一、算法分析:
由于語句執行一次的實際所需時間與機器的軟硬件有關,則算法分析是針對語句執行次數,而非執行時間。
時間復雜度
計算時間復雜度:


常量階
如果算法中的n是固定的,或者說n是常數,或者時間復雜度計算出來是一個常數(1萬,1億都是),不隨n變化,則直接T(n)=O(1).
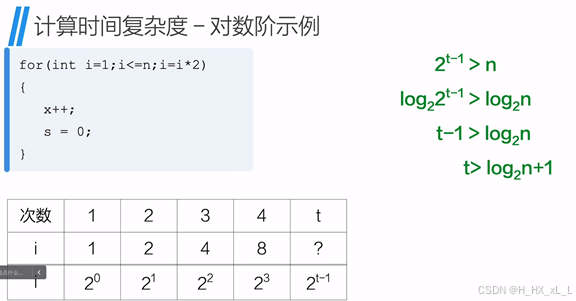
對于對數階的情況,可以先列出最后t次的i值,因為i最終要>n才能跳出循環,則假設等于n,即可算出最終的次數t
空間復雜度
因為一般情況下空間較為充足,則一般只討論時間復雜度
抽象數據類型ADT?
二、線性表
????????A、線性表的定義與特點
????????線性表意思n個相同數據類型的數據元素的有序列表
????????其中的元素個數n定義為線性表的長度,當n=0時,稱之為空表,對于非空的線性表或線性結構,特點:
????????????????存在唯一的“第一個”與“最后一個”的數據元素
????????????????除第一個元素外,結構中的每個數據元素均只有一個前驅
????????????????除最后一個外,結構中的每個數據均只有一個后繼
????????B、線性表的順序表示與實現
????????????????1、順序表的初始化:


#include <stdio.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType data[MAXSIZE];int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化
void initList(SeqList *L)
{L->length = 0;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個順序表并初始化SeqList list;initList(&list);printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list.length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list.data));return 0;
}????????????????2、順序表的尾部添加元素:
????????????????
#include <stdio.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType data[MAXSIZE];int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化
void initList(SeqList *L)
{L->length = 0;
}//尾部添加元素
int appendElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length>=MAXSIZE){printf("順序表已滿\n");return 0;}L->data[L->length] = e;L->length++;return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個線性表并初始化SeqList list;initList(&list);printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list.length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list.data));appendElem(&list, 88);return 0;
}????????????????3、順序表的遍歷:

#include <stdio.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType data[MAXSIZE];int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化
void initList(SeqList *L)
{L->length = 0;
}//尾部添加元素
int appendElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length>=MAXSIZE){printf("順序表已滿\n");return 0;}L->data[L->length] = e;L->length++;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listElem(SeqList *L)
{for (int i = 0; i < L->length; i++){printf("%d ", L->data[i]);}printf("\n");
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個線性表并初始化SeqList list;initList(&list);printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list.length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list.data));appendElem(&list, 88);appendElem(&list, 45);appendElem(&list, 43);appendElem(&list, 17);listElem(&list);return 0;
}將順序表的全部值,從頭到尾打印一遍
????????????????4、循環表的插入元素:

#include <stdio.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType data[MAXSIZE];int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化
void initList(SeqList *L)
{L->length = 0;
}//尾部添加元素
int appendElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length>=MAXSIZE){printf("順序表已滿\n");return 0;}L->data[L->length] = e;L->length++;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listElem(SeqList *L)
{for (int i = 0; i < L->length; i++){printf("%d ", L->data[i]);}printf("\n");
}//插入數據
int insertElem(SeqList *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{if(L->length >= MAXSIZE){printf("表已經滿了\n");return 0;}if (pos < 1 || pos > L->length){printf("插入位置錯誤\n");return 0;}if (pos <= L->length){for (int i = L->length-1; i >= pos-1; i--){L->data[i+1] = L->data[i];}L->data[pos-1] = e;L->length++; }return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個線性表并初始化SeqList list;initList(&list);printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list.length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list.data));appendElem(&list, 88);appendElem(&list, 67);appendElem(&list, 40);appendElem(&list, 8);appendElem(&list, 23);listElem(&list);insertElem(&list, 2, 18);listElem(&list);return 0;
}????????????????5、對表與插入位置進行檢測
?

????????????????6、表中的刪除元素:

????????????????對于刪除的數的定義與傳值,利用指針
????????????????利用指針意思是通過形參來改變實參,因為這樣可以對函數外的值進行改變

????????????????對于表的情況檢測:

#include <stdio.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType data[MAXSIZE];int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化
void initList(SeqList *L)
{L->length = 0;
}//尾部添加元素
int appendElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length>=MAXSIZE){printf("順序表已滿\n");return 0;}L->data[L->length] = e;L->length++;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listElem(SeqList *L)
{for (int i = 0; i < L->length; i++){printf("%d ", L->data[i]);}printf("\n");
}//插入數據
int insertElem(SeqList *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{if(L->length >= MAXSIZE){printf("表已經滿了\n");return 0;}if (pos < 1 || pos > L->length){printf("插入位置錯誤\n");return 0;}if (pos <= L->length){for (int i = L->length-1; i >= pos-1; i--){L->data[i+1] = L->data[i];}L->data[pos-1] = e;L->length++; }return 1;
}//刪除數據
int deleteElem(SeqList *L, int pos, ElemType *e)
{if(L->length == 0){printf("空表\n");return 0;}if (pos < 1 || pos > L->length){printf("刪除數據位置有誤\n");return 0;}*e = L->data[pos-1];if (pos < L->length){for (int i = pos; i < L->length; i++){L->data[i-1] = L->data[i];}}L->length--;return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個線性表并初始化SeqList list;initList(&list);printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list.length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list.data));appendElem(&list, 88);appendElem(&list, 67);appendElem(&list, 40);appendElem(&list, 8);appendElem(&list, 23);listElem(&list);insertElem(&list, 1, 18);listElem(&list);ElemType delData;deleteElem(&list, 2, &delData);printf("被刪除的數據為:%d\n", delData);listElem(&list);return 0;
}????????????????7、表的查找:

(對于動態分配:使用malloc函數來對于堆中開辟空間,創造一個數據)
[使用注意事項:
1、需要包含標準庫頭文件<stdlib.h>
2、一般返回viod* 通用數據類型指針,則使用時需要進行數據強轉換,可結構體或int之類
3、函數會分配指定字節數的內存空間,并且返回一個指向這塊內存起始位置的void*指針。要是內存分配失敗,就會返回NULL。#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>int main() {int* ptr;// 分配4個int大小的內存空間ptr = (int*)malloc(4 * sizeof(int)); //int型強轉,if (ptr == NULL){printf("內存分配失敗\n");return 1;}// 使用分配的內存for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {ptr[i] = i * 10;}for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {printf("ptr[%d] = %d\n", i, ptr[i]);}// 釋放內存free(ptr);return 0; }
4、在使用malloc時,一定要使用sizeof操作符來計算所需內存的大小。就像前面的例子,sizeof(int)能根據不同的系統環境確定一個整數所占的字節數。(利于代碼移植)
申請的空間是: ?指針 ?指向的那塊內存申請的空間
5、通過malloc分配的內存,在使用完畢后必須調用free()函數進行釋放,以避免出現內存泄漏的問題。
6、malloc分配的內存中可能包含之前殘留的數據,也就是這些內存不會被自動初始化。如果需要初始化為 0,可以使用calloc函數。]
????????????????8、表的動態分配地址初始化:

????????????????對于此時L所接收的是地址,返回的也是,則對于之前的函數是直接在棧區進行創建數據,使用時對地址進行操作需要使用&(取地址符),現在直接返回地址,則可直接對返回的值進行操作:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//順序表定義
typedef struct{ElemType *data;int length;
}SeqList;//順序表初始化-動態分配內存
SeqList* initList()
{SeqList *L = (SeqList*)malloc(sizeof(SeqList));L->data = (ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(ElemType) * MAXSIZE);L->length = 0;return L;
}//尾部添加元素
int appendElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length>=MAXSIZE){printf("順序表已滿\n");return 0;}L->data[L->length] = e;L->length++;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listElem(SeqList *L)
{for (int i = 0; i < L->length; i++){printf("%d ", L->data[i]);}printf("\n");
}//插入數據
int insertElem(SeqList *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{if(L->length >= MAXSIZE){printf("表已經滿了\n");return 0;}if (pos < 1 || pos > L->length){printf("插入位置錯誤\n");return 0;}if (pos <= L->length){for (int i = L->length-1; i >= pos-1; i--){L->data[i+1] = L->data[i];}L->data[pos-1] = e;L->length++; }return 1;
}//刪除數據
int deleteElem(SeqList *L, int pos, ElemType *e)
{if(L->length == 0){printf("空表\n");return 0;}if (pos < 1 || pos > L->length){printf("刪除數據位置有誤\n");return 0;}*e = L->data[pos-1];if (pos < L->length){for (int i = pos; i < L->length; i++){L->data[i-1] = L->data[i];}}L->length--;return 1;
}//查找數據位置
int findElem(SeqList *L, ElemType e)
{if (L->length == 0){printf("空列表\n");return 0;}for (int i = 0; i < L->length; i++){if(L->data[i] == e){return i + 1;}}return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//聲明一個線性表并初始化SeqList *list = initList();printf("初始化成功,目前長度占用%d\n",list->length);printf("目前占用內存%zu字節\n", sizeof(list->data));appendElem(list, 88);appendElem(list, 67);appendElem(list, 40);appendElem(list, 8);appendElem(list, 23);listElem(list);insertElem(list, 1, 18);listElem(list);ElemType delData;deleteElem(list, 2, &delData);printf("被刪除的數據為:%d\n", delData);listElem(list);printf("%d\n", findElem(list, 40));return 0;
}
????????C、線性表的鏈式表達與實現
????????????????1、定義:
????????它是一種物理存儲單元上非連續、非順序的存儲結構 ,數據元素的邏輯順序通過鏈表中的指針鏈接次序實現。由一系列結點組成,結點可在運行時動態生成。
????????????????2、結點:
????????每個結點包含兩部分,一是存儲數據元素的數據域 ,用于存放具體數據;二是存儲下一個結點地址的指針域 (最后一個指針域為NULL)(在雙向鏈表中還有指向前驅結點的指針域 ),通過指針將各個結點連接起來,形成鏈表結構。
????????????????3、單鏈表-存儲結構:
使用結構體來編寫節點。
typedef ?int ?ElemType;
typedef ?struct ?node
{ElemType ?data;//數據域struct ?node ?*next;//指針域
}Node; //別名
????????????????4、單鏈表-初始化:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();return 0;
}
????????????????5、單鏈表-頭插法
頭插法-插入節點,創建新結點并且將指針域值變換
為什么是頭插法,因為傳入的一直是第一個結點

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();insertHead(list, 10);insertHead(list, 20);return 0;
}????????????????6、單鏈表-遍歷

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();insertHead(list, 10);insertHead(list, 20);insertHead(list, 30);listNode(list);return 0;
}????????????????7、單鏈表-尾插法
????????尾插法就是在末尾插入結點
????????但尾插法需要先知道尾部值的地址,則需要通過遍歷找到最后結點指針域是NULL的Node* get_tail(Node ?*L) {Node ?*p=L;while( p -> next != ?NULL) {p = p -> next ; }return ?p; }????????然后再返回新的尾結點
????????????
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);listNode(list);return 0;
}??????????? ? 8、單鏈表-在指定位置插入數據
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//指定位置插入
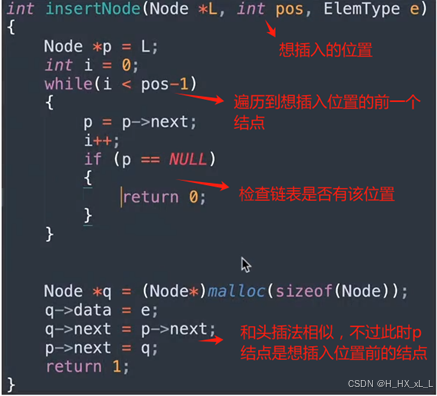
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{//用來保存插入位置的前驅節點Node *p = L;int i = 0;//遍歷鏈表找到插入位置的前驅節點while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}//要插入的新節點Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);listNode(list);insertNode(list, 2, 15);listNode(list);return 0;
}
????????????????9、單鏈表-刪除節點


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{//要刪除節點的前驅Node *p = L;int i = 0;//遍歷鏈表,找到要刪除節點的前驅。while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}//q指向要刪除的節點Node *q = p->next;//讓要刪除節點的前驅指向要刪除節點的后繼p->next = q->next;//釋放要刪除節點的內存空間free(q);return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);listNode(list);insertNode(list, 2, 15);listNode(list);deleteNode(list, 2);listNode(list);return 0;
}注意刪除節點,一定要釋放所刪除節點的空間(因為是在堆區中創建的)
????????????????10、單鏈表-獲取鏈表長度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);listNode(list);insertNode(list, 2, 15);listNode(list);deleteNode(list, 2);listNode(list);printf("%d\n", listLength(list));return 0;
}
????????????????????????和遍歷相似
????????????????11、單鏈表-釋放鏈表
????????????????釋放鏈表:釋放除頭結點之后的所有節點

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);listNode(list);insertNode(list, 2, 15);listNode(list);deleteNode(list, 2);listNode(list);printf("%d\n", listLength(list));freeList(list);printf("%d\n", listLength(list));return 0;
}????????D、線性表的應用
????????????????1、單鏈表--現只給出了頭指針,在不改變鏈表的情況下查找到其中的倒數第K個位置上的data域的值

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 10);tail = insertTail(tail, 20);tail = insertTail(tail, 30);tail = insertTail(tail, 40);tail = insertTail(tail, 50);tail = insertTail(tail, 60);tail = insertTail(tail, 70);listNode(list);findNodeFS(list, 3);return 0;
}????????????????2、單鏈表--對于兩個不同長度鏈表,其末尾是相同的幾個結點,要找到最開始相同的結點的指針域
????????獲取兩個鏈表長度進行相減得到步差,這時就也可以使用快慢指針從兩個鏈表中進行尋找,同時走到同一個地址時,則該的結點為要求節點
????????????????3、單鏈表--刪除絕對值相同的節點

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef char ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%c ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;//遍歷鏈表A,獲取鏈表A的長度while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}//遍歷鏈表B,獲取鏈表B的長度p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;//快指針Node *n;//慢指針int step;//兩個單詞之間數量的差值,可以用于快指針先走的步數if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}//讓快指針先走step步for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}//快慢指針同步走,直到指向同一個節點退出循環while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *listA = initList();Node *listB = initList();Node *tailA = get_tail(listA);Node *tailB = get_tail(listB);tailA = insertTail(tailA, 'l');tailA = insertTail(tailA, 'o');tailA = insertTail(tailA, 'a');tailA = insertTail(tailA, 'd');tailB = insertTail(tailB, 'b');tailB = insertTail(tailB, 'e');Node *nodeI = initListWithElem('i');tailA = insertTailWithNode(tailA, nodeI);tailB = insertTailWithNode(tailB, nodeI);Node *nodeN = initListWithElem('n');tailA = insertTailWithNode(tailA, nodeN);tailB = insertTailWithNode(tailB, nodeN);Node *nodeG = initListWithElem('g');tailA = insertTailWithNode(tailA, nodeG);tailB = insertTailWithNode(tailB, nodeG);listNode(listA);listNode(listB);printf("%c\n",findIntersectionNode(listA,listB)->data);return 0;
}????????該代碼思路就是通過數來控制數組下標,再通過該數組下標對應的數進行判斷是否有重復的,可以進行除重使用
注:
????????對于為什么使用指針接收或初始化數組,因為在堆區中申請空間使用malloc函數,其的使用方法是:
????????(void*)malloc(申請的空間大小),其返回的也是指針型的空間地址。
????????所以應該使用指針去接收
????????并且為了防止在之前的堆區數據未釋放干凈,使申請堆區內存時,申請失敗
????????則可以在申請后進行一次判斷if (p == NULL) {printf("內存分配失敗\n");return; }
????????????????4、單鏈表--反轉鏈表

????????????????進行編寫的圖示經過
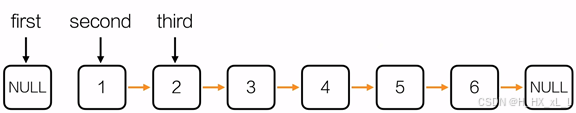
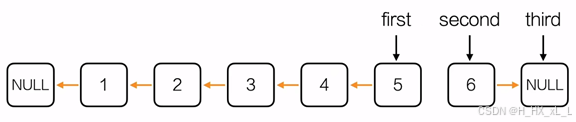
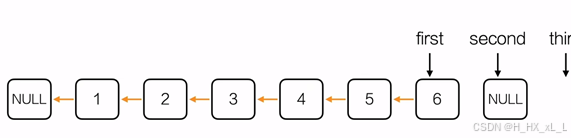
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;Node *n;int step;if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}//刪除絕對值相同的節點
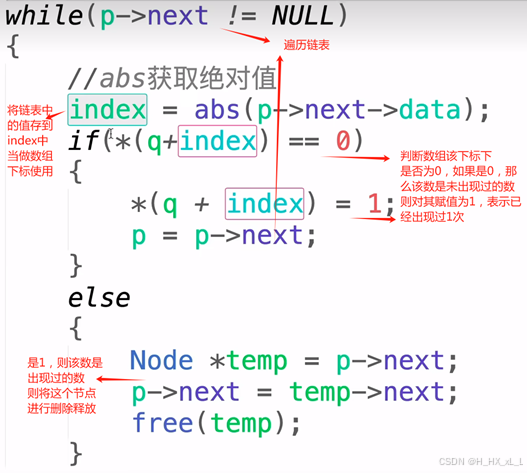
void removeNode(Node *L, int n)
{Node *p = L;int index;int *q = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1));for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){*(q + i) = 0;}while(p->next != NULL){index = abs(p->next->data);if(*(q+index) == 0){*(q + index) = 1;p = p->next;}else{Node *temp = p->next;p->next = temp->next;free(temp);}}free(q);
}//反轉鏈表
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{Node *first = NULL;Node *second = head->next;Node *third;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *hd = initList();hd->next = first;return hd;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 1);tail = insertTail(tail, 2);tail = insertTail(tail, 3);tail = insertTail(tail, 4);tail = insertTail(tail, 5);tail = insertTail(tail, 6);listNode(list);Node* reverse = reverseList(list);listNode(reverse);return 0;
}
????????????????5、單鏈表--刪除中間節點
????????????????????????主要是利用快慢指針來進行尋找中間位置
????????????????????????針對奇數鏈表

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;Node *n;int step;if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}//刪除絕對值相同的節點
void removeNode(Node *L, int n)
{Node *p = L;int index;int *q = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1));for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){*(q + i) = 0;}while(p->next != NULL){index = abs(p->next->data);if(*(q+index) == 0){*(q + index) = 1;p = p->next;}else{Node *temp = p->next;p->next = temp->next;free(temp);}}free(q);
}//反轉鏈表
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{Node *first = NULL;Node *second = head->next;Node *third;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *hd = initList();hd->next = first;return hd;
}//刪除中間節點
int delMiddleNode(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head->next;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *q = slow->next;slow->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 1);tail = insertTail(tail, 2);tail = insertTail(tail, 3);tail = insertTail(tail, 4);tail = insertTail(tail, 5);tail = insertTail(tail, 6);tail = insertTail(tail, 7);listNode(list);delMiddleNode(list);listNode(list);return 0;
}????????????????6、單鏈表--將鏈表:a,a1,a2.....an-2,an-1,an 變為a,an,a1,an-1,a2,an-2......
????????????????????????設計思路為:先找到中間的位置將其斷開,然后將后半部分反轉,再進行插空鏈接

????????????????????????成為這樣紙
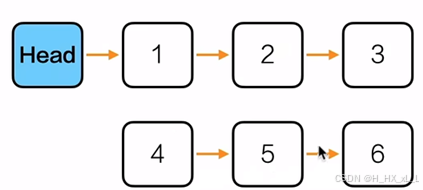


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;Node *n;int step;if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}//刪除絕對值相同的節點
void removeNode(Node *L, int n)
{Node *p = L;int index;int *q = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1));for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){*(q + i) = 0;}while(p->next != NULL){index = abs(p->next->data);if(*(q+index) == 0){*(q + index) = 1;p = p->next;}else{Node *temp = p->next;p->next = temp->next;free(temp);}}free(q);
}//反轉鏈表
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{Node *first = NULL;Node *second = head->next;Node *third;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *hd = initList();hd->next = first;return hd;
}//刪除中間節點
int delMiddleNode(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head->next;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *q = slow->next;slow->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//鏈表重新排序
void reOrderList(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head->next;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *first = NULL;Node *second = slow->next;slow->next = NULL;Node *third = NULL;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *p1 = head->next;Node *q1 = first;Node *p2, *q2;while(p1 != NULL && q1 != NULL){p2 = p1->next;q2 = q1->next;p1->next = q1;q1->next = p2;p1 = p2;q1 = q2;}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 1);tail = insertTail(tail, 2);tail = insertTail(tail, 3);tail = insertTail(tail, 4);tail = insertTail(tail, 5);tail = insertTail(tail, 6);listNode(list);reOrderList(list);listNode(list);return 0;
}
????????????????7、單鏈表--判斷鏈表是否有環
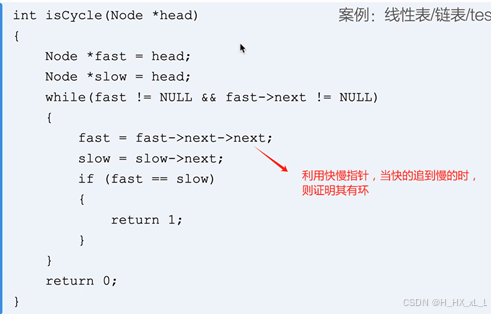
????????????????????????????????就是利用快慢指針來看是否能追到,因為快慢,所以只要有環不論多少次都會追到,則可運用其來進行判斷。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;Node *n;int step;if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}//刪除絕對值相同的節點
void removeNode(Node *L, int n)
{Node *p = L;int index;int *q = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1));for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){*(q + i) = 0;}while(p->next != NULL){index = abs(p->next->data);if(*(q+index) == 0){*(q + index) = 1;p = p->next;}else{Node *temp = p->next;p->next = temp->next;free(temp);}}free(q);
}//反轉鏈表
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{Node *first = NULL;Node *second = head->next;Node *third;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *hd = initList();hd->next = first;return hd;
}//刪除中間節點
int delMiddleNode(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head->next;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *q = slow->next;slow->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//鏈表重新排序
void reOrderList(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *first = NULL;Node *second = slow->next;slow->next = NULL;Node *third = NULL;while(second !=NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *p1 = head->next;Node *q1 = first;Node *p2, *q2;while(p1 != NULL && q1 != NULL){p2 = p1->next;q2 = q1->next;p1->next = q1;q1->next = p2;p1 = p2;q1 = q2;}
}//判斷鏈表是否有環
int isCycle(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;if (fast == slow){return 1;}}return 0;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 1);tail = insertTail(tail, 2);tail = insertTail(tail, 3);Node *three = tail;tail = insertTail(tail, 4);tail = insertTail(tail, 5);tail = insertTail(tail, 6);tail = insertTail(tail, 7);tail = insertTail(tail, 8);tail->next = three;//listNode(list);if (isCycle(list)){printf("有環\n");}else{printf("無環\n");}return 0;
}????????????????8、單鏈表--判斷鏈表有環的入口在哪
????????????????????????也可運用快慢指針,當第一次相遇后,讓一個停止,另一個繼續走,這時記錄他們所走的次數,則可知道這個環中有幾個節點,再讓其快慢指針重新走,并讓快指針先走這幾步,再同步走,當相遇時,此節點則為入口節點



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;typedef struct node{ElemType data;struct node *next;
}Node;//初化鏈表
Node* initList()
{Node *head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));head->data = 0;head->next = NULL;return head;
}//初始化節點(帶節點數據域參數)
Node* initListWithElem(ElemType e)
{Node *node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->data = e;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//頭插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;p->next = L->next;L->next = p;return 1;
}//遍歷
void listNode(Node* L)
{Node *p = L->next;while(p != NULL){printf("%d ", p->data);p = p->next;}printf("\n");
}//獲取尾部結點
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;while(p->next != NULL){p = p->next;}return p;
}//尾插法
Node* insertTail(Node *tail, ElemType e)
{Node *p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->data = e;tail->next = p;p->next = NULL;return p;
}//尾插法(節點)
Node* insertTailWithNode(Node *tail, Node *node)
{tail->next = node;node->next = NULL;return node;
}//指定位置插入
int insertNode(Node *L, int pos, ElemType e)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}Node *q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));q->data = e;q->next = p->next;p->next = q;return 1;
}//刪除節點
int deleteNode(Node *L, int pos)
{Node *p = L;int i = 0;while(i < pos-1){p = p->next;i++;if (p == NULL){return 0;}}if(p->next == NULL){printf("要刪除的位置錯誤\n");return 0;}Node *q = p->next;p->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//獲取鏈表長度
int listLength(Node *L)
{Node *p = L;int len = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;len++;}return len;
}//釋放鏈表
void freeList(Node *L)
{Node *p = L->next;Node *q;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}L->next = NULL;
}//查找倒數第k個節點
int findNodeFS(Node *L, int k)
{Node *fast = L->next;Node *slow = L->next;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != NULL){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}printf("倒數第%d個節點值為:%d\n", k, slow->data);return 1;
}
//查找兩個節點共同后綴的起始位置
Node* findIntersectionNode(Node *headA, Node *headB)
{if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){return NULL;}Node *p = headA;int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenA++;}p = headB;while(p != NULL){p = p->next;lenB++;}Node *m;Node *n;int step;if (lenA > lenB){step = lenA - lenB;m = headA;n = headB;}else{step = lenB - lenA;m = headB;n = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < step; i++){m = m->next;}while(m != n){m = m->next;n = n->next;}return m;
}//刪除絕對值相同的節點
void removeNode(Node *L, int n)
{Node *p = L;int index;int *q = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1));for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++){*(q + i) = 0;}while(p->next != NULL){index = abs(p->next->data);if(*(q+index) == 0){*(q + index) = 1;p = p->next;}else{Node *temp = p->next;p->next = temp->next;free(temp);}}free(q);
}//反轉鏈表
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{Node *first = NULL;Node *second = head->next;Node *third;while(second != NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *hd = initList();hd->next = first;return hd;
}//刪除中間節點
int delMiddleNode(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head->next;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *q = slow->next;slow->next = q->next;free(q);return 1;
}//鏈表重新排序
void reOrderList(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}Node *first = NULL;Node *second = slow->next;slow->next = NULL;Node *third = NULL;while(second !=NULL){third = second->next;second->next = first;first = second;second = third;}Node *p1 = head->next;Node *q1 = first;Node *p2, *q2;while(p1 != NULL && q1 != NULL){p2 = p1->next;q2 = q1->next;p1->next = q1;q1->next = p2;p1 = p2;q1 = q2;}
}//判斷鏈表是否有環
int isCycle(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;if (fast == slow){return 1;}}return 0;
}//找到鏈表環的入口
Node* findBegin(Node *head)
{Node *fast = head;Node *slow = head;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;if (fast == slow){Node *p = fast;int count = 1;while(p->next != slow){count++;p = p->next;}fast = head;slow = head;for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){fast = fast->next;}while(fast != slow){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow;}}return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{Node *list = initList();Node *tail = get_tail(list);tail = insertTail(tail, 1);tail = insertTail(tail, 2);tail = insertTail(tail, 3);Node *three = tail;tail = insertTail(tail, 4);tail = insertTail(tail, 5);tail = insertTail(tail, 6);tail = insertTail(tail, 7);tail = insertTail(tail, 8);tail->next = three;Node *p = findBegin(list);printf("%d\n", p->data);return 0;
}????????E、雙向鏈表
????????????????1、雙向鏈表--初始化
????????????????????????比單鏈表多了一個指向前驅的指針
????????????????
????????????????2、雙向鏈表--頭插法
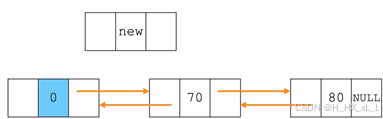
????????????????????????????????變為
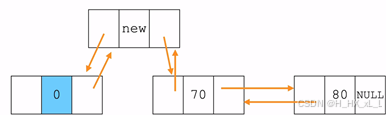

?????????????????3、雙向鏈表--尾插法
????????????????????????????????與單鏈表相同需要通過遍歷找到最后結點指針域是NULL的
Node* get_tail(Node *L)
{Node *p=L;while( p -> next != NULL){p = p -> next ;}return p;
}
????????????????????????再進行尾插法

????????????????4、雙向鏈表--在指定位置插入數據
????????????????????????首先先找到所插入位置的前一個節點(利用遍歷)

????????????????????????再進行插入:

????????????????5、雙向鏈表--刪除節點
????????????????????????相同先通過遍歷找到所刪除節點的前驅位置,再進行操作

????????????????????????刪除節點為將該節點前驅和后繼進行相連,并將本節點申請的空間進行釋放

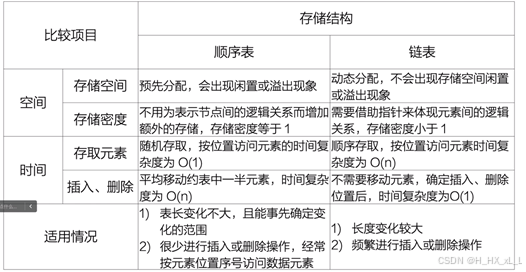
????????F、順序表與鏈表的對比
結語
學習于B站的 遜哥帶你學計算機?up主?的 《數據結構(C 語言描述)》也許是全站最良心最通俗易懂最好看的數據結構課(最遲每周五更新~~)
還在學習中,如有錯誤還請大佬們指出,有問題可相互交流
《數據結構(C 語言描述)》也許是全站最良心最通俗易懂最好看的數據結構課(最遲每周五更新~~)_嗶哩嗶哩_bilibili

:,及解決)


















