文章目錄
- 優先級隊列
- 模擬實現優先級隊列
- 向下調整建堆
- 向上調整建堆
- 堆的刪除
- priorityQueue
- 構造方法
- 大根堆和小根堆的向上調整比較方法
- 擴容
- 面試題
- 堆排序
優先級隊列
priorityqueue:底層是一顆完全二叉樹
- 小根堆:根比左右孩子都小
- 大根堆:根比左右孩子都大
- 用數組存儲

模擬實現優先級隊列
向下調整建堆
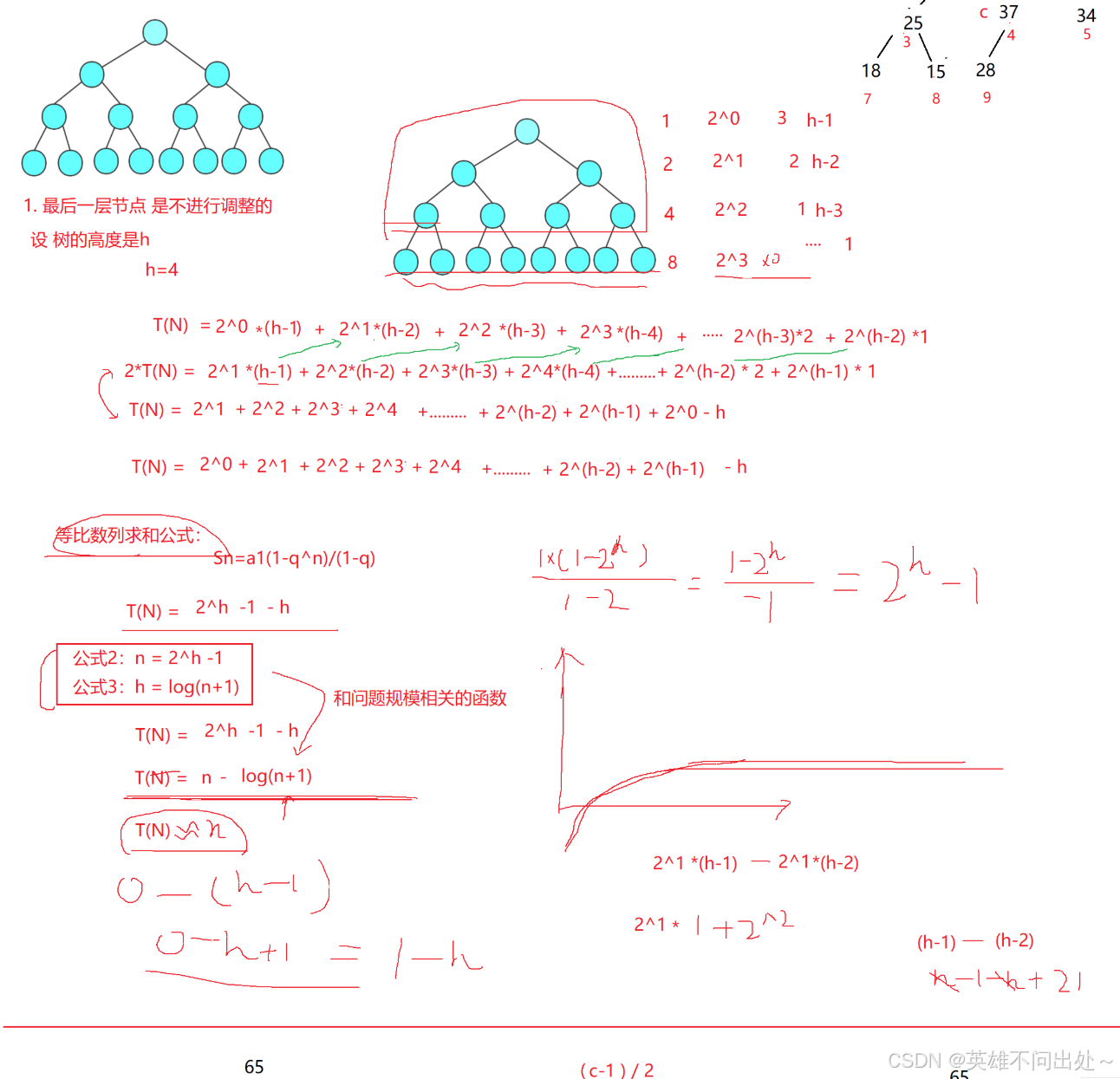
- 向下調整算法的時間復雜度:O(N)
建堆的算法
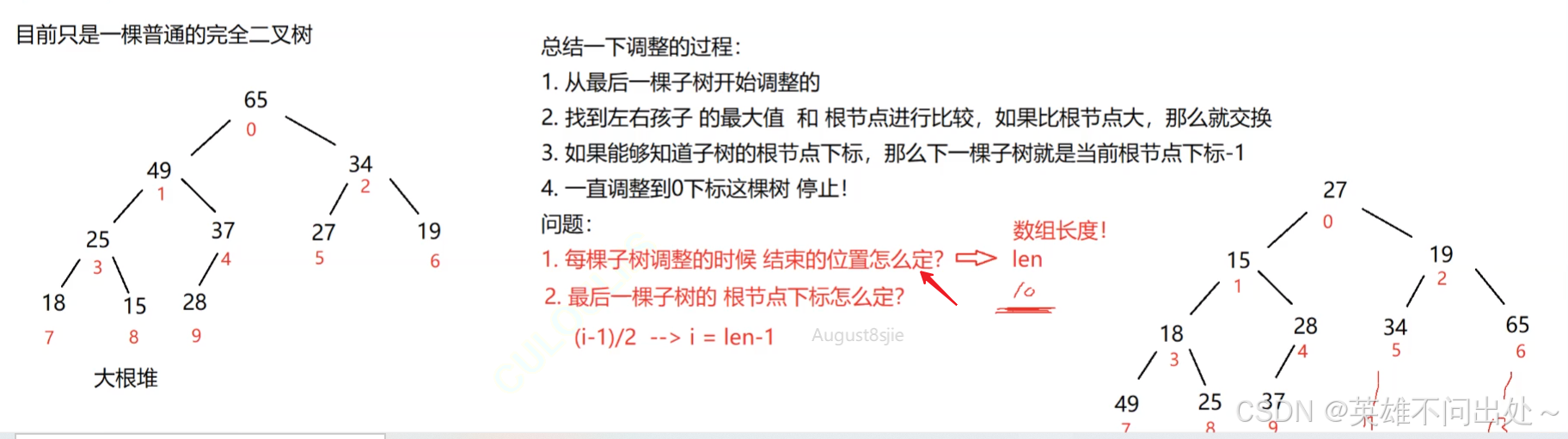
2. 推導過程:
// 向下調整算法public void shifDown(int parent,int len){// parent每次從根節點開始向下調整// usedSize來檢測是否還有得調,是否調結束了int child = 2 * parent + 1;// 至少有右孩子while(child < len){// 左右孩子比較大小,如果右孩子大,那么child+1if(child + 1 < len && elem[child] < elem[child + 1]){child = child + 1;}// if語句走完,證明child是左右孩子中大的那個的下標if(elem[child] > elem[parent]){int tmp = elem[child];elem[child] = elem[parent];elem[parent] = tmp;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{// 證明左右孩子中最大的那個都比父親節點小,// 是大根堆,不用調整了break;}}}
向上調整建堆
- 新插入一個節點并且向上調整為大根堆
- 向上調整建堆的時間復雜度是:O(N * logN)
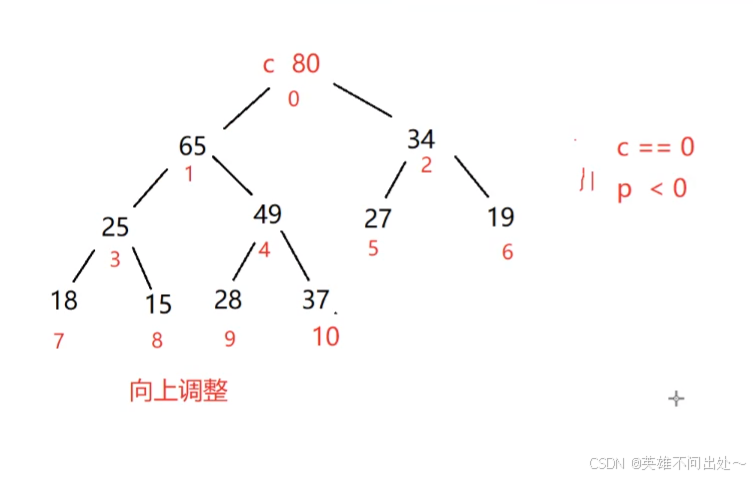
// 插入一個節點向上調整算法public void push(int val){// 滿了,擴容if(isFull()){elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);}elem[usedSize] = val;// 向上調整,usedSize為新插入元素的下標siftUp(usedSize);usedSize++;}public void swap(int i,int j){int tmp = elem[i];elem[i] = elem[j];elem[j] = tmp;}public boolean isFull(){return usedSize == elem.length;}public void siftUp(int child){// 通過孩子節點找到父親節點下標// 只要child大于0還需要調整,=0就不需要調整了while(child > 0) {int parent = (child - 1) / 2;if (elem[parent] < elem[child]) {swap(child, parent);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;} else {// parent下標對應的元素大于child下標對應的元素// 不需要交換break;}}}
堆的刪除
- 讓堆頂元素和最后一個元素交換
- 然后讓usedSize–,就刪除了最后一個元素
- 最后只需要調整0下標這棵樹就行了,使用向下調整算法
public int pop(){// 判空if(empty()){return -1;}int tmp = elem[0];swap(0,usedSize - 1);usedSize--;shifDown(0,usedSize);return tmp;}public boolean empty(){return usedSize == 0;}
priorityQueue
- Java中的優先級隊列默認是小根堆
public static void main(String[] args) {// 默認是小根堆PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();priorityQueue.offer(1);priorityQueue.offer(5);priorityQueue.offer(6);System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());// 1System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());// 5}
- PriorityQueue必須存放可以比較大小的元素
- 不能插入null對象,否則會拋出空指針異常
- 沒有容量限制,可以插入任意多個元素,其內部可以自動擴容,在堆上開空間的
- 插入和刪除的時間復雜度都是O(logN)
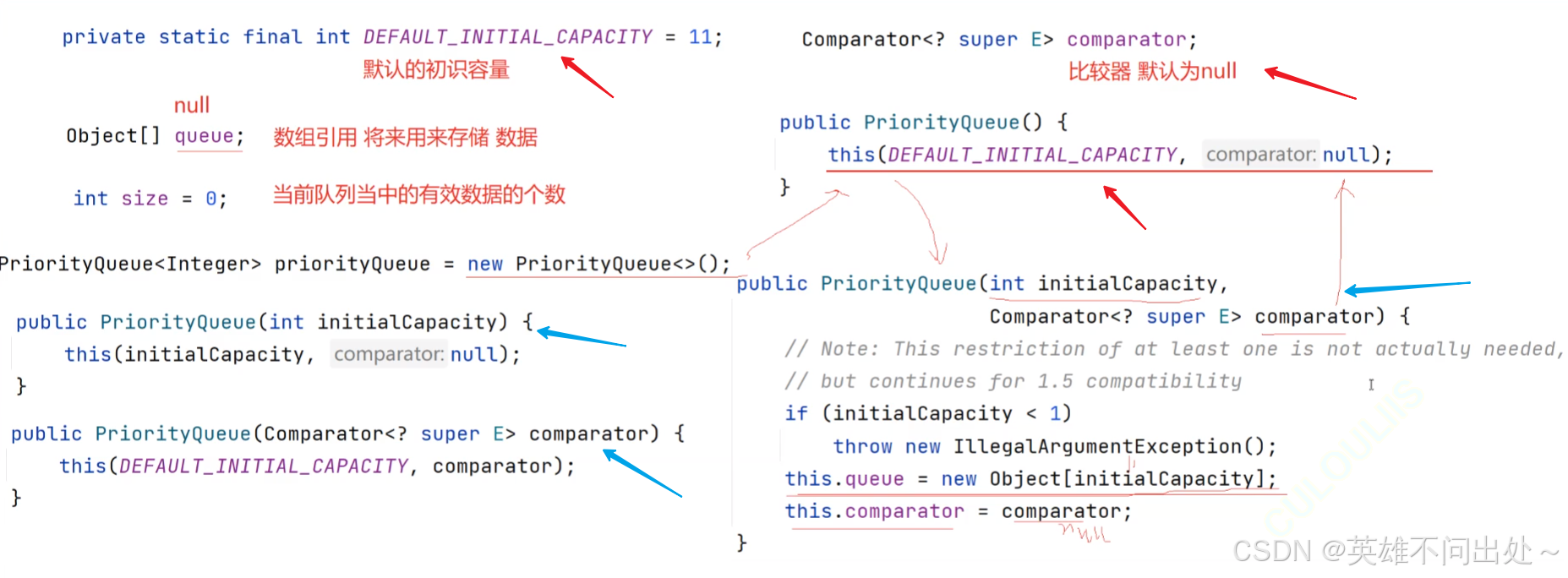
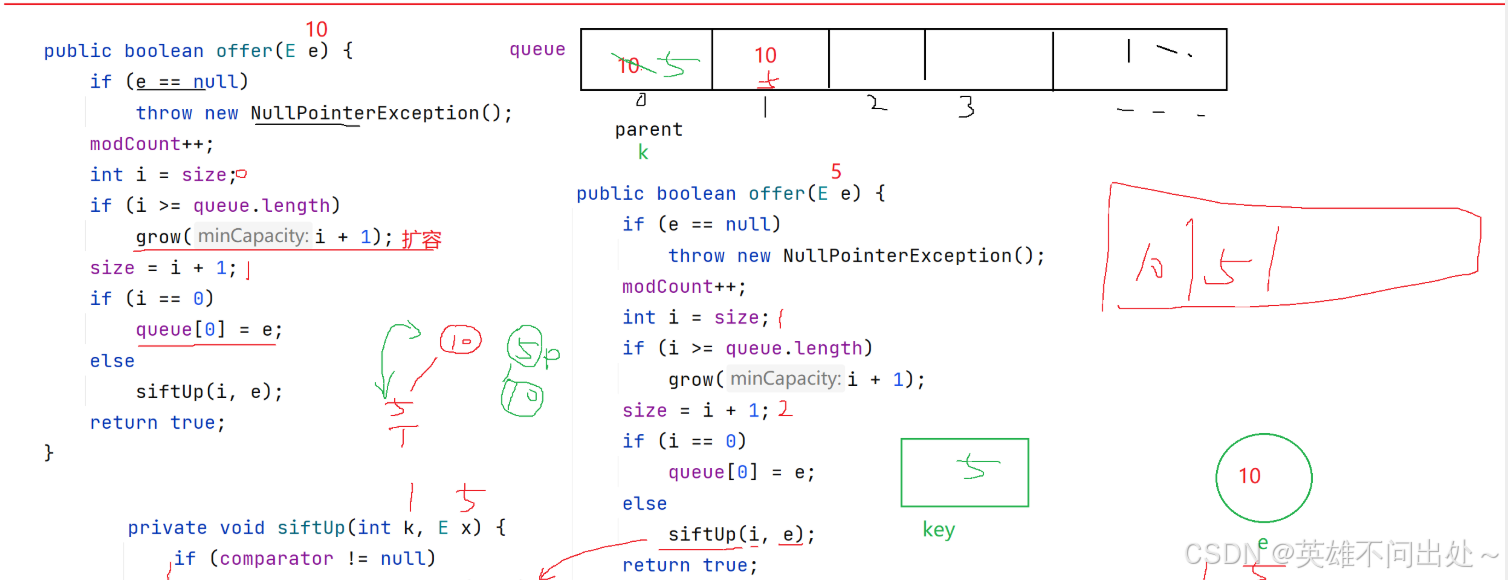
構造方法
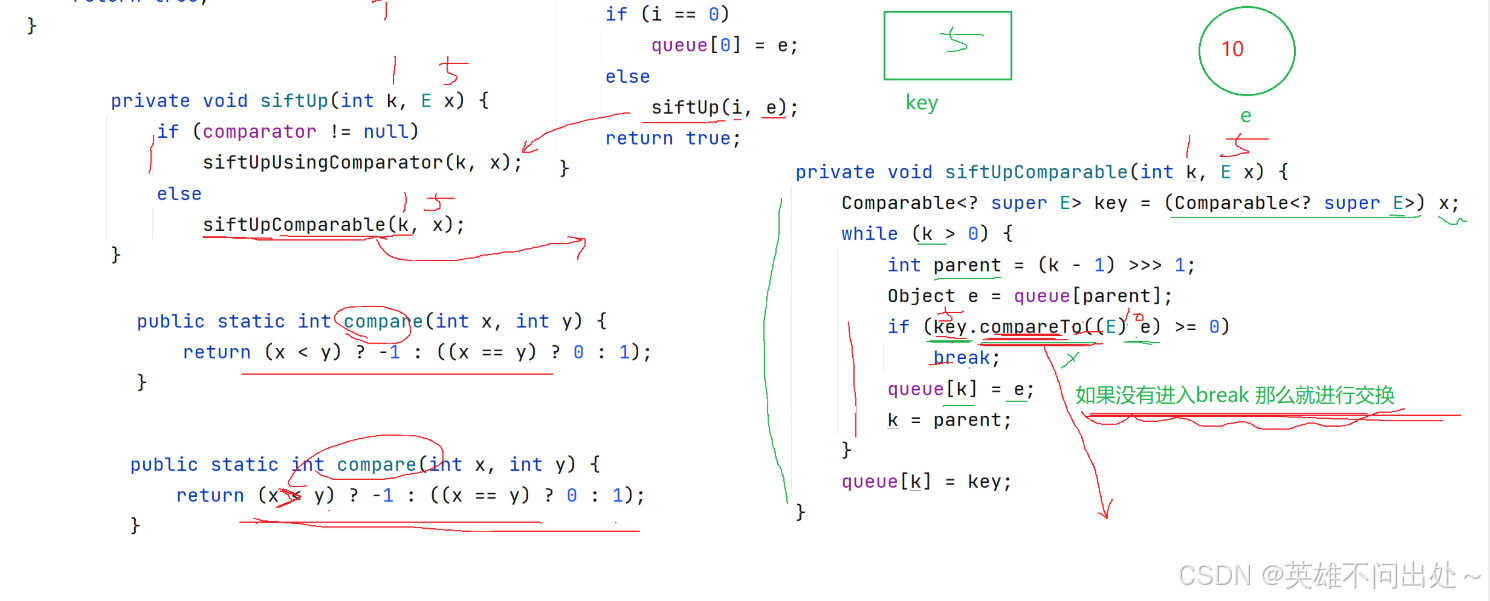
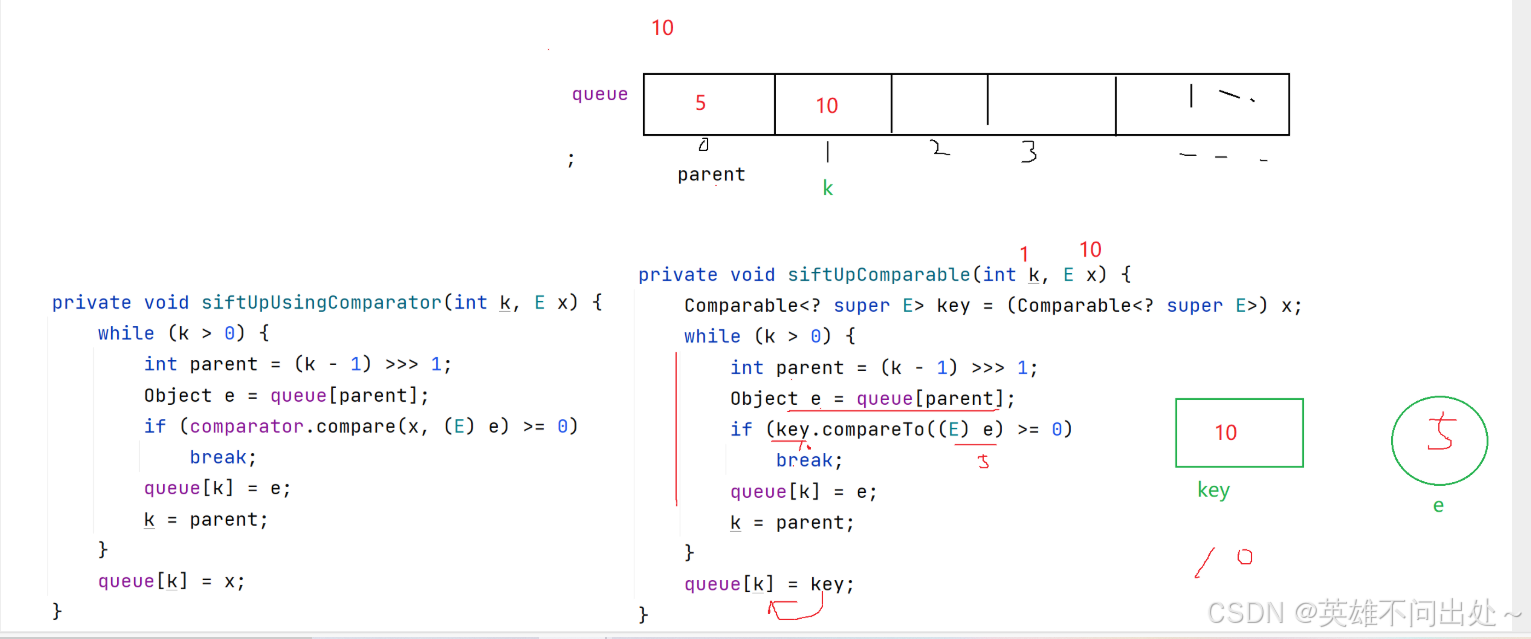
大根堆和小根堆的向上調整比較方法
- 插入元素,向上調整,向上調整的比較方法
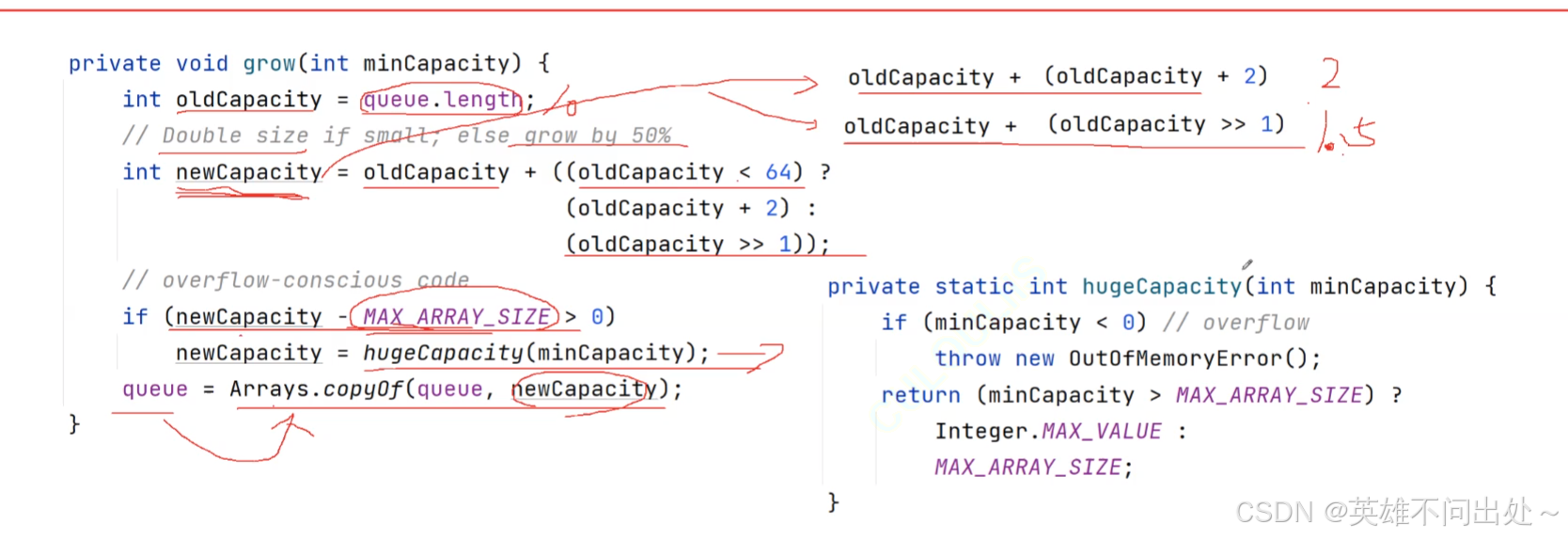
擴容
- 要么2倍擴容,要么1.5倍擴容
面試題
- top-k問題:
解法一:
比如得到最小的前k個元素
建立一個小根堆
出k次元素得到最小的前k個元素
解法二:
求最小的前k個元素,先把前k個元素建立大根堆,再和k+1位置的元素比較,如果小于堆頂元素就入堆,并且刪除堆頂元素,以此類推,最后剩下的k個元素就是最小的元素
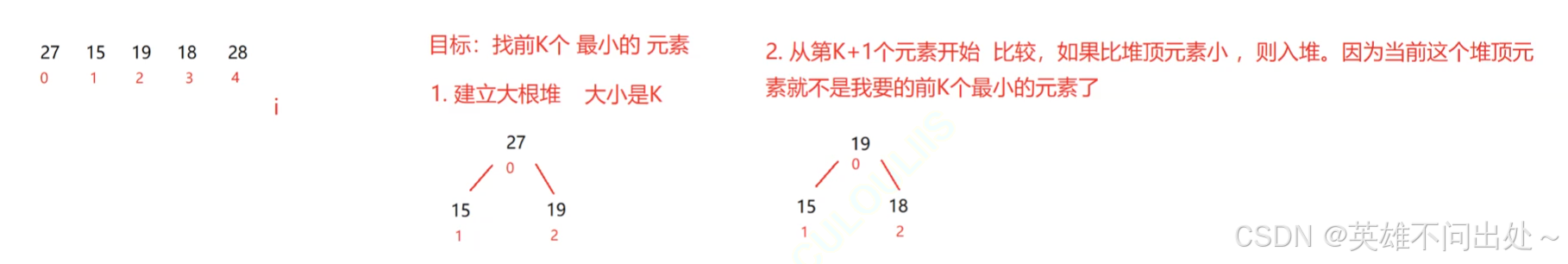
3. top-k問題的時間復雜度是:O(N * logK)
求最小的K個數
// class Imp implements Comparator<Integer> {
// public int compare(Integer o1,Integer o2){
// return o2.compareTo(o1);
// }
// }class Solution {public int[] smallestK(int[] arr, int k) {int[] ret = new int[k];if(arr == null || k <= 0){return ret;}// new一個比較器,匿名內部類的方法PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>(){public int compare(Integer o1,Integer o2){return o2.compareTo(o1);}});// 建立k個元素的大根堆// K * logKfor(int i = 0;i < k;i++){priorityQueue.offer(arr[i]);}// O((N-k) * logK)for(int i = k;i < arr.length;i++){int top = priorityQueue.peek();if(top > arr[i]){priorityQueue.poll();priorityQueue.offer(arr[i]);}}// 總的時間復雜度: O(N * logK)// K * logK// 整理元素不算入top-k問題中for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){ret[i] = priorityQueue.poll();}return ret;}
}
堆排序
- 從大到小或者是從小到大排序
- 從小到大排序,建立大根堆,每次最后一個元素和堆頂元素交換,usedSize–,向下調整為大根堆,以此類推
- 堆排序的時間復雜度:O(N * logN)
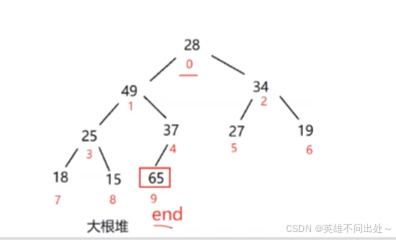
// 堆排序public void heapSort(){int end = usedSize - 1;while(end > 0){swap(0,end);shifDown(0,end);end--;}}public static void main(String[] args) {TestHeap testHeap = new TestHeap();int array[] = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};testHeap.initElem(array);// 向下調整建堆:O(N)testHeap.createHeap();System.out.println("======");// O(N * logN)testHeap.heapSort();System.out.println("======");}

)
)


:解決@vitejs plugin-vue@5.0.5對Vite^5.0.0的依賴沖突)
)


探索優化量子糾錯算法,提升量子算法準確性)

與對象聲明)




指南)

)
)