HashMap 構造器
HashMap 共有四個構造器:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {// 對于傳入的初始容量(loadFactor) 及 負載因子(loadFactor)的一些邊界判斷if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);// 設值this.loadFactor = loadFactor;// 返回給定目標容量的二次方大小this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 調用了 HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor),其中 loadFactor 取默認值 DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }
// 容量及負載因子皆使用默認值
public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; }
// 調用 putMapEntries 將值存入當前 hashmap
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;putMapEntries(m, false);
}
在上面構造器中存在一個方法【tableSizeFor】,這個方法的作用是:返回給定目標容量的二次方大小。
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {int n = cap - 1;n |= n >>> 1;n |= n >>> 2;n |= n >>> 4;n |= n >>> 8;n |= n >>> 16;return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
換句話說,HashMap 的默認容量為16,而容量是以2的次方擴充的(即使是自定義傳入,也一定會經過轉換,如傳入30,則返回32),一是為了提高性能使用足夠大的數組,二是為了能使用位運算代替取模預算;
HashMap 的實現原理
數據存儲方式示例圖:
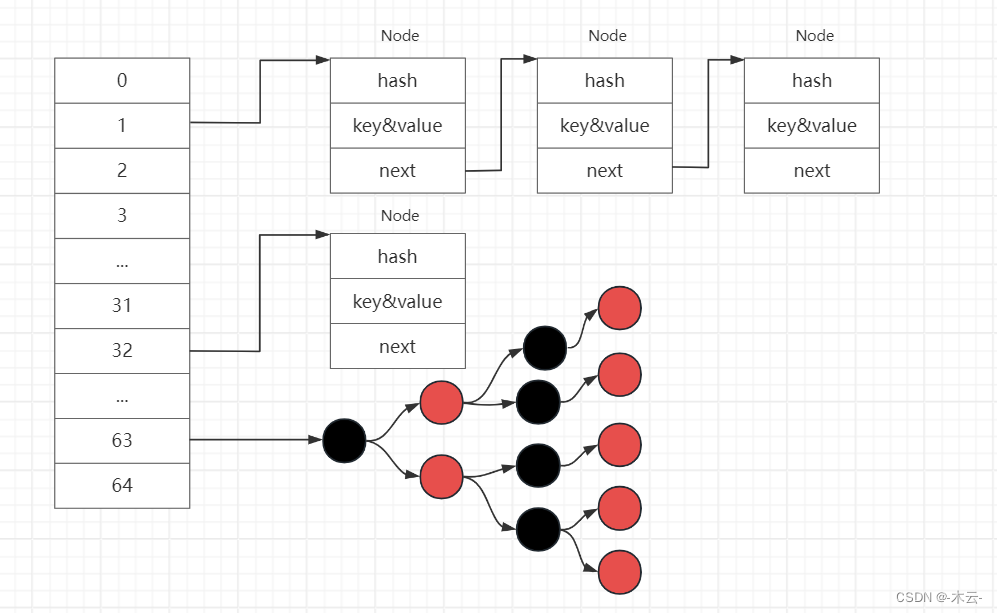
在 JDK1.8 中,HashMap采用【位桶(數組table)+鏈表+紅黑樹】實現,當鏈表長度超過閾值(8)時,將鏈表轉換為紅黑樹(table長度大于等于64),這樣大大減少了查找時間;鏈表長度大于8時轉化為紅黑樹,小于6時轉化為鏈表;
HashMap put 方法:
/*** Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old* value is replaced.** @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)*/
public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
其中 hash 方法:
// 計算 hash code
static final int hash(Object key) {int h;// key.hashCode 的調用方法:Object 中的原生方法 public native int hashCode();return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
重頭戲,putVal 方法:
/*** Implements Map.put and related methods.** @param hash hash for key* @param key the key* @param value the value to put* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.* @return previous value, or null if none*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length;if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else {Node<K,V> e; K k;if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;else if (p instanceof TreeNode)e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else {for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {if ((e = p.next) == null) {p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}if (e != null) { // existing mapping for keyV oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)e.value = value;afterNodeAccess(e);return oldValue;}}++modCount;if (++size > threshold)resize();afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null;
}
頭大,分解來看:
總體結構:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;/*** tab 用于保存 table 引用* 1、若 tab 為 null 或者 tab 的長度為 0,則調用 resize 方法進行初始化或者擴容*/if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length;/*** 2、到了這一步,tab 一定存在* i = (n - 1) & hash 確定元素存放在 tab 中的下標,p = tab[i] */// 2.1、若 p 為 null,表示當前 tab 的 i 位置空,則可以直接直接構建 Node 插入if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else { // 2.2、若 p 不為 null,表示 tab 的 i 位置已經有值,則繼續進行內部判斷Node<K,V> e; K k;// ... 后續單獨理解}/*** modCount 自增,記錄操作行為次數* 3、++size > threshold,即判斷下一次增加一個結點后size是否大于最大容量,如果是,則進行一次擴容*/++modCount;if (++size > threshold)resize();// 插入成功時會調用的方法(默認實現為空)afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null;
}
從 1 ~ 3 共三個步驟中,理解 putVal 方法大的執行方向。其中最復雜的是 2.2 中 else 中 的內容:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;// ...else {Node<K,V> e; K k;// 已知:p = tab[i],是 tab[i] 中鏈表或者紅黑樹第一個結點// 如果 p.hash 和 p.key 與傳入參數中的 hash 和 key 相同,表示對應 key 已經存在,則直接使用原結點,只需要后面改變value即可if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;// 如果 p 是紅黑樹結點類型,則將其插入 tab[i] 位置中的紅黑樹中else if (p instanceof TreeNode)e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else { // p 是鏈表結點類型,則將其插入 tab[i] 位置中的鏈表中// 循環,尾插法for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {// 鏈表尾部if ((e = p.next) == null) {// 構建新結點,并修改 p 的 next 指向p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);/*** TREEIFY_THRESHOLD:將鏈表轉換為紅黑樹的閾值(默認為8),超過該閾值執行 treeifyBin 方法* 注意:執行 treeifyBin 方法并不代表一定會將鏈表轉換為紅黑樹,它會根據 table 的總長度來決定,即:* 只有當 table 的長度大于等于 64 后,才會執行轉換紅黑樹操作,否則只會對 table 進行擴容*/if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}// 這里會判斷整條鏈表上的結點的key、Hash值與插入的元素的key、Hash值是否相等(前面只判斷了鏈表中的第一個結點 p)// 如果相等,同前面一樣,表示已經存在key值相同的結點【e = p.next,其中 e 已經賦值了】,則直接退出循環if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}if (e != null) {V oldValue = e.value;/*** public V put(K key, V value) {* return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);* }* 這里 onlyIfAbsent 為 false,則 !onlyIfAbsent 為 true,進而執行 e.value = value 【新值替換舊值】*/if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)e.value = value;/*** 在HashMap中:void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }* 實際上,afterNodeAccess 是提供給LinkedHashMap類【繼承HashMap】使用,LinkedHashMap 可以保證輸入輸出順序的一致性* 類似的還有 afterNodeInsertion、afterNodeRemoval 這兩個方法*/afterNodeAccess(e); // 這里默認實現為空return oldValue;}}// ...return null;
}
putVal 方法中還涉及一些其他方法,如:
- resize:初始化或加倍表大小。如果 table 為空,則會根據字段閾值中保持的初始容量目標進行分配。
- treeifyBin:判斷是否需要將鏈表替換為紅黑樹
a. replacementTreeNode:將鏈表結點 Node 轉換為樹結點 TreeNode
b. treeify:形成從該節點鏈接的節點的樹 - Node:鏈表結點
- TreeNode:紅黑樹結點,關于紅黑樹的實現及對應操作,后續有機會再另講
putVal 方法流程圖(僅用于輔助理解源碼):

其他
關于其他的方法,如 get、entrySet、ketSet 等,都可以在理解上述代碼后再去看源碼即可
關于紅黑樹:需要首先理解紅黑樹概念,再回頭來看這里的源碼更有效果(TODO:紅黑樹及HashMap紅黑樹源碼理解)
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree linksTreeNode<K,V> left;TreeNode<K,V> right;TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletionboolean red;TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {super(hash, key, val, next);}/*** Returns root of tree containing this node.*/final TreeNode<K,V> root() {for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {if ((p = r.parent) == null)return r;r = p;}}// ...省略幾百行
}
補充1:HashSet
HashSet 的底層實現是 HashMap,來看 HashSet 的無參構造器:
/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).*/
public HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();
}
add 方法:
public boolean add(E e) {return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
這里是把傳入的值,作為 map 的 key 傳入,而 value 統一為 PRESENT【private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();】
HashSet 之所以可以保證數據不會重復,其關鍵在于調用了 HashMap 的 put 方法:
// ...
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length; // 初始化
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 通過hash計算【add】方法傳入的e的下標i,若在table[i]不存在則構建結點保存
else {// 如果結點存在,則判斷 key 與 hash 值是否都相同,具體流程此處不再贅述Node<K,V> e; K k;if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;// ...
}// ...
也就是說,HashSet 利用 HashMap 中 key 值不能重復的特性來保證其存入的值不會重復。
HashSet 中其他方法基本都基于 HashMap 的方法,此處不再贅述。
)




)













