
0 前言
2024年的網絡安全檢查又開始了,對于使用基于Linux的國產電腦,我們可以編寫一個腳本來收集系統的有關信息。在收集的信息中,應該有一條是搜索信息的時間。
1. date命令 的功能、格式和選項說明
我們可以使用命令 date?--help 來查看 date命令的幫助信息。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date --help
Usage: date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]or: date [-u|--utc|--universal] [MMDDhhmm[[CC]YY][.ss]]
Display the current time in the given FORMAT, or set the system date.Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.-d, --date=STRING display time described by STRING, not 'now'-f, --file=DATEFILE like --date once for each line of DATEFILE-I[TIMESPEC], --iso-8601[=TIMESPEC] output date/time in ISO 8601 format.TIMESPEC='date' for date only (the default),'hours', 'minutes', 'seconds', or 'ns' for dateand time to the indicated precision.-r, --reference=FILE display the last modification time of FILE-R, --rfc-2822 output date and time in RFC 2822 format.Example: Mon, 07 Aug 2006 12:34:56 -0600--rfc-3339=TIMESPEC output date and time in RFC 3339 format.TIMESPEC='date', 'seconds', or 'ns' fordate and time to the indicated precision.Date and time components are separated bya single space: 2006-08-07 12:34:56-06:00-s, --set=STRING set time described by STRING-u, --utc, --universal print or set Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)--help display this help and exit--version output version information and exitFORMAT controls the output. Interpreted sequences are:%% a literal %%a locale's abbreviated weekday name (e.g., Sun)%A locale's full weekday name (e.g., Sunday)%b locale's abbreviated month name (e.g., Jan)%B locale's full month name (e.g., January)%c locale's date and time (e.g., Thu Mar 3 23:05:25 2005)%C century; like %Y, except omit last two digits (e.g., 20)%d day of month (e.g., 01)%D date; same as %m/%d/%y%e day of month, space padded; same as %_d%F full date; same as %Y-%m-%d%g last two digits of year of ISO week number (see %G)%G year of ISO week number (see %V); normally useful only with %V%h same as %b%H hour (00..23)%I hour (01..12)%j day of year (001..366)%k hour, space padded ( 0..23); same as %_H%l hour, space padded ( 1..12); same as %_I%m month (01..12)%M minute (00..59)%n a newline%N nanoseconds (000000000..999999999)%p locale's equivalent of either AM or PM; blank if not known%P like %p, but lower case%r locale's 12-hour clock time (e.g., 11:11:04 PM)%R 24-hour hour and minute; same as %H:%M%s seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC%S second (00..60)%t a tab%T time; same as %H:%M:%S%u day of week (1..7); 1 is Monday%U week number of year, with Sunday as first day of week (00..53)%V ISO week number, with Monday as first day of week (01..53)%w day of week (0..6); 0 is Sunday%W week number of year, with Monday as first day of week (00..53)%x locale's date representation (e.g., 12/31/99)%X locale's time representation (e.g., 23:13:48)%y last two digits of year (00..99)%Y year%z +hhmm numeric time zone (e.g., -0400)%:z +hh:mm numeric time zone (e.g., -04:00)%::z +hh:mm:ss numeric time zone (e.g., -04:00:00)%:::z numeric time zone with : to necessary precision (e.g., -04, +05:30)%Z alphabetic time zone abbreviation (e.g., EDT)By default, date pads numeric fields with zeroes.
The following optional flags may follow '%':- (hyphen) do not pad the field_ (underscore) pad with spaces0 (zero) pad with zeros^ use upper case if possible# use opposite case if possibleAfter any flags comes an optional field width, as a decimal number;
then an optional modifier, which is either
E to use the locale's alternate representations if available, or
O to use the locale's alternate numeric symbols if available.Examples:
Convert seconds since the epoch (1970-01-01 UTC) to a date$ date --date='@2147483647'Show the time on the west coast of the US (use tzselect(1) to find TZ)$ TZ='America/Los_Angeles' dateShow the local time for 9AM next Friday on the west coast of the US$ date --date='TZ="America/Los_Angeles" 09:00 next Fri'GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
Report date translation bugs to <http://translationproject.org/team/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'date invocation'
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]1.1 date 命令的功能
顯示或設置系統時間與日期。
轉換時間到選定的格式,默認為當前。
1.2 date 命令的格式
date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]
或
date [-u|--utc|--universal] [MMDDhhmm[[CC]YY][.ss]]
1.3? FORMAT可用的轉義序列
| 轉義序列 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| %% | 百分號 |
| %a | 當地縮寫的工作日名稱(例如,Sun) |
| %A | 當地完整的工作日名稱(例如,Sunday) |
| %b | 當地縮寫的月份名稱(例如,Jan) |
| %B | 當地完整的月份名稱(例如,January) |
| %c | 當地的日期和時間(例如,Thu Mar 3 23:05:25 2005) |
| %C | 世紀,和%Y類似,但是省略后兩位(例如,20) |
| %d | 一月中的一天(例如,01) |
| %D | 日期,等價于%m/%d/%y |
| %e | 一月中的一天,格式使用空格填充,等價于%_d |
| %F | 完整的日期;等價于%+4Y-%m-%d |
| %g | ISO標準計數周的年份的最后兩位數字 |
| %G | ISO標準計數周的年份,通常只對%V有用 |
| %h | 等價于%b |
| %H | 小時,范圍(00..23) |
| %I | 小時,范圍(01..12) |
| %j | 一年中的一天,范圍(001..366) |
| %k | 小時,使用空格填充,范圍(0..23),等價于%_H |
| %l | 小時,使用空格填充,范圍(1..12),等價于%_I |
| %m | 月,范圍(01..12) |
| %M | 分鐘,范圍(00..59) |
| %n | 換行符 |
| %N | 納秒,范圍(000000000..000000000) |
| %p | 用于表示當地的AM或PM,如果未知則為空白 |
| %P | 類似于%p,但用小寫表示 |
| %q | 季度,范圍(1..4) |
| %r | 當地以12小時表示的時鐘時間(例如,11:11:04 PM) |
| %R | 24小時每分鐘;等價于%H:%M |
| %s | 自協調世界時1970年01月01日00時00分以來的秒數 |
| %S | 秒數,范圍(00..60) |
| %t | 水平制表符 |
| %T | 時間;等價于%H:%M:%S |
| %u | 一周中的一天(1..7),1代表星期一 |
| %U | 一年中的第幾周,周日作為一周的起始(00..53) |
| %V | ISO標準計數周,該方法將周一作為一周的起始(01..53) |
| %w | 一周中的一天(0..6),0代表星期天 |
| %W | 一年中的第幾周,周一作為一周的起始(00..53) |
| %x | 當地的日期表示(例如,12/31/99) |
| %X | 當地的時間表示(例如,23:13:48) |
| %y | 年份后兩位數字,范圍(00..99) |
| %Y | 年份 |
| %z | +hhmm格式的數值化時區格式(例如,-0400) |
| %:z | +hh:mm格式的數值化時區格式(例如,-04:00) |
| %::z | +hh:mm:ss格式的數值化時區格式(例如,-04:00:00) |
| %:::z | 數值化時區格式,相比上一個格式增加':'以顯示必要的精度(例如,-04,+05:30) |
| %Z | 時區縮寫(如EDT) |
1.4?date 命令的選項說明
| 選項 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| -d STRING --date=STRING --date STRING | 解析字符串并按照指定格式輸出,字符串不能是'now'。 |
| -f?DATEFILE --file=DATEFILE | 類似于--date; 一次從DATEFILE處理一行。 |
| -I[FMT], --iso-8601[=FMT] | 按照ISO 8601格式輸出 FMT可以為'date'(默認),'hours','minutes','seconds','ns'。 例如:2006-08-14T02:34:56-06:00 |
| -R --rfc-email | 按照RFC 5322格式輸出, 例如: Mon, 14 Aug 2006 02:34:56 -0600 |
| --rfc-3339=FMT | 按照RFC 3339格式輸出,FMT可以為'date', 'seconds','ns'中的一個,例如:2006-08-14 02:34:56-06:00 |
| -r, --reference=FILE | 顯示文件的上次修改時間。 |
| -s --set=STRING | 根據字符串設置系統時間。 |
| -u --utc --universal | 顯示或設置世界協調時(UTC)。 |
| --help | 顯示幫助信息并退出。 |
| --version | 顯示版本信息并退出。 |
2 date命令實例
2.1 date : 顯示當前系統日期和時間
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date
2024年 06月 02日 星期日 17:18:03 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]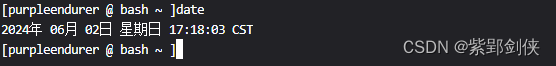
2.2 date +格式化字符串:格式化輸出
?
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date
2024年 06月 02日 星期日 17:53:04 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date +"%Y-%m-%d %l:%M:%S %A"
2024-06-02 5:53:05 星期日
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]?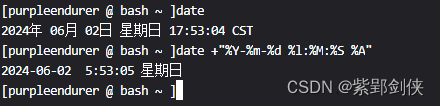
?
2.3?date -d 字符串 或 date --date=字符串 或 date --date 字符串:解析字符串并按照指定格式輸出
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d="2000-01-01"
date: invalid date ‘=2000-01-01’
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d="20000101"
date: invalid date ‘=20000101’
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "20000101"
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "2000-01-01"
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date --date="2000-01-01"
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date --date "2000-01-01"
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]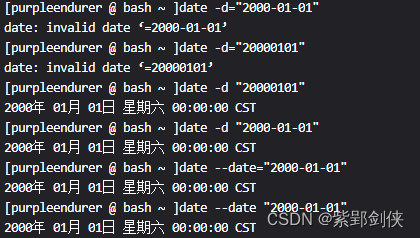
2.4?date -I :按照ISO 8601格式輸出
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date
2024年 06月 02日 星期日 18:16:22 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -I
2024-06-02
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]?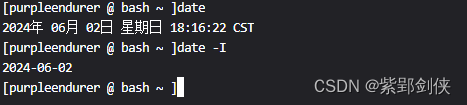
2.5 date -d "3 day ago" :輸出3天前的日期
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "3 day ago" +"%c" # 輸出3天前的日期
2024年05月30日 星期四 18時15分13秒
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]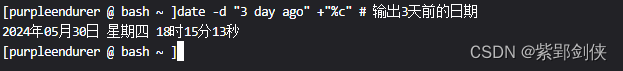
?
2.6 date -d "3 month ago" -R?:按照RFC 5322格式輸出3個月前的日期
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date
2024年 06月 02日 星期日 18:14:08 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "3 month ago" -R # 按照RFC 5322格式輸出3個月前的日期
Sat, 02 Mar 2024 18:14:21 +0800
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]
2.7? date -d 字符串:解析字符串并輸出
?
purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "19880907" +"%c" # 解析字符串"19880907"按照當地格式輸出
1988年09月07日 星期三 00時00分00秒
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]
?2.8?顯示兩年后的日期
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date
2024年 06月 02日 星期日 18:26:35 CST
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date -d "+2 year" +%Y-%m-%d # 顯示兩年后的日期
2026-06-02
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]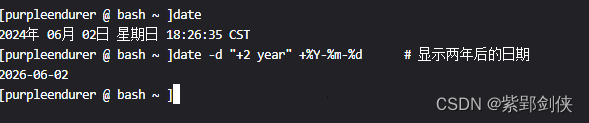
?2.9 生成日志的時間
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]date +"日志生成時間:%c"
日志生成時間:2024年06月02日 星期日 18時30分01秒
[purpleendurer @ bash ~ ]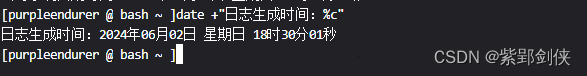















![[原創][Delphi多線程]TThreadedQueue的經典使用案例.](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[原創][Delphi多線程]TThreadedQueue的經典使用案例.)



