SELinux 介紹
SELinux 概述
文件權限控制了哪些用戶或用戶組可以訪問哪些特定文件,但未限定用戶訪問文件的方式。
例如:對于文件的寫入權限而言, 結構化數據文件是否應當設計為只能使用特定的程序寫入,但其他編輯器仍可以打開和修改此文件,而這可能會導致損壞。文件權限僅僅是控制誰可以讀取、寫入或運行文件,無法控制如何使用文件。
Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux)是一個額外的系統安全層,主要目標是防止已遭泄露的系統服務訪問用戶數據。
例如:惡意人員成功入侵了 Web服務器進程,獲得進程的權限,也就是apache用戶和apache組的權限。該用戶和組對文檔根目錄/var/www/html具有讀取權限,還可以訪問/tmp和/var/tmp,以及全局可寫的其他任何文件和目錄。
SELinux 強制執行一組訪問規則,明確定義進程和資源之間允許的操作。每個進程、文件、目錄和端口都具有專門的安全標簽, 稱為SELinux上下文。上下文是一個名稱, SELinux策略使用它來確定某個進程能否訪問文件、目錄或端口。除非顯式規則授予訪問權限,否則,在默認情況下,策略不允許任何交互。
SELinux 標簽有多個內容:用戶,角色,類型和敏感度。rhel中默認策略targeted,基于類型部分。類型部分通常以_t結尾。
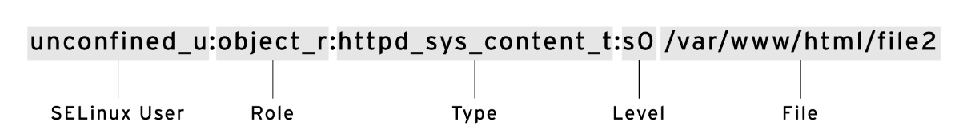
示例:
- web 服務器守護進程類型是 httpd_exec_t
- web 服務器的網頁類型是 httpd_sys_content_t
- web 服務器的端口類型是 http_port_t
- /tmp 標簽 tmp_t
基本原理
- SELinux默認策略允許apache進程訪問在/var/www/html文件夾下的文件和文件夾,以及其他一些具有httpd_sys_content_t上下文的文件夾,禁止訪問具有其他不匹配標簽的目錄。
- 在 SELinux 的保護下,apache進程不允許訪問/tmp和/var/tmp目錄。因為/tmp、/var/tmp目錄的標簽是tmp_t,與默認策略不匹配。
命令選項 -Z
許多處理文件的命令都一個-Z 選項,用于顯示和設置SELinux上下文。
[root@server ~]# ps -C sshd -Z
LABEL PID TTY TIME CMD
system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 951 ? 00:00:00 sshd
system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 1261 ? 00:00:00 sshd
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 1276 ? 00:00:00 sshd
system_u:system_r:sshd_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 2455 ? 00:00:00 sshd
unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 2459 ? 00:00:00 sshd[root@server ~]# ls -Z /home
unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 furongwang# 其他命令中 -Z 選項
# cp -Z set SELinux security context of destination file to default type
# mkdir -Z set SELinux security context of each created directory to the default type
SELinux 模式
- enforcing 模式: SELinux強制執行訪問控制規則。 在強制模式下,如果規則沒有明確允許訪問,則拒絕訪問,并寫入日志。此模式是默認模式。
- Permissive 模式:SELinux 加載策略并處于活動狀態,但不強制執行訪問控制規則,?是記錄訪問違規。此模式有助于對應用和規則進行測試和故障排除。
- disable 模式:完全關閉 SELinux。不拒絕任何SELinux違規,不予記錄。
查看當前模式
[root@server ~]# getenforce
更改當前模式
[root@server ~]# setenforce
usage: setenforce [ Enforcing | Permissive | 1 | 0 ]# 強制模式臨時切換為允許模式
[root@server ~]# setenforce 0
# 或者
[root@server ~]# setenforce Permissive# 允許模式臨時切換為強制模式
[root@server ~]# setenforce 1
# 或者
[root@server ~]# setenforce Enforcing
模式切換注意事項:
- 強制模式和允許模式之間變更,不需要重啟系統。
- 從強制模式或者允許模式變更到禁用模式,或者從禁用模式變更到強制模式或者允許模式都需要重啟系統。
更改 SELinux 默認模式
[root@server ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=enforcing
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
在啟動時通過將向內核傳遞參數來設置SELinux 模式:
- enforcing=1,設置強制模式。
- enforcing=0,設置許可模式。
- selinux=0,來徹底禁用 SELinux。
- selinux=1,啟用 SELinux(當設置enforcing參數是,該參數可以省略)。
實驗: selinux模式為enforcing情況下,破解root密碼。破解完成后不執行 touch /.autorelabel命令。
重啟測試:使用正確的密碼登錄。結果:登錄失敗。原因:用戶驗證程序無法訪問/etc/shadow,因為破解密碼過程中/etc/shadow文件標簽被破壞了。
處理方法:系統啟動時,內核添加參數 selinux=1 enforcing=0
控制文件 SELinux 上下文
新文件默認 SELinux 上下文
新文件通常從父目錄繼承其SELinux上下文,從而確保它們具有適當的上下文。
[root@server ~]# touch /tmp/ruike1
[root@server ~]# ls -dZ /tmp /tmp/ruike1
drwxrwxrwt. root root system_u:object_r:tmp_t:s0 /tmp
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /tmp/ruike1[root@server ~]# cp /tmp/ruike1 /root/ruike5
[root@server ~]# ls -dZ /tmp /tmp/ruike1 /root /root/ruike5
dr-xr-x---. root root system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 /root
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 /root/ruike5
drwxrwxrwt. root root system_u:object_r:tmp_t:s0 /tmp
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /tmp/ruike1
以下兩種情況,文件的 SELinux 上下文保持不變:
- cp -a 命令復制
- 移動文件
[root@server ~]# cp -a /tmp/ruike1 /root/ruike1-a
[root@server ~]# ls -dZ /tmp /tmp/ruike1 /root /root/ruike1*
dr-xr-x---. root root system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 /root
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /root/ruike1-a
drwxrwxrwt. root root system_u:object_r:tmp_t:s0 /tmp
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /tmp/ruike1[root@server ~]# mv /tmp/furongwang /root/furongwang-mv
[root@server ~ ]# ls -1dZ /tmp /root /root/furongwang*system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 /root
unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 /root/furongwang1unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /root/furongwang-aunconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /root/furongwang-mvsystem_u:object_r:tmp_t:s0 /tmp
設置文件 SELinux 上下文
設置文件上下文命令
-
chcon 命令,直接更改文件SELinux上下文。但是,它不會將上下文更改保存到 SELinux 上下文數據庫中。系統下一次對所有文件進行 relabel 操作時,將導致該上下文恢復。它對于測試和實驗很有用。
-
restorecon 命令,根據 SELinux上下文數據庫中規則,恢復文件SELinux上下文。原先通過 chcon命令所做的更改,將失效。
示例:
[root@server ~]# mkdir /www
[root@server ~]# ls -Zd /www
unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /www[root@server ~]# chcon -t httpd_sys_content_t /www
[root@server ~]# ls -Zd /www
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /www[root@server ~]# restorecon -v /www
Relabeled /www from unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0
[root@server ~]# ls -Zd /www
unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /www
semanage fcontext 命令用于管理SELinux上下文數據庫中規則,restorecon 命令根據這些規則恢復文件上下文。semanage fcontext命令使用擴展的正則表達式指定路徑和文件名。比較常見的擴展正則表達式 (/.*)? ,表示隨意匹配/后面接任意數量字符,遞歸匹配文件夾下的子文件和子文件夾。
示例:
[root@server ~]# echo Hello World > /www/index.html
[root@server ~]# ls -Zd /www/index.html
unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /www/index.html# 安裝 semanage 工具
[root@server ~]# yum install -y policycoreutils-python# 添加默認規則
[root@server ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t '/www(/.*)?'
[root@server ~]# semanage fcontext -l |grep '^/www(/.*)?'
/www(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 # 只查看非默認策略
[root@server ~]# semanage fcontext -lC
SELinux fcontext type Context
/www(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0# 恢復文件上下文
[root@server ~]# restorecon -Rv /www/
Relabeled /www from unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /www/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@server ~]# ls -1Zd /www/ /www/index.html
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /www/
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /www/index.html# 刪除默認規則
[root@server ~]# semanage fcontext -d -t httpd_sys_content_t '/www(/.*)?'# 刪除目錄
[root@server ~]# rm -fr /www
示例:配置 web 站點主目錄
# 準備目錄
[root@server ~]# mkdir /www
[root@server ~]# echo woshichuantongpai > /www/index.html
[root@server ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t '/www(/.*)?'
[root@server ~]# restorecon -Rv /www/# 安裝 httpd
[root@server ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@server ~]# systemctl enable httpd --now
[root@server ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# 注釋122 行DocumentRoot,在122行后,添加如下內容:
# DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
DocumentRoot "/www"
<Directory "/www">AllowOverride None# Allow open access:Require all granted
</Directory>
# 重啟服務
[root@server ~]# systemctl restart httpd# 訪問驗證
[root@server ~]# curl http://server.furongwang.cloud/
woshichuantongpai
控制端口 SELinux 上下文
端口 SELinux 上下文
SELinux還可以對端口標記。 當某個進程希望偵聽端口時, SELinux將檢查是否允許與該進程相關聯的標簽綁定該端口標簽。 這可以阻止惡意服務控制本應由其他網絡服務使用的端口。
在 targeted 策略中:
- 端口 22/TCP ,具有標簽 ssh_port_t。
- 端口 80/TCP 和 443/TCP ,具有標簽 http_port_t。
# 查看端口標記
[root@server ~]# semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
http_port_t tcp 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988# 添加端口標記
[root@server ~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 18020
[root@server ~]# semanage port -l|grep 18020
http_port_t tcp 18020, 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000# 修改網絡端口標記
[root@server ~]# semanage port -m -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 18020
[root@server ~]# semanage port -l | grep 18020
ssh_port_t tcp 18020, 22# 刪除端口標記
[root@server ~]# semanage port -d -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 18020
[root@server ~]# semanage port -l | grep 18020
示例:配置 web 站點監聽端口
[root@server ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# 修改原先的 Listen 80 為 Listen 18020
Listen 18020# 重啟服務
[root@server ~]# systemctl restart httpd
Job for httpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See "systemctl status httpd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details[root@server ~]# systemctl status httpd.service |cat |grep Per
......
Nov 29 11:55:26 server.furongwang.cloud httpd[3939]: (13)Permission denied: AH00072: make_sock: could not bind to address 0.0.0.0:18020
......# 配置端口
[root@server ~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 18020
[root@server ~]# semanage port -l | grep 18020
http_port_t tcp 18020, 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000# 只查看改動標簽
[root@server ~]# semanage port -lC
SELinux Port Type Proto Port Number
http_port_t tcp 18020# 重啟服務并訪問
[root@server ~]# systemctl restart httpd# 訪問驗證
[root@server ~]# curl http://server.furongwang.cloud:18020/
Hello World
控制 SELinux 布爾值
SELinux 布爾值
SELinux 布爾值是可更改SELinux策略行為的開關,可以啟用和禁用。
# 查看SELinux布爾值
[root@server ~]# getsebool -a |grep httpd_enable_homedirs
httpd_enable_homedirs --> off
[root@server ~]# getsebool httpd_enable_homedirs
httpd_enable_homedirs --> off# 設置SELinux布爾值
[root@server ~]# setsebool
Usage: setsebool [ -NPV ] boolean value | bool1=val1 bool2=val2...
# 啟用value為1或者on或者true
# 禁用value為0或者off或者false[root@server ~]# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs=1或者on或者true
[root@server ~]# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs=0或者off或者false# 持久化設置布爾值,使用-P選項修改將寫入SELinux數據庫。
[root@server ~]# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs=1
[root@server ~]# setsebool -P httpd_enable_homedirs=1
還可以semanage boolean 命令管理 SELinux 布爾值。
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean
usage: semanage boolean [-h] [-n] [-N] [-S STORE] [ --extract | --deleteall | --list -C | --modify ( --on | --off ) boolean ]# 查看 SELinux 布爾值
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean -l
# 只查看非默認的 SELinux 布爾值
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean -l -C# 設置 SELinux 布爾值
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean -m -1|--on use_nfs_home_dirs
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean -m -0|--off use_nfs_home_dirs
# 相當于setsebool -P# 刪除原先自定義的 SELinux 布爾值
[root@server ~]# semanage boolean -D
示例:允許 httpd 訪問用戶家目錄
[root@server ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf
# 修改以下兩個參數UserDir enabledUserDir public_html
# 重啟服務
[root@server ~]# systemctl restart httpd# 設置權限
[furongwang@server ~]$ mkdir public_html
[furongwang@server ~]$ echo "Welcome to litang" > public_html/index.html
[root@server ~]# ll -d /home/furongwang
drwx-----x. 2 furongwang furongwang 83 8月 1 16:20 /home/furongwan
[furongwang@server ~]$ chmod o+x /home/furongwang/# 未啟用布爾值訪問
[root@server ~]# curl http://server.furongwang.cloud:18020/~furongwang/
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>403 Forbidden</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Forbidden</h1>
<p>You don't have permission to access this resource.</p>
</body></html># 啟用布爾值訪問
[root@server ~]# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs=1
[root@server ~]# curl http://server.furongwang.cloud:18020/~furongwang/
Welcome to litang
SELinux 問題處理思路
- 確定是否是 SELinux 引起的。
- 在做調整前,首先考慮 SELinux 是否正確的阻止了訪問。例如web服務器嘗試訪問/home目錄,如果web的內容不是用戶發布的,那么發生阻止信號是正確的阻止。如果這個訪問是被允許的,參考下面步驟。
- 最常見的 SELinux 問題是不正確的文件上下文。當文件是另外一個地方創建的,然后移動到新的地方,而新的地方需要新的上下文。在大多數情況,執行restorecon可以修復這個問題。這種修復問題方式對系統其他部分安全影響非常小。
- 另外一個問題可能是布爾值設置不當導致拒絕訪問。例如ftpd_anon_write布爾值控制匿名ftp用戶是否可以上傳文件。如果如需匿名用戶上傳文件,需要打開這個布爾值。調整布爾值需要小心,因為對系統影響范圍比較大。
- 還有可能是 端口上下文不匹配。
- 還有可能是 SELinux bug。

)

















