double v) {System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);}});//遍歷map集合,傳遞Lambda表達式map.forEach(( k, v) -> {System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);});}
}
二、Map集合的實現類
2.1 HashMap類
HashMap底層原理和HashSet是一樣的。我們往HashSet集合中添加元素時,實際上是把元素作為添加添加到了HashMap集合中。故兩個類的常用方法都一樣
下面是Map集合的體系結構,HashMap集合的特點是由鍵決定的: 它的鍵是無序、不能重復,而且沒有索引的。再各種Map集合中也是用得最多的一種集合。

Hash和HashMap在本質上是一樣的,底層原理都依賴于哈希表來實現
2.2 LinkedHashMap
與單列結合的哈希表一樣,底層是基于雙鏈表實現的
public class Test2LinkedHashMap {public static void main(String[] args) {// Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 按照鍵 無序,不重復,無索引。LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 按照鍵 有序,不重復,無索引。map.put("手表", 100);map.put("手表", 220);map.put("手機", 2);map.put("Java", 2);map.put(null, null);System.out.println(map);}
}
運行結果:
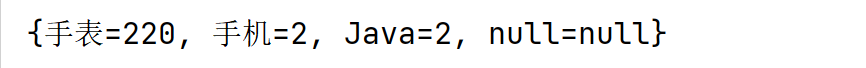
可見:
- 鍵值相同時,值會被覆蓋
- 存入與取出的次序一致
2.3 TreeMap
TreeMap集合的特點也是由鍵決定的,默認按照鍵的升序排列,鍵不重復,也是無索引的。
TreeMap集合的底層原理和TreeSet也是一樣的,底層都是紅黑樹實現的。所以可以對鍵進行排序。
TreeMap類在排序是和TreeSet一樣也有兩種方法
排序方式1:寫一個Student類,讓Student類實現Comparable接口
//第一步:先讓Student類,實現Comparable接口
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private int age;private double height;//無參數構造方法public Student(){}//全參數構造方法public Student(String name, int age, double height){this.name=name;this.age=age;this.height=height;}//...get、set、toString()省略//按照年齡進行比較,只需要在方法中讓this.age和o.age相減就可以。/*原理:在往TreeSet集合中添加元素時,add方法底層會調用compareTo方法,根據該方法的結果是正數、負數、還是零,決定元素放在后面、前面還是不存。*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//this:表示將要添加進去的Student對象//o: 表示集合中已有的Student對象return this.age-o.age;}
}
排序方式2:在創建TreeMap集合時,直接傳遞Comparator比較器對象。
public class Test3TreeMap {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight());}});
// Map<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(( o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()));map.put(new Student("蜘蛛精", 25, 168.5), "盤絲洞");map.put(new Student("蜘蛛精", 25, 168.5), "水簾洞");map.put(new Student("至尊寶", 23, 163.5), "水簾洞");map.put(new Student("牛魔王", 28, 183.5), "牛頭山");System.out.println(map);}
}
三、可變參數
當函數接收的數據數量不確定時,可以用到可變參數
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(getSum(1,2,3,4,5));}//普通參數放在可變參數之前,且方法中最多只接收一個可變參數public static int getSum(double agg,int... args){int sum=0;for (int i : args) {sum += i;}return sum;}
}
注意:
- 方法的形參最多接收一個可變參數
- 可變參數的本質時數組
- 普通參數應該放在可變參數之前
四、Collections類
該類是一個集合的工具類
public class CollectionsDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//該類的兩個常用方法ArrayList<String> arr=new ArrayList<>();//1.集合的批量添加Collections.addAll(arr,"1","2","3","4");System.out.println(arr);//2.集合的打亂Collections.shuffle(arr);}
}
五、集合的嵌套
當有如下的需求時,一個鍵對應著多個值:

而又因為一個省份有多個城市,同一個省份的多個城市可以再用一個List集合來存儲。
所以Map集合的鍵是String類型,而指是List集合類型
HashMap<String, List> map = new HashMap<>();
/*** 江蘇省 = "南京市","揚州市","蘇州市“,"無錫市","常州市"* 湖北省 = "武漢市","孝感市","十堰市","宜昌市","鄂州市"* 河北省 = "石家莊市","唐山市", "邢臺市", "保定市", "張家口市"*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1、定義一個Map集合存儲全部的省份信息,和其對應的城市信息。Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();List<String> cities1 = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(cities1, "南京市","揚州市","蘇州市" ,"無錫市","常州市");map.put("江蘇省", cities1);List<String> cities2 = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(cities2, "武漢市","孝感市","十堰市","宜昌市","鄂州市");map.put("湖北省", cities2);List<String> cities3 = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(cities3, "石家莊市","唐山市", "邢臺市", "保定市", "張家口市");map.put("河北省", cities3);System.out.println(map);List<String> cities = map.get("湖北省");for (String city : cities) {System.out.println(city);}map.forEach((p, c) -> {System.out.println(p + "----->" + c);});}
}






![[面試題]計算機網絡](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[面試題]計算機網絡)












